3RD TERM
3RD TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of Last Term’s Examination and work
2. Speech Work: Consonants /s/ and /z/: Structure: Verbs – Active verbs; Comprehension/Vocabulary Development; Reading Skill – Reading for Spatial Description: Literature: Poetry; Introduction. Recommended Text.
3. Speech Work: /Ɔi/; Structure: Verbs: Highlighting Active Voice. Comprehension/ Vocabulary Development. Writing Skill – giving specific answers. Composition: Expository; Elements of writing (Introduction, Body and conclusion, Stages of writing). Literature: Poetry, Types of Poems. (Use recommended texts.
4. Speech Work: /a/and /au/ Structure: Verbs – making sentences with active voices. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Listening Skill – Listening for maximum retention and recall; Composition: Expository – Arrangement of ideas in logical sequence. Literature: Poetry – read selections of poems (oral and written poetry)
5. Speech Work: Nasal Sounds /m, n, ŋ / Structure: Verbs – Passive Verbs. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Writing Skill: Composition: Expository (Guided writing). Literature: Poetry – Figure of Speech, Literary terms.
6. Speech Work: Stress; Introduction to Stress. Structure: Verbs – Highlighting Passive Voice. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Reading to follow direction in written communication. Composition: Expository (Guided writing). Literature: Poetry: More on Literary terms, use recommended poems.
7. Speech Work: Stress: Stress Patterns. Structure: Verbs: Making sentences with Passive Voice. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Listening Skill – listening to follow direction in written communication. Composition; Narrative, Descriptive, Argumentative and expository – identifying the differences.
8. Speech Work: Stress: Compound Words. Structure: Verbs. Making sentences with active and passive voices. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Writing Skill (given passage). Composition: Informal letters; writing to suit different situations. Literature: Poetry; Themes, Features, Structure, Language.
9. Speech Work: Consonant Clusters. Structure; Pronouns: Forms, positions and functions of Pronouns. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development: Listening Skill (given passage). Composition: Formal Letters; writing to suit different situations. Literature: Poetry – more on figures of speech. Encourage students to write a poem.
10. Revision
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of Last Term’s Examination and work
2. Speech Work: Consonants /s/ and /z/: Structure: Verbs – Active verbs; Comprehension/Vocabulary Development; Reading Skill – Reading for Spatial Description: Literature: Poetry; Introduction. Recommended Text.
3. Speech Work: /Ɔi/; Structure: Verbs: Highlighting Active Voice. Comprehension/ Vocabulary Development. Writing Skill – giving specific answers. Composition: Expository; Elements of writing (Introduction, Body and conclusion, Stages of writing). Literature: Poetry, Types of Poems. (Use recommended texts.
4. Speech Work: /a/and /au/ Structure: Verbs – making sentences with active voices. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Listening Skill – Listening for maximum retention and recall; Composition: Expository – Arrangement of ideas in logical sequence. Literature: Poetry – read selections of poems (oral and written poetry)
5. Speech Work: Nasal Sounds /m, n, ŋ / Structure: Verbs – Passive Verbs. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Writing Skill: Composition: Expository (Guided writing). Literature: Poetry – Figure of Speech, Literary terms.
6. Speech Work: Stress; Introduction to Stress. Structure: Verbs – Highlighting Passive Voice. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Reading to follow direction in written communication. Composition: Expository (Guided writing). Literature: Poetry: More on Literary terms, use recommended poems.
7. Speech Work: Stress: Stress Patterns. Structure: Verbs: Making sentences with Passive Voice. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Listening Skill – listening to follow direction in written communication. Composition; Narrative, Descriptive, Argumentative and expository – identifying the differences.
8. Speech Work: Stress: Compound Words. Structure: Verbs. Making sentences with active and passive voices. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Writing Skill (given passage). Composition: Informal letters; writing to suit different situations. Literature: Poetry; Themes, Features, Structure, Language.
9. Speech Work: Consonant Clusters. Structure; Pronouns: Forms, positions and functions of Pronouns. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development: Listening Skill (given passage). Composition: Formal Letters; writing to suit different situations. Literature: Poetry – more on figures of speech. Encourage students to write a poem.
10. Revision
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonant sounds
SUB-TOPIC: Consonants /s/ and /z/
CONTENT: CONSONANTS /S/ AND /Z/
1. The /s/ sound

For the articulation of /s/, the tip and blade of the tongue make a light contact with the alveolar ridge while the air stream passes through the groove created by the partial obstruction. There is no vibration of the vocal cord as /s/ is produced.
It is therefore, voiceless alveolar fricative. The common spellings symbols for /s/ are as follows:
‘s’ e.g seat, slide, sink, sign
‘sl’ e.g science, school, scheme
‘c’ e.g cease, race, price, hence
‘ss’ e.g success, pass, boss, hiss
2. The /z/ sound
This consonant has the same place and manner of articulation with /s/. The only difference between /z/ and /s/ is that the vocal cords vibrate as the articulation with /z/ takes place while there is no vibration of the vocal cords during the production of /s/. That is why /z/ is a voiced alveolar fricative which has the following spelling symbols; ‘z’ e.g zoo, zink, seize, zeal, zealous, zip ‘s’ e.g. raise, rise, lice, eyes knees, bees, news.
SOUND CONTRASTS

The following pairs of words show the contrast between /s/ and /z/.
/s/ /z/
fleece fleas
advice advise
fierce fears
sink Zink
place plays
loose lose
hence hens
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/0e5Y5Qpr_Sc[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
Below are ten words. Each of them contains either /s/ or /z/. Put the words that contain /s/ under /s/ and those that contain /z/ under /z/.
The words are: has, just, habits, books, example, advise, his, is, noises, listener.
ASSIGNMENT: indicate the consonants at the final position in each of the following words: legs, peace, sits, goes, nose.
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Active verbs

CONTENT
ACTIVE VERBS
Assuming Paul performed a particular action which is expressed by a verb; it therefore, means that Paul will be regarded as the doer or performer of the action. In English grammar, Paul will be referred to as the subject and the verb in that sentence will be in the Active voice.
For example, Paul wrote a letter.
Here, wrote is in the active voice since the subject of the verb (Paul) is doing the writing.
So, a verb is said to be in the Active voice when the subject performs the action described by the verb.
Examples
1. I called Paul
2. We ate some mangoes
3. The driver drove the car carelessly.
4. Bola sang the song melodiously.
5. Ade killed a goat.
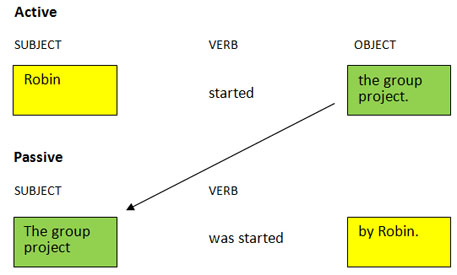
EVALUATION:
Change the following sentences from Active into passive.
i. Mustapha swept the floor.
ii. We sang a new song.
iii. The girl read an interesting book.
iv. I own a new school bag
v. They fought a serious war.
ASSIGNMENT:
Change the following sentences from Active to passive.
i. Dare bought six tubers of yam
ii. The teacher gave us some difficult sums.
iii. She spoke to me.
iv. A dog bit the old woman.
v. Ikechukwu lifted the heavy basket.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: The Wanderer

CONTENT
THE WANDERER
Note the following tips to aid you in understanding the poem.
I. The first two lines of each stanza contain pictures.
II. The next lines contain the effect of these on the poet.
III. The last line is a strong chorus throughout the poem.
The poet emphasized what he blames for his travelling spirit.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for JSS1; Exercise 15.2.1; pages 145-146.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for JSS1; Exercise 15.2.2; pages 146-149.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Types of Essay
SUB-TOPIC: Expository (Introduction)

CONTENT: EXPOSITORY (INTRODUCTION)
An expository essay is one in which the writer tries to explain how something works, how something is done or how something is made. Expository essays demand the ‘how of things. Such essays call for explanation of a process or an idea.
EVALUATION:
1. What is an expository essay?
2. What does expository essay demand?
ASSIGNMENT: Explain how to play a local game of your choice to someone who has not seen the game played before.
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonant sounds
SUB-TOPIC: Consonants /s/ and /z/
CONTENT: CONSONANTS /S/ AND /Z/
1. The /s/ sound

For the articulation of /s/, the tip and blade of the tongue make a light contact with the alveolar ridge while the air stream passes through the groove created by the partial obstruction. There is no vibration of the vocal cord as /s/ is produced.
It is therefore, voiceless alveolar fricative. The common spellings symbols for /s/ are as follows:
‘s’ e.g seat, slide, sink, sign
‘sl’ e.g science, school, scheme
‘c’ e.g cease, race, price, hence
‘ss’ e.g success, pass, boss, hiss
2. The /z/ sound
This consonant has the same place and manner of articulation with /s/. The only difference between /z/ and /s/ is that the vocal cords vibrate as the articulation with /z/ takes place while there is no vibration of the vocal cords during the production of /s/. That is why /z/ is a voiced alveolar fricative which has the following spelling symbols; ‘z’ e.g zoo, zink, seize, zeal, zealous, zip ‘s’ e.g. raise, rise, lice, eyes knees, bees, news.
SOUND CONTRASTS

The following pairs of words show the contrast between /s/ and /z/.
/s/ /z/
fleece fleas
advice advise
fierce fears
sink Zink
place plays
loose lose
hence hens
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/0e5Y5Qpr_Sc[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
Below are ten words. Each of them contains either /s/ or /z/. Put the words that contain /s/ under /s/ and those that contain /z/ under /z/.
The words are: has, just, habits, books, example, advise, his, is, noises, listener.
ASSIGNMENT: indicate the consonants at the final position in each of the following words: legs, peace, sits, goes, nose.
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Active verbs

CONTENT
ACTIVE VERBS
Assuming Paul performed a particular action which is expressed by a verb; it therefore, means that Paul will be regarded as the doer or performer of the action. In English grammar, Paul will be referred to as the subject and the verb in that sentence will be in the Active voice.
For example, Paul wrote a letter.
Here, wrote is in the active voice since the subject of the verb (Paul) is doing the writing.
So, a verb is said to be in the Active voice when the subject performs the action described by the verb.
Examples
1. I called Paul
2. We ate some mangoes
3. The driver drove the car carelessly.
4. Bola sang the song melodiously.
5. Ade killed a goat.

