SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1 - 2 Human Issues:
(a) Computer Professionals: (i) Computer Manager (ii) System Analyst
(iii) Programmers (iv) Computer Educator (v) Computer Engineers and Technicians (vi) Computer Operators
(b) Qualities of good Computer professionals
(c) Computer Professional Bodies: (i) Nigeria Computer Society (NCS) (ii) Institute of Management Information System (IMIS) (iii) Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria (CPRN) (iv) Information Technology Association of Nigeria (ITAN) (v) Nigerian Internet Group (NIG)
3 - 4 Computer Viruses:
(a) Meaning
(b) Types of computer virus: (i) Boot Sector (ii) Executable file virus (iii) Attack on document.
(c) Examples of viruses: (i) Trojan horse (ii) Sleeper (iii) Logic bomb (iv) Alabama virus (v) Christmas virus.
(d) Sources of Viruses: (i) infected diskettes (ii) infected CD-ROMS (iii) e-mails (iv) Internet downloads (v) illegal duplication of software etc.
(e) Virus Warning Signs: (i) slowing down of response time (ii) presence of tiny dots (iii) wandering across the screen (iv) incomplete saving of file (v) corruption of the system set-up instructions. (vi) Appearance of strange characters
(f) Virus detection (Antivirus): (i) Norton Anti-virus (ii) McAfee Virus scan (iii) Dr. Solomon’s Took Kit (iv) Penicillin, etc.
g. Logic Gate
5 - 7 Revision and Mock Examination
8 - 12 BEC/JSC Examinations.
3RD TERM
WEEK 1
TOPIC: HUMAN ISSUES
Content: - Computer Professional
- Qualities of good computer professionals
Sub-Topic 1
(a) Computer Professionals:
Computer personnel embrace those personnel who involve in assemble, install, maintain, repair and operate the computer system. The term equally includes the programmer. The computer personnel know the rules and regulations guiding the computer usage.
Administrative structure of computer professionals
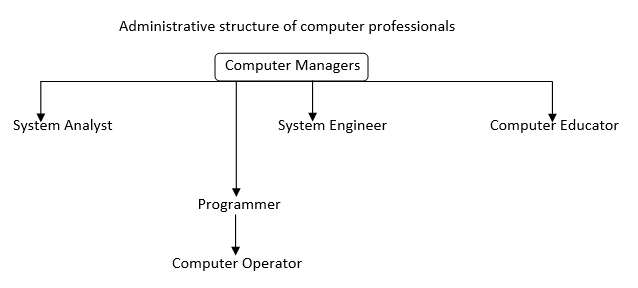
The administrative structure varies from one organization to another depending on the management of the organisation. However the structure is somehow similar.
Computer Manager:
He heads the computer department; he oversees the entire day to day running of the computer department.
System Analyst
A system analyst carries out feasibility study on a system. He is the person who thinks of likely problems that may arise from the system and application software and he proffers solution.
System Engineer
Is in control of all installation of hardware and software of the computer system. He is in charge of servicing, repairs and general maintenance of the system.
Programmer
Is the person who writes computer programmes according to the specification written by the system analyst.
Computer Educator
A computer educator trains up user to have knowledge of computer hardware and software.
Computer Operator
Is the person who operates the computer.
Evaluation:
1. Who is a computer operator?
2. List all the computer professional you know.
Sub-Topic 2 : Qualities of Good Computer Professionals
A good computer professional must possess the following qualities.

