2ND TERM
2ND TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last term’s examination. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development- Revision of prefixes, English Structure, Expressing exception using except, except for, but, apart from, without, e.g. (a) we are all students apart from John (b) everyone was present but for my friend. Composition- Narrative essay “My most memorable day” Speech work– consonants /o/ and /t/ e.g. thin, tin, thick, tick, Literature-In-English-use recommended text.
2. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (suffixes – noun derivations: -ness, -ment, -er, ship- action, -ant, -hood, -al e.g. mildness, friendship, inhabitant, etc.), English structure – conjunctions, Composition – report writing– “the school’s Inter- house sports” Speech work – consonant contrast /t/, /s/ e.g. thumb, sum, mouth, mouse, path, pass, etc, Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
3. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (suffixes – verb derivations:- -ify, -ize, -en, e.g. popularize, dignify, lighten)- English structure interjections, Composition – article writing, Speech work – consonant contrast /s/, /z/ e.g. mission, vision, pressure, pleasure, etc, Literature-In-English – use of recommended text.
4. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (suffixes – adjective derivations:- -ful, -ment, -al, -less, -ish, -ive, e.g grateful, intentional, faithless, childish, attentive)- English structure–question tags, Composition– informal letter e.g. “A letter to a friend” Speech work – Nasal sounds /m/, /n/, /g/ e.g. man, nap, song, Literature-In-English – use of recommended text.
5. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (word associated with value of judgment e.g. delicious, unpleasant etc)- English structure – Personal and possessive pronouns, Composition – Formal letter - “A letter of invitation to a programme” Speech work – vowels /i/ and /i:/, Literature-In-English, recommended text.
6. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Words associated with moral appraisal e.g. callous, generous, faithful etc)- English Structure – reflexive and relative pronouns, Composition – Expository essay “Why students fail examinations” Speech Work – Vowels /a:/ and /z/ e.g. bath, birth, arm, earn, farm, firm etc, Literature-In-English, Use recommended text.
7. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (synonyms – words similar in meaning/context to holy e.g pious, religious, godly, God fearing etc)- English Structure – indefinite and reciprocal pronouns, Composition – Descriptive essay – “My Schools inter-house sports” Speech Work – Vowels / /, / :/ and / / e.g cot, court, come, Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
8. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Synonyms– words similar in meaning/context to active e.g. Agile, energetic, quick, dynamic etc)- English Structure, Demonstrative Pronouns, Composition, Argumentative essay “Teachers are better than farmers in a society” Speech Work – Vowels /u/, and /u:/ e.g. pull, pool, soup, sue etc. Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
9. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Synonyms – words similar in meaning/context to callous e.g. unsympathetic, unfeeling etc)- English Structure – active voice e.g. I bought the dog, my parent bought my books.Composition, Expository writing (story writing), Background/ introduction, Speech Work – Vowels / / e.g. among,
above, about etc, Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
10. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Synonyms – words similar in meaning/context to law e.g. rule, regulation, legislation etc)- Structure passive voice e.g. the dog was bought by me, my books were bought by my parents, Composition expository writing proper (story writing ii) – (choose a relevant topic), Speech Work – revise the diphthongs, Literature-In-English – (use recommended text).
11-12. Revision
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last term’s examination. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development- Revision of prefixes, English Structure, Expressing exception using except, except for, but, apart from, without, e.g. (a) we are all students apart from John (b) everyone was present but for my friend. Composition- Narrative essay “My most memorable day” Speech work– consonants /o/ and /t/ e.g. thin, tin, thick, tick, Literature-In-English-use recommended text.
2. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (suffixes – noun derivations: -ness, -ment, -er, ship- action, -ant, -hood, -al e.g. mildness, friendship, inhabitant, etc.), English structure – conjunctions, Composition – report writing– “the school’s Inter- house sports” Speech work – consonant contrast /t/, /s/ e.g. thumb, sum, mouth, mouse, path, pass, etc, Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
3. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (suffixes – verb derivations:- -ify, -ize, -en, e.g. popularize, dignify, lighten)- English structure interjections, Composition – article writing, Speech work – consonant contrast /s/, /z/ e.g. mission, vision, pressure, pleasure, etc, Literature-In-English – use of recommended text.
4. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (suffixes – adjective derivations:- -ful, -ment, -al, -less, -ish, -ive, e.g grateful, intentional, faithless, childish, attentive)- English structure–question tags, Composition– informal letter e.g. “A letter to a friend” Speech work – Nasal sounds /m/, /n/, /g/ e.g. man, nap, song, Literature-In-English – use of recommended text.
5. Comprehension/Vocabulary development (word associated with value of judgment e.g. delicious, unpleasant etc)- English structure – Personal and possessive pronouns, Composition – Formal letter - “A letter of invitation to a programme” Speech work – vowels /i/ and /i:/, Literature-In-English, recommended text.
6. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Words associated with moral appraisal e.g. callous, generous, faithful etc)- English Structure – reflexive and relative pronouns, Composition – Expository essay “Why students fail examinations” Speech Work – Vowels /a:/ and /z/ e.g. bath, birth, arm, earn, farm, firm etc, Literature-In-English, Use recommended text.
7. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (synonyms – words similar in meaning/context to holy e.g pious, religious, godly, God fearing etc)- English Structure – indefinite and reciprocal pronouns, Composition – Descriptive essay – “My Schools inter-house sports” Speech Work – Vowels / /, / :/ and / / e.g cot, court, come, Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
8. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Synonyms– words similar in meaning/context to active e.g. Agile, energetic, quick, dynamic etc)- English Structure, Demonstrative Pronouns, Composition, Argumentative essay “Teachers are better than farmers in a society” Speech Work – Vowels /u/, and /u:/ e.g. pull, pool, soup, sue etc. Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
9. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Synonyms – words similar in meaning/context to callous e.g. unsympathetic, unfeeling etc)- English Structure – active voice e.g. I bought the dog, my parent bought my books.Composition, Expository writing (story writing), Background/ introduction, Speech Work – Vowels / / e.g. among,
above, about etc, Literature-In-English – use recommended text.
10. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development (Synonyms – words similar in meaning/context to law e.g. rule, regulation, legislation etc)- Structure passive voice e.g. the dog was bought by me, my books were bought by my parents, Composition expository writing proper (story writing ii) – (choose a relevant topic), Speech Work – revise the diphthongs, Literature-In-English – (use recommended text).
11-12. Revision
WEEK 1
ASPECT:
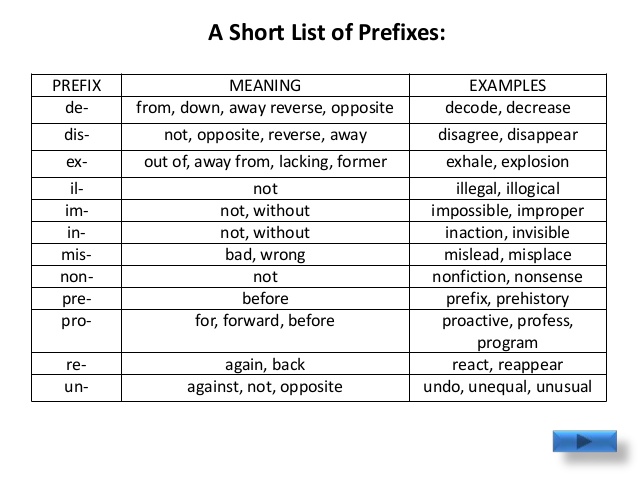
COMPREHENSION/VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT – REVISION OF PREFIXES

Further Studies
[youtube]https://youtu.be/l170VTskxKA[/youtube]
Worksheets
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: EXPRESSING EXCEPTION USING EXCEPT
CONTENT:
We express exception by using except..., expect for..., but for... and apart from....
We often use except and except for as prepositions to mean ‘not including’ or ‘excluding’. They are followed by a noun or noun phrase or a wh-clause. Both except and except for are correct after a noun:
I like all fruit except (for) oranges. (excluding oranges)
Except for Louisa, who’s away in Berlin this weekend, we’ll all be at the party.
She likes going to most sports events, except cricket matches.
Except can also be used as a conjunction. We don’t use except for in this way:
The brothers are very alike, except (that) Mark is slightly taller than Kevin.
Except and except for are used in similar ways to apart and apart from.
They all have exactly the same meaning and each of them may be followed by a noun, a noun phrase or a pronoun e.g.
Except... ,
Except for...,
But for...,
Apart from... ,
Abdu,
my eldest son,
him,
Everyone is present.
Note the Comma in the examples above.
2. The order of the sentence may be reversed, eg.:
Everyone is present
except...
except for...
but for...
Audu.
my eldest son.
him.
Note that there is no Comma in the examples above.
3. Except..., except for..., but for... and apart from... may be followed by a gerund, e.g.:
Except...
Except for...
But for...
Apart from -
phoning the bank,
cleaning the car,
washing the plates,
you have done everything I said.
Note: Again, note the commas in these examples.
4. These sentences may also be reversed, e.g.
You have done everything I said
You have done everything I said
except...
except for...
but for...
apart from ...
phoning the bank.
cleaning the car.
washing the plates.
Again, note the commas in these examples.
5. We express a different kind of exception by using without followed by a noun, a noun phrase, a pronoun or a gerund, e.g.:
Without Audu
Audu’s help,
him,
asking Audu,
we couldn’t do it.
We couldn’t do it without Audu.
Audu’s help.
him.
Asking Audu.
Note which examples have commas and which have not.
Evaluation
Rewrite these sentences using except, except for, but for and apart from, each once only:
1. I finished everything. But I did not type this letter
2. We were all laughing. But Eta was not laughing.
Assignment
Fill in the column with the right word
1. Everyone was present ___________ Audu was not present.
2. All the employees were sacked. _________ the manager’s daughter was not sacked.
3. The police caught the whole gang. ____________ they did not catch Bassey.
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Narrative essay
CONTENT: A narrative essay tells a story. In planning a narrative essay there are essential tips to note.
First think about the topic and jot down the main ideas that come to your mind concerning the topic.
Suppose you are asked to write on an incident that made you cry. Immediately, you know that you will write on a sad event. Think of any sad event in your life. Is it going to be on death? Loss of a valuable item? A bad decision that landed you in trouble? An unhappy journey you regretted making? Choose one of these as your topic.
Your composition must have at least three sections- Introduction, the body and the conclusion. Start each with a paragraph. The body may have many paragraphs, depending on the number of main ideas you want to bring into it.
Think of an interesting way of introducing the topic. For example: I now believe that the voice of the elders is the voice of wisdom. I wish I had believed that before August 10, 2006, when I had to pay dearly for not heeding my mother’s golden advice. I wept very much that day and still weep whenever my mind goes back on the incident. If only I had listened!
Example
Topic: My most memorable day
First paragraph: Mention the day and where the event happened. Mention the people involved and what happened in the morning of the day.
Second paragraph: Narrate what happened in the afternoon of that day, mentioning at least two pleasant things that happened.
Third paragraph: Mention what happened in the evening, through to night.
Fourth paragraph: How did the day end? Why is it your most memorable day?
Remember to use the past tense and dialogue while writing.
Evaluation
1. Write four paragraphs on the topic:
‘How I met my Best Friend’.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC – Consonant /Ɵ/ and /t/
CONTENT: Consonants / Ɵ/ /t/
To pronounce / Ɵ / the tip of the tongue is made to almost touch the back of the upper teeth and is almost sticking out between the lower and upper teeth. The air in the mouth is pressed out through the little opening between the tip of the tongue and the upper teeth. No activity is going on in the voice box. This means that the sound is voiceless.
The consonants / Ɵ/ is heard in the following sentences.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/yNtz_ZwLzKE[/youtube]
i. A moth flies through the window.
ii. A mosquito is thin; a moth is fat.
iii. In Maths, Amina won the third prize.
iv. Open your mouth and throw out the bad water.
v. Ade’s birthday is the fourth of June.
Consonant /t/
To pronounce /t/, the front of the tongue is pressed hard behind the root of the upper teeth. There is no activity in the voice box. The air in the mouth is released suddenly with force and the sound is faint. /t/ is a voiceless consonant.
The consonants /t/ is heard in the following sentences.
i. I want to take some time to visit Abuja.
ii. I please turn off the tap; don’t waste water.
iii. The cat is looking at the rat.
iv. I don’t take tea in the afternoon.
v. Peter visited his auntie yesterday.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/L0ptN3jfTR8[/youtube]
EVALUATION
1. Write out 5 words each for consonants /ϴ/ and /t/.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Write and construct 8 sentences each with consonants /ϴ/ and /t/.
2. Write a narrative essay on any of the following topics:
i. First day at school
ii. A marriage ceremony
COMPREHENSION/VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT – REVISION OF PREFIXES


Further Studies
[youtube]https://youtu.be/l170VTskxKA[/youtube]
Worksheets
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: EXPRESSING EXCEPTION USING EXCEPT
CONTENT:
We express exception by using except..., expect for..., but for... and apart from....
We often use except and except for as prepositions to mean ‘not including’ or ‘excluding’. They are followed by a noun or noun phrase or a wh-clause. Both except and except for are correct after a noun:
I like all fruit except (for) oranges. (excluding oranges)
Except for Louisa, who’s away in Berlin this weekend, we’ll all be at the party.
She likes going to most sports events, except cricket matches.
Except can also be used as a conjunction. We don’t use except for in this way:
The brothers are very alike, except (that) Mark is slightly taller than Kevin.
Except and except for are used in similar ways to apart and apart from.
They all have exactly the same meaning and each of them may be followed by a noun, a noun phrase or a pronoun e.g.
Except... ,
Except for...,
But for...,
Apart from... ,
Abdu,
my eldest son,
him,
Everyone is present.
Note the Comma in the examples above.
2. The order of the sentence may be reversed, eg.:
Everyone is present
except...
except for...
but for...
Audu.
my eldest son.
him.
Note that there is no Comma in the examples above.
3. Except..., except for..., but for... and apart from... may be followed by a gerund, e.g.:
Except...
Except for...
But for...
Apart from -
phoning the bank,
cleaning the car,
washing the plates,
you have done everything I said.
Note: Again, note the commas in these examples.
4. These sentences may also be reversed, e.g.
You have done everything I said
You have done everything I said
except...
except for...
but for...
apart from ...
phoning the bank.
cleaning the car.
washing the plates.
Again, note the commas in these examples.
5. We express a different kind of exception by using without followed by a noun, a noun phrase, a pronoun or a gerund, e.g.:
Without Audu
Audu’s help,
him,
asking Audu,
we couldn’t do it.
We couldn’t do it without Audu.
Audu’s help.
him.
Asking Audu.
Note which examples have commas and which have not.
Evaluation
Rewrite these sentences using except, except for, but for and apart from, each once only:
1. I finished everything. But I did not type this letter
2. We were all laughing. But Eta was not laughing.
Assignment
Fill in the column with the right word
1. Everyone was present ___________ Audu was not present.
2. All the employees were sacked. _________ the manager’s daughter was not sacked.
3. The police caught the whole gang. ____________ they did not catch Bassey.
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Narrative essay
CONTENT: A narrative essay tells a story. In planning a narrative essay there are essential tips to note.
First think about the topic and jot down the main ideas that come to your mind concerning the topic.
Suppose you are asked to write on an incident that made you cry. Immediately, you know that you will write on a sad event. Think of any sad event in your life. Is it going to be on death? Loss of a valuable item? A bad decision that landed you in trouble? An unhappy journey you regretted making? Choose one of these as your topic.
Your composition must have at least three sections- Introduction, the body and the conclusion. Start each with a paragraph. The body may have many paragraphs, depending on the number of main ideas you want to bring into it.
Think of an interesting way of introducing the topic. For example: I now believe that the voice of the elders is the voice of wisdom. I wish I had believed that before August 10, 2006, when I had to pay dearly for not heeding my mother’s golden advice. I wept very much that day and still weep whenever my mind goes back on the incident. If only I had listened!
Example
Topic: My most memorable day
First paragraph: Mention the day and where the event happened. Mention the people involved and what happened in the morning of the day.
Second paragraph: Narrate what happened in the afternoon of that day, mentioning at least two pleasant things that happened.
Third paragraph: Mention what happened in the evening, through to night.
Fourth paragraph: How did the day end? Why is it your most memorable day?
Remember to use the past tense and dialogue while writing.
Evaluation
1. Write four paragraphs on the topic:
‘How I met my Best Friend’.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC – Consonant /Ɵ/ and /t/
CONTENT: Consonants / Ɵ/ /t/
To pronounce / Ɵ / the tip of the tongue is made to almost touch the back of the upper teeth and is almost sticking out between the lower and upper teeth. The air in the mouth is pressed out through the little opening between the tip of the tongue and the upper teeth. No activity is going on in the voice box. This means that the sound is voiceless.
The consonants / Ɵ/ is heard in the following sentences.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/yNtz_ZwLzKE[/youtube]
i. A moth flies through the window.
ii. A mosquito is thin; a moth is fat.
iii. In Maths, Amina won the third prize.
iv. Open your mouth and throw out the bad water.
v. Ade’s birthday is the fourth of June.
Consonant /t/
To pronounce /t/, the front of the tongue is pressed hard behind the root of the upper teeth. There is no activity in the voice box. The air in the mouth is released suddenly with force and the sound is faint. /t/ is a voiceless consonant.
The consonants /t/ is heard in the following sentences.
i. I want to take some time to visit Abuja.
ii. I please turn off the tap; don’t waste water.
iii. The cat is looking at the rat.
iv. I don’t take tea in the afternoon.
v. Peter visited his auntie yesterday.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/L0ptN3jfTR8[/youtube]
EVALUATION
1. Write out 5 words each for consonants /ϴ/ and /t/.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Write and construct 8 sentences each with consonants /ϴ/ and /t/.
2. Write a narrative essay on any of the following topics:
i. First day at school
ii. A marriage ceremony
WEEK 2
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: A LETTER