EVALUATION:
Change the following sentences from Active into passive.
i. Mustapha swept the floor.
ii. We sang a new song.
iii. The girl read an interesting book.
iv. I own a new school bag
v. They fought a serious war.
ASSIGNMENT:
Change the following sentences from Active to passive.
i. Dare bought six tubers of yam
ii. The teacher gave us some difficult sums.
iii. She spoke to me.
iv. A dog bit the old woman.
v. Ikechukwu lifted the heavy basket.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: The Wanderer

CONTENT
THE WANDERER
Note the following tips to aid you in understanding the poem.
I. The first two lines of each stanza contain pictures.
II. The next lines contain the effect of these on the poet.
III. The last line is a strong chorus throughout the poem.
The poet emphasized what he blames for his travelling spirit.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for JSS1; Exercise 15.2.1; pages 145-146.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for JSS1; Exercise 15.2.2; pages 146-149.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Types of Essay
SUB-TOPIC: Expository (Introduction)

CONTENT: EXPOSITORY (INTRODUCTION)
An expository essay is one in which the writer tries to explain how something works, how something is done or how something is made. Expository essays demand the ‘how of things. Such essays call for explanation of a process or an idea.
EVALUATION:
1. What is an expository essay?
2. What does expository essay demand?
ASSIGNMENT: Explain how to play a local game of your choice to someone who has not seen the game played before.
WEEK 2
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Vowels: /ɔi /
CONTENT
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/87C55WKKBP4[/youtube]
Vowel /ɔi /
For the articulation of /ɔi /, the tongue glide begins from the back towards the front and the lips which are ‘rounded’, generally become spread as the tongue glide moves towards /I/.
There are only two spelling symbols for the diphthong. These are seen below:
‘oi’: boil, coil,
‘oy’: boy, toy,
‘uoy’ is an exceptional spelling as in ‘bouy’ which is pronounced as ‘boy’.
It is necessary to show the contrast between /ɔi / and / ɔ / as in the following words;
/ɔ: / /ɔi /
corn coin
bore boy
ball boil
call coil
jaw joy
tore toy
lawn loin
EVALUATION:
Indicate the vowel used in each of the following words. Endorse the vowel symbols in slanting lines.
(i) dawn (ii) point (iii) buoy (iv) corn (v) coy.
ASSIGNMENT:
Indicate the vowel used in each of the following words. Enclose the vowel symbols in slanting lines.
(i) Course (ii) curse (iii) cot (iv) coarse (v) worse.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/M-8ZqxVJMf8[/youtube]
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Highlighting Active voice
CONTENT: HIGHLIGHTING ACTIVE VOICE
There are two ways to express an ‘action’; active and passive voices.
A sentence in which the logical subject is the same as the grammatical subject is called an active sentence.
Logical subject is the subject that is the one who is actually said to be performing the actions of the verbs. When the subject in a sentence comes before the verb, we call this subject the grammatical subject.
Examples
i. Aisha ate the food.
ii. The girl has beaten the boy.
iii. A carpenter will make the chair.
iv. The police must arrest that thief.
v. My wife was drawing a picture.
EVALUATION:
Identify the active voices in the following passage.
Labi was checking through the carton of empty bottles which had been returned from chief Fadaka’s house when he found a paper bag which had slipped between the wrinkled flap and the side of the carton. He took it out, and to his surprise he found it contained a thick bundle of bank notes of a high denomination, totaling nearly ten thousand naira.
ASSIGNMENT:
Construct five sentences containing active voice.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: Skimming

CONTENT: SKIMMING
Skimming is most useful when you read with a definite question in mind and have an intention to find answers to the question.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 16.2.2; pages 152- 154.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 16.2. 3 and 16.3.4; pages 154-160.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Expository Essay
SUB-TOPIC: Elements of writing

CONTENT: ELEMENTS OF WRITING
An expository essay is one in which the writer attempts an exposition or explanation of an idea, or hoe to do or make something.
The elements of writing are:
i. Introduction
ii. The body of the essay
iii. Conclusion
EVALUATION: State the elements of writing.
ASSIGNMENT:
From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that contains the sound represented by the given phonetic symbol.
1. /ɔi /
(a) yell (b) holy (c) boy (d) idiot
2. / ɔi /
(a) Oyster (b) lure (c) couch (d) theory
3. /ai/
(a) stale (b) train (c) rain (d) dye
Change the following passive voice to active voice.
4. The cat was chased by the dog.
5. Jude was betrayed by the girls.
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Vowels: /ɔi /
CONTENT
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/87C55WKKBP4[/youtube]
Vowel /ɔi /
For the articulation of /ɔi /, the tongue glide begins from the back towards the front and the lips which are ‘rounded’, generally become spread as the tongue glide moves towards /I/.
There are only two spelling symbols for the diphthong. These are seen below:
‘oi’: boil, coil,
‘oy’: boy, toy,
‘uoy’ is an exceptional spelling as in ‘bouy’ which is pronounced as ‘boy’.
It is necessary to show the contrast between /ɔi / and / ɔ / as in the following words;
/ɔ: / /ɔi /
corn coin
bore boy
ball boil
call coil
jaw joy
tore toy
lawn loin
EVALUATION:
Indicate the vowel used in each of the following words. Endorse the vowel symbols in slanting lines.
(i) dawn (ii) point (iii) buoy (iv) corn (v) coy.
ASSIGNMENT:
Indicate the vowel used in each of the following words. Enclose the vowel symbols in slanting lines.
(i) Course (ii) curse (iii) cot (iv) coarse (v) worse.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/M-8ZqxVJMf8[/youtube]
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Highlighting Active voice
CONTENT: HIGHLIGHTING ACTIVE VOICE
There are two ways to express an ‘action’; active and passive voices.
A sentence in which the logical subject is the same as the grammatical subject is called an active sentence.
Logical subject is the subject that is the one who is actually said to be performing the actions of the verbs. When the subject in a sentence comes before the verb, we call this subject the grammatical subject.
Examples
i. Aisha ate the food.
ii. The girl has beaten the boy.
iii. A carpenter will make the chair.
iv. The police must arrest that thief.
v. My wife was drawing a picture.
EVALUATION:
Identify the active voices in the following passage.
Labi was checking through the carton of empty bottles which had been returned from chief Fadaka’s house when he found a paper bag which had slipped between the wrinkled flap and the side of the carton. He took it out, and to his surprise he found it contained a thick bundle of bank notes of a high denomination, totaling nearly ten thousand naira.
ASSIGNMENT:
Construct five sentences containing active voice.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: Skimming

CONTENT: SKIMMING
Skimming is most useful when you read with a definite question in mind and have an intention to find answers to the question.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 16.2.2; pages 152- 154.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 16.2. 3 and 16.3.4; pages 154-160.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Expository Essay
SUB-TOPIC: Elements of writing

CONTENT: ELEMENTS OF WRITING
An expository essay is one in which the writer attempts an exposition or explanation of an idea, or hoe to do or make something.
The elements of writing are:
i. Introduction
ii. The body of the essay
iii. Conclusion
EVALUATION: State the elements of writing.
ASSIGNMENT:
From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that contains the sound represented by the given phonetic symbol.
1. /ɔi /
(a) yell (b) holy (c) boy (d) idiot
2. / ɔi /
(a) Oyster (b) lure (c) couch (d) theory
3. /ai/
(a) stale (b) train (c) rain (d) dye
Change the following passive voice to active voice.
4. The cat was chased by the dog.
5. Jude was betrayed by the girls.
WEEK 3
LESSON 1
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Vowel /a:/and /au/.
/a: /:
This is a long vowel sound and it is found in the following words.

/a:/ as in cart, mark, dark, bark, clerk, heart, our, pass, father, barrage, pajamas, path, bath, vase, fast, answer, grass, laugh, aunt, draught, calm, balm, psalm, half, qualm, guard, reservoir, memoir, bourgeois, repertoire.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/1F47WdIjn5U[/youtube]
/au/: This is a diphthong sound. It is found in; now, how, town mouth, brown, how, blouse, plough, drought, bough, cow, allow, vow, out, stout, shout, about, around, voucher, gouge, proud, pronounce, sound etc.