i. Excellent Analytical Skills: Computer professionals must have excellent analytical skills that can be applied to solve problems or develop new ideas.
ii. An attention to detail: Computer personnel must pay attention to detail to ensure everything works correctly and efficiently because any slighted mistake can affect how a web page looks or how a program will run.
iii. A commitment to learning: Technology is constantly changing it is dynamic and those who keep abreast the latest trend in information technology are the ones who will be the most successful.
iv. Good communication skills: Communication skills are important to those working in information technology because understanding a client’s needs and apply a solution depend heavily on a steady stream of open communication.
v. An interest for maths: Strong likeness for maths is essential because knowledge of maths is used in many computers application e.g. programming.
vi. The ability to learn and memorise programming language: Computer professionals must know many programming language and how to use a wide variety of computer software programs.
vii. The ability to handle multitasking: A good professional must possess the ability to perform many tasks at once and must be able to manage all his responsibilities simultaneously. Time management is highly essential.
viii. Solve problem, solving/trouble shooting capabilities: Computer professionals should be able to solve problems with network, software and other programs. They are expected to solve those problems very quickly and possess sharp trouble shooting and skills.
ix. Technical writing skills: A good computer professional must possess a technical writing skill.
Evaluation:
1. List five (5) qualities of good computer professionals and explain three (3)
2. Make a chart of computer professionals.
Reading Assignment
Read the following computer professional bodies: NCS, IMIS, CPRN, ITAN, NIG.
Assignment
1. ____ heads the computer department and she/he oversees the entire day to day running of the computer department. (a) Computer Educator (b) Computer Manager (c) System analyst
(d) Computer Operator
2. __ carries out feasibility study on a system. (a) Computer Manager (b) System analyst
(c) Computer Manager (d) System engineer
3. The person that operates(s) the computer is called _____ (a) Teacher (b) Engineer (c) Operator (d) Analyst
4. ___ is the person who writes computer programmes based on the specification written down by the system analyst. (a) System engineer (b) Operator (c) Programmer (d) Teacher
5. ___ installs hardware and software of the computer system as well as servicing, and maintaining the system. (a) Computer Manager (b) System engineer (c) Operator (d) Educator
6. A good computer professional must possess the following qualities except. (a) Excellent analytical skills (b) Attention to detail (c) Good communication skills (d) None of the above
Content: - Computer Professional
- Qualities of good computer professionals
Sub-Topic 1
(a) Computer Professionals:
Computer personnel embrace those personnel who involve in assemble, install, maintain, repair and operate the computer system. The term equally includes the programmer. The computer personnel know the rules and regulations guiding the computer usage.
Administrative structure of computer professionals

The administrative structure varies from one organization to another depending on the management of the organisation. However the structure is somehow similar.
Computer Manager:
He heads the computer department; he oversees the entire day to day running of the computer department.
System Analyst
A system analyst carries out feasibility study on a system. He is the person who thinks of likely problems that may arise from the system and application software and he proffers solution.
System Engineer
Is in control of all installation of hardware and software of the computer system. He is in charge of servicing, repairs and general maintenance of the system.
Programmer
Is the person who writes computer programmes according to the specification written by the system analyst.
Computer Educator
A computer educator trains up user to have knowledge of computer hardware and software.
Computer Operator
Is the person who operates the computer.
Evaluation:
1. Who is a computer operator?
2. List all the computer professional you know.
Sub-Topic 2 : Qualities of Good Computer Professionals
A good computer professional must possess the following qualities.

i. Excellent Analytical Skills: Computer professionals must have excellent analytical skills that can be applied to solve problems or develop new ideas.
ii. An attention to detail: Computer personnel must pay attention to detail to ensure everything works correctly and efficiently because any slighted mistake can affect how a web page looks or how a program will run.
iii. A commitment to learning: Technology is constantly changing it is dynamic and those who keep abreast the latest trend in information technology are the ones who will be the most successful.
iv. Good communication skills: Communication skills are important to those working in information technology because understanding a client’s needs and apply a solution depend heavily on a steady stream of open communication.
v. An interest for maths: Strong likeness for maths is essential because knowledge of maths is used in many computers application e.g. programming.
vi. The ability to learn and memorise programming language: Computer professionals must know many programming language and how to use a wide variety of computer software programs.
vii. The ability to handle multitasking: A good professional must possess the ability to perform many tasks at once and must be able to manage all his responsibilities simultaneously. Time management is highly essential.
viii. Solve problem, solving/trouble shooting capabilities: Computer professionals should be able to solve problems with network, software and other programs. They are expected to solve those problems very quickly and possess sharp trouble shooting and skills.
ix. Technical writing skills: A good computer professional must possess a technical writing skill.
Evaluation:
1. List five (5) qualities of good computer professionals and explain three (3)
2. Make a chart of computer professionals.
Reading Assignment
Read the following computer professional bodies: NCS, IMIS, CPRN, ITAN, NIG.
Assignment
1. ____ heads the computer department and she/he oversees the entire day to day running of the computer department. (a) Computer Educator (b) Computer Manager (c) System analyst
(d) Computer Operator
2. __ carries out feasibility study on a system. (a) Computer Manager (b) System analyst
(c) Computer Manager (d) System engineer
3. The person that operates(s) the computer is called _____ (a) Teacher (b) Engineer (c) Operator (d) Analyst
4. ___ is the person who writes computer programmes based on the specification written down by the system analyst. (a) System engineer (b) Operator (c) Programmer (d) Teacher
5. ___ installs hardware and software of the computer system as well as servicing, and maintaining the system. (a) Computer Manager (b) System engineer (c) Operator (d) Educator
6. A good computer professional must possess the following qualities except. (a) Excellent analytical skills (b) Attention to detail (c) Good communication skills (d) None of the above
WEEK 2
Topic: Human Issues (Cont.)
Content: - Computer Professional Bodies
Sub-topic 3:
Computer Professional bodies
1. Nigerian Computer Society (NCS)
2. Institute of Management Information System (IMIS)
3. Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria (CPRN)
4. Information Technology Association of Nigeria (ITAN)
5. Nigerian Internet Group (NIG)
NIGERIAN COMPUTER SOCIETY (NCS)
Nigerian Computer Society is a place where people interested in computing Technology within Nigeria gather to share ideas and knowledge. You can become a member by completing the form below on line and supply them with the following information:
First Name, Last Name, e-mail, Change password and Register me.