CONTENT: Unit 9 Page 86-87
A letter from Mary to her young cousin Elizabeth. Mary is a teacher. In writing to
Elizabeth, she uses her own experience as a candidate and as a teacher who marks
school examination. Note that the letter is friendly, but it has a serious purpose, the
Writer has gone to some trouble to set out her points in order using paragraphs.
Evaluation: Junior English Project Book 111. Read the letter as quickly you can, then answer
Questions 1-5
ASSIGNMENT:
Junior English Project Book 3. Using Mary’s letter as a guide, write six or seven short sentences under the heading Examination Tips.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: Suffixes
SUB- TOPIC: Noun Derivations
CONTENT: Noun Derivations
A suffix is the part of a word which is put after a given word also to form a new word. You can see this in these diagrams.

Suffix
-Ful : Meaning + Ful = Meaningful
[youtube]https://youtu.be/pYdIjc85tRc[/youtube]
Some suffixes can help us form nouns from other words. Let us look at some of these in the table below.
Suffixes
-ness
Original/root word
happy
wicked
sick
like
good
gentle
tired
rough
New word
happiness
wickedness
sickness
likeness
goodness
gentleness
tiredness
roughness
-ment
Original/root word
punish
move
nourish
establish
amaze
agree
disappoint
New word
punishment
movement
nourishment
establishment
amazement
agreement
disappointment
-er
Original/root word
box
neat
do
sing
teach
preach
own
New word
boxer
neater
doer
singer
teacher
preacher
owner
-or
Original/root word
Sail
sect
conduct
direct
prosecute
tail
suit
New word
sailor
sector
conductor
direct
prosecutor
tailor
suitor
-ship
Original/root word
friend
scholar
apprentice
court
lord
steward
New word
friendship
scholarship
apprentice
courtship
lordship
stewardship
-hood
Original/root word
Boy
state
child
parent
man
New word
boyhood
statehood
childhood
parenthood
manhood
-ation
Original/root word
Organize
associate
institute
rotate
graduate
mature
segregate
distribute
New word
organization
association
institution
rotation
graduation
maturation
segregate
distribution
-ant
Original/root word
inhabit
disinfect
resist
repent
import
New word
inhabitant
disinfectant
resistant
repentant
important
Evaluation:
1. Using the following suffixes, write down ten nouns that can be formed with them:
(a) –ment
(b) –or
(c) –ship
(d) –ant
Assignment:
Use the suffixes –al to form five new words.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: FEATURES, POSITION AND FUNCTIONS OF CONJUNCTIONS.
CONTENT:
1. Definition of conjunctions
2. Types of conjunctions
3. Features, positions and functions of conjunctions
Definition of conjunctions:
Conjunction comes from a Latin word meaning joined. A conjunction joins words, phrases or sentences together.
EVALUATION
1. What is conjunction
2. Conjunction joins-------------.
3. comes from a Latin word meaning _____
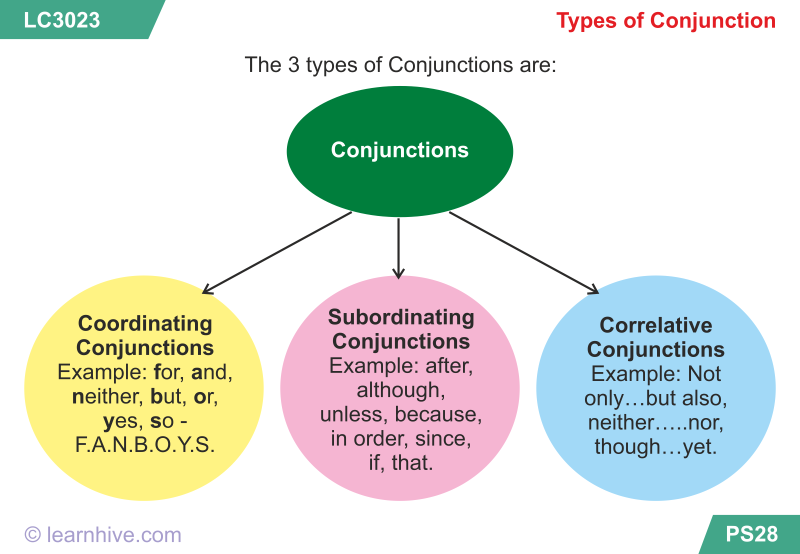
TYPES OF CONJUNCTIONS
1. Coordinating conjunction
These are conjunctions that link words/phrases or clauses that are of equal status. They are called co-coordinators, there are three major co-coordinators viz: and, but, and, or.
EXAMPLES
- Mary is a student and her mother is a nurse
- Argentina won the match but the opponents played better.
- You should pay for the items now or write a cheque covering the mount.
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
A subordinating conjunction is used to join words phrases or clauses of equal status that, is, one is dependent on the other. They are also known as subordinators.
Examples:
Before, since, because, yet, as, if, when, that, now, even, while, in order o, as soon as, unless, etc.
1. He worked hard because he was paid well.
2. They hard finished before we realized we hard made a mistake.
3. The students stood up as soon as the teacher entered.
4. They left the site while it was day.
5. Mrs. Ama arrived when her children where crying
Evaluation:
1. Mention 2 types of conjunction
2. Give 2 examples of each
FEATURES OF CONJUNCTIONS
Conjunctions join words, phrases, clauses or sentences together. Words, phrases, clauses or a sentence joined by a subordinator is dependent on the other.
Position of conjunctions
- Conjunctions occur between the items that the link
- The split between other words in the construction.
- They join words, phrases, clauses and sentences of equal status.
- A subordinator can come at the beginning of a sentence
FUNCTIONS OF CONJUNCTIONS
- They act as coordinators
- They act as subordinators
- They act as correctives
EVALUATION
1. Write 2 functions of conjunctions
2. A subordinator can come at the beginning of the sentence. True/False
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Further Studies 5
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: REPORT WRITING
CONTENT:
DEFINITION
1. To give people information about something that you have heard, seen, done, etc.
2. A written statement about a student’s work at school, college etc.: a school report.
There are many types of Reports you should know how to write.
i. Report of a science experiment
ii. Report of formal meeting deliberations
iii. Report to the Police on an incident you witnessed
iv. Report to your Principal on an issue pertaining to your school
Your approach to each is different, but generally the following tips serve as a guideline
Essential Tips on Report Writing
1. Be brief and clear
2. Give only the most important information
3. Give the exact time, date and place, where necessary
4. Avoid embellishments – go straight to the point without colouring it
5. Make sure your report has answers to the following- when? Where? Why? How? What? Who?
6. You may use sub-headings in your report, especially in reporting scientific experiments and writing minutes of meetings.
7. Give your report in sequential order.
ASPECT: LITERATURE.
TOPIC: PROSE

CONTENT:
Prose is a continuous piece of writing which gives detailed analysis and description of events, setting and characters. It uses the ordinary day to day language without having any regular rhythmic pattern.
Prose in terms of content is divided into two- fiction and non-fiction; while in terms of length it is divided into three- short story, novella and novel.
1. Fiction: This is any unreal story which deals with people, and events invented from the imagination of the author. It is neither a historical occurrence nor a documented fact. The main purpose of fiction if to entertain the audience. This is not to say that it doesn’t perform other functions.
2. Non-Fiction: This is the opposite of fiction. It is an account based on real life experience. Non-fiction could be biography or autobiography.
Biography: One’s life history written by another person.
Autobiography: One’s life history written by himself.
Example, The African Child by Camera Laye.
FORMS OF PROSE
1. Short Story: This is a short and simple story that is straight forward meant to be read at a stretch.
2. Novella: This is a form of prose with an intermediate length. It is longer than a short story, but shorter than a novel. It could also be called novelette.
3. Novel: This is a form of prose with lengthy story(ies) that deals with either imaginary or historical events. A major feature of a novel is that it has a detailed study of people and events.
Evaluation:
Explain the following terms Biography and Autobiography.
Assignment
1. Discuss the following literary
i. Setting
ii. Theme
iii. Plot
2. Write a report on your school’s inter-house sports
3. Write out five words each for consonant /Ɵ/, /s/.
TOPIC: A LETTER

CONTENT: Unit 9 Page 86-87
A letter from Mary to her young cousin Elizabeth. Mary is a teacher. In writing to
Elizabeth, she uses her own experience as a candidate and as a teacher who marks
school examination. Note that the letter is friendly, but it has a serious purpose, the
Writer has gone to some trouble to set out her points in order using paragraphs.
Evaluation: Junior English Project Book 111. Read the letter as quickly you can, then answer
Questions 1-5
ASSIGNMENT:
Junior English Project Book 3. Using Mary’s letter as a guide, write six or seven short sentences under the heading Examination Tips.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: Suffixes
SUB- TOPIC: Noun Derivations
CONTENT: Noun Derivations
A suffix is the part of a word which is put after a given word also to form a new word. You can see this in these diagrams.

Suffix
-Ful : Meaning + Ful = Meaningful
[youtube]https://youtu.be/pYdIjc85tRc[/youtube]
Some suffixes can help us form nouns from other words. Let us look at some of these in the table below.
Suffixes
-ness
Original/root word
happy
wicked
sick
like
good
gentle
tired
rough
New word
happiness
wickedness
sickness
likeness
goodness
gentleness
tiredness
roughness
-ment
Original/root word
punish
move
nourish
establish
amaze
agree
disappoint
New word
punishment
movement
nourishment
establishment
amazement
agreement
disappointment
-er
Original/root word
box
neat
do
sing
teach
preach
own
New word
boxer
neater
doer
singer
teacher
preacher
owner
-or
Original/root word
Sail
sect
conduct
direct
prosecute
tail
suit
New word
sailor
sector
conductor
direct
prosecutor
tailor
suitor
-ship
Original/root word
friend
scholar
apprentice
court
lord
steward
New word
friendship
scholarship
apprentice
courtship
lordship
stewardship
-hood
Original/root word
Boy
state
child
parent
man
New word
boyhood
statehood
childhood
parenthood
manhood
-ation
Original/root word
Organize
associate
institute
rotate
graduate
mature
segregate
distribute
New word
organization
association
institution
rotation
graduation
maturation
segregate
distribution
-ant
Original/root word
inhabit
disinfect
resist
repent
import
New word
inhabitant
disinfectant
resistant
repentant
important
Evaluation:
1. Using the following suffixes, write down ten nouns that can be formed with them:
(a) –ment
(b) –or
(c) –ship
(d) –ant
Assignment:
Use the suffixes –al to form five new words.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: FEATURES, POSITION AND FUNCTIONS OF CONJUNCTIONS.
CONTENT:
1. Definition of conjunctions
2. Types of conjunctions
3. Features, positions and functions of conjunctions
Definition of conjunctions:
Conjunction comes from a Latin word meaning joined. A conjunction joins words, phrases or sentences together.
EVALUATION
1. What is conjunction
2. Conjunction joins-------------.
3. comes from a Latin word meaning _____

TYPES OF CONJUNCTIONS
1. Coordinating conjunction
These are conjunctions that link words/phrases or clauses that are of equal status. They are called co-coordinators, there are three major co-coordinators viz: and, but, and, or.
EXAMPLES
- Mary is a student and her mother is a nurse
- Argentina won the match but the opponents played better.
- You should pay for the items now or write a cheque covering the mount.
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
A subordinating conjunction is used to join words phrases or clauses of equal status that, is, one is dependent on the other. They are also known as subordinators.
Examples:
Before, since, because, yet, as, if, when, that, now, even, while, in order o, as soon as, unless, etc.
1. He worked hard because he was paid well.
2. They hard finished before we realized we hard made a mistake.
3. The students stood up as soon as the teacher entered.
4. They left the site while it was day.
5. Mrs. Ama arrived when her children where crying
Evaluation:
1. Mention 2 types of conjunction
2. Give 2 examples of each
FEATURES OF CONJUNCTIONS
Conjunctions join words, phrases, clauses or sentences together. Words, phrases, clauses or a sentence joined by a subordinator is dependent on the other.
Position of conjunctions
- Conjunctions occur between the items that the link
- The split between other words in the construction.
- They join words, phrases, clauses and sentences of equal status.
- A subordinator can come at the beginning of a sentence
FUNCTIONS OF CONJUNCTIONS
- They act as coordinators
- They act as subordinators
- They act as correctives
EVALUATION
1. Write 2 functions of conjunctions
2. A subordinator can come at the beginning of the sentence. True/False
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Further Studies 5
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: REPORT WRITING
CONTENT:
DEFINITION
1. To give people information about something that you have heard, seen, done, etc.
2. A written statement about a student’s work at school, college etc.: a school report.
There are many types of Reports you should know how to write.
i. Report of a science experiment
ii. Report of formal meeting deliberations
iii. Report to the Police on an incident you witnessed
iv. Report to your Principal on an issue pertaining to your school
Your approach to each is different, but generally the following tips serve as a guideline
Essential Tips on Report Writing
1. Be brief and clear
2. Give only the most important information
3. Give the exact time, date and place, where necessary
4. Avoid embellishments – go straight to the point without colouring it
5. Make sure your report has answers to the following- when? Where? Why? How? What? Who?
6. You may use sub-headings in your report, especially in reporting scientific experiments and writing minutes of meetings.
7. Give your report in sequential order.
ASPECT: LITERATURE.
TOPIC: PROSE