[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/JrWuLH_AYM4[/youtube]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cdPImmffXzc
LESSON 2
ASPECT: STRUCTURE:
TOPIC: VERBS
Verbs are the action words in the sentences.
Active Structure is when the action is performed by the subject. e.g. I kick a ball
Examples of Active Verbs: e.g. come, sit, stand, write, do, kick, draw, eat, etc.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE:
1. Active: I kick a ball.
2. Active: He writes two letters.
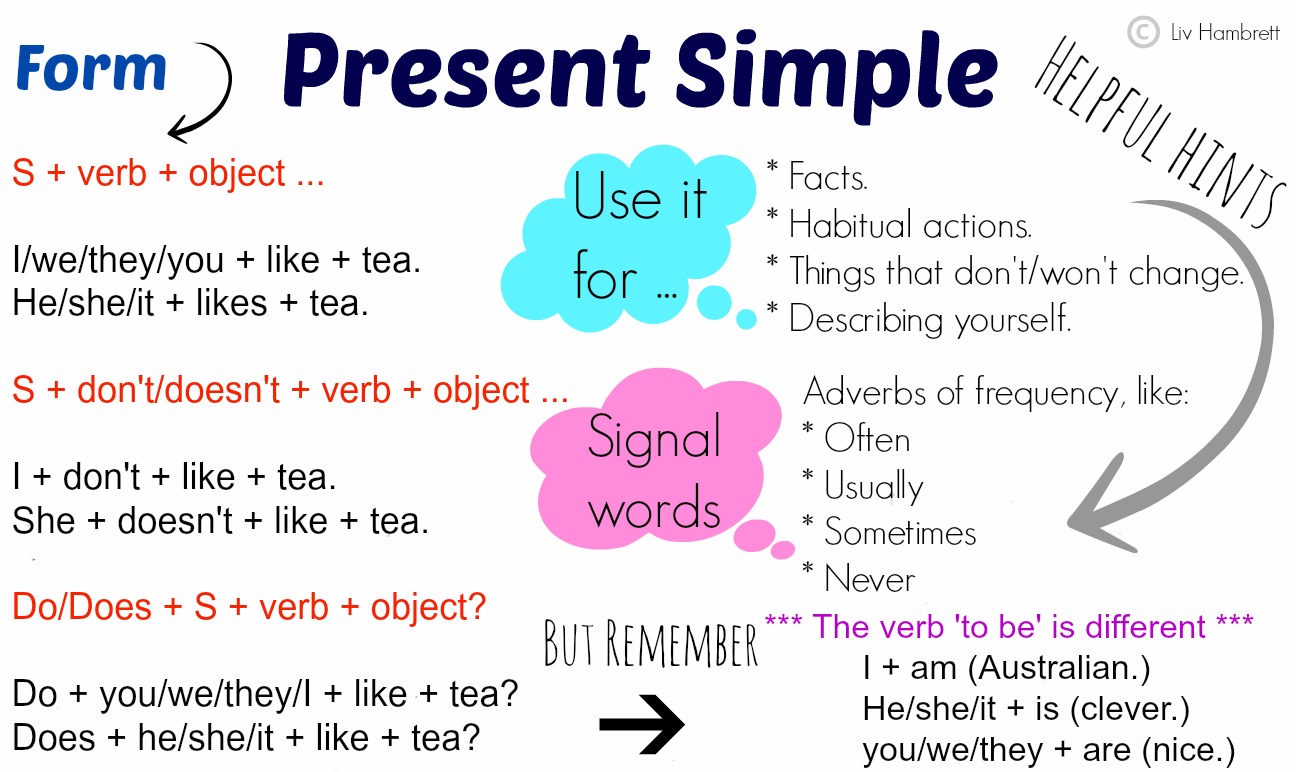
PAST TENSE:
1. Active: I kicked the ball.
2. Active: The boy wrote a letter.

PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE:
1. Active: I am kicking a ball.
2. Active: He is writing two letters.
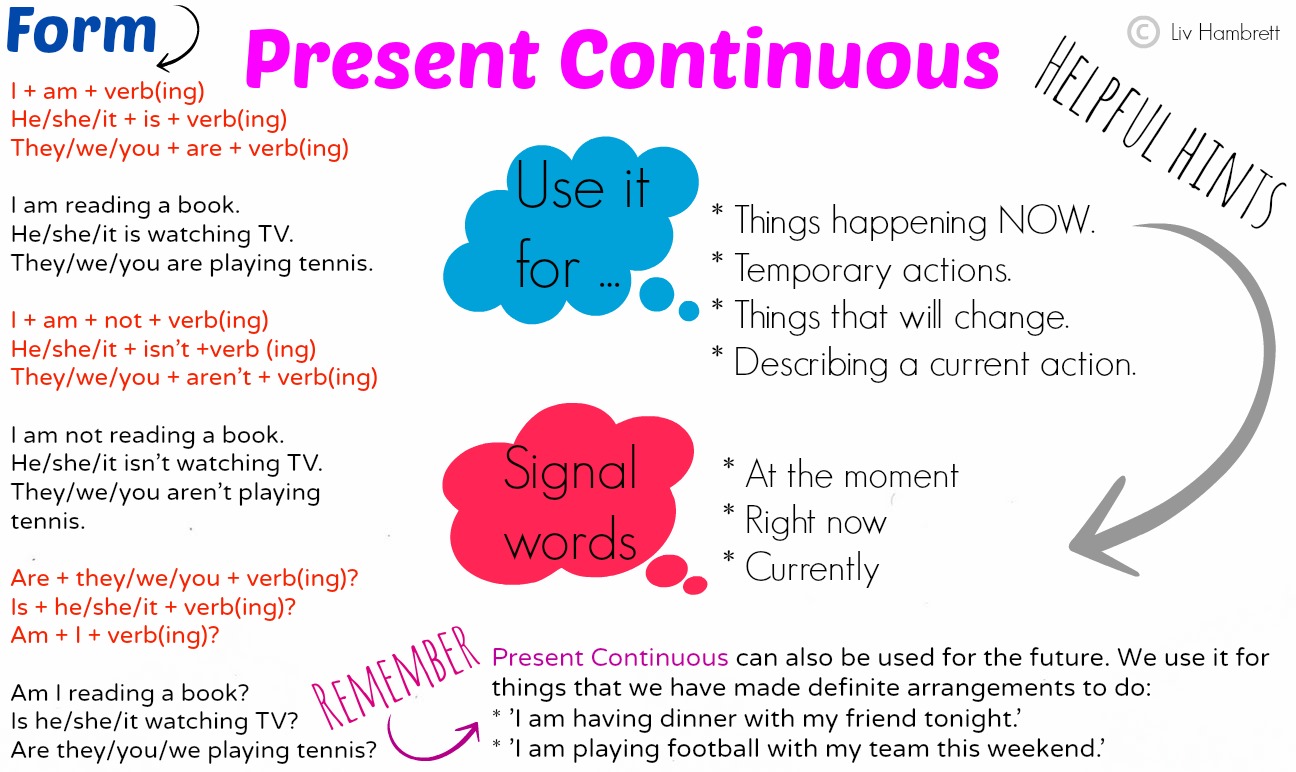
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE:
1. I have kicked a ball.
2. He has written two letters.

PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE:
1. I was writing my note.
2. We were reading many novels.
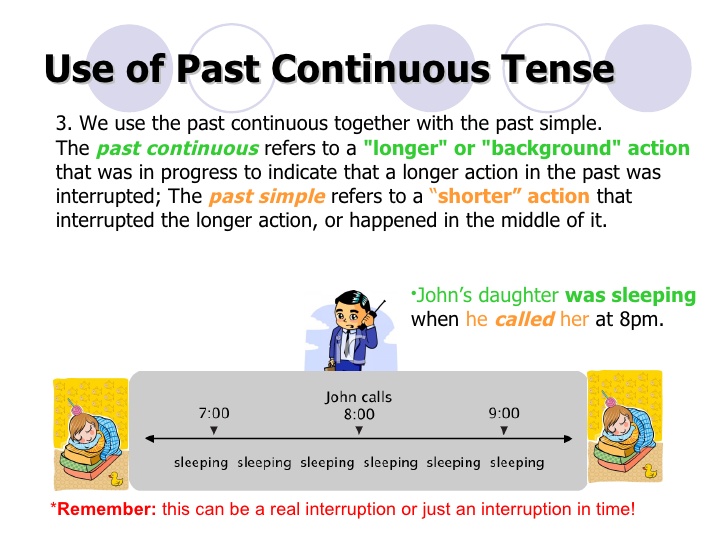
PAST PERFECT TENSE:
1. I had kicked the ball before he arrived.
2. She had washed her clothes before her friend came.

LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Silver
The poem is full of pictures. The poem describes a quiet moonlight night when most things are either asleep or motionless. There are a couple of uncommon words used in the poem. They are the following with their meanings shown.

shoon; shoes
casements; window frames
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 17.2.2; pages 162-164.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 17.2. 3 & 17.3.5; pages 164-169.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Expository Essay (Arrangement of ideas in logical sequence).
Title of essay
Introduction
Body of the essay
Conclusion
EVALUATION:
Discuss this topic in the class with your classmates: The Evil of Unemployment in My Country.
You may use the following points as guidelines in developing your composition (essay). Discuss each point in one paragraph. Some common problems associated with unemployment are:
I. Prostitution
II. Armed robbery
III. Hired assassination
IV. Thuggery
V. Affliction by diseases
VI. Broken marriages
VII. Untimely death (e.g. suicide)
VIII. Malnutrition
Use any three of these points to develop the body of your essay.
LITERATURE: Poetry-Read the selected poem (oral and writing poetry.)
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Vowel /a:/and /au/.
/a: /:
This is a long vowel sound and it is found in the following words.