Functions of NCS
i. To promote the education and training of computer and information scientist, computer engineers, information architects and information technology and system professionals.
ii. To actively encourage research in the advancement of computer and information sciences.
iii. To promote the inter change of information about the science and arts of information processing.
iv. To promote and protect the professional interest of the members.
v. To work for the recognition by government of the ‘Digital Divide’ and to collaborate with relevant government.
INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM (IMIS)
The Institute of Management Information System is the teaching independent professional association for both users and developers of today’s information technologies.

VISION/FUNCTIONS OF IMIS
The IMIS is to see information system management recognised as one of the key professionals’ influencing the future of our world.
Mission is to further the cause of professionals in the cause of professionalism in the use of information system through Life-long learning and to increase the awareness by the public as an individual or as an organization of the advances, implication and potential in information system.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION OF NIGERIA (ITAN)

Functions
1. The ITAN provides learning opportunities within the engineering science research and broadly technology.
2. The goal of the ITAN education programs is to ensure the growth of skill and knowledge among the technician profession and to foster individual commitment to continuing education among ITAN members, the engineering and scientific community and the general public.
Sub-Topic 4: COMPUTER PROFESSIONAL REGISTRATION COUNCIL OF NIGERIA (CPRN)
Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria is a corporate entity charged with the control and supervision of computing profession in the country. The computer professionals were established through Act No. 49 of 1993 promulgated on June 10 and gazetted on August 9.

FUNCTIONS OF CPRN
1. The body is charged with the responsibility of determining the standard of knowledge and skills to be attained by persons seeking to become members of the profession and improve those standards from time to time as circumstance may permit.
2. It is also part of the responsibility of CPRN to maintain a register or persons seeking to be registered under the Act to practice computing profession and the publication from time to time of the list of such (it is illegal for anybody to practice Information Technology in Nigeria without registering with computer professionals.)
3. They conduct exams as Computer Professional Examinations to other professionals that are interested in building career in Information Technology (IT). Upon completion of the exams, the person would be registered under a full member category.
NIGERIAN INTERNET GROUP (NIG)
It is the largest online community of youth interested in global issues and creating positive changes.
The Nigerian Internet group is a non-governmental, non profit making organization with the primary objectives of promoting access to the internet.

FUNCTIONS OF NIG
The Nigerian internet group intends to reserve the trend whereby Nigeria ((despite her last human and material resources) lags behind much of the world in terms of access to the global information infrastructure which is vital to attracting new investment and enhancing global competitiveness.
Evaluation:
1. What is the full meaning of the following: NCS, IMIS, CPRN, ITAN, NIG.
2. List and explain the functions of NCS.
Reading Assignment
Read from your text book the topic ‘computer viruses’.
Assignment
1. Computer professional bodies include the following except__ (a) Nigeria Computer Society (NCS) (b) Institute of management Information System (c) Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria (d) None of the above
2. ___ is a place where people interested in computing Technology within Nigeria gather to share rank and knowledge. (a) Nigeria Computer Society (b) ITAN (c) IMIS (s) None of the above
Content: - Computer Professional Bodies
Sub-topic 3:
Computer Professional bodies
1. Nigerian Computer Society (NCS)
2. Institute of Management Information System (IMIS)
3. Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria (CPRN)
4. Information Technology Association of Nigeria (ITAN)
5. Nigerian Internet Group (NIG)
NIGERIAN COMPUTER SOCIETY (NCS)
Nigerian Computer Society is a place where people interested in computing Technology within Nigeria gather to share ideas and knowledge. You can become a member by completing the form below on line and supply them with the following information:
First Name, Last Name, e-mail, Change password and Register me.

Functions of NCS
i. To promote the education and training of computer and information scientist, computer engineers, information architects and information technology and system professionals.
ii. To actively encourage research in the advancement of computer and information sciences.
iii. To promote the inter change of information about the science and arts of information processing.
iv. To promote and protect the professional interest of the members.
v. To work for the recognition by government of the ‘Digital Divide’ and to collaborate with relevant government.
INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM (IMIS)
The Institute of Management Information System is the teaching independent professional association for both users and developers of today’s information technologies.