CONTENT:
Prose is a continuous piece of writing which gives detailed analysis and description of events, setting and characters. It uses the ordinary day to day language without having any regular rhythmic pattern.
Prose in terms of content is divided into two- fiction and non-fiction; while in terms of length it is divided into three- short story, novella and novel.
1. Fiction: This is any unreal story which deals with people, and events invented from the imagination of the author. It is neither a historical occurrence nor a documented fact. The main purpose of fiction if to entertain the audience. This is not to say that it doesn’t perform other functions.
2. Non-Fiction: This is the opposite of fiction. It is an account based on real life experience. Non-fiction could be biography or autobiography.
Biography: One’s life history written by another person.
Autobiography: One’s life history written by himself.
Example, The African Child by Camera Laye.
FORMS OF PROSE
1. Short Story: This is a short and simple story that is straight forward meant to be read at a stretch.
2. Novella: This is a form of prose with an intermediate length. It is longer than a short story, but shorter than a novel. It could also be called novelette.
3. Novel: This is a form of prose with lengthy story(ies) that deals with either imaginary or historical events. A major feature of a novel is that it has a detailed study of people and events.
Evaluation:
Explain the following terms Biography and Autobiography.
Assignment
1. Discuss the following literary
i. Setting
ii. Theme
iii. Plot
2. Write a report on your school’s inter-house sports
3. Write out five words each for consonant /Ɵ/, /s/.
WEEK 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: The Ancient Kingdom of Zimbabwe
CONTENT: UNIT 10 Page 94-96
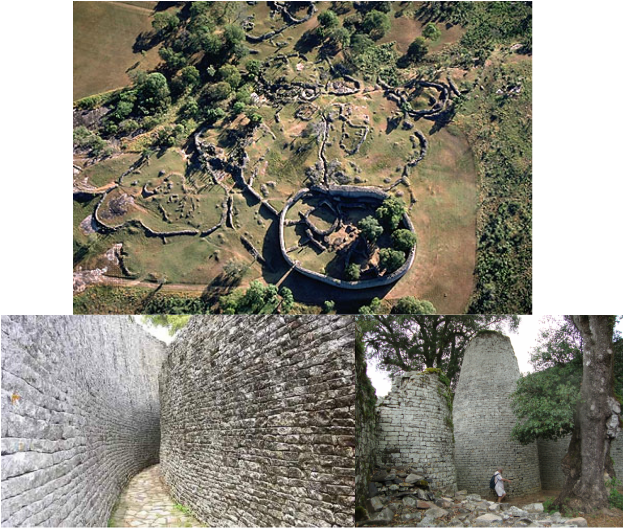


EVALUATION: Junior English Project Book 3.
Why do we preview a text?
ASSIGNMENT: Junior English Project Book 3.
Read the passage on The ancient Kingdom Of Zimbabwe and answer questions1-8.
Further Studies
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: Suffixes- Verb Derivations.
CONTENT:
Some suffixes help us turn some words into verbs. Now, study the following:
Suffix Word Verb
-ify
beauty
simple
deity
false
null
solid
terror
beautify
simplify
deify
falsify
nullify
solidify
terrify
-ize
synthesis
popular
practical
actual
organ
sensitive
critic
synthesize
popularize
practicalize
actualize
organize
sensitive
criticize
-en
sharp
dark
damp
length
broad
strength
straight
sharpen
darken
dampen
length
broaden
strength
straighten
EVALUATION:
1. State what a suffix is in one sentence.
2. Write down three suffixes that can help change some words to verbs
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Choose any two of the suffixes studied in this unit and find ten verbs that can be formed from each of them.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: ADVERBIAL CLAUSES
Adverbials are words that tell us more about adverbs

CONTENT:
Adverbial Clause of Time
1. Here are some of the linkers that can introduce adverbial clauses of time:
After, as, as soon, before, since, till, until, when, and while
2. In adverbial clauses of time you can use any verb forms your meaning requires, except forms containing will or shall. So we use present simple, present continuous or present perfect forms to refer to the future:
Chike’s mother will be relieved when he is discharged from hospital.
I shall not write to her until I have saved up enough money for a house.
While you are doing the cooking, Tome will be arranging the drinks.
3. When an adverbial clause of time begins with since, the main clause usually has a perfect form of the verb:
Since the General arrived, we have been waiting to speak to him
4. When no sooner begins a clause, an auxiliary verb is put in front of the subject:
No sooner had I shut the door than I realized I had left the key in the kitchen.
No sooner do the curtains open than the hero rushes on to stage brandishing a rifle.
However, this is not so when no sooner is placed with the verb:
I had no sooner shut the door than I realized I had left the key in the kitchen.
The curtains no sooner open than the hero rushes on to the stage brandishing a rifle.
Adverbial Clauses of Reason
1. Adverbial clauses of reason may begin with as, because, for or since:
As I had no money, I could not buy any.
He did not speak because he was very shy.
Since you can’t use a word –processor, I’m afraid we can’t offer you a job.
2. The conjunction for is used only in formal English.
Adverbial Clauses of Manner
1. Adverbial clauses of manner usually begin with as:
You should arrive by eight, as the other typists do.
If you feel sleepy after lunch, as many people do, just have a short snooze
Evaluation: Write and discuss four types of adverbials.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: CONSONANT CONTRAST
CONTENT:
Consonant contrast /s/, /ʒ/
To pronounce /s/, the tip of the tongue is raised towards the root/ridge of the front teeth. The sides of the tongue touch the upper teeth. There is a little opening between the tongue and the teeth. The air from the mouth passes through this opening. No activity is going on in the voice box. /s/ is a voiceless consonant. When there is a lot of noise in a place of meeting sometimes we use /s/ to make people keep quiet: sh sh sh…….
[youtube]https://youtu.be/XVo3hzplTiw[/youtube]
To pronounce /ʒ/, the tongue remains in the position for /s/ but we use the air from the lungs.
Activity is going on in the voice box. /ʒ/ is a voiced consonant.
In written English, /s/ is spelt in the following forms.
Sh (shut, shore, cushion…), ch (machine, chalet, chassis…), ce (ocean…), ti (nation), ci (ancient, special, species…)
Notice that in written English, /ʒ/ may be spelt in any of the following forms.
S(measure, pleasure, visual,….), si (decision, confusion, division,….), g(garage, regime, genre,….).
[youtube]https://youtu.be/ubg0FlUcdO0[/youtube]
Contrast /s/ /ʒ/
Mission - Vision
Marshal - Measure
Pressure - Pleasure
Shave -Save
Addition - Division
Pleasant - Pleasure
Sentences
/s/ is heard in the following sentences.
1. Shut the door please
2. Parts of Lagos is on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean
3. I want only two cubes of sugar in my tea.
4. The ancient Songhai empire was destroyed.
5. Do you know the passion flower?
/ʒ/ is heard in the following sentences.
1. You need a ruler to measure this room.
2. There are two garages for our cars.
3. The referee’s decision is final in a match.
4. Usually our day begins with prayers.
5. In a democratic regime people vote to elect their leaders.
EVALUATION:
Write out five words each for consonants /s/ and /ʒ/.
ASSIGNMENT
Underline the /ʒ/ consonant from the following sentences.
1. The man has lost his vision; he is blind.
2. The casualty ward of the hospital is empty.
3. I spend my leisure time reading novels.
4. His regime as president was peaceful.
5. We need revision exercises before our exam.
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: TYPES OF POETRY

CONTENT:
1. Traditional Poem: This is a poem which has its root from the indigenous and oral poem which is often chanted. They are praise songs recited in honor of some heroic persons, animals or events. “Salute of the Elephant” is a good example
2. A ballad: This is a poem that is presented in form of a song telling old stories.
3. Ode: This is a long narrative lyrical poem written in form of an address to somebody, ideas or objects. It is often written in celebration of that which it is addressed to. Example “ Ode to a Nightingale” by John Keats.
4. Lyric: This is a poem which directly expresses the poet’s personal emotion of love, sorrow, disappointment or fulfillment. It is highly emotional, full of thoughts and feelings. It could be sung during burial or other ceremonies. It has a regular rhythm with end rhym
5. Elegy: This is a poem written in the meditation of any sorrow or ordeal. It is like a dirge but not specifically meant for only the deceased.
6. Dirge: This is a poem specially written to mourn the dead. It is primarily written to lament the departure of a loved one. “My Jewel is No More” by F.I Akilaki is a good example.
7. Sonnet: This is a poem of fourteen lines divided into two stanzas of eight lines( octave) and six lines (sestet). A sonnet could also be divided into three stanzas of four lines in the first two stanzas and six lines. It was classically dedicated to the theme of love.
8. Narrative poem: This is a long poem that tells of story. It gives the details of events and people whose story is tells.
9. Epic: This is a poetic account of a hero. It is a poem that narrates the heroic deeds of a people or great man. Epics are usually very voluminous; they are the longest set of poems.
10. Lullaby: This is a poem of pleasant song chanted in a low gentle voice to lure children to sleep.
11. Idyll: This is a poetic form of short and idealized story which describes an incident or an interesting event.
12. Pastoral Poem: This is a poem that describes characters and symbols to represent the speech and action of human being.
13. Epitaph: This is a poetic inscription on a tomb stone. It is written to express respect or disrespect for the deceased.
14. Limerick: This is an amusing poem of five lines.
Evaluation:
Write out five types of poetry
Assignment:
1. Identify five figures of speech from a recommended poem.
2. Write five sentences on each of the following.
1. Adverbial clauses of Purpose
2. Adverbial clauses of Concession
3. Adverbial clauses of result
4. Adverbial clauses of condition
TOPIC: The Ancient Kingdom of Zimbabwe
CONTENT: UNIT 10 Page 94-96


EVALUATION: Junior English Project Book 3.
Why do we preview a text?
ASSIGNMENT: Junior English Project Book 3.
Read the passage on The ancient Kingdom Of Zimbabwe and answer questions1-8.
Further Studies
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: Suffixes- Verb Derivations.
CONTENT:
Some suffixes help us turn some words into verbs. Now, study the following:
Suffix Word Verb
-ify
beauty
simple
deity
false
null
solid
terror
beautify
simplify
deify
falsify
nullify
solidify
terrify
-ize
synthesis
popular
practical
actual
organ
sensitive
critic
synthesize
popularize
practicalize
actualize
organize
sensitive
criticize
-en
sharp
dark
damp
length
broad
strength
straight
sharpen
darken
dampen
length
broaden
strength
straighten
EVALUATION:
1. State what a suffix is in one sentence.
2. Write down three suffixes that can help change some words to verbs
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Choose any two of the suffixes studied in this unit and find ten verbs that can be formed from each of them.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: ADVERBIAL CLAUSES
Adverbials are words that tell us more about adverbs

CONTENT:
Adverbial Clause of Time
1. Here are some of the linkers that can introduce adverbial clauses of time:
After, as, as soon, before, since, till, until, when, and while
2. In adverbial clauses of time you can use any verb forms your meaning requires, except forms containing will or shall. So we use present simple, present continuous or present perfect forms to refer to the future:
Chike’s mother will be relieved when he is discharged from hospital.
I shall not write to her until I have saved up enough money for a house.
While you are doing the cooking, Tome will be arranging the drinks.
3. When an adverbial clause of time begins with since, the main clause usually has a perfect form of the verb:
Since the General arrived, we have been waiting to speak to him
4. When no sooner begins a clause, an auxiliary verb is put in front of the subject:
No sooner had I shut the door than I realized I had left the key in the kitchen.
No sooner do the curtains open than the hero rushes on to stage brandishing a rifle.
However, this is not so when no sooner is placed with the verb:
I had no sooner shut the door than I realized I had left the key in the kitchen.
The curtains no sooner open than the hero rushes on to the stage brandishing a rifle.
Adverbial Clauses of Reason
1. Adverbial clauses of reason may begin with as, because, for or since:
As I had no money, I could not buy any.
He did not speak because he was very shy.
Since you can’t use a word –processor, I’m afraid we can’t offer you a job.
2. The conjunction for is used only in formal English.
Adverbial Clauses of Manner
1. Adverbial clauses of manner usually begin with as:
You should arrive by eight, as the other typists do.
If you feel sleepy after lunch, as many people do, just have a short snooze
Evaluation: Write and discuss four types of adverbials.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: CONSONANT CONTRAST
CONTENT:
Consonant contrast /s/, /ʒ/
To pronounce /s/, the tip of the tongue is raised towards the root/ridge of the front teeth. The sides of the tongue touch the upper teeth. There is a little opening between the tongue and the teeth. The air from the mouth passes through this opening. No activity is going on in the voice box. /s/ is a voiceless consonant. When there is a lot of noise in a place of meeting sometimes we use /s/ to make people keep quiet: sh sh sh…….
[youtube]https://youtu.be/XVo3hzplTiw[/youtube]
To pronounce /ʒ/, the tongue remains in the position for /s/ but we use the air from the lungs.
Activity is going on in the voice box. /ʒ/ is a voiced consonant.
In written English, /s/ is spelt in the following forms.
Sh (shut, shore, cushion…), ch (machine, chalet, chassis…), ce (ocean…), ti (nation), ci (ancient, special, species…)
Notice that in written English, /ʒ/ may be spelt in any of the following forms.
S(measure, pleasure, visual,….), si (decision, confusion, division,….), g(garage, regime, genre,….).
[youtube]https://youtu.be/ubg0FlUcdO0[/youtube]
Contrast /s/ /ʒ/
Mission - Vision
Marshal - Measure
Pressure - Pleasure
Shave -Save
Addition - Division
Pleasant - Pleasure
Sentences
/s/ is heard in the following sentences.
1. Shut the door please
2. Parts of Lagos is on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean
3. I want only two cubes of sugar in my tea.
4. The ancient Songhai empire was destroyed.
5. Do you know the passion flower?
/ʒ/ is heard in the following sentences.
1. You need a ruler to measure this room.
2. There are two garages for our cars.
3. The referee’s decision is final in a match.
4. Usually our day begins with prayers.
5. In a democratic regime people vote to elect their leaders.
EVALUATION:
Write out five words each for consonants /s/ and /ʒ/.
ASSIGNMENT
Underline the /ʒ/ consonant from the following sentences.
1. The man has lost his vision; he is blind.
2. The casualty ward of the hospital is empty.
3. I spend my leisure time reading novels.
4. His regime as president was peaceful.
5. We need revision exercises before our exam.
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: TYPES OF POETRY

CONTENT:
1. Traditional Poem: This is a poem which has its root from the indigenous and oral poem which is often chanted. They are praise songs recited in honor of some heroic persons, animals or events. “Salute of the Elephant” is a good example
2. A ballad: This is a poem that is presented in form of a song telling old stories.
3. Ode: This is a long narrative lyrical poem written in form of an address to somebody, ideas or objects. It is often written in celebration of that which it is addressed to. Example “ Ode to a Nightingale” by John Keats.
4. Lyric: This is a poem which directly expresses the poet’s personal emotion of love, sorrow, disappointment or fulfillment. It is highly emotional, full of thoughts and feelings. It could be sung during burial or other ceremonies. It has a regular rhythm with end rhym
5. Elegy: This is a poem written in the meditation of any sorrow or ordeal. It is like a dirge but not specifically meant for only the deceased.
6. Dirge: This is a poem specially written to mourn the dead. It is primarily written to lament the departure of a loved one. “My Jewel is No More” by F.I Akilaki is a good example.
7. Sonnet: This is a poem of fourteen lines divided into two stanzas of eight lines( octave) and six lines (sestet). A sonnet could also be divided into three stanzas of four lines in the first two stanzas and six lines. It was classically dedicated to the theme of love.
8. Narrative poem: This is a long poem that tells of story. It gives the details of events and people whose story is tells.
9. Epic: This is a poetic account of a hero. It is a poem that narrates the heroic deeds of a people or great man. Epics are usually very voluminous; they are the longest set of poems.
10. Lullaby: This is a poem of pleasant song chanted in a low gentle voice to lure children to sleep.
11. Idyll: This is a poetic form of short and idealized story which describes an incident or an interesting event.
12. Pastoral Poem: This is a poem that describes characters and symbols to represent the speech and action of human being.
13. Epitaph: This is a poetic inscription on a tomb stone. It is written to express respect or disrespect for the deceased.
14. Limerick: This is an amusing poem of five lines.
Evaluation:
Write out five types of poetry
Assignment:
1. Identify five figures of speech from a recommended poem.
2. Write five sentences on each of the following.
1. Adverbial clauses of Purpose
2. Adverbial clauses of Concession
3. Adverbial clauses of result
4. Adverbial clauses of condition
WEEK 4
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: A Chance to Enjoy Normal School Life.