/a:/ as in cart, mark, dark, bark, clerk, heart, our, pass, father, barrage, pajamas, path, bath, vase, fast, answer, grass, laugh, aunt, draught, calm, balm, psalm, half, qualm, guard, reservoir, memoir, bourgeois, repertoire.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/1F47WdIjn5U[/youtube]
/au/: This is a diphthong sound. It is found in; now, how, town mouth, brown, how, blouse, plough, drought, bough, cow, allow, vow, out, stout, shout, about, around, voucher, gouge, proud, pronounce, sound etc.

[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/JrWuLH_AYM4[/youtube]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cdPImmffXzc
LESSON 2
ASPECT: STRUCTURE:
TOPIC: VERBS
Verbs are the action words in the sentences.
Active Structure is when the action is performed by the subject. e.g. I kick a ball
Examples of Active Verbs: e.g. come, sit, stand, write, do, kick, draw, eat, etc.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE:
1. Active: I kick a ball.
2. Active: He writes two letters.

PAST TENSE:
1. Active: I kicked the ball.
2. Active: The boy wrote a letter.

PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE:
1. Active: I am kicking a ball.
2. Active: He is writing two letters.

PRESENT PERFECT TENSE:
1. I have kicked a ball.
2. He has written two letters.

PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE:
1. I was writing my note.
2. We were reading many novels.

PAST PERFECT TENSE:
1. I had kicked the ball before he arrived.
2. She had washed her clothes before her friend came.

LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Silver
The poem is full of pictures. The poem describes a quiet moonlight night when most things are either asleep or motionless. There are a couple of uncommon words used in the poem. They are the following with their meanings shown.

shoon; shoes
casements; window frames
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 17.2.2; pages 162-164.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 17.2. 3 & 17.3.5; pages 164-169.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Expository Essay (Arrangement of ideas in logical sequence).
Title of essay
Introduction
Body of the essay
Conclusion

EVALUATION:
Discuss this topic in the class with your classmates: The Evil of Unemployment in My Country.
You may use the following points as guidelines in developing your composition (essay). Discuss each point in one paragraph. Some common problems associated with unemployment are:
I. Prostitution
II. Armed robbery
III. Hired assassination
IV. Thuggery
V. Affliction by diseases
VI. Broken marriages
VII. Untimely death (e.g. suicide)
VIII. Malnutrition
Use any three of these points to develop the body of your essay.
LITERATURE: Poetry-Read the selected poem (oral and writing poetry.)
WEEK 4
LESSON 1
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
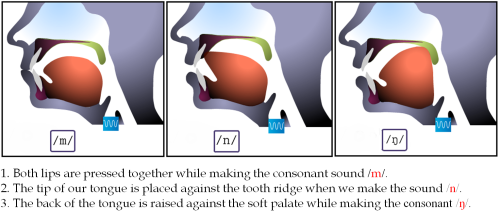
TOPIC: Nasal Sounds / m/ / n/ /ŋ/

The nasal sounds are produced as a result of closure in the mouth and the air flow escaped through the nose. The examples are stated below;
/m/ man, moon, make, name, bomb, claim, frame, lame, damn, hymn, condemn, bomb, comb, dumb, climb, plumb, crumb, grammar, commission, etc
a. In the following words, ‘m’ and not ‘b’ is the end sound even though ‘b’ can be seen. It is not pronounced. Plumb, dumb, climb, comb, tomb, bomb, numb, lamb, crumb.
b. More so, ‘m’ is the end-sound of these words and not ‘n’. Hymn, condemn, solemn.
/n/ name, nose, neck, new, note, stone, brain, gnash, gnat, gnaw, know, knowledge, knot, knit, knew, manner, banner, nanny, funnel, cranny, etc.
a. When ‘n’ is used after ‘m’ at word final positions, it is not pronounced. Examples: damn, hymn, condemn, column.
b. When ‘n’ is used after ‘k’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘k’ is silent. Examples: know, knot, knew, knit,etc
c. When ‘n’ is placed after ‘g’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘g’ is silent. Examples: gnash, gnaw, gnat, etc.
/ ŋ/ sing, king, ring, bank, bring, ink, spring, song, hang, tongue, bang, plank, bangle, anxious, drink, function, precinct, minx, etc
EVALUATION:
From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that has the same consonant sound(s) as the one represented by the letter(s) underlined.
1. bomb
A. Bubble B. stay C. come D. bone
2. Sing
A. hing B. king C. huge D. rinse
http://player.slideplayer.com/13/3936939/#
Further Studies
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/0Te4Us8Tsv8[/youtube]
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: Beware, soul Brother
CONTENT:
BEWARE, SOUL BROTHER
The poem warns the dancers to watch over their father’s land as they are dancing because if they don’t, the enemy will take it from them and their children will not have an inheritance later in life.

EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 19.2.2; pages 184-185.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 19.2. 3; page 185.
Further Reading...
Further Reading...
LESSON 3
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: VERB
Passive Structure: This is when the sentence is reversed from the object form to subject form. E.g. A ball is kicked by me.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE:
(1) Active: I kick a ball.
(2)Passive: A ball is kicked by me.
(3)Active: He writes two letters.
(4)Passive: Two letters are written by him.
PAST TENSE:
(1)Active: I kicked the ball.
(2)Passive: The ball was kicked by me.
(3)Active: The boy wrote a letter.
(4)Passive: A letter was written by the boy
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
(1)Active: I am kicking a ball.
(2)Passive: A ball is being kicked by me.
(3) Active: He is writing two letters.
(4) Passive: Two letters are being written by him.
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE:
(1) I have kicked a ball.
(2) He has written two letters.
LESSON 4
COMPOSITION: Expository Essay.
This kind of composition reveals the systematic way of doing things .It exposes the facts, characteristics and methods of doing it. Also it uncovers what was hidden about the fact .It should be discussed in sequential and logical order.
EVALUATION:
Write an article for publication in your school’s magazine on the topic: The Evil of Unemployment in My Country.
You may use the following points as guidelines in developing your composition (essay). Discuss each point in one paragraph. Some common problems associated with unemployment are:
I. Prostitution
II. Armed robbery
III. Hired assassination
IV. Thuggery
V. Affliction by diseases
VI. Broken marriages
VII. Untimely death (e.g. suicide)
VIII. Malnutrition
Use any three of these points to develop the body of your essay. Do not write address, salutation and complementary closing.
POETRY-Figures of speech and Literary terms in the poem should be read and discussed.
REVISION QUESTIONS:
Choose the right option to complete the following sentences below.
(1)I have ________ the tree down. (A) cuts (B) cut (C) cutting (D) cut
(2) The ball was kicked________ me. (A) with (B) in (C) by (D) on
(3)We _______ reading our books at that time. (A) are (B) was (C) were (D) will
Choose the right option that contains the sound below
(4)/ au/ (A) new (B) now ( C) do ( D) load
(5)/ m/ (A) low (B)moon (C) we ( D)thin
Change the following sentences into passive sentences.
1. My father built that house.
2. The policeman arrests the offender.
3. He hid the money under the bed.
4. The car knocked over a pedestrian.
5. I’m sending the book by express delivery.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Nasal Sounds / m/ / n/ /ŋ/

The nasal sounds are produced as a result of closure in the mouth and the air flow escaped through the nose. The examples are stated below;
/m/ man, moon, make, name, bomb, claim, frame, lame, damn, hymn, condemn, bomb, comb, dumb, climb, plumb, crumb, grammar, commission, etc
a. In the following words, ‘m’ and not ‘b’ is the end sound even though ‘b’ can be seen. It is not pronounced. Plumb, dumb, climb, comb, tomb, bomb, numb, lamb, crumb.
b. More so, ‘m’ is the end-sound of these words and not ‘n’. Hymn, condemn, solemn.
/n/ name, nose, neck, new, note, stone, brain, gnash, gnat, gnaw, know, knowledge, knot, knit, knew, manner, banner, nanny, funnel, cranny, etc.
a. When ‘n’ is used after ‘m’ at word final positions, it is not pronounced. Examples: damn, hymn, condemn, column.
b. When ‘n’ is used after ‘k’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘k’ is silent. Examples: know, knot, knew, knit,etc
c. When ‘n’ is placed after ‘g’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘g’ is silent. Examples: gnash, gnaw, gnat, etc.
/ ŋ/ sing, king, ring, bank, bring, ink, spring, song, hang, tongue, bang, plank, bangle, anxious, drink, function, precinct, minx, etc

EVALUATION:
From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that has the same consonant sound(s) as the one represented by the letter(s) underlined.
1. bomb
A. Bubble B. stay C. come D. bone
2. Sing
A. hing B. king C. huge D. rinse
http://player.slideplayer.com/13/3936939/#
Further Studies
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/0Te4Us8Tsv8[/youtube]
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: Beware, soul Brother
CONTENT:
BEWARE, SOUL BROTHER
The poem warns the dancers to watch over their father’s land as they are dancing because if they don’t, the enemy will take it from them and their children will not have an inheritance later in life.

EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 19.2.2; pages 184-185.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 19.2. 3; page 185.
Further Reading...
Further Reading...
LESSON 3
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: VERB
Passive Structure: This is when the sentence is reversed from the object form to subject form. E.g. A ball is kicked by me.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE:
(1) Active: I kick a ball.
(2)Passive: A ball is kicked by me.
(3)Active: He writes two letters.
(4)Passive: Two letters are written by him.
PAST TENSE:
(1)Active: I kicked the ball.
(2)Passive: The ball was kicked by me.
(3)Active: The boy wrote a letter.
(4)Passive: A letter was written by the boy
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
(1)Active: I am kicking a ball.
(2)Passive: A ball is being kicked by me.
(3) Active: He is writing two letters.
(4) Passive: Two letters are being written by him.
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE:
(1) I have kicked a ball.
(2) He has written two letters.
LESSON 4
COMPOSITION: Expository Essay.
This kind of composition reveals the systematic way of doing things .It exposes the facts, characteristics and methods of doing it. Also it uncovers what was hidden about the fact .It should be discussed in sequential and logical order.
EVALUATION:
Write an article for publication in your school’s magazine on the topic: The Evil of Unemployment in My Country.
You may use the following points as guidelines in developing your composition (essay). Discuss each point in one paragraph. Some common problems associated with unemployment are:
I. Prostitution
II. Armed robbery
III. Hired assassination
IV. Thuggery
V. Affliction by diseases
VI. Broken marriages
VII. Untimely death (e.g. suicide)
VIII. Malnutrition
Use any three of these points to develop the body of your essay. Do not write address, salutation and complementary closing.
POETRY-Figures of speech and Literary terms in the poem should be read and discussed.
REVISION QUESTIONS:
Choose the right option to complete the following sentences below.
(1)I have ________ the tree down. (A) cuts (B) cut (C) cutting (D) cut
(2) The ball was kicked________ me. (A) with (B) in (C) by (D) on
(3)We _______ reading our books at that time. (A) are (B) was (C) were (D) will
Choose the right option that contains the sound below
(4)/ au/ (A) new (B) now ( C) do ( D) load
(5)/ m/ (A) low (B)moon (C) we ( D)thin
Change the following sentences into passive sentences.
1. My father built that house.
2. The policeman arrests the offender.
3. He hid the money under the bed.
4. The car knocked over a pedestrian.
5. I’m sending the book by express delivery.
WEEK 5
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Stress

SUB-TOPIC: Introduction to stress.
Stress, in English Language is when part of a word receives strong pronunciation than the other. In English the part or chunk that the word is divisible into is called syllable. Therefore, a particular syllable (sound unit) that is pronounced more or louder than the other is called the stressed syllable. In speech, stress helps us to differentiate the meaning of a word that has the same spelling but different meaning and belong to different part of speech. Stress is define as the degree of prominence given to a particular syllable.
Example:
Noun / Verb
IM-port / im-PORT
EX-port / ex-PORT
CON-duct / con-DUCT
ES-cort / es-CORT
NOTE: A word cannot be stressed in English because it has only one syllable; stress can only start from two syllables.
Pronounce these words: EN-ter, O-pen, PA-per, MO-ney, BO-rrow, a-LIVE, di-VINE, a-PPLY, be-WARE, en-JOY etc
EVALUATION:
1. Define stress in your own word.
2. What is the part that pronounced more the other called?
3. Give examples of stressed words.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Highlighting Passive Voice
Passive voice is when the object of a sentence takes the place of the subject and the subject is placed in the position of the object while the verb “be” is used with the past participle. In other words, when the subject receives the action described by the verb, then the verb is in the Passive Voice.
For example, “Mary beat the boy “(active voice) becomes “The boy was beaten by Mary” (passive voice).
In the active voice, “Mary” is the subject of the sentence while “the boy” is the subject in the passive voice though the sentences mean the same thing. The verb “be” comprises “is, are, was and were”. More examples:
1. I saw Paul (Active voice).
2. Paul was seen by me (Passive voice).
3. We ate some mangoes (Active voice).
4. Some mangoes were eaten by us (Passive voice).
Now, take note of the changes that usually occur while writing passive sentences from an active one.
Active Passive
I Me
He Him
She Her
We Us
They Them
The verbs also change apart from these pronouns.
Active Passive
Saw Seen
Ate Eaten
Wrote Written
Drove Driven
Sang Sung
EVALUATION:
(a) Change the following sentences from active into passive.
1. Mustapha swept the floor.
2. We sang a new song.
3. The girl read an interesting book.
4. I own a new school bag.
5. They fought a serious war.
(b) Define passive verb.
(c)Explain the transformation that take place in passive voice of verb.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: THE RIVERS OSUN AND OBA

CONTENT:
Skim through the passage and find out the answers to the following questions.
I. What were the names of Sango’s three wives?
II. What did Sango’s wives do in turn for him?
III. What did Sango do when Oba told him what the soup was made of?
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 20.2.; pages 189-194.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 20.2.1 & 20.3(B); pages 194-196.
Further Reading...
Further Reading...
Further Reading...
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Expository (Guided Composition)
The Food I like Best.

There are many types of food. Now write a composition on the food you like best. Here are some questions to guide you. Remember not to number your points but write them in paragraphs.
1. Which type of food do you enjoin most?
2. Describe it generally, the source and manner of preparation etc.
3. Why do you like that kind of food more than the others?
4. When did you first begin to like that kind of food?
5. How often do you eat it?
6. What do you benefit from it?
7. Would you recommend it to your friends? If yes, why?
EVALUATION: What is an expository essay?
ASSIGNMENT: Write a composition on why you like English Language.
LESSON 5
ASPECT: Poetry
TOPIC: Literary terms used in the recommended poems.

EVALUATION:
Identify five the literary terms used in the poems read.
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Stress

SUB-TOPIC: Introduction to stress.
Stress, in English Language is when part of a word receives strong pronunciation than the other. In English the part or chunk that the word is divisible into is called syllable. Therefore, a particular syllable (sound unit) that is pronounced more or louder than the other is called the stressed syllable. In speech, stress helps us to differentiate the meaning of a word that has the same spelling but different meaning and belong to different part of speech. Stress is define as the degree of prominence given to a particular syllable.
Example:
Noun / Verb
IM-port / im-PORT
EX-port / ex-PORT
CON-duct / con-DUCT
ES-cort / es-CORT
NOTE: A word cannot be stressed in English because it has only one syllable; stress can only start from two syllables.
Pronounce these words: EN-ter, O-pen, PA-per, MO-ney, BO-rrow, a-LIVE, di-VINE, a-PPLY, be-WARE, en-JOY etc
EVALUATION:
1. Define stress in your own word.
2. What is the part that pronounced more the other called?
3. Give examples of stressed words.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Highlighting Passive Voice
Passive voice is when the object of a sentence takes the place of the subject and the subject is placed in the position of the object while the verb “be” is used with the past participle. In other words, when the subject receives the action described by the verb, then the verb is in the Passive Voice.
For example, “Mary beat the boy “(active voice) becomes “The boy was beaten by Mary” (passive voice).
In the active voice, “Mary” is the subject of the sentence while “the boy” is the subject in the passive voice though the sentences mean the same thing. The verb “be” comprises “is, are, was and were”. More examples:
1. I saw Paul (Active voice).
2. Paul was seen by me (Passive voice).
3. We ate some mangoes (Active voice).
4. Some mangoes were eaten by us (Passive voice).
Now, take note of the changes that usually occur while writing passive sentences from an active one.
Active Passive
I Me
He Him
She Her
We Us
They Them
The verbs also change apart from these pronouns.
Active Passive
Saw Seen
Ate Eaten
Wrote Written
Drove Driven
Sang Sung
EVALUATION:
(a) Change the following sentences from active into passive.
1. Mustapha swept the floor.
2. We sang a new song.
3. The girl read an interesting book.
4. I own a new school bag.
5. They fought a serious war.
(b) Define passive verb.
(c)Explain the transformation that take place in passive voice of verb.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Comprehension
TOPIC: THE RIVERS OSUN AND OBA

CONTENT:
Skim through the passage and find out the answers to the following questions.
I. What were the names of Sango’s three wives?
II. What did Sango’s wives do in turn for him?
III. What did Sango do when Oba told him what the soup was made of?
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 20.2.; pages 189-194.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 20.2.1 & 20.3(B); pages 194-196.
Further Reading...
Further Reading...
Further Reading...
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Expository (Guided Composition)
The Food I like Best.

There are many types of food. Now write a composition on the food you like best. Here are some questions to guide you. Remember not to number your points but write them in paragraphs.
1. Which type of food do you enjoin most?
2. Describe it generally, the source and manner of preparation etc.
3. Why do you like that kind of food more than the others?
4. When did you first begin to like that kind of food?
5. How often do you eat it?
6. What do you benefit from it?
7. Would you recommend it to your friends? If yes, why?
EVALUATION: What is an expository essay?
ASSIGNMENT: Write a composition on why you like English Language.
LESSON 5
ASPECT: Poetry
TOPIC: Literary terms used in the recommended poems.