VISION/FUNCTIONS OF IMIS
The IMIS is to see information system management recognised as one of the key professionals’ influencing the future of our world.
Mission is to further the cause of professionals in the cause of professionalism in the use of information system through Life-long learning and to increase the awareness by the public as an individual or as an organization of the advances, implication and potential in information system.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION OF NIGERIA (ITAN)

Functions
1. The ITAN provides learning opportunities within the engineering science research and broadly technology.
2. The goal of the ITAN education programs is to ensure the growth of skill and knowledge among the technician profession and to foster individual commitment to continuing education among ITAN members, the engineering and scientific community and the general public.
Sub-Topic 4: COMPUTER PROFESSIONAL REGISTRATION COUNCIL OF NIGERIA (CPRN)
Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria is a corporate entity charged with the control and supervision of computing profession in the country. The computer professionals were established through Act No. 49 of 1993 promulgated on June 10 and gazetted on August 9.

FUNCTIONS OF CPRN
1. The body is charged with the responsibility of determining the standard of knowledge and skills to be attained by persons seeking to become members of the profession and improve those standards from time to time as circumstance may permit.
2. It is also part of the responsibility of CPRN to maintain a register or persons seeking to be registered under the Act to practice computing profession and the publication from time to time of the list of such (it is illegal for anybody to practice Information Technology in Nigeria without registering with computer professionals.)
3. They conduct exams as Computer Professional Examinations to other professionals that are interested in building career in Information Technology (IT). Upon completion of the exams, the person would be registered under a full member category.
NIGERIAN INTERNET GROUP (NIG)
It is the largest online community of youth interested in global issues and creating positive changes.
The Nigerian Internet group is a non-governmental, non profit making organization with the primary objectives of promoting access to the internet.

FUNCTIONS OF NIG
The Nigerian internet group intends to reserve the trend whereby Nigeria ((despite her last human and material resources) lags behind much of the world in terms of access to the global information infrastructure which is vital to attracting new investment and enhancing global competitiveness.
Evaluation:
1. What is the full meaning of the following: NCS, IMIS, CPRN, ITAN, NIG.
2. List and explain the functions of NCS.
Reading Assignment
Read from your text book the topic ‘computer viruses’.
Assignment
1. Computer professional bodies include the following except__ (a) Nigeria Computer Society (NCS) (b) Institute of management Information System (c) Computer Professional Registration Council of Nigeria (d) None of the above
2. ___ is a place where people interested in computing Technology within Nigeria gather to share rank and knowledge. (a) Nigeria Computer Society (b) ITAN (c) IMIS (s) None of the above
WEEK 3
Topic: COMPUTER VIRUSES
Content: - Meaning
- Types of Computer Virus
- Examples of Viruses
- Sources of Viruses
Sub-Topic 1: - Meaning and Types of Computer Viruses
(a) Meaning
Computer virus is a program intentionally written by some software developer to cause damage to the computer, programs and files in which it found itself. The computer virus may be designed to display unwanted message
The computer virus is a program that has the ability to replicates itself by changing other programs to include a copy of itself. A virus causes the infected computer system to function in way not originally planned. The computer virus cannot be seen with your natural eyes yet the effects can be notified on an infected system.

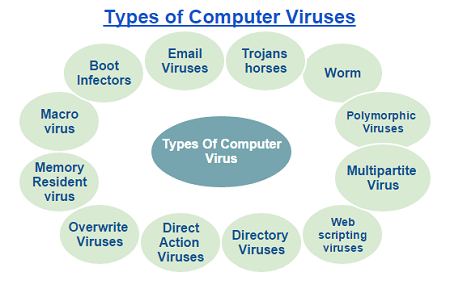
(b) Types of Computer Virus
There are basically three ways in which a virus will infect your micro computer.
i. Boot sector
ii. Executable file virus
iii. Document
BOOT SECTOR: Boot sector infect hard drives and flash disks by making itself available on the boot sector of the disk. Booting up from an infected flash disk can cause damage to the hard drive.
EXECUTABLE FILE VIRUS: They spread the infection by attacking the code to executable files (EXE.COM) in this way; the virus program will be executable before the host program is executed.
DOCUMENT VIRUS: Virus can affect the document by moving from disk partition table to a different sector and replace it with its own code, therefore infecting document as they are accessed.
Evaluation:
1. Explain the three ways in which computer virus can infect your computer.
2. What is computer virus?
(c) Examples of Viruses
The following are example of computer virus:
i. Trojan horse
ii. Sleeper
iii Logic bomb
iv. Alabama virus
v. Christmas virus
vi. Worm
vii. Data crime virus
viii Jerusalem Virus
ix. Barcelona virus
x. April 1st virus