CONTENT: Unit 11 page 104-105]
EVALUATION: Junior English Project Book 3.
Read the passage again more carefully and answer questions 1-5.
ASPECT: Vocabulary Development.
TOPIC: Suffixes-Adjective Derivations.
CONTENT:
VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT SUFFIXES – ADJECTIVE DERIVATIONS.
Suffix
-ful
Use - useful
mouth - mouthful
fruit - fruitful
-al
practice - practical
president - presidential
music - musical
-less
Point - pointless
use - useless
child - childless
-ish
Fool - foolish
book - bookish
amateur - amateurish
-ive
Attend - attentive
attract - attractive
possess - possessive
-ous
Grace - gracious
riot - riotous
peril - perilous
EVALUATION:
1. Using the appropriate suffix e.g –er, -ment, -ese, and –ship, turn the following words into nouns.
Speak barren
Read bright
Red swift
Hardy humiliate
Form girl
Priest fellow
Merry remain
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Which suffixes can help you turn words into adjectives? Use some of them to turn the following into adjectives.
Sense relent
Marvel shame
Wonder fallacy
Thought
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: QUESTION TAGS
CONTENT:
QUESTION TAGS
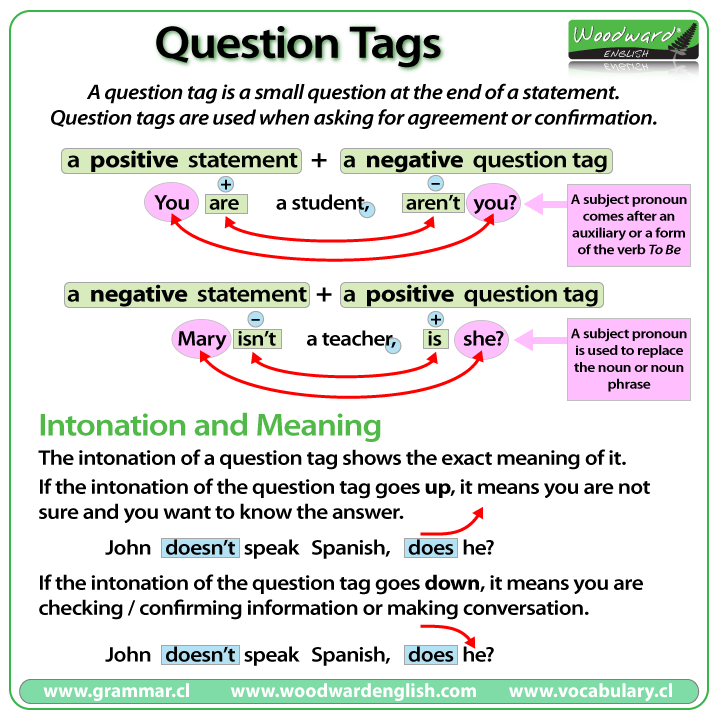
Questions are a means of getting information. In some matters a speaker is totally ignorant; so he asks questions to get new information. For example. ‘Is Yankari Game Reserve in Abia state? ‘In some other matters, he already has some ideas; he seems to be fairly certain about them. He then asks a question to get a confirmation of his previous ideas. He makes a statement and adds a tag to his statement. This is called a question tag. For example: ‘Pretoria is in South Africa, isn’t it?
Affirmation statements with Negative Tags.
(i) John was in school yesterday, wasn’t he?
(ii) The sun rises in the east, doesn’t it?
(iii) This term will end shortly , won’t it?
(iv) Our teachers are very decent people, aren’t they?
(v) I can come to your house if I like, can’t I?
Negative statements with Affirmative Tags.
(i) John was not in school yesterday, was he?
(ii) The driver did not come back, did he?
(iii) There is no football match today, is there any?
(iv) Lagos is no longer the seat of the Federal Government, is it?
(v) We shall not lose our next match, shall we?
EVALUATION:
Read the following sentences and add their question tags to them
(i) The game is not over yet, ----------?
(ii) The Super Eagles did not win their last match, -----------?
(iii) A river flows downhill, ------------?
(iv) Mary is not older than Susan, --------------?
(v) A lion cannot be tamed, ------------?
ASSIGNMENT:
Answer these tags question correctly.
(i) Good food is necessary for good health, -------------?
(ii) You can find a mangrove forest in Kano, -----------?
(iii) The River Nile does not flow into the Atlantic Ocean, ----------?
(iv) Chinua Achebe is the author of Things Fall Apart, ------------?
(v) You must study hard in order to pass, ----------------?
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: INFORMAL LETTERS
CONTENT:
INFORMAL LETTERS
An informal letter is the type of letter you write to people you know very well-relations, friends and close acquaintances. As such, the language you show is conversational, chatty. However, for the elderly ones, like your father or mother, you show some respect. That is, you do not use slangs for them or too much colloquial English.
ESSENTIAL TIPS
Writing Informal letters
1. Use only one address- You own address written at the top right hand side of your paper.
2. Punctuate the address and date as shown in the format.
3. Use any of these as opening greeting- Dear…..; My dear……; Dearest…… follow with the person’s first name of designation (Brother; Sister; Father; Mother) and a comma.
4. Introductory paragraph should begin with compliments, but don’t overdo it.
5. Use short forms, colloquial English and slang (but no slang for Father and Mother, Aunt, Uncle).
6. Use conversational English. Chat as if you are writing to a real friend or relation.
7. Close with ‘Your sincerely, ‘followed by your first name only.
EXAMPLE
.........................................................................................................18, Acme Road,
.........................................................................................................Omole Estate,
.........................................................................................................Ikeja.
.........................................................................................................Lagos State
.........................................................................................................6th February, 2006.
Dear Uncle,
I am writing to inform you that I arrived here safely after a journey of six hours. The journey from Owerri to Ibadan was really tiring. This is party because the bus was over-crowded. Besides, the driver stopped anywhere he saw some passengers. Even though the bus was full, he continued to take more and more passengers. He did not even mind the way we shouted at him against this. The good thing is that I have arrived safely and found all my people very happy.
Uncle, I want to thank you very much for all you did for me while I was there. I also thank Mama, your wife, for all those nice meals. Give my regards to all your friends who receive me very warmly each time you took me out in your car.
Finally, uncle, please remember my request for a pair of tennis shoes. As you said you would send them through Mr. Kobari, your friend, I will be looking forward to receiving them.
Greetings from my father, mother, brother and sisters. Bye for now, sir.
Yours sincerely,
Bimbo.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Sounds / m/ / n/ /ŋ/
The nasal sounds are produced as a result of closure in the mouth and the air flow escaped through the nose. The examples are stated below;
/m/ man, moon, make, name, bomb, claim, frame, lame, damn, hymn, condemn, bomb, comb, dumb, climb, plumb, crumb, grammar, commission, etc
a. In the following words, ‘m’ and not ‘b’ is the end sound even though ‘b’ can be seen. It is not pronounced. Plumb, dumb, climb, comb, tomb, bomb, numb, lamb, crumb.
b. More so, ‘m’ is the end-sound of these words and not ‘n’. Hymn, condemn, solemn.
/n/ name, nose, neck, new, note, stone, brain, gnash, gnat, gnaw, know, knowledge, knot, knit, knew, manner, banner, nanny, funnel, cranny, etc.
a. When ‘n’ is used after ‘m’ at word final positions, it is not pronounced. Examples: damn, hymn, condemn, column.
b. When ‘n’ is used after ‘k’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘k’ is silent. Examples: know, knot, knew, knit,etc
c. When ‘n’ is placed after ‘g’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘g’ is silent. Examples: gnash, gnaw, gnat, etc.
/ ŋ/ sing, king, ring, bank, bring, ink, spring, song, hang, tongue, bang, plank, bangle, anxious, drink, function, precinct, minx, etc
[youtube]https://youtu.be/QY-lIYjJGBY[/youtube]
EVALUATION: From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that has the same consonant sound(s) as the one represented by the letter(s) underlined.
1. bomb
A. Bubble B. stay C. come D. bone
2. Sing
A. hing B. king C. huge D. rinse
ASSIGNMENT: Write a letter to your father telling him how far you have prepared for your JSCE exanimation.
TOPIC: A Chance to Enjoy Normal School Life.

CONTENT: Unit 11 page 104-105]
EVALUATION: Junior English Project Book 3.
Read the passage again more carefully and answer questions 1-5.
ASPECT: Vocabulary Development.
TOPIC: Suffixes-Adjective Derivations.
CONTENT:
VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT SUFFIXES – ADJECTIVE DERIVATIONS.
Suffix
-ful
Use - useful
mouth - mouthful
fruit - fruitful
-al
practice - practical
president - presidential
music - musical
-less
Point - pointless
use - useless
child - childless
-ish
Fool - foolish
book - bookish
amateur - amateurish
-ive
Attend - attentive
attract - attractive
possess - possessive
-ous
Grace - gracious
riot - riotous
peril - perilous
EVALUATION:
1. Using the appropriate suffix e.g –er, -ment, -ese, and –ship, turn the following words into nouns.
Speak barren
Read bright
Red swift
Hardy humiliate
Form girl
Priest fellow
Merry remain
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Which suffixes can help you turn words into adjectives? Use some of them to turn the following into adjectives.
Sense relent
Marvel shame
Wonder fallacy
Thought
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: QUESTION TAGS
CONTENT:
QUESTION TAGS

Questions are a means of getting information. In some matters a speaker is totally ignorant; so he asks questions to get new information. For example. ‘Is Yankari Game Reserve in Abia state? ‘In some other matters, he already has some ideas; he seems to be fairly certain about them. He then asks a question to get a confirmation of his previous ideas. He makes a statement and adds a tag to his statement. This is called a question tag. For example: ‘Pretoria is in South Africa, isn’t it?
Affirmation statements with Negative Tags.
(i) John was in school yesterday, wasn’t he?
(ii) The sun rises in the east, doesn’t it?
(iii) This term will end shortly , won’t it?
(iv) Our teachers are very decent people, aren’t they?
(v) I can come to your house if I like, can’t I?
Negative statements with Affirmative Tags.
(i) John was not in school yesterday, was he?
(ii) The driver did not come back, did he?
(iii) There is no football match today, is there any?
(iv) Lagos is no longer the seat of the Federal Government, is it?
(v) We shall not lose our next match, shall we?
EVALUATION:
Read the following sentences and add their question tags to them
(i) The game is not over yet, ----------?
(ii) The Super Eagles did not win their last match, -----------?
(iii) A river flows downhill, ------------?
(iv) Mary is not older than Susan, --------------?
(v) A lion cannot be tamed, ------------?
ASSIGNMENT:
Answer these tags question correctly.
(i) Good food is necessary for good health, -------------?
(ii) You can find a mangrove forest in Kano, -----------?
(iii) The River Nile does not flow into the Atlantic Ocean, ----------?
(iv) Chinua Achebe is the author of Things Fall Apart, ------------?
(v) You must study hard in order to pass, ----------------?
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: INFORMAL LETTERS
CONTENT:
INFORMAL LETTERS
An informal letter is the type of letter you write to people you know very well-relations, friends and close acquaintances. As such, the language you show is conversational, chatty. However, for the elderly ones, like your father or mother, you show some respect. That is, you do not use slangs for them or too much colloquial English.
ESSENTIAL TIPS
Writing Informal letters
1. Use only one address- You own address written at the top right hand side of your paper.
2. Punctuate the address and date as shown in the format.
3. Use any of these as opening greeting- Dear…..; My dear……; Dearest…… follow with the person’s first name of designation (Brother; Sister; Father; Mother) and a comma.
4. Introductory paragraph should begin with compliments, but don’t overdo it.
5. Use short forms, colloquial English and slang (but no slang for Father and Mother, Aunt, Uncle).
6. Use conversational English. Chat as if you are writing to a real friend or relation.
7. Close with ‘Your sincerely, ‘followed by your first name only.
EXAMPLE
.........................................................................................................18, Acme Road,
.........................................................................................................Omole Estate,
.........................................................................................................Ikeja.
.........................................................................................................Lagos State
.........................................................................................................6th February, 2006.
Dear Uncle,
I am writing to inform you that I arrived here safely after a journey of six hours. The journey from Owerri to Ibadan was really tiring. This is party because the bus was over-crowded. Besides, the driver stopped anywhere he saw some passengers. Even though the bus was full, he continued to take more and more passengers. He did not even mind the way we shouted at him against this. The good thing is that I have arrived safely and found all my people very happy.
Uncle, I want to thank you very much for all you did for me while I was there. I also thank Mama, your wife, for all those nice meals. Give my regards to all your friends who receive me very warmly each time you took me out in your car.
Finally, uncle, please remember my request for a pair of tennis shoes. As you said you would send them through Mr. Kobari, your friend, I will be looking forward to receiving them.
Greetings from my father, mother, brother and sisters. Bye for now, sir.
Yours sincerely,
Bimbo.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Sounds / m/ / n/ /ŋ/
The nasal sounds are produced as a result of closure in the mouth and the air flow escaped through the nose. The examples are stated below;
/m/ man, moon, make, name, bomb, claim, frame, lame, damn, hymn, condemn, bomb, comb, dumb, climb, plumb, crumb, grammar, commission, etc
a. In the following words, ‘m’ and not ‘b’ is the end sound even though ‘b’ can be seen. It is not pronounced. Plumb, dumb, climb, comb, tomb, bomb, numb, lamb, crumb.
b. More so, ‘m’ is the end-sound of these words and not ‘n’. Hymn, condemn, solemn.
/n/ name, nose, neck, new, note, stone, brain, gnash, gnat, gnaw, know, knowledge, knot, knit, knew, manner, banner, nanny, funnel, cranny, etc.
a. When ‘n’ is used after ‘m’ at word final positions, it is not pronounced. Examples: damn, hymn, condemn, column.
b. When ‘n’ is used after ‘k’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘k’ is silent. Examples: know, knot, knew, knit,etc
c. When ‘n’ is placed after ‘g’ at word beginnings, it is pronounced while ‘g’ is silent. Examples: gnash, gnaw, gnat, etc.
/ ŋ/ sing, king, ring, bank, bring, ink, spring, song, hang, tongue, bang, plank, bangle, anxious, drink, function, precinct, minx, etc
[youtube]https://youtu.be/QY-lIYjJGBY[/youtube]
EVALUATION: From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that has the same consonant sound(s) as the one represented by the letter(s) underlined.
1. bomb
A. Bubble B. stay C. come D. bone
2. Sing
A. hing B. king C. huge D. rinse
ASSIGNMENT: Write a letter to your father telling him how far you have prepared for your JSCE exanimation.
WEEK 5
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: HUMANITY AT RISK
CONTENT: Unit 12 Page 112-113