EVALUATION:
Identify five the literary terms used in the poems read.
WEEK 6
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Stress
SUB-TOPIC: Stress Pattern.
Stress occurs in different places in a word, and this, we called stress pattern.
1. Stress on the first syllable of some words
e.g.
STUdent, PICture, MOther,TEAcher, TEAches, FAther,BUtcher,TAIlor,VENdor,TRAder,DOCtor,
WORker,DRIver,BUILder,FARmer,LAWyer,JANuary,FEBruary,April,August,JUNE,MAY etc.
2. Stress on the second syllable of some words (middle syllable) E.g JuLY,SeptEMber,OcTOber,NoVEMber,DeCEMber,meCHAnic,exAMple,mosQUIto,muSIcian,reVIsion,sucCESSful,proTECT,exPLAIN,reLIgion,poSItion,toMORrow,perMIssion,traDItion etc.
3. Stress on the third syllable of some words, examples are: uniVERsity, typoGRAphical, elecTRIcity, psychoLOgical, distriBUtion etc.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/Wbs5aoqFtVQ?lis ... B32F6C27F9[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
1. What is stress pattern?
2. Mention the stress pattern you know.
3. Give examples of the stress pattern.
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Making sentences with passive voice.
The subject in a passive sentence is not the person or thing that does the action of the verb. It is the person or thing that is acted on by the verb.
1. The injured man was helped by a passer-by.
2. The man was being questioned by the police.
3. The patient was operated on by a team of five surgeons.
4. An elderly man was run over while crossing the road.
5. Roger has been given his promotion.
6. The window was broken by someone.
7. My brother was given extra tuition by his teacher.
8. The sorting is done by machine.
9. The safe was blown open with dynamite.
10. I was showered with presents on my eighteenth birthday.
EVALUATION:
Change the following sentences from active voice to passive voice without changing the tense or meaning.
1. The games master coaches the football team.
2. John is playing ball.
3. The farmer has killed a snake.
4. The butcher was killing a goat.
5. Will the messenger deliver the letter?
6. Lawal saw the cave.
7. Bunmi has read the novel.
8. Did you buy this book?
9. The watchman arrested the thief.
10. The traders bought all the yams.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Narrative, Descriptive, Argumentative and Expository---Identifying their differences.
Narrative composition is employed to narrate events that have happened in the past; descriptive composition is employed to describe place, location, school and it is used to give directive to a particular location.
Description is usually used in narrative composition to describe how an event took place and what and what happened right there.
Expository composition, on the one hand, is used to expose the things we do not know how to do, examples are: How to prepare “ogbono soup”, “The traditional festival in my town” etc. This is used to explain to or teach those who are not familiar with the concept in question.
Argumentative composition, on the other hand, is purely used to argue in other to win the listener or reader to the speaker or writer’s side. This is the type used in debating competition.
From the on-going, the differences between the four types of composition are clear.
EVALUATION: Identify the differences that exist between the four types of the composition.
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Stress
SUB-TOPIC: Stress Pattern.
Stress occurs in different places in a word, and this, we called stress pattern.
1. Stress on the first syllable of some words
e.g.
STUdent, PICture, MOther,TEAcher, TEAches, FAther,BUtcher,TAIlor,VENdor,TRAder,DOCtor,
WORker,DRIver,BUILder,FARmer,LAWyer,JANuary,FEBruary,April,August,JUNE,MAY etc.
2. Stress on the second syllable of some words (middle syllable) E.g JuLY,SeptEMber,OcTOber,NoVEMber,DeCEMber,meCHAnic,exAMple,mosQUIto,muSIcian,reVIsion,sucCESSful,proTECT,exPLAIN,reLIgion,poSItion,toMORrow,perMIssion,traDItion etc.
3. Stress on the third syllable of some words, examples are: uniVERsity, typoGRAphical, elecTRIcity, psychoLOgical, distriBUtion etc.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/Wbs5aoqFtVQ?lis ... B32F6C27F9[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
1. What is stress pattern?
2. Mention the stress pattern you know.
3. Give examples of the stress pattern.
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Making sentences with passive voice.
The subject in a passive sentence is not the person or thing that does the action of the verb. It is the person or thing that is acted on by the verb.
1. The injured man was helped by a passer-by.
2. The man was being questioned by the police.
3. The patient was operated on by a team of five surgeons.
4. An elderly man was run over while crossing the road.
5. Roger has been given his promotion.
6. The window was broken by someone.
7. My brother was given extra tuition by his teacher.
8. The sorting is done by machine.
9. The safe was blown open with dynamite.
10. I was showered with presents on my eighteenth birthday.
EVALUATION:
Change the following sentences from active voice to passive voice without changing the tense or meaning.
1. The games master coaches the football team.
2. John is playing ball.
3. The farmer has killed a snake.
4. The butcher was killing a goat.
5. Will the messenger deliver the letter?
6. Lawal saw the cave.
7. Bunmi has read the novel.
8. Did you buy this book?
9. The watchman arrested the thief.
10. The traders bought all the yams.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Narrative, Descriptive, Argumentative and Expository---Identifying their differences.
Narrative composition is employed to narrate events that have happened in the past; descriptive composition is employed to describe place, location, school and it is used to give directive to a particular location.
Description is usually used in narrative composition to describe how an event took place and what and what happened right there.
Expository composition, on the one hand, is used to expose the things we do not know how to do, examples are: How to prepare “ogbono soup”, “The traditional festival in my town” etc. This is used to explain to or teach those who are not familiar with the concept in question.
Argumentative composition, on the other hand, is purely used to argue in other to win the listener or reader to the speaker or writer’s side. This is the type used in debating competition.
From the on-going, the differences between the four types of composition are clear.
EVALUATION: Identify the differences that exist between the four types of the composition.
WEEK 7
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech Work
TOPIC: Stress: Compound Words
Definition of Stress
This refers to the emphasis laid on one word or part of a word more than others. In a given word the syllable which is pronounced strongly or on which the emphasis is, is called Stressed Syllable.
Describing stress pattern words begin as one syllable, syllable means any of the units into which a word may be divided usually consisting of a vowel sound with a consonant before and after it. Syllable is the most basic unit in speech.
While one syllable words can be pronounced strongly, words of two or more syllables often have one of their parts pronounced strongly while the other part receives weak pronunciation. When an English word is pronounced a particular syllable (sound unit) often stands out above the others. That is usually the stressed syllable.
Practicing Stress Patterns
Words of two syllables that function as nouns are often stressed on the first syllable from the beginning of a noun and on the second syllable if a verb. The parts of the word in capital letters are stressed but the part in small letters is unstressed.
Examples
Noun Verb
IM-port / im-PORT
EX-port / ex-PORT
CON-duct / con-DUCT
ES-cort / es-CORT
PRO-ject / pro-JECT
IN-crease / In-CREASE
CON-test / con-TEST
CON-tact / con-TACT
AB-stract / ab-STRACT, etc
EVALUATION
1. What is Stress?
2. What is Stressed Syllable?
3. What is a syllable?
4. Another name for syllable is?
5. Words of two syllables are stressed on the first if it is a ____?
6. On the second if it is ________?
LESSON 2
ASPECT: STRUCTURE:
TOPIC: Verbs (Making Sentences with Active and Passive Voices)
DEFINITION OF VERBS
A verb is used to express an action or a state of being. A verb changes its form to mark such categories as tense, aspects, voice etc.
ACTIVE VOICE: This refers to a situation where the action is done by the subject in the sentence.
Examples;
(1) The dog chased the postman.
(2) Obi cleaned the blackboard.
PASSIVE VOICE: Refers to a case whereby the action is done to the subject in the sentence.
Examples
1. The postman was chased by the dog.
2. The blackboard was cleaned by Obi.
Making Sentence with Active and Passive Voices
1. Obi cleaned the blackboard. The blackboard was cleaned by obi.
2. The dog chased the postman. The postman was chased by the dog.
3. I wash the clothes. The clothes are washed by me.
4. The mother feeds the baby. The baby is fed by the mother.
5. Adana cooks the meals. The meals are cooked by Adana
EVALUATION
1. What is a verb?
2. A verb changes its form to mark such categories as voice. True/False
3. Change these sentences to passive voice
a. The cat ate the fish
b. Emeka dusts the chairs.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: INFORMAL LETTERS
An informal letter is a letter written to any of the following persons: father, mother, brother, sister, uncle, aunt, nephew, niece cousin, in-law, close friend, pen-friend, classmate, neighbour, etc. It requires only one address.
FEATURES OF INFORMAL LETTERS
1. Address of writer (written at the top right-hand corner of your writing sheet of paper)
2. Date (written under the writers address).
3. Opening salutation (e.g.; Dear Uncle, Aunt, Brother, Sister, etc).
4. Body
5. Closing salutation
Yours sincerely, your loving son, daughter, brother, etc (no signature or surname is allowed.
Writing to suit different situation with the knowledge of what informal letters are and the features, informal letters could be written to suit different situation such; congratulating, appreciating, demanding, etc.
EVALUATION