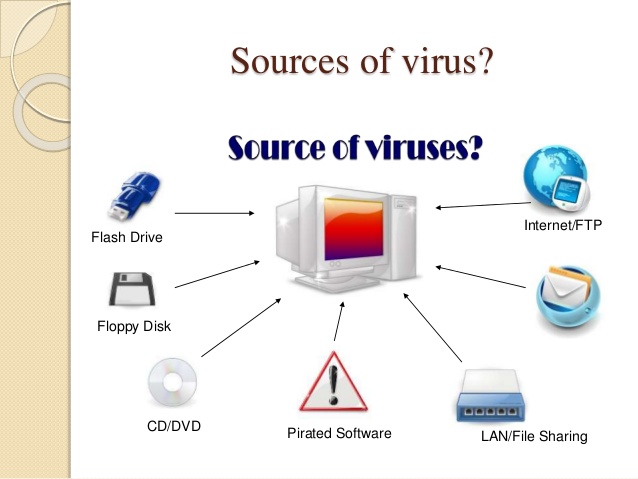
(d) Sources of Viruses
Virus infection can happen through the following:
i. Infected diskettes
ii. Hard drive
iii. Infected CD ROMS
iv. Internet download
v. E-mail
vi. Illegal duplication of software
vii. Bad handling of computer
Evaluation
1. List ten (10) of computer viruses you know.
2. Explain four out of (1) above how it can infect your computer.
3. List and explain three sources of viruses.
Reading Assignment
Read the source of viruses and how it can be protected.
Assignment:
Objective Test:
1. Avast, MacAfee, Disk and Dr. Solomon are example of __ (a) Computer Virus (b) Computer Stone (c) Computer Antivirus (d) Computer system
2. The program used in protecting and detecting virus in the computer system is called. (a)anti-protection program (b) ant-virus program (c) diskette program (d) high level program
3. Which of the following is NOT a virus warning sign? (a) illegal duplication of software
(b) incomplete saving of file (c) presence of tiny dots (d) programs take a long time to load
4. Computer virus is ____ (a) A program (b) A disease (c) Bacteria (d) Hardware
5. The followings are Anti-virus software except __ (a) McAfee (b) Norton (c) Avast (d) June 12
Content: - Meaning
- Types of Computer Virus
- Examples of Viruses
- Sources of Viruses
Sub-Topic 1: - Meaning and Types of Computer Viruses
(a) Meaning
Computer virus is a program intentionally written by some software developer to cause damage to the computer, programs and files in which it found itself. The computer virus may be designed to display unwanted message
The computer virus is a program that has the ability to replicates itself by changing other programs to include a copy of itself. A virus causes the infected computer system to function in way not originally planned. The computer virus cannot be seen with your natural eyes yet the effects can be notified on an infected system.

(b) Types of Computer Virus
There are basically three ways in which a virus will infect your micro computer.
i. Boot sector
ii. Executable file virus
iii. Document
BOOT SECTOR: Boot sector infect hard drives and flash disks by making itself available on the boot sector of the disk. Booting up from an infected flash disk can cause damage to the hard drive.
EXECUTABLE FILE VIRUS: They spread the infection by attacking the code to executable files (EXE.COM) in this way; the virus program will be executable before the host program is executed.
DOCUMENT VIRUS: Virus can affect the document by moving from disk partition table to a different sector and replace it with its own code, therefore infecting document as they are accessed.

Evaluation:
1. Explain the three ways in which computer virus can infect your computer.
2. What is computer virus?
(c) Examples of Viruses
The following are example of computer virus:
i. Trojan horse
ii. Sleeper
iii Logic bomb
iv. Alabama virus
v. Christmas virus
vi. Worm
vii. Data crime virus
viii Jerusalem Virus
ix. Barcelona virus
x. April 1st virus

(d) Sources of Viruses
Virus infection can happen through the following:
i. Infected diskettes
ii. Hard drive
iii. Infected CD ROMS
iv. Internet download
v. E-mail
vi. Illegal duplication of software
vii. Bad handling of computer