EVALUATION: Junior English Project Book 3. Read the newspaper report to get the gist of it
And answer questions 1-5.
ASSIGNMENT: Junior English Project Book3.Read the summary passage on page115 and answer
The questions.1-3.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: Words Associated with Value Judgment.
CONTENT:

Words associated with value judgment.
Lucky, rudely, beautiful, cruel, harsh, lovely, unpleasant, coarse, puzzling, promising.
SENTENCES
1. Chief Taiwo’s family is a hospitable one. The wife is very caring. Chief Taiwo himself is benevolent and kind-hearted. He wife is quite supportive.
2. I want to warn you not to associate yourself with deceitful, immoral and dishonest people who craftily entice your innocent youths.
3. It is malicious and callous for a person to go about saying things that are untrue about others.
EVALUATION:
Words associated with value judgment.
Fill in the gaps in the following sentences with the appropriate words chosen from the list below.
Lucky, rudely, beautiful, cruel, harsh, lovely, unpleasant, coarse, puzzling, promising, frightening.
1. Still think my mother was very _______, she narrated her ________ experience in the hands of two_______ armed robbers. The two hefty men accosted her on a ________ road and _______ asked her to surrender her______ handbag. The drugs and alcohol. Mother was saved by a crowd of school children returning from school.
Though mother escaped unhurt and without losing anything, the emotional trauma of that experience will remain with her for a long time. The _______ thing, future if they had been properly managed.
ASSIGNMENT:
DICTIONARY WORK
Use your dictionary to write out the meaning of the following words and construct good sentences with them.
(1) Malicious (2) callous (3) benevolent (4) promising (5) cruel
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: FORMAL LETTERS
CONTENT:
Formal letters cover various types of official letters, such as:
1. Application letters.
2. Letters to Editors of newspapers and magazines.
3. Letter of Complaints; Requests to business houses.
4. Letters of Reports/statements to Principals/Police Officers
5. Invitation letters, etc.
The format for such letters is different from the format for informal letters. The differences between the two are listed below. Check also Book One and Two for additional information.
ESSENTIAL TIPS
The Differences between Formal and Informal Letters
Formal Informal
1. Two addresses are needed – your address and the address of the recipient. One address is needed- own address.
2. Salute with Dear Sir, or Dear Madam;. Start with Dear followed by the person’s name; if a relation, use the right designation- Mother; Sister, Uncle etc.
3. Give a heading to your letter and underline it. No heading is needed.
4. Write in a formal language- no short forms, abbreviations. Write in colloquial English using short forms, slang (not for elders), and jokes abbreviations.
5. No exchange of pleasantries Exchange pleasantries
6. Go straight to the point of writing form the first paragraph. Play around with exchange of pleasantries in the first paragraph.
7. Close with ‘Yours faithfully’ followed by your signature and full names Close with ‘Yours sincerely’, followed by your first name only. You can also use other forms of closing, depending on whom you are writing to, such as: ‘Yours affectionately, Yours ever, Your loving son, Your friend’.
Example
.................................................................................................10, Johnson Street,
.................................................................................................Ijeshatedo,
.................................................................................................Surulere,
.................................................................................................Lagos State.
.................................................................................................15th June, 2007.
The Registrar,
Obafemi Awolowo University,
Ile-Ife,
Osun State.
Dear Sir,
Request for Application Forms for Traffic Wardens.
I refer to your recent advertisement of vacancies for Traffic Wardens in your University.
I wish to apply for the post and would be very pleased if you could send me an application form.
I enclose a stamped, self-addressed envelope and a Postal Order for N50.00 as demanded.
Thanks for an anticipated urgent reply.
Yours faithfully,
Oluremi Ige
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Vowel/i/ and /i:/
CONTENT:
Vowel /i/:
To pronoun /i/ the tongue is in the same position for /i:/. The lips are spread but /i/ is a short vowel.
Vowel/i/ is heard and showed in bold print in the following utterances.
(i) This boy is picking up some oranges.
(ii) My parents lived in the village.
(iii) Our classroom is spick- and span.
(iv) Fill out this form and give it to me.
Notice that in written English, /I/ may appear in different spelling forms:
i. (Big, pit…), y (lorry, city…) e (wounded, wicked, u (busy, business…) o (women).
Vowel /i: /
To pronounce /i: / the front of the tongue is raised closed to the roof of the mouth. The tips are spread. /i: / is a long vowel.
Vowel/i: / is heard and showed in bold print in the following utterances.
(i) These boys and girls are speaking good English.
(ii) There is nothing as sweet as honey.
(iii) The police seized the key of the car.
(iv) Leave the field at once.
(v) Put the book on your seat.
Notice that in written English, /i:/ may be spelt in different forms: ee, ea, i, ie, ey, ea.
Examples:
(i) eel, cheese, teeth, green, bee, beetle
(ii) clean, please, leave, leaf, dream
(iii) machine, police, margarine
(iv) achieve, relief
(v) receipt, deceive
(vi) key
(vii) people
Contrast between /i/ and /i:/
/i/ /i:/
Sit seat
Live leave
Rid read
Ship sheep
Sin seen
Did deed
[youtube]https://youtu.be/TNFKG0yvDx4[/youtube]
EVALUATION
Practice saying the following pairs of words:
I. Leave - live;
II. receipt –resist
III. Wheel – will;
IV. eel - ill
V. Seat – sit;
VI. beach - bitch
VII. Deep – dip;
VIII. fleet - flit
IX. Reach – rich;
X. wheat – wit
Assignment
Underline the /i:/ and /i/ vowel sounds from the following sentences.
(i) Did he sit on this seat?
(ii) Leave the book for me where I live.
(iii) If you want to read here, first get rid of this rubbish.
(iv) Don’t dip your hand into a deep pit.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: PRONOUNS
CONTENT:
A pronoun can simple be described as a replacement for a noun to avoid repetition. It can also be defined as the words that are used instead of a noun.
EXAMPLE:
I gave Sola the money; Sola’s father sent to money to Sola, to avoid the repetition of the noun, Sola, the above sentence can read thus:
I gave Sola the money her (pronoun) father sent to her.
Note the pronoun “her” replaced Sola in the sentence.
Pronoun include: he, she, they, us, it, this, these, that, those, we, I, you, each, somebody, nobody, number, many, few, several, something, myself, himself, herself, and themselves etc.
TYPES OF PRONOUNS
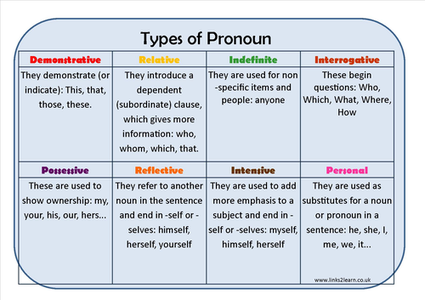
1. Personal pronoun: These are: I, you, he, she, it, they, him, her, us, we, and them.
2. Demonstrative Pronouns: These are: this, that, (singular) these, those.
Plural: This and these point out people or thing that are close to the person speaking while that and these point out things that are distant.
EXAMPLES
i. This is my father
These are my brother standing across the road.
3. Possessive pronouns: These are called possesses pronouns because they show or indicate possession, they include my, mine, our, ours, your, yours, her, hers, his, their, theirs, it, its.
(4) Interrogative pronouns: This is derived from the word interrogation. These pronouns are used to asking question they are: who, what, where, when, whose, whom, which.
EXAMPLES
1. Who sent you on this dangerous journey?
2. What is your favorite food?
(5) Reflexive pronouns: This pronoun makes reference to the subject in a subject. Reflexive pronouns are: himself, myself, itself, themselves, ourselves, and yourselves.
EXAMPLE
My mother washes her cloths herself.
(6) Relative pronouns: These are the same set of other pronouns. However, write interrogative pronouns are used to as to questions; relative pronouns are used to introduce. Relative clause these are who, whom, which, that, whose, when.
EXAMPLES
This is the house I was born
(7) Indefinite pronouns: These pronouns are called indefinite pronouns because they do not refer to particular or specific people or things. They are used in general sense they include somebody, someone, everybody, everything much etc.
(8) Reciprocal pronouns: These indicate an exchange of an action between two more people. These are each other and one another; each other refer to two people while one another refer to more than two people.
TABLE CLASSIFYING THE VARIOUS PRONOUNS
First person Subject Object Possessive Reflexive
Singular I me mine myself
Second person
Singular You you yours yourself
Third person
Singular He him his himself
She her hers herself
First person
Plural We us ours ourselves
Second person
Plural You you yours yourselves
Third person
Plural They them theirs themselves
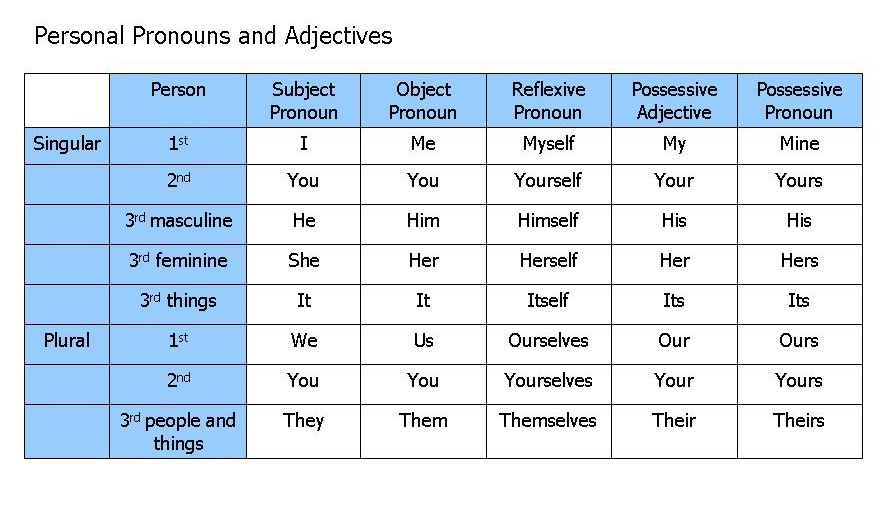
EVALUATION:
Pick out the pronouns in the passage below:
Obi would want his parents to meet his friend today so he invited him to their house for dinner. Before Obi’s friend arrived, Obi and his two brothers cleaned their house. They swept every corner and dusted the chairs and tables. Everything in their house was sparkling. Nothing was left unattended to.
ASSIGNMENT:
Rewrite the following sentences replacing the nouns with the correct pronouns.
a. Etim and Eno will be here this afternoon.
b. My mother and I usually sing together.
c. Ngozi is my sister.
d. Does Mr. Obi visit regularly?
e. Let Obi and Nduka come back this evening.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Further Studies 2
Practice Test 3
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: DRAMA
Drama is the imitation of human action presented by performers on stage to an audience. It is the penetration of life through artificial means. In drama real-life people pretend to be imagined people; thus imitating what people do in real life. It is the only genre of literature that can be acted on stage.

TYPES OF DRAMA

1. Tragedy: This is a form of drama that has a sad ending, a hero who could be admired by audience because of his qualities and achievements could just fall suddenly as a result of his tragic flaw or hubris. Such fall may even lead to his death. The Gods Are Not To Blame by Ola Rotimi and Macbeth by William Shakespeare are good examples.
2. Comedy: This is a form of drama that aims primarily at amusing the audience and it has a happy ending.
3. Melodrama: This is a romantic play characterized by music and exciting events with exaggerated characters.
4. Tragic-Comedy: This is a form of drama that employs a plot suitable to tragedy, it has a serious beginning, but finally ends happily like comedy. D.O. Odigie’s Verdict of the Gods is a good example, Merchant of Venice by Shakespeare is also a good example.
5. Satire: This is a kind of drama that uses elements of comedy such as wit, irony, and exaggeration to criticize and expose human and social vices. It ridicules the foolishness or wickedness of a particular practice, custom or a bad government. Its aim is to attack and expose specific in the society for a positive change.
6. Fable: This is a story with animals as characters used to teach moral. This is very common in African folktales. Animal Farm by George Orwell is the most popular fable written so far.
Assignment:
A. From a recommended text you read this term, identify five (5):
1. Themes
2. Characters
3. Figures of speech
B. Write a letter to your parents inviting them to your end of year party.
TOPIC: HUMANITY AT RISK
CONTENT: Unit 12 Page 112-113

EVALUATION: Junior English Project Book 3. Read the newspaper report to get the gist of it
And answer questions 1-5.
ASSIGNMENT: Junior English Project Book3.Read the summary passage on page115 and answer
The questions.1-3.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: Words Associated with Value Judgment.
CONTENT:

Words associated with value judgment.
Lucky, rudely, beautiful, cruel, harsh, lovely, unpleasant, coarse, puzzling, promising.
SENTENCES
1. Chief Taiwo’s family is a hospitable one. The wife is very caring. Chief Taiwo himself is benevolent and kind-hearted. He wife is quite supportive.
2. I want to warn you not to associate yourself with deceitful, immoral and dishonest people who craftily entice your innocent youths.
3. It is malicious and callous for a person to go about saying things that are untrue about others.
EVALUATION:
Words associated with value judgment.
Fill in the gaps in the following sentences with the appropriate words chosen from the list below.
Lucky, rudely, beautiful, cruel, harsh, lovely, unpleasant, coarse, puzzling, promising, frightening.
1. Still think my mother was very _______, she narrated her ________ experience in the hands of two_______ armed robbers. The two hefty men accosted her on a ________ road and _______ asked her to surrender her______ handbag. The drugs and alcohol. Mother was saved by a crowd of school children returning from school.
Though mother escaped unhurt and without losing anything, the emotional trauma of that experience will remain with her for a long time. The _______ thing, future if they had been properly managed.
ASSIGNMENT:
DICTIONARY WORK
Use your dictionary to write out the meaning of the following words and construct good sentences with them.
(1) Malicious (2) callous (3) benevolent (4) promising (5) cruel
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: FORMAL LETTERS
CONTENT:
Formal letters cover various types of official letters, such as:
1. Application letters.
2. Letters to Editors of newspapers and magazines.
3. Letter of Complaints; Requests to business houses.
4. Letters of Reports/statements to Principals/Police Officers
5. Invitation letters, etc.
The format for such letters is different from the format for informal letters. The differences between the two are listed below. Check also Book One and Two for additional information.
ESSENTIAL TIPS
The Differences between Formal and Informal Letters
Formal Informal
1. Two addresses are needed – your address and the address of the recipient. One address is needed- own address.
2. Salute with Dear Sir, or Dear Madam;. Start with Dear followed by the person’s name; if a relation, use the right designation- Mother; Sister, Uncle etc.
3. Give a heading to your letter and underline it. No heading is needed.
4. Write in a formal language- no short forms, abbreviations. Write in colloquial English using short forms, slang (not for elders), and jokes abbreviations.
5. No exchange of pleasantries Exchange pleasantries
6. Go straight to the point of writing form the first paragraph. Play around with exchange of pleasantries in the first paragraph.
7. Close with ‘Yours faithfully’ followed by your signature and full names Close with ‘Yours sincerely’, followed by your first name only. You can also use other forms of closing, depending on whom you are writing to, such as: ‘Yours affectionately, Yours ever, Your loving son, Your friend’.
Example
.................................................................................................10, Johnson Street,
.................................................................................................Ijeshatedo,
.................................................................................................Surulere,
.................................................................................................Lagos State.
.................................................................................................15th June, 2007.
The Registrar,
Obafemi Awolowo University,
Ile-Ife,
Osun State.
Dear Sir,
Request for Application Forms for Traffic Wardens.
I refer to your recent advertisement of vacancies for Traffic Wardens in your University.
I wish to apply for the post and would be very pleased if you could send me an application form.
I enclose a stamped, self-addressed envelope and a Postal Order for N50.00 as demanded.
Thanks for an anticipated urgent reply.
Yours faithfully,
Oluremi Ige
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: Vowel/i/ and /i:/
CONTENT:
Vowel /i/:
To pronoun /i/ the tongue is in the same position for /i:/. The lips are spread but /i/ is a short vowel.
Vowel/i/ is heard and showed in bold print in the following utterances.
(i) This boy is picking up some oranges.
(ii) My parents lived in the village.
(iii) Our classroom is spick- and span.
(iv) Fill out this form and give it to me.
Notice that in written English, /I/ may appear in different spelling forms:
i. (Big, pit…), y (lorry, city…) e (wounded, wicked, u (busy, business…) o (women).
Vowel /i: /
To pronounce /i: / the front of the tongue is raised closed to the roof of the mouth. The tips are spread. /i: / is a long vowel.
Vowel/i: / is heard and showed in bold print in the following utterances.
(i) These boys and girls are speaking good English.
(ii) There is nothing as sweet as honey.
(iii) The police seized the key of the car.
(iv) Leave the field at once.
(v) Put the book on your seat.
Notice that in written English, /i:/ may be spelt in different forms: ee, ea, i, ie, ey, ea.
Examples:
(i) eel, cheese, teeth, green, bee, beetle
(ii) clean, please, leave, leaf, dream
(iii) machine, police, margarine
(iv) achieve, relief
(v) receipt, deceive
(vi) key
(vii) people
Contrast between /i/ and /i:/
/i/ /i:/
Sit seat
Live leave
Rid read
Ship sheep
Sin seen
Did deed
[youtube]https://youtu.be/TNFKG0yvDx4[/youtube]
EVALUATION
Practice saying the following pairs of words:
I. Leave - live;
II. receipt –resist
III. Wheel – will;
IV. eel - ill
V. Seat – sit;
VI. beach - bitch
VII. Deep – dip;
VIII. fleet - flit
IX. Reach – rich;
X. wheat – wit
Assignment
Underline the /i:/ and /i/ vowel sounds from the following sentences.
(i) Did he sit on this seat?
(ii) Leave the book for me where I live.
(iii) If you want to read here, first get rid of this rubbish.
(iv) Don’t dip your hand into a deep pit.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: PRONOUNS
CONTENT:
A pronoun can simple be described as a replacement for a noun to avoid repetition. It can also be defined as the words that are used instead of a noun.