1. What is an informal letter?
2. Mention five persons an informal letter could be written to?
3. Mention 4 features of informal letters
4. In informal letters, the writers address is written at _____?
ASSIGNMENT: Write a letter appreciating your uncle for the Christmas gifts he sent to you.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: Poetry; Themes, features, structure, language
Themes of poetry
These refer to the main idea in a poem that is the subject matter of a poem this could be love, nature, beauty, etc.
Features and structure of poetry
A poem is always written in verse. Poetry uses language in a compressed form. It expresses real life.
1. A poem is always written in a ___?
2. Poetry uses language in a ________form?
The language of poetry.
The language of poetry refers to its elements. These elements are as follows:
1. Imagery: Images are created in poetry by means of figures of speech.
2. Rhythm: This refers to the alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables.
3. Sound: Sound is one of the simple elements that compose vocal utterance.
EVALUATION
1. The subject matter of a poem is called_______
2. What is a poem?
1. The language of poetry refers to ______-?
2. Mention 2 elements of poetry
ASPECT: Speech Work
TOPIC: Stress: Compound Words
Definition of Stress
This refers to the emphasis laid on one word or part of a word more than others. In a given word the syllable which is pronounced strongly or on which the emphasis is, is called Stressed Syllable.
Describing stress pattern words begin as one syllable, syllable means any of the units into which a word may be divided usually consisting of a vowel sound with a consonant before and after it. Syllable is the most basic unit in speech.
While one syllable words can be pronounced strongly, words of two or more syllables often have one of their parts pronounced strongly while the other part receives weak pronunciation. When an English word is pronounced a particular syllable (sound unit) often stands out above the others. That is usually the stressed syllable.
Practicing Stress Patterns
Words of two syllables that function as nouns are often stressed on the first syllable from the beginning of a noun and on the second syllable if a verb. The parts of the word in capital letters are stressed but the part in small letters is unstressed.
Examples
Noun Verb
IM-port / im-PORT
EX-port / ex-PORT
CON-duct / con-DUCT
ES-cort / es-CORT
PRO-ject / pro-JECT
IN-crease / In-CREASE
CON-test / con-TEST
CON-tact / con-TACT
AB-stract / ab-STRACT, etc
EVALUATION
1. What is Stress?
2. What is Stressed Syllable?
3. What is a syllable?
4. Another name for syllable is?
5. Words of two syllables are stressed on the first if it is a ____?
6. On the second if it is ________?
LESSON 2
ASPECT: STRUCTURE:
TOPIC: Verbs (Making Sentences with Active and Passive Voices)
DEFINITION OF VERBS
A verb is used to express an action or a state of being. A verb changes its form to mark such categories as tense, aspects, voice etc.
ACTIVE VOICE: This refers to a situation where the action is done by the subject in the sentence.
Examples;
(1) The dog chased the postman.
(2) Obi cleaned the blackboard.
PASSIVE VOICE: Refers to a case whereby the action is done to the subject in the sentence.
Examples
1. The postman was chased by the dog.
2. The blackboard was cleaned by Obi.
Making Sentence with Active and Passive Voices
1. Obi cleaned the blackboard. The blackboard was cleaned by obi.
2. The dog chased the postman. The postman was chased by the dog.
3. I wash the clothes. The clothes are washed by me.
4. The mother feeds the baby. The baby is fed by the mother.
5. Adana cooks the meals. The meals are cooked by Adana
EVALUATION
1. What is a verb?
2. A verb changes its form to mark such categories as voice. True/False
3. Change these sentences to passive voice
a. The cat ate the fish
b. Emeka dusts the chairs.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: INFORMAL LETTERS
An informal letter is a letter written to any of the following persons: father, mother, brother, sister, uncle, aunt, nephew, niece cousin, in-law, close friend, pen-friend, classmate, neighbour, etc. It requires only one address.
FEATURES OF INFORMAL LETTERS
1. Address of writer (written at the top right-hand corner of your writing sheet of paper)
2. Date (written under the writers address).
3. Opening salutation (e.g.; Dear Uncle, Aunt, Brother, Sister, etc).
4. Body
5. Closing salutation
Yours sincerely, your loving son, daughter, brother, etc (no signature or surname is allowed.
Writing to suit different situation with the knowledge of what informal letters are and the features, informal letters could be written to suit different situation such; congratulating, appreciating, demanding, etc.
EVALUATION
1. What is an informal letter?
2. Mention five persons an informal letter could be written to?
3. Mention 4 features of informal letters
4. In informal letters, the writers address is written at _____?
ASSIGNMENT: Write a letter appreciating your uncle for the Christmas gifts he sent to you.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: Poetry; Themes, features, structure, language
Themes of poetry
These refer to the main idea in a poem that is the subject matter of a poem this could be love, nature, beauty, etc.
Features and structure of poetry
A poem is always written in verse. Poetry uses language in a compressed form. It expresses real life.
1. A poem is always written in a ___?
2. Poetry uses language in a ________form?
The language of poetry.
The language of poetry refers to its elements. These elements are as follows:
1. Imagery: Images are created in poetry by means of figures of speech.
2. Rhythm: This refers to the alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables.
3. Sound: Sound is one of the simple elements that compose vocal utterance.
EVALUATION
1. The subject matter of a poem is called_______
2. What is a poem?
1. The language of poetry refers to ______-?
2. Mention 2 elements of poetry
WEEK 8
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonant Clusters
Describing Consonant Clusters
Describing consonant clusters consonant clusters refers to a situation where a word begins with two or three consonants or ends with two, three or four consonants. Note that, no vowel sound intervenes between a consonant clusters.
Recognizing the forms of clusters
There are three forms of consonant cluster namely
- two consonant cluster
- three consonant cluster
- four consonant cluster
I. Two consonant cluster
INITIAL ... FINAL
Black /bl/ ... best /st/
Bread/br/ ... sons /nz/
Cloud /kl/ ... bells /lz/
Cry /kr/ ... pots /ts/
Drop /dr/ ... caps /ps/
Great /gr/ ... books /ks/
Play /pl/ ... teams /mz/
Speak /sp/... legs /gz/
Tree /tr/ ... inflict /kt/
Dwell/dw/... ant /nt/
Frog /fr/ ... task /sk/
Pray /pr/ ... lump /mp/, etc
II. Three-consonant cluster
Initial ... final
Splash /spl/... nest /sts/
Spray /spr/... bands /ndz/
Square /skw/... next /kst/
Street /str/... ants /nts/
Scroll /skr/... tasks /rs/
Spread /spr/... lumps /mpz/
Strong /str/ ... posts /sts/
Practising Consonant Clusters
Pronounce the following words that comprise consonant clusters
Double... strong
Grab ... beast
Spread ... lumps
Plead ... flee
Crowd ... mats, etc
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/ZxKUWoNfetE[/youtube]
EVALUATION
1. What is consonant cluster?
2. A vowel always comes in between a consonant cluster True/False?
3. How many types of consonant clusters do we have?
4. Give 3 examples each of 2 of them at the initial and final positions.
ASSIGNMENT: Underline the Consonant Cluster in the following:
a. spring, strong, spread
b. tasks, next bands
c. glad bribe, crowd
d. dish, ribs, castle
LESSON 2
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: Pronouns: Forms, Position and Functions of pronouns
Definition of pronouns
A pronoun takes the place of a noun “pro” is a Latin prefix meaning for. Pronoun = for a noun.
Forms and Position of Pronouns
1. Personal pronouns which is further classified as subject and object.
Subject object
I me
You you
He him
She her
It it
We us
They them
2. Possessive pronoun
Subject object
My mine
His his
Her hers
Its its
Our ours
Their their
3. Reflexive pronoun example myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, etc.
4. Demonstrative pronoun
Examples: This, these, that, those, etc
5. Interrogative pronoun: Examples: What, whom, whom, which, whose, etc.
6. Indefinite pronoun: Examples All, anybody, anything, every one, everybody, more, some, etc.
7. Relative pronoun: Examples who, whose, whom, which, that etc
Pronouns take the position of a noun.
Function of Pronouns
- A pronoun stands for a noun
- Takes the place of a noun.
- Pronouns help to avoid repetition in a sentence
- Pronouns indicate number as in singular or plural number
- Pronouns indicate persons
a. 1st person - the speaker
b. 2nd person - the person spoken to
c. 3rd person – the person or thing spoken about
Pronouns indicate gender (masculine, feminine, neuter or general) EVALUATION
1. What is a pronoun?
2. A Latin prefix meaning for is ____?
3. List 5 types of pronouns
4. What is the position of a pronoun in a sentence?
ASSIGNMENT
1. Write 3 functions of a pronoun
2. What is 3rd person?
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Formal letters: Writing to Suit Different Situations
Definition of formal letters
Formal letters are letters written to offices. They are otherwise known as official letters.
Features of Formal Letters
Formal letters have the following features
1. Address of the writer & date (written at the top right hand corner of the sheet of paper).
2. Address of the addressee (writer below the writers address at the left hand corner of the writing paper)
3. Salutation (written below the addressee’s address
4. The letter heading (This comes below the salutation on the centre between the writer’s address and the addressee’s address.
5. The body of the letter (written in paragraphs)
6. Conclusion
Writing to Suit Different Situations
Our exposure to the definition and features of formal letters should enable us write to suit different situations such as;
Application for employment, application for admission, application for supplies, etc.