Evaluation
1. List ten (10) of computer viruses you know.
2. Explain four out of (1) above how it can infect your computer.
3. List and explain three sources of viruses.
Reading Assignment
Read the source of viruses and how it can be protected.
Assignment:
Objective Test:
1. Avast, MacAfee, Disk and Dr. Solomon are example of __ (a) Computer Virus (b) Computer Stone (c) Computer Antivirus (d) Computer system
2. The program used in protecting and detecting virus in the computer system is called. (a)anti-protection program (b) ant-virus program (c) diskette program (d) high level program
3. Which of the following is NOT a virus warning sign? (a) illegal duplication of software
(b) incomplete saving of file (c) presence of tiny dots (d) programs take a long time to load
4. Computer virus is ____ (a) A program (b) A disease (c) Bacteria (d) Hardware
5. The followings are Anti-virus software except __ (a) McAfee (b) Norton (c) Avast (d) June 12
WEEK 4
Topic: Computer Viruses (Cont.) & Logic Gate
Content:¬ - Virus Warning
- Virus detection (Anti-virus)
Sub-Topic 1: Virus warning signs and Virus detection (ANTIVIRUS)
(e) Virus warning signs
Virus infection can cause a malfunction of the computer system in the following ways:
i. Slowing down of the response time.
ii. Presence of tiny dots.
iii. Wandering across the screen.
iv. Incomplete saving of file.
v. Corruption of the system set up instruction.
vi. Appearance of strange characters.
vii. It can cause organized program into a disorganized program and making them not to execute.
viii. It destroys the partition task file, even the entire system of hard drive.
ix. It causes damage to valuables stored on any storage media.

(f) Virus detection (ANTIVIRUS)
Antivirus is a program developed to destroy computer virus wherever it is found in the system. It is designed to eradicate the infection act of the virus program.


Examples of Antivirus software
i. Norton-Antivirus
ii. McAfee Virus scan
iii. Dr. Solomon’s Took kit
iv. Penicillin
v. Microsoft
vi. Check point antivirus
vii. Central point antivirus