EXAMPLE:
I gave Sola the money; Sola’s father sent to money to Sola, to avoid the repetition of the noun, Sola, the above sentence can read thus:
I gave Sola the money her (pronoun) father sent to her.
Note the pronoun “her” replaced Sola in the sentence.
Pronoun include: he, she, they, us, it, this, these, that, those, we, I, you, each, somebody, nobody, number, many, few, several, something, myself, himself, herself, and themselves etc.
TYPES OF PRONOUNS

1. Personal pronoun: These are: I, you, he, she, it, they, him, her, us, we, and them.
2. Demonstrative Pronouns: These are: this, that, (singular) these, those.
Plural: This and these point out people or thing that are close to the person speaking while that and these point out things that are distant.
EXAMPLES
i. This is my father
These are my brother standing across the road.
3. Possessive pronouns: These are called possesses pronouns because they show or indicate possession, they include my, mine, our, ours, your, yours, her, hers, his, their, theirs, it, its.
(4) Interrogative pronouns: This is derived from the word interrogation. These pronouns are used to asking question they are: who, what, where, when, whose, whom, which.
EXAMPLES
1. Who sent you on this dangerous journey?
2. What is your favorite food?
(5) Reflexive pronouns: This pronoun makes reference to the subject in a subject. Reflexive pronouns are: himself, myself, itself, themselves, ourselves, and yourselves.
EXAMPLE
My mother washes her cloths herself.
(6) Relative pronouns: These are the same set of other pronouns. However, write interrogative pronouns are used to as to questions; relative pronouns are used to introduce. Relative clause these are who, whom, which, that, whose, when.
EXAMPLES
This is the house I was born
(7) Indefinite pronouns: These pronouns are called indefinite pronouns because they do not refer to particular or specific people or things. They are used in general sense they include somebody, someone, everybody, everything much etc.
(8) Reciprocal pronouns: These indicate an exchange of an action between two more people. These are each other and one another; each other refer to two people while one another refer to more than two people.
TABLE CLASSIFYING THE VARIOUS PRONOUNS
First person Subject Object Possessive Reflexive
Singular I me mine myself
Second person
Singular You you yours yourself
Third person
Singular He him his himself
She her hers herself
First person
Plural We us ours ourselves
Second person
Plural You you yours yourselves
Third person
Plural They them theirs themselves

EVALUATION:
Pick out the pronouns in the passage below:
Obi would want his parents to meet his friend today so he invited him to their house for dinner. Before Obi’s friend arrived, Obi and his two brothers cleaned their house. They swept every corner and dusted the chairs and tables. Everything in their house was sparkling. Nothing was left unattended to.
ASSIGNMENT:
Rewrite the following sentences replacing the nouns with the correct pronouns.
a. Etim and Eno will be here this afternoon.
b. My mother and I usually sing together.
c. Ngozi is my sister.
d. Does Mr. Obi visit regularly?
e. Let Obi and Nduka come back this evening.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Further Studies 2
Practice Test 3
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: DRAMA
Drama is the imitation of human action presented by performers on stage to an audience. It is the penetration of life through artificial means. In drama real-life people pretend to be imagined people; thus imitating what people do in real life. It is the only genre of literature that can be acted on stage.

TYPES OF DRAMA

1. Tragedy: This is a form of drama that has a sad ending, a hero who could be admired by audience because of his qualities and achievements could just fall suddenly as a result of his tragic flaw or hubris. Such fall may even lead to his death. The Gods Are Not To Blame by Ola Rotimi and Macbeth by William Shakespeare are good examples.
2. Comedy: This is a form of drama that aims primarily at amusing the audience and it has a happy ending.
3. Melodrama: This is a romantic play characterized by music and exciting events with exaggerated characters.
4. Tragic-Comedy: This is a form of drama that employs a plot suitable to tragedy, it has a serious beginning, but finally ends happily like comedy. D.O. Odigie’s Verdict of the Gods is a good example, Merchant of Venice by Shakespeare is also a good example.
5. Satire: This is a kind of drama that uses elements of comedy such as wit, irony, and exaggeration to criticize and expose human and social vices. It ridicules the foolishness or wickedness of a particular practice, custom or a bad government. Its aim is to attack and expose specific in the society for a positive change.
6. Fable: This is a story with animals as characters used to teach moral. This is very common in African folktales. Animal Farm by George Orwell is the most popular fable written so far.
Assignment:
A. From a recommended text you read this term, identify five (5):
1. Themes
2. Characters
3. Figures of speech
B. Write a letter to your parents inviting them to your end of year party.
WEEK 6
ASPECT : COMPREHENSION .
TOPIC-THE LION AND THE JEWEL
CONTENT: The passage, an extract from Wole Soyinka’s famous play start with a scene on the edge of a market in a village .Sidi is a traditional village maiden who has gone to fetch water. She is met by Lakunle,the village school teacher,who aspire to western ways. He tries to carry a bucket (pail) of water,but sidi refuse to let him do so. Read the details on page 124 of junior English project Bk 3.

EVALUATION : Junior English Project unit 13 page 126
ASSIGNMENT: Summary and discussion on the drama extract ( THE LION AND THE JEWEL )junior English project unit 13 page 127.
Watch Video of The Lion & the Jewel
[youtube]https://youtu.be/PUCN_Sw3q_w[/youtube]
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT.
TOPIC : WORDS ASSOCIATED WITH MORAL APPRAISAL
CONTENT :An appraisal is a judgement of the value,performance or nature of somebody or something. A moral appraisal are such words that are used to describe somebody’s values, nature or performance. Examples of such words can be ; generous, faithful, callous as in the sentences below;
(a) Mr. Ojo’s efforts were so helpful in the arrangements of the event.
(b) The boy’s action was callous against the poor old woman.
(c) We have a generous grandmother.
(d) Bingo is such a faithful guide dog.
(e) He is a liberal neighbor.
Other words that can be used to appraise include: careless, loving, careful, diligent, hardworking, liberal etc
EVALUATION:
Make sentences with the under listed words of appraisal:
(a) Naughty
(b) Kind
(c) Dutiful
(d) Cunning
(e) Honest
(f) Proud
(g) Polite
(h) Careful
(i) Selfwilled
(j) Sluggish
ASPECT : STRUCTURE
TOPIC : REFLEXIVE AND RELATIVE PRONOUNS

CONTENT : Reflexive pronouns are such pronouns that shows that the action of a noun or pronoun, affects the person who performs it. They are commonly used as objects when the action mentioned in a sentence is reflected or thrown back on the subject i.e. the performer or doer of the action. These kinds of pronouns end with the word ‘ self ‘ in the singular and ‘selves’ in the plural. There are three kinds of reflexive pronouns.They are:
1st person –myself/ourselves
2nd person-yourself/yourselves
3rd person-himself/herself and themselves
Examples (a) He cut Himself with a knife.
(b) They bought themselves some packs of peanuts.
(c) We taught ourselves to swim.
(d) The kitten found itself in the barn.
(e) She made herself happy with a song.
RELATIVE PRONOUN
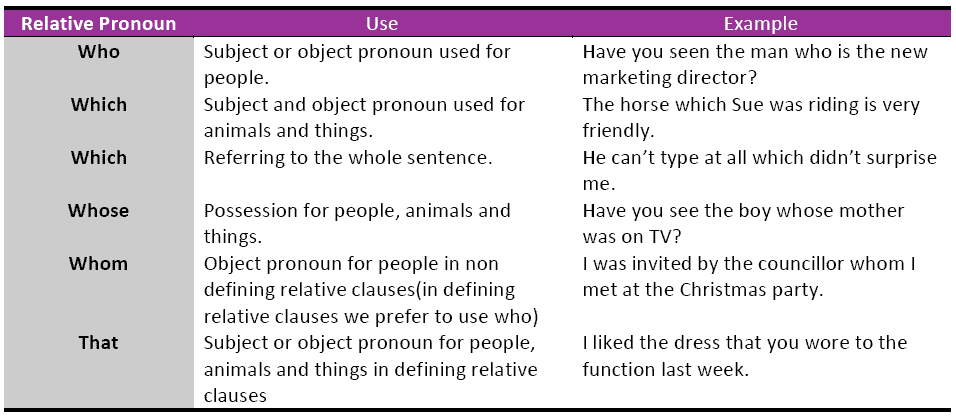
These are words used to combine or relate sentences or clauses together. Relative pronouns are often used at the beginning of a relative clause and include words like: which, whom, whose, what, why, when, where, but and that. As we have in the examples below:
(i) The girl whose father died in the accident is my classmate.
(ii) The man who cheated you is my cousin.
(iii) He came with the woman whom he had worked with for two years.
(iv) She was the student that was nominated for the post.
(v) He is the young man that I spoke to you about earlier.
EVALUATION
(a) What is a relative pronoun?
(b) Make five sentences using the following relative pronouns
(i) Why
(ii) Whom
(iii) Which
(iv) Who
(v) When
ASSIGNMENT- Fill in the blank spaces below with reflexive pronouns
(i) Father cut ............... when he was shaving.
(ii) Mary saw .............. in the mirror.
(iii) I taught ................ to play piano.
(iv) We saw ............... in the mirror.
(v) The kitten tried to biteme, but bit ..........accidentally.
(vi) One can easily miss .............. step on the staircase.
(vii) We injured ......... while playing football.
(viii) If you would like some cake, children, help .........
(ix) Heaven help those who help ...........
(x) There are plenty of peanuts for you here, please help ...............
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
ASPECT: COMPOSITION.
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY ESSAY.
CONTENT: WHY STUDENTS FAIL EXAMINATION.
Expository essays are such essays that rather than describe people like descriptive essay does, describes how something is done, how something works and how something is planned or organized and how something is made. Example of such essay topics can be : Describe how the game you like best is played or how your favourite meal is prepared.
The content of such an essay is determined by the various aspects to the topic on which it is written. For example if you are asked to write an expository essay on how your favourite meal is prepared, you should try to identify the various steps in the preparation of the meal such as :
----- Getting the required ingredient
....... Preparing the ingredient
....... Cooking the meal and getting it ready for eating.
Each of these stages, beginning with the first of them is described in each paragraph of the essay.
To write an essay on why students fail examinations therefore, efforts should be made to identify and discuss on some of these factors that can contribute to the problem.
(i) Lack of desired goal .
(ii) Wrong choice of subjects.
(iii) Hatred for subjects and subject teachers.
(iv) Poor study habit .
(v) Lateness and absenteeism.
(vi) Playfulness.
(vii) Laziness and and lack of confidence.
(viii) Procrastination.
(ix) Poor self concept.
(x) Reliance on ‘Expo’ during examination
EVALUATION: What is an expository essay?.
ASSIGNMENT: In not less than 250 words, write an expository essay on: Why Students Fail Examinations.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK.
TOPIC: VOWEL /a:/ and /3:/
CONTENT:
VOWEL /a:/
The vowel above is one of the long vowels and can be described as a back vowel though it is actually articulated with the part of the tongue between the centre and the back. In the process of articulation, while the lips are in neutral position, the jaw is fully open. The vowel is pronounced as aah- aah –aah—aah in speech sound. The vowel /a:/ is represented in words by the following letters:
LETTERS WORDS
ar ----- as in part, mark, dark and bark.
ar ------- as in clerk ,Berkshire
e ------ as in genre
ear ---- as in heart
our ------ as in our
a ----- as in path, vase, grasp guava.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/uDHMuMQdBNw?list=PLD6B222E02447DC07[/youtube]
THE VOWEL /3:/
This central vowel is often spelt ‘er’. It is pronounced with the middle of the tongue raised while the lip position is neutral. It is pronounced in words like ‘arr’ as in (r) and can be sounded in the following words:
LETTERS WORDS
Our --------as in journey, tournament, scourge.
Ir---------- as in First, third, girl skirt and firm.
Ur-------- as in burn, church, fur, incur and turn.
Or---------- as in work , worse, worst and word.
Er ------------ as in her, fertile and servant.
Eu------------ as in milieu.
Ear------------ as in earth, search and earn.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/zSJJWHymEPw?list=PLD6B222E02447DC07[/youtube]
EVALUATION: Give five examples of each of these phonetic symbols:
I. /æ/
II. /a/
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: LITERARY APPRECIATION
CONTENT: Reading and appreciation of literary text (prose)
EVALUATION:
Students are to bring out literary devices identified from chapters read in school class discussion and teacher’s evaluation.
TOPIC-THE LION AND THE JEWEL
CONTENT: The passage, an extract from Wole Soyinka’s famous play start with a scene on the edge of a market in a village .Sidi is a traditional village maiden who has gone to fetch water. She is met by Lakunle,the village school teacher,who aspire to western ways. He tries to carry a bucket (pail) of water,but sidi refuse to let him do so. Read the details on page 124 of junior English project Bk 3.