EVALUATION
1. What is a formal letter?
2. A formal letter is otherwise referred to as ___?
3. Mention 3 features of a formal letter.
4. What position does the addressee’s address take in the writing sheet.
ASSIGNMENT: Write an application for permission to be absent from school for one week.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: Poetry: More on figures of speech
Definition of Poetry and Figures of Speech
Poetry is a collection of poem. Figures of speech refer to a word or phrase which does not have its normal or basic meaning.
Examples of Figures of Speech
1. Simile: This is a figure of speech, in which something is compared with another using “like” or “as” as fast as a deer, as feeble as a child, as gentle as a dove, as agile as a monkey, as light as feather,
2. Metaphor: A metaphor is a figure of speech which compares two things that posses similar features by saying that one thing is another. It is a direct comparison between two things without the use of “like” and “as”
Examples
i. Ade was a lion in the fight
ii. She is the pillar of our family
iii. He is a giant among men etc
3. Irony: This involves the use of words to convey the opposite of their literal meaning. A situation where the meaning is contradicted by the appearance or presentation of idea.
Examples
i. The boy is so intelligent that he failed his exam.
ii. The students are so respectful that they insult their teacher.
4. Personification: This is a figure of speech in which an inanimate object is endowed with human qualities or abilities.
Examples
i. My car was happy to be washed
ii. The picture in that magazine screamed for attention.
iii. The carved pumpkin smiled at me.
5. Alliteration: This refers to the repetition of an initial consonant sound.
Examples
i. Dusks demands daylight.
ii. Sara’s seven sisters slept soundly in the sand.
6. Onomatopoeia- The use of words that imitates the sounds associated with the objects or actions they refer to.
Examples:
i. The buzzing of bees
ii. The clatter of utensils
iii. The flutter of birds, etc
7. Hyperbole: This is a figure of speech that uses exaggerated words.
Examples
i. The whole word is staring at me.
ii. Bill Gates winning a computer
iii. I’m so busy trying to accomplish one million things at a time.
8. Pun: A play or on words, sometimes on different senses of the same word and sometimes on similar sense or sound of different word.
Examples
i. Santa’s helpers are subordinate clauses.
ii. I’m a shoe maker; I can mend your soul.
9. Litotes: A figure of speech consisting of an understatement in which an affirmative is expressed by negating its opposite.
Examples
i. Einstein is not a bad Mathematician.
10. Synecdoche: This is a figure of speech in which a part is used to represent the whole or the whole for part.
Examples
1. ABC for Alphabets
2. The grey beard for old man, etc.
EVALUATION
1. What poetry?
2. Give 2 of figures of speech
ASSIGNMENT: Give five examples each of the following figures of speech:
1. Metaphor
2. Hyperbole
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonant Clusters
Describing Consonant Clusters
Describing consonant clusters consonant clusters refers to a situation where a word begins with two or three consonants or ends with two, three or four consonants. Note that, no vowel sound intervenes between a consonant clusters.
Recognizing the forms of clusters
There are three forms of consonant cluster namely
- two consonant cluster
- three consonant cluster
- four consonant cluster
I. Two consonant cluster
INITIAL ... FINAL
Black /bl/ ... best /st/
Bread/br/ ... sons /nz/
Cloud /kl/ ... bells /lz/
Cry /kr/ ... pots /ts/
Drop /dr/ ... caps /ps/
Great /gr/ ... books /ks/
Play /pl/ ... teams /mz/
Speak /sp/... legs /gz/
Tree /tr/ ... inflict /kt/
Dwell/dw/... ant /nt/
Frog /fr/ ... task /sk/
Pray /pr/ ... lump /mp/, etc
II. Three-consonant cluster
Initial ... final
Splash /spl/... nest /sts/
Spray /spr/... bands /ndz/
Square /skw/... next /kst/
Street /str/... ants /nts/
Scroll /skr/... tasks /rs/
Spread /spr/... lumps /mpz/
Strong /str/ ... posts /sts/
Practising Consonant Clusters
Pronounce the following words that comprise consonant clusters
Double... strong
Grab ... beast
Spread ... lumps
Plead ... flee
Crowd ... mats, etc
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/ZxKUWoNfetE[/youtube]
EVALUATION
1. What is consonant cluster?
2. A vowel always comes in between a consonant cluster True/False?
3. How many types of consonant clusters do we have?
4. Give 3 examples each of 2 of them at the initial and final positions.
ASSIGNMENT: Underline the Consonant Cluster in the following:
a. spring, strong, spread
b. tasks, next bands
c. glad bribe, crowd
d. dish, ribs, castle
LESSON 2
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: Pronouns: Forms, Position and Functions of pronouns
Definition of pronouns
A pronoun takes the place of a noun “pro” is a Latin prefix meaning for. Pronoun = for a noun.
Forms and Position of Pronouns
1. Personal pronouns which is further classified as subject and object.
Subject object
I me
You you
He him
She her
It it
We us
They them
2. Possessive pronoun
Subject object
My mine
His his
Her hers
Its its
Our ours
Their their
3. Reflexive pronoun example myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, etc.
4. Demonstrative pronoun
Examples: This, these, that, those, etc
5. Interrogative pronoun: Examples: What, whom, whom, which, whose, etc.
6. Indefinite pronoun: Examples All, anybody, anything, every one, everybody, more, some, etc.
7. Relative pronoun: Examples who, whose, whom, which, that etc
Pronouns take the position of a noun.
Function of Pronouns
- A pronoun stands for a noun
- Takes the place of a noun.
- Pronouns help to avoid repetition in a sentence
- Pronouns indicate number as in singular or plural number
- Pronouns indicate persons
a. 1st person - the speaker
b. 2nd person - the person spoken to
c. 3rd person – the person or thing spoken about
Pronouns indicate gender (masculine, feminine, neuter or general) EVALUATION
1. What is a pronoun?
2. A Latin prefix meaning for is ____?
3. List 5 types of pronouns
4. What is the position of a pronoun in a sentence?
ASSIGNMENT
1. Write 3 functions of a pronoun
2. What is 3rd person?
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Formal letters: Writing to Suit Different Situations
Definition of formal letters
Formal letters are letters written to offices. They are otherwise known as official letters.
Features of Formal Letters
Formal letters have the following features
1. Address of the writer & date (written at the top right hand corner of the sheet of paper).
2. Address of the addressee (writer below the writers address at the left hand corner of the writing paper)
3. Salutation (written below the addressee’s address
4. The letter heading (This comes below the salutation on the centre between the writer’s address and the addressee’s address.
5. The body of the letter (written in paragraphs)
6. Conclusion
Writing to Suit Different Situations
Our exposure to the definition and features of formal letters should enable us write to suit different situations such as;
Application for employment, application for admission, application for supplies, etc.
EVALUATION
1. What is a formal letter?
2. A formal letter is otherwise referred to as ___?
3. Mention 3 features of a formal letter.
4. What position does the addressee’s address take in the writing sheet.
ASSIGNMENT: Write an application for permission to be absent from school for one week.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: Poetry: More on figures of speech
Definition of Poetry and Figures of Speech
Poetry is a collection of poem. Figures of speech refer to a word or phrase which does not have its normal or basic meaning.
Examples of Figures of Speech
1. Simile: This is a figure of speech, in which something is compared with another using “like” or “as” as fast as a deer, as feeble as a child, as gentle as a dove, as agile as a monkey, as light as feather,
2. Metaphor: A metaphor is a figure of speech which compares two things that posses similar features by saying that one thing is another. It is a direct comparison between two things without the use of “like” and “as”
Examples
i. Ade was a lion in the fight
ii. She is the pillar of our family
iii. He is a giant among men etc
3. Irony: This involves the use of words to convey the opposite of their literal meaning. A situation where the meaning is contradicted by the appearance or presentation of idea.
Examples
i. The boy is so intelligent that he failed his exam.
ii. The students are so respectful that they insult their teacher.
4. Personification: This is a figure of speech in which an inanimate object is endowed with human qualities or abilities.
Examples
i. My car was happy to be washed
ii. The picture in that magazine screamed for attention.
iii. The carved pumpkin smiled at me.
5. Alliteration: This refers to the repetition of an initial consonant sound.
Examples
i. Dusks demands daylight.
ii. Sara’s seven sisters slept soundly in the sand.
6. Onomatopoeia- The use of words that imitates the sounds associated with the objects or actions they refer to.
Examples:
i. The buzzing of bees
ii. The clatter of utensils
iii. The flutter of birds, etc
7. Hyperbole: This is a figure of speech that uses exaggerated words.
Examples
i. The whole word is staring at me.
ii. Bill Gates winning a computer
iii. I’m so busy trying to accomplish one million things at a time.
8. Pun: A play or on words, sometimes on different senses of the same word and sometimes on similar sense or sound of different word.
Examples
i. Santa’s helpers are subordinate clauses.
ii. I’m a shoe maker; I can mend your soul.
9. Litotes: A figure of speech consisting of an understatement in which an affirmative is expressed by negating its opposite.
Examples
i. Einstein is not a bad Mathematician.
10. Synecdoche: This is a figure of speech in which a part is used to represent the whole or the whole for part.
Examples
1. ABC for Alphabets
2. The grey beard for old man, etc.
EVALUATION
1. What poetry?
2. Give 2 of figures of speech
ASSIGNMENT: Give five examples each of the following figures of speech:
1. Metaphor
2. Hyperbole