Evaluation:
1. List and explain 5 signs of virus infection.
2. What is the cure of computer virus infection?
3. List 5 you know of anti-virus of virus infection.
Sub-Topic 2: Logic Gate
This can be described as an act or reasoning which enables man to reach valid and reasonable conclusion and decision.
Logic functions are shown usually in a TRUTH TABLE which indicates exactly what will happen according to alternative (input) conditions. The fundamental property of any statement is either True or False. The truth-value of any statement is the truthfulness or falsity of that statement.
Boolean algebra is a means for expressing the relationship between a logic circuits inputs and output. Two values 0’s and 1’s are the possible values in Boolean algebra.
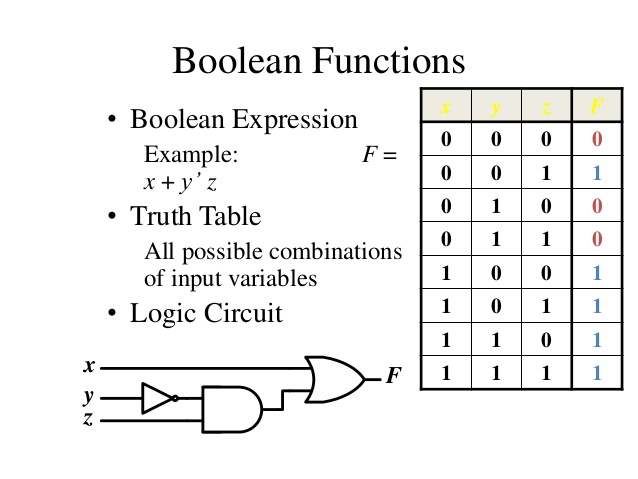
Truth Table
A truth table is a means for describing how logic circuit’s output depends on the logic level present at the circuit’s input.
Types of Logic Gate
The principal or five types of logical operators are (a) OR gate (b) AND gate (c) NOT (Inverter) gate (d) NOR gate (e) NAND.
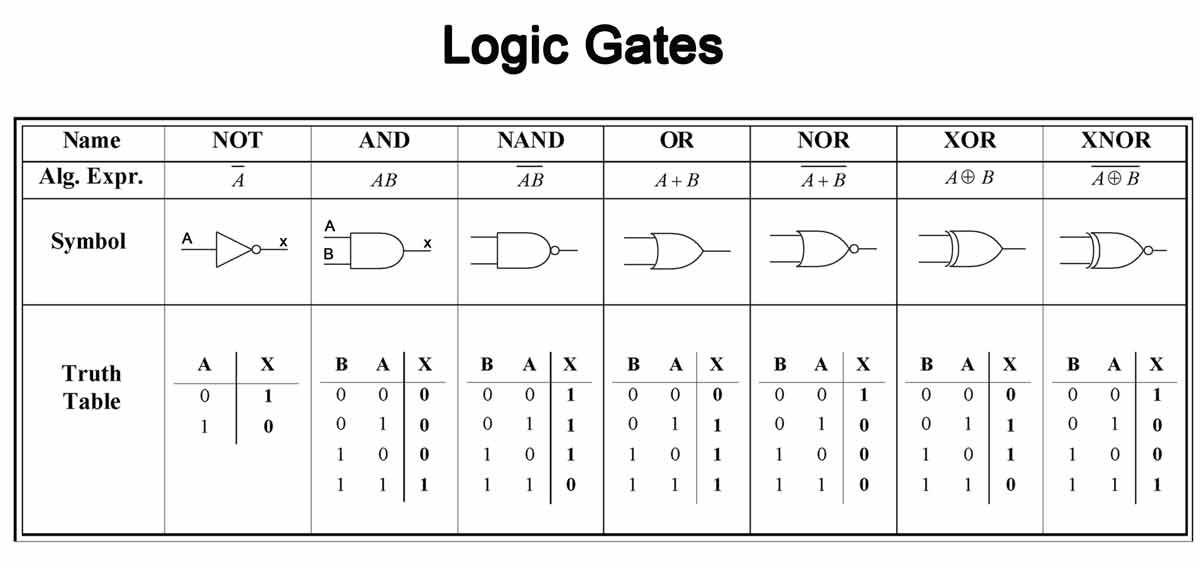
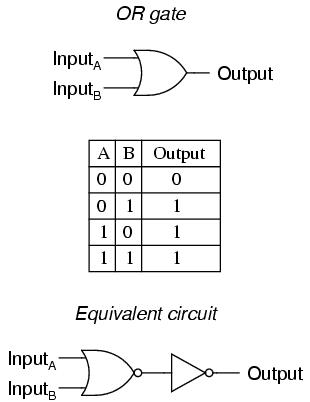
1. OR gate: The OR gate gets its name from the fact that it behaves after the fashion of the logical inclusive ‘or.’ The output is “true” if either or both of the inputs are “true.” If both inputs are “false,” then the output is “false.”
OR gate
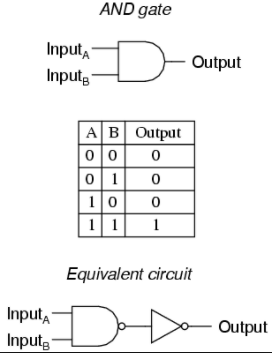
2. AND gate: The AND gate is so named because, if 0 is called “false” and 1 is called “true”, the gate acts in the same way as the logical “and” operator. The following illustration and table show the circuit symbol and logic combinations for an AND gate. (In the symbol, the input terminals are at left and the output terminal is at right.) The output is “true” when both inputs are “true”. Otherwise, the output is “false”.
ANDgate
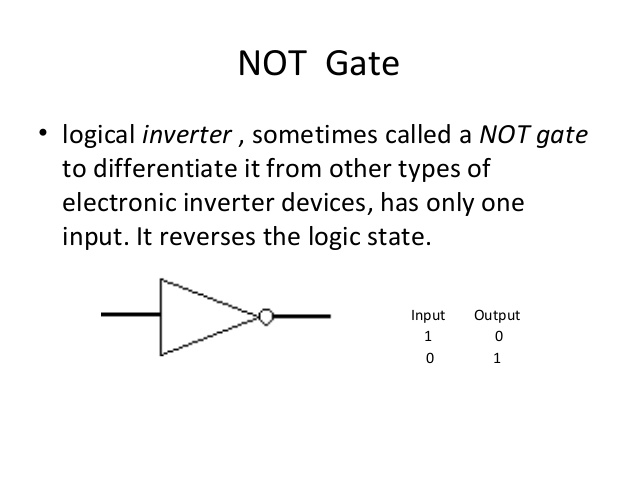
3. NOT gate: A logical inverter sometimes called a NOT gate to differentiate it from other types of electronic inverter devices, has only one input. It reverses the logic state.
NOT gate
4. NOR gate: The NOR gate is a combination of OR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is “true” if both inputs are “false”. Otherwise, the output is “false”.
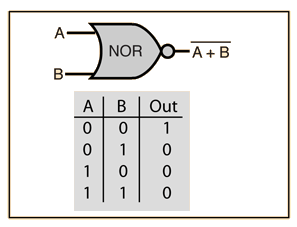
5. NAND gate: The NAND gate operates as an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. It acts in the manner of the logical operation “and” followed by negation. The output is “false” if both inputs are “true”. Otherwise, the output is “true”.
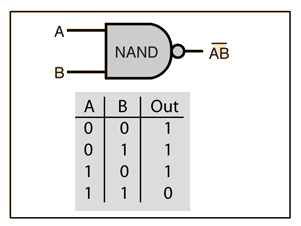
Evaluation:
1. The possible values of Boolean algebra are ___ and ___ (a) 1 or 0 (b) 2 or 3 (c) 4 pr 6 (d) 5 or 6
2. The ___ gate produces an output when all the switches are ON. (a) OR (b) NOR (c) AND
(d) NAND (e) NOT
3. There are ____ types of logic gate. (a) Two (b) Three (c) Four (d) Five
4. The expression X = A + B is ___ (a) NAND gate (b) NOR gate (c) INVERTER (d) OR gate
5. The NAND gate is equal to ____ (a) AND plus OR gate (b) NOT plus AND gate (c) NOT plus OR gate (d) AND gate only
Read Assignment
Read all the topics from JS 1, 2 and 3.
Assignment
Preparation for Mock Examination
Content:¬ - Virus Warning
- Virus detection (Anti-virus)
Sub-Topic 1: Virus warning signs and Virus detection (ANTIVIRUS)
(e) Virus warning signs
Virus infection can cause a malfunction of the computer system in the following ways:
i. Slowing down of the response time.
ii. Presence of tiny dots.
iii. Wandering across the screen.
iv. Incomplete saving of file.
v. Corruption of the system set up instruction.
vi. Appearance of strange characters.
vii. It can cause organized program into a disorganized program and making them not to execute.
viii. It destroys the partition task file, even the entire system of hard drive.
ix. It causes damage to valuables stored on any storage media.