EVALUATION : Junior English Project unit 13 page 126
ASSIGNMENT: Summary and discussion on the drama extract ( THE LION AND THE JEWEL )junior English project unit 13 page 127.
Watch Video of The Lion & the Jewel
[youtube]https://youtu.be/PUCN_Sw3q_w[/youtube]
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT.
TOPIC : WORDS ASSOCIATED WITH MORAL APPRAISAL
CONTENT :An appraisal is a judgement of the value,performance or nature of somebody or something. A moral appraisal are such words that are used to describe somebody’s values, nature or performance. Examples of such words can be ; generous, faithful, callous as in the sentences below;
(a) Mr. Ojo’s efforts were so helpful in the arrangements of the event.
(b) The boy’s action was callous against the poor old woman.
(c) We have a generous grandmother.
(d) Bingo is such a faithful guide dog.
(e) He is a liberal neighbor.
Other words that can be used to appraise include: careless, loving, careful, diligent, hardworking, liberal etc
EVALUATION:
Make sentences with the under listed words of appraisal:
(a) Naughty
(b) Kind
(c) Dutiful
(d) Cunning
(e) Honest
(f) Proud
(g) Polite
(h) Careful
(i) Selfwilled
(j) Sluggish
ASPECT : STRUCTURE
TOPIC : REFLEXIVE AND RELATIVE PRONOUNS

CONTENT : Reflexive pronouns are such pronouns that shows that the action of a noun or pronoun, affects the person who performs it. They are commonly used as objects when the action mentioned in a sentence is reflected or thrown back on the subject i.e. the performer or doer of the action. These kinds of pronouns end with the word ‘ self ‘ in the singular and ‘selves’ in the plural. There are three kinds of reflexive pronouns.They are:
1st person –myself/ourselves
2nd person-yourself/yourselves
3rd person-himself/herself and themselves
Examples (a) He cut Himself with a knife.
(b) They bought themselves some packs of peanuts.
(c) We taught ourselves to swim.
(d) The kitten found itself in the barn.
(e) She made herself happy with a song.
RELATIVE PRONOUN

These are words used to combine or relate sentences or clauses together. Relative pronouns are often used at the beginning of a relative clause and include words like: which, whom, whose, what, why, when, where, but and that. As we have in the examples below:
(i) The girl whose father died in the accident is my classmate.
(ii) The man who cheated you is my cousin.
(iii) He came with the woman whom he had worked with for two years.
(iv) She was the student that was nominated for the post.
(v) He is the young man that I spoke to you about earlier.
EVALUATION
(a) What is a relative pronoun?
(b) Make five sentences using the following relative pronouns
(i) Why
(ii) Whom
(iii) Which
(iv) Who
(v) When
ASSIGNMENT- Fill in the blank spaces below with reflexive pronouns
(i) Father cut ............... when he was shaving.
(ii) Mary saw .............. in the mirror.
(iii) I taught ................ to play piano.
(iv) We saw ............... in the mirror.
(v) The kitten tried to biteme, but bit ..........accidentally.
(vi) One can easily miss .............. step on the staircase.
(vii) We injured ......... while playing football.
(viii) If you would like some cake, children, help .........
(ix) Heaven help those who help ...........
(x) There are plenty of peanuts for you here, please help ...............
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
ASPECT: COMPOSITION.
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY ESSAY.
CONTENT: WHY STUDENTS FAIL EXAMINATION.
Expository essays are such essays that rather than describe people like descriptive essay does, describes how something is done, how something works and how something is planned or organized and how something is made. Example of such essay topics can be : Describe how the game you like best is played or how your favourite meal is prepared.
The content of such an essay is determined by the various aspects to the topic on which it is written. For example if you are asked to write an expository essay on how your favourite meal is prepared, you should try to identify the various steps in the preparation of the meal such as :
----- Getting the required ingredient
....... Preparing the ingredient
....... Cooking the meal and getting it ready for eating.
Each of these stages, beginning with the first of them is described in each paragraph of the essay.
To write an essay on why students fail examinations therefore, efforts should be made to identify and discuss on some of these factors that can contribute to the problem.
(i) Lack of desired goal .
(ii) Wrong choice of subjects.
(iii) Hatred for subjects and subject teachers.
(iv) Poor study habit .
(v) Lateness and absenteeism.
(vi) Playfulness.
(vii) Laziness and and lack of confidence.
(viii) Procrastination.
(ix) Poor self concept.
(x) Reliance on ‘Expo’ during examination
EVALUATION: What is an expository essay?.
ASSIGNMENT: In not less than 250 words, write an expository essay on: Why Students Fail Examinations.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK.
TOPIC: VOWEL /a:/ and /3:/
CONTENT:
VOWEL /a:/
The vowel above is one of the long vowels and can be described as a back vowel though it is actually articulated with the part of the tongue between the centre and the back. In the process of articulation, while the lips are in neutral position, the jaw is fully open. The vowel is pronounced as aah- aah –aah—aah in speech sound. The vowel /a:/ is represented in words by the following letters:
LETTERS WORDS
ar ----- as in part, mark, dark and bark.
ar ------- as in clerk ,Berkshire
e ------ as in genre
ear ---- as in heart
our ------ as in our
a ----- as in path, vase, grasp guava.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/uDHMuMQdBNw?list=PLD6B222E02447DC07[/youtube]
THE VOWEL /3:/
This central vowel is often spelt ‘er’. It is pronounced with the middle of the tongue raised while the lip position is neutral. It is pronounced in words like ‘arr’ as in (r) and can be sounded in the following words:
LETTERS WORDS
Our --------as in journey, tournament, scourge.
Ir---------- as in First, third, girl skirt and firm.
Ur-------- as in burn, church, fur, incur and turn.
Or---------- as in work , worse, worst and word.
Er ------------ as in her, fertile and servant.
Eu------------ as in milieu.
Ear------------ as in earth, search and earn.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/zSJJWHymEPw?list=PLD6B222E02447DC07[/youtube]
EVALUATION: Give five examples of each of these phonetic symbols:
I. /æ/
II. /a/
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: LITERARY APPRECIATION
CONTENT: Reading and appreciation of literary text (prose)
EVALUATION:
Students are to bring out literary devices identified from chapters read in school class discussion and teacher’s evaluation.
WEEK 7
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION .
TOPIC: MY EXPERIENCE IN CALIFONIA
CONTENT: Dr. Mohammed Garba has just returned to Nigeria after a two year stay in California. The school principal had invited him to give a talk about his experiences. Read the passage properly to enable you give appropriate answers to the questions that follow.
EVALUATION: JEP. Unit 14, page 139, Exercise 3c Factual questions
ASSIGNMENT: JEP Unit 14, page 139, Exercise 4 Summary questions.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/PcsT4ZtUCuc[/youtube]
Watch the Video above and write out what can pick from the tour.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: SYNONYMS

CONTENT: Synonyms are words that have the same meaning or are close in meaning and still be saying basically the same thing as a given word. Example, The word ‘holy’. The words similar in meaning to the word ‘holy’ are words like: pious, religious, godly, God fearing, saintly. Other words synonymous to holy include: consecrate, hallowed, sanctified, blessed, divine, sacred, saintly, righteous, devote, virtuous and religious
EVALUATION: Make 10 sentences with the words: Sacred, consecrate, divine, blessed, saintly, hallowed, pious, godly, holy and sanctified.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: INDEFINITE AND RECIPROCAL PRONOUNS.
CONTENT:
Indefinite pronouns are such pronouns that are not specific or exact about what they are used to refer to, or about the quality or number of what they are used to describe. The following are some examples of indefinite pronouns.
1. Many came for the party.
2. Few were there in the morning.
3. I bought some.
4. You can take any.
5. Both are missing .
6. I have left all in the room.
7. Each has a different view.

These pronouns are used when an action is reciprocated or shared. When an action is shared by just two people or between two things such pronouns used are referred to as reciprocal pronouns. Examples of these pronouns are reflected in the sentences below:
1. James and Joseph spoke to each other regularly on the phone.
2. The dog and the cat do not like each other.
3. The boys pulled each other in the ear.
4. The girl and her mother smiled at each other
5. The man and his wife love each other.
Note that when the action is shared between just two people then it is appropriate to use“each other” as the reciprocal pronoun. But when the action involves more than two people as we have in the examples below, then it is most appropriate to use ‘one another’: Examples are:
1. The students brought presents for one another.
2. The sheep, the goat and the dog often play with one another.
3. The students often laugh at one another’s mistakes
4. The passengers in the train exchanged pleasantries with one another.
5. The mothers helped one another to carry their babies and baskets
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
ASPECT: COMPOSITION.
TOPIC: MY SCHOOLS’ INTER-HOUSE SPORTS.

CONTENT: The topic above is aimed at describing the events of a schools’ inter-house competition. It is an example of a descriptive essay.
A descriptive essay is an essay written to give the reader a mental picture of either a person, a place or an object like in other essay types. A descriptive essay should contain paragraphs where each of the major aspects of the topic is vividly explained for a good understanding by any reader.
My school Inter-house sports therefore should highlight on points like:
1. The date of the inter -house sports competition.
2. The venue of the inter-house sports competition.
3. The various events featured in the sports competition.
4. Participating houses or clubs and schools in various events .
5. The officials and officers of the events groups.
6. The overall winner in the events.
EVALUATION: Explain what is meant by an’ inter house sports’
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: VOWELS \ ↄ \, \ ↄ:\ and \ ᴧ \
CONTENT: The vowel \ ↄ \ and \ ↄ: \ sounds are produced with the back of the tongue. In making these sounds, the lips form an ‘O’ shape and the tongue is raised as if tensed up to a level. The place and manner of articulation of the two sounds are the same. The only difference between the sounds\ↄ:\ and \ ↄ \ is that the \ ↄ: \ sound is long while the \ ↄ \ sound is short. The sounds are found in words like
\ ↄ\ \ ↄ: \
1. Off ore
2. Pot Paul
3. Spot sport
4. Cod cord
5. Moth mourn
6. Fox fork
7. Dog darn
8. Not naught
9. Cough caught
[youtube]https://youtu.be/MAk-XtHsyzM?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
[youtube]https://youtu.be/35rzq87Ck3M[/youtube]
EVALUATION: Write out the vowel sounds in the words listed below:
1. Tore
2. Fault
3. Court
4. Ought
5. Dwart
6. Bald
7. Force
8. Crawl
9. Wherewithal
10. Thwart
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: Literary Appreciation in poetry
CONTENT: Use Recommended Text
EVALUATION: Bringing out some literary devices in the poems read.
ASSIGNMENT: Your school had recently had her inter –house sports competition, write to your friend in another school, describing vividly some remarkable events in the sports programme.
TOPIC: MY EXPERIENCE IN CALIFONIA
CONTENT: Dr. Mohammed Garba has just returned to Nigeria after a two year stay in California. The school principal had invited him to give a talk about his experiences. Read the passage properly to enable you give appropriate answers to the questions that follow.
EVALUATION: JEP. Unit 14, page 139, Exercise 3c Factual questions
ASSIGNMENT: JEP Unit 14, page 139, Exercise 4 Summary questions.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/PcsT4ZtUCuc[/youtube]
Watch the Video above and write out what can pick from the tour.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: SYNONYMS

CONTENT: Synonyms are words that have the same meaning or are close in meaning and still be saying basically the same thing as a given word. Example, The word ‘holy’. The words similar in meaning to the word ‘holy’ are words like: pious, religious, godly, God fearing, saintly. Other words synonymous to holy include: consecrate, hallowed, sanctified, blessed, divine, sacred, saintly, righteous, devote, virtuous and religious
EVALUATION: Make 10 sentences with the words: Sacred, consecrate, divine, blessed, saintly, hallowed, pious, godly, holy and sanctified.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: INDEFINITE AND RECIPROCAL PRONOUNS.
CONTENT:
Indefinite pronouns are such pronouns that are not specific or exact about what they are used to refer to, or about the quality or number of what they are used to describe. The following are some examples of indefinite pronouns.
1. Many came for the party.
2. Few were there in the morning.
3. I bought some.
4. You can take any.
5. Both are missing .
6. I have left all in the room.
7. Each has a different view.

These pronouns are used when an action is reciprocated or shared. When an action is shared by just two people or between two things such pronouns used are referred to as reciprocal pronouns. Examples of these pronouns are reflected in the sentences below:
1. James and Joseph spoke to each other regularly on the phone.
2. The dog and the cat do not like each other.
3. The boys pulled each other in the ear.
4. The girl and her mother smiled at each other
5. The man and his wife love each other.
Note that when the action is shared between just two people then it is appropriate to use“each other” as the reciprocal pronoun. But when the action involves more than two people as we have in the examples below, then it is most appropriate to use ‘one another’: Examples are:
1. The students brought presents for one another.
2. The sheep, the goat and the dog often play with one another.
3. The students often laugh at one another’s mistakes
4. The passengers in the train exchanged pleasantries with one another.
5. The mothers helped one another to carry their babies and baskets
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
ASPECT: COMPOSITION.
TOPIC: MY SCHOOLS’ INTER-HOUSE SPORTS.

CONTENT: The topic above is aimed at describing the events of a schools’ inter-house competition. It is an example of a descriptive essay.
A descriptive essay is an essay written to give the reader a mental picture of either a person, a place or an object like in other essay types. A descriptive essay should contain paragraphs where each of the major aspects of the topic is vividly explained for a good understanding by any reader.
My school Inter-house sports therefore should highlight on points like:
1. The date of the inter -house sports competition.
2. The venue of the inter-house sports competition.
3. The various events featured in the sports competition.
4. Participating houses or clubs and schools in various events .
5. The officials and officers of the events groups.
6. The overall winner in the events.
EVALUATION: Explain what is meant by an’ inter house sports’
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: VOWELS \ ↄ \, \ ↄ:\ and \ ᴧ \
CONTENT: The vowel \ ↄ \ and \ ↄ: \ sounds are produced with the back of the tongue. In making these sounds, the lips form an ‘O’ shape and the tongue is raised as if tensed up to a level. The place and manner of articulation of the two sounds are the same. The only difference between the sounds\ↄ:\ and \ ↄ \ is that the \ ↄ: \ sound is long while the \ ↄ \ sound is short. The sounds are found in words like
\ ↄ\ \ ↄ: \
1. Off ore
2. Pot Paul
3. Spot sport
4. Cod cord
5. Moth mourn
6. Fox fork
7. Dog darn
8. Not naught
9. Cough caught
[youtube]https://youtu.be/MAk-XtHsyzM?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
[youtube]https://youtu.be/35rzq87Ck3M[/youtube]
EVALUATION: Write out the vowel sounds in the words listed below:
1. Tore
2. Fault
3. Court
4. Ought
5. Dwart
6. Bald
7. Force
8. Crawl
9. Wherewithal
10. Thwart
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: Literary Appreciation in poetry
CONTENT: Use Recommended Text
EVALUATION: Bringing out some literary devices in the poems read.
ASSIGNMENT: Your school had recently had her inter –house sports competition, write to your friend in another school, describing vividly some remarkable events in the sports programme.
WEEK 8
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: MALNUTRITION