(f) Virus detection (ANTIVIRUS)
Antivirus is a program developed to destroy computer virus wherever it is found in the system. It is designed to eradicate the infection act of the virus program.


Examples of Antivirus software
i. Norton-Antivirus
ii. McAfee Virus scan
iii. Dr. Solomon’s Took kit
iv. Penicillin
v. Microsoft
vi. Check point antivirus
vii. Central point antivirus

Evaluation:
1. List and explain 5 signs of virus infection.
2. What is the cure of computer virus infection?
3. List 5 you know of anti-virus of virus infection.
Sub-Topic 2: Logic Gate
This can be described as an act or reasoning which enables man to reach valid and reasonable conclusion and decision.
Logic functions are shown usually in a TRUTH TABLE which indicates exactly what will happen according to alternative (input) conditions. The fundamental property of any statement is either True or False. The truth-value of any statement is the truthfulness or falsity of that statement.
Boolean algebra is a means for expressing the relationship between a logic circuits inputs and output. Two values 0’s and 1’s are the possible values in Boolean algebra.

Truth Table
A truth table is a means for describing how logic circuit’s output depends on the logic level present at the circuit’s input.
Types of Logic Gate
The principal or five types of logical operators are (a) OR gate (b) AND gate (c) NOT (Inverter) gate (d) NOR gate (e) NAND.

1. OR gate: The OR gate gets its name from the fact that it behaves after the fashion of the logical inclusive ‘or.’ The output is “true” if either or both of the inputs are “true.” If both inputs are “false,” then the output is “false.”
OR gate

2. AND gate: The AND gate is so named because, if 0 is called “false” and 1 is called “true”, the gate acts in the same way as the logical “and” operator. The following illustration and table show the circuit symbol and logic combinations for an AND gate. (In the symbol, the input terminals are at left and the output terminal is at right.) The output is “true” when both inputs are “true”. Otherwise, the output is “false”.
ANDgate

3. NOT gate: A logical inverter sometimes called a NOT gate to differentiate it from other types of electronic inverter devices, has only one input. It reverses the logic state.
NOT gate

4. NOR gate: The NOR gate is a combination of OR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is “true” if both inputs are “false”. Otherwise, the output is “false”.

5. NAND gate: The NAND gate operates as an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. It acts in the manner of the logical operation “and” followed by negation. The output is “false” if both inputs are “true”. Otherwise, the output is “true”.

Evaluation:
1. The possible values of Boolean algebra are ___ and ___ (a) 1 or 0 (b) 2 or 3 (c) 4 pr 6 (d) 5 or 6
2. The ___ gate produces an output when all the switches are ON. (a) OR (b) NOR (c) AND
(d) NAND (e) NOT
3. There are ____ types of logic gate. (a) Two (b) Three (c) Four (d) Five
4. The expression X = A + B is ___ (a) NAND gate (b) NOR gate (c) INVERTER (d) OR gate
5. The NAND gate is equal to ____ (a) AND plus OR gate (b) NOT plus AND gate (c) NOT plus OR gate (d) AND gate only
Read Assignment
Read all the topics from JS 1, 2 and 3.
Assignment
Preparation for Mock Examination
WEEK 5, 6 & 7
REVISION, JSCE & NECO BECE