CONTENT:
Very often in our studies, we do not have time to study closely everything we should like to do. It often happens that there is only time to read through a chapter or a section of a textbook very quickly. During this quick read, we try to pick out the main points, or gist of what we read. Now read the passage properly, and answer the questions at the end.
EVALUATION: Answer the comprehension questions on page 149- 150 EXERCISE 15 OF JEP BOOK 3.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: SYNONYMS
CONTENT: Words similar in meaning and content to active. Active is a word meaning always doing things or moving around a lot. Active like every other word has a number of words sharing its meaning. Some of the examples are listed below:
Active: Lively ------- He is such a lively baby.
Dynamic -------- Our math’s educator is so dynamic.
On the go ------- The house masters are always on the go.
Full of life ------- The club members are full of life.
Enthusiastic ------ the whole clan is enthusiastic.
Other related words to active include: vigorous, functioning, effective, in action, involved, practicing working.
EVALUATION: Make sentences with the following words; Effective, Involved, On the go, Practicing,, Committed, Vigorous, Energetic, Agile, and Quick.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: VOWELS \U\, and \U:\
CONTENT: The vowels \U\ and \U:\ are articulated with the back of the tongue raised to a height just below the position where the side of the tongue touches the back of the teeth. In making the sounds, the lips are pushed out and form a round shape. The lips come together, but do not fully meet. The \U\ sound is a short sound while the \U:\ is a long sound. Below are a list of words that has the short \u\ and the long \U\ sounds respectively.
\U\ \U:\
1. Foot hoot
2. Took tool
3. Pull pool
4. Full fool
5. Wood would
6. Should shoot
7. Foot food
8. Wood wooed
[youtube]https://youtu.be/eJ7dM_LU9t4?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
[youtube]https://youtu.be/TBp_5yKC2OA?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
The various spelling of the sounds are listed as:
1. “O”------------------------ as in do.
2. “OO”--------------------- as in spoon.
3. “cw”============== as in chew.
4. “ eau”============= as in beauty.
5. “u--------------------------” as in rule.
6. “ue================ as in true.
7. “ui”------------------------- as in fruit.
8. “iew----------------------” as in view.
9. “oe”---------------------- as in shoe.
10. “ou”----------------------- as in you.
EVALUATION: Write out the spelling sounds in the under listed words:
1. Tomb
2. Canoe
3. Troop
4. Loose
5. Rude
6. Ruler
7. Juice
8. Glue
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: Drama
CONTENT: Reading and analyzing of recommended drama text
EVALUATION:( Discuss) What roles do drama play in the development of a peaceful civil society.
ASSIGNMENT: Using your note, write a summary of this passage in not more than 100 words. (page 149- 150 EXERCISE 15 OF JEP BOOK 3).
TOPIC: MALNUTRITION

CONTENT:
Very often in our studies, we do not have time to study closely everything we should like to do. It often happens that there is only time to read through a chapter or a section of a textbook very quickly. During this quick read, we try to pick out the main points, or gist of what we read. Now read the passage properly, and answer the questions at the end.
EVALUATION: Answer the comprehension questions on page 149- 150 EXERCISE 15 OF JEP BOOK 3.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: SYNONYMS
CONTENT: Words similar in meaning and content to active. Active is a word meaning always doing things or moving around a lot. Active like every other word has a number of words sharing its meaning. Some of the examples are listed below:
Active: Lively ------- He is such a lively baby.
Dynamic -------- Our math’s educator is so dynamic.
On the go ------- The house masters are always on the go.
Full of life ------- The club members are full of life.
Enthusiastic ------ the whole clan is enthusiastic.
Other related words to active include: vigorous, functioning, effective, in action, involved, practicing working.
EVALUATION: Make sentences with the following words; Effective, Involved, On the go, Practicing,, Committed, Vigorous, Energetic, Agile, and Quick.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: VOWELS \U\, and \U:\
CONTENT: The vowels \U\ and \U:\ are articulated with the back of the tongue raised to a height just below the position where the side of the tongue touches the back of the teeth. In making the sounds, the lips are pushed out and form a round shape. The lips come together, but do not fully meet. The \U\ sound is a short sound while the \U:\ is a long sound. Below are a list of words that has the short \u\ and the long \U\ sounds respectively.
\U\ \U:\
1. Foot hoot
2. Took tool
3. Pull pool
4. Full fool
5. Wood would
6. Should shoot
7. Foot food
8. Wood wooed
[youtube]https://youtu.be/eJ7dM_LU9t4?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
[youtube]https://youtu.be/TBp_5yKC2OA?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
The various spelling of the sounds are listed as:
1. “O”------------------------ as in do.
2. “OO”--------------------- as in spoon.
3. “cw”============== as in chew.
4. “ eau”============= as in beauty.
5. “u--------------------------” as in rule.
6. “ue================ as in true.
7. “ui”------------------------- as in fruit.
8. “iew----------------------” as in view.
9. “oe”---------------------- as in shoe.
10. “ou”----------------------- as in you.
EVALUATION: Write out the spelling sounds in the under listed words:
1. Tomb
2. Canoe
3. Troop
4. Loose
5. Rude
6. Ruler
7. Juice
8. Glue
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: Drama
CONTENT: Reading and analyzing of recommended drama text
EVALUATION:( Discuss) What roles do drama play in the development of a peaceful civil society.
ASSIGNMENT: Using your note, write a summary of this passage in not more than 100 words. (page 149- 150 EXERCISE 15 OF JEP BOOK 3).
WEEK 9
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION.
TOPIC: CONFLICT RESOLUTION.

CONTENT: Conflicts exist in every walks of life and there are ways of meditating between opposing parts. Find out the various reasons for conflicts and means of resolving them in the passage as you read the text carefully and answer the questions that follow.
EVALUATION: JEP Book 3 Unit 16 Section 2 Page 159.
ASSIGNMENT: JEP Book 3 Unit 16 Section 4 Page 160 Critical Reading.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT.
TOPIC: SYNONYNMS
CONTENT: Words similar in meaning and context to callous; meaning, not caring about other people’s feelings or suffering. Other words synonymous to callous are: cruel, unfeeling, heartless, uncaring, insensitive, unsympathetic, cold, pitiless, hard, thick-skinned, and cold-hearted. For example:-
i. The soldiers were unsympathetic on the invaders.
ii. The Kidnappers were heartless against the poor widow.
iii. The armed robbers acted without feeling on their poor victims.
iv. He is such a hard man.
v. They were so uncaring about the man’s plight.
EVALUATION: Make sentences with the following words: Cruel, Pitiless, thick-skinned, unfeeling, cold-hearted.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: ACTIVE VOICE

CONTENT: A verb is said to be in the active voice, when the action described in the sentence is being performed by the subject. For example in the sentences below:
i. The Policemen stopped the man.
ii. The boy stole the car.
iii. She sang a beautiful song.
iv. Harmattan kills flowers.
v. He married a fat woman.
vi. Ghananians grow cocoa.
vii. My Aunt sells cloth.
viii. The boys killed the ball.
ix. The teacher taught the class.
x. The boys ate all the mangoes.
When the subject of the sentence is the doer of the action, we say the verb is in the active voice but when the subject of the sentence is the receiver of the action, we say the verb is in the passive voice.
EVALUATION:
Change the following sentences from passive voice to active voice.
i. The car was repaired by the Mechanic.
ii. The book was taken by Miss Biba.
iii. The dinner was cooked by Mrs. Glory.
iv. The letters were delivered by the Postman.
v. The windows were broken by Usher.
vi. The poems were learned by Mary.
vii. The nest was built by a bird.
viii. The ring was stolen by the thief.
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY WRITING
CONTENT: - Expository essays or writings are written in careful and formal language, the type used in formal letters. Such letters does not tolerate the use of shortened forms or slangs. It should be noted that the verb forms used in expository essays are in the present tense form as in descriptive essays.
A MODEL EXPOSITORY ESSAY: THE GAME I LIKE BEST
The game I like best is Football. It is also known as Soccer. It is played between two teams of eleven players each. The game is controlled by the Referee. He is assisted by the Linesman.
Football game is played with football which is a large ball filled with air. It is played on a rectangular area of grass with the edge and parts clearly marked out in white. This area is called the field. On each side of the short side of the field is the goal area. A goal post is made of two upright posts connected at the top with a crossbar. The goal is where each of the team tries to get the ball in order to score a point.
At the beginning of the game, a team occupies one half of the field and faces the other team. There is a goal post behind each team. One player at the team usually stays at the entrance of its goal during the game. His special l duty is to try to prevent the other team from scoring when the Referee blows his whistle to start off the game. All the other players kick or head the ball towards the opponent’s goal. When a point is scored, the Referee blows the whistle, and starts off the game afresh. He also blows the whistle when an infringement of the rules is committed, and metes out the appropriate punishment. Finally he blows the whistle to end the game. And the winner is the team with the highest number of goals.
Note: The paragraphs are organized around the major aspects of the game.
Paragraph 1. The players and officials
2. The Equipment and Facilities needed for the game.
3. The game itself.
Also note the use of present tense verb forms throughout.
EVALUATION; Describe the preparation of your favorite meals.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write a story about two school friends who had a quarrel. Describe what happened, and how the problem was resolved.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: VOWELS /æ/
CONTENT: The vowel /æ/ is articulated with by the front part of the tongue slightly raised to a height above the open position while the lips are spread. The spelling symbols of the word “a’ as in hat,’ ai’ as in the word plait.
Other words where the vowel sounds are found are: bat, than, fail, lag, shall, man, and pen. Evaluation: Make a comparison between the sound (e) as we have in the word (e)bet, then fed all the sound /æ/ as we have in cat, man, can, and pan.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/qVhaIHk88a8?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: FEATURE OF A PLAY
CONTENT: A Play has the following features:

The Speaker’s name is printed in capital letters at the beginning of their speech with a colon following the name.
A play may also contain stage directions e.g. (takes her hands). These also appear in Italics and in brackets.
The setting of play may also change from time to time. For example the scene takes place in the morning, in the clearing of the edge of the market. They are put in brackets and italics.
The costumes can be very important for example, Soyinka suggests that Lakunle dressed in old English suit- whereas, Sidi is dressed in traditional clothing. Costumes tell us a lot about the characters.
Other important items, objects or equipment are called props for properties.
The performance features not just the words spoken by the actors but the singing and the dancing as well.
The director of the play decides how, where, the actors should stand and exactly how singing and dancing should be performed.
Sometimes the director may wish to encourage the audience to take part in singing and dancing – this is referred to as audience participation.
EVALUATION:
Read through your recommended text and identify some or all these features discussed above in them.
ASSIGNMENT:
Attempt the food puzzle on page 152 of JEP Exercise 1—17.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: SYNONYMS.
CONTENT: Law is a whole system of rules that everyone in a country or society must obey. Words synonymous to law in context are: rules, regulations, decree, legislature, act, ruling, commandment, direction, principle, directive, and bye-law. They are commonly used as in the examples below:
1. It is against the law to drink while driving.
2. The Presidency has issued a decree to stop Okada riding on the Nation’s highways.
3 .The Company’s regulation states that you pay your taxes before any service is rendered to you.
EVALUATION:
Make five sentences with some of the above written law synonyms.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE.
TOPIC: PASSIVE VOICE.
CONTENT:Unlike the active voice where the subject of a sentence is the doer of the action,the passive voice indicates that the subject of the sentence is the receiver of the action described in the given sentence.Below is a list of sentence showimg the active and the passive voice.
ACTIVE VOICE------------------------------------ PASSIVE VOICE.
(1 ) Margaret sang a song. A song was sung by Margaret.
( 2)The Policeman caught the thief. The thief was caught by the Policeman.
( 3 )Did you write this letter? Was the letter written by you?
(4)John answered the questions. The questions were answered by John.
(5 )The boys kicked the ball. The ball was kicked by the boys.
Please note that when the subject changes from singular to plural, then plural verbs are used to realise a correct tense in the sentence. Also note that the subject in the passive sentence is turned to be object in the active voice.
EVALUATION
Change the following statements from active into passive voice.
( A) The cat chased the rat.
(B) Mary hit the ball.
(C) The train was pulled by a powerful engine;
(D )The wind blew two big trees down
(E ) The gardener cleanned up the mess.
(F) Thieves stole his car last night.
(G) Rose has not swept the room yet.
(H) Nobody took the temperature of the boy.
(I) They boiled the yam for too long.
(J )Somebody else did that.
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY WRITING
CONTENT: PROPER STORY WRITING
In the examination, you may be given a choice of several topics. Our advice is that you choose a topic that is most familiar to you. Narrative or descriptive topics are easier. Normally you will be required to write not less than 200-250 words. We advise you to get use to writing within that constraint as examiners may ignore anything written exceeding the number of words allowed.
In writing an expository essay, planning and organization are very important. You are advised to follow these fives stages as they will be of great help:
Stage 1 PREPARATION
a—initial thinking or brainstorming
b---minor ideas
c---drawing up the plan
Stage 2 Rough Draft
Stage 3 Making Improvements
Stage 4 Final Draft
Stage 5 Check For Corrections
EVALUATION: Write a composition of not less than 200 words describing how your local community has developed over the past few years.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: DIPHTHONGS (A REVISION).
CONTENT: The word diphthongs is said to be a Greek word meaning double sound. Diphthongs are vowel sounds but differ from pure vowels because their articulation involves a glide from one vowel quality to the other.
There are eight diphthongs in English and their phonetic symbols indicate the initial and final vowels represented in the articulation. Below are a list of the eight English diphthongs:
/ei/: As in pay, again
/ǝu/: As in go, home
/ai/: As in rice, kite
/au/: As in cow, house
/ↄi/: As in toy voice
/iǝ/: As in ear, here
/eǝ/: As in air, hair
/Ʊe/: As in poor, tour
[youtube]https://youtu.be/d1HZPx8DuDw[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
Choose the word that contains the sounds indicated in the list below
(1) /ei/ (A) Fight (B) Feet (C) Fate (D) Hair (E) Niece
(2) /eə/ (A) Weather (B) Share (C) Here (D) Tyre (E) Afraid
(3) /ai/ (A) Sky (B) Play (C) Make (D) Veil (E) Pail
(4) /iə/ (A) Spare (B) Tired (C) Weather (D) Fear (E) Careful
(5) /ɔi/ (A) Closed (B) Fly (C) Story (D) Noise (E) Quiet
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH.
TOPIC: Reading of recommended text in poetry.
CONTENT: Using already learned literary devices to appreciate the poems.
EVALUATION: Answer relevant questions on the passage to ensure proper understanding of the poem read.
ASSIGNMENT: Write a composition of not less than 200 words describing how your local community has developed over the past few years.
TOPIC: CONFLICT RESOLUTION.

CONTENT: Conflicts exist in every walks of life and there are ways of meditating between opposing parts. Find out the various reasons for conflicts and means of resolving them in the passage as you read the text carefully and answer the questions that follow.
EVALUATION: JEP Book 3 Unit 16 Section 2 Page 159.
ASSIGNMENT: JEP Book 3 Unit 16 Section 4 Page 160 Critical Reading.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT.
TOPIC: SYNONYNMS
CONTENT: Words similar in meaning and context to callous; meaning, not caring about other people’s feelings or suffering. Other words synonymous to callous are: cruel, unfeeling, heartless, uncaring, insensitive, unsympathetic, cold, pitiless, hard, thick-skinned, and cold-hearted. For example:-
i. The soldiers were unsympathetic on the invaders.
ii. The Kidnappers were heartless against the poor widow.
iii. The armed robbers acted without feeling on their poor victims.
iv. He is such a hard man.
v. They were so uncaring about the man’s plight.
EVALUATION: Make sentences with the following words: Cruel, Pitiless, thick-skinned, unfeeling, cold-hearted.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE
TOPIC: ACTIVE VOICE

CONTENT: A verb is said to be in the active voice, when the action described in the sentence is being performed by the subject. For example in the sentences below:
i. The Policemen stopped the man.
ii. The boy stole the car.
iii. She sang a beautiful song.
iv. Harmattan kills flowers.
v. He married a fat woman.
vi. Ghananians grow cocoa.
vii. My Aunt sells cloth.
viii. The boys killed the ball.
ix. The teacher taught the class.
x. The boys ate all the mangoes.
When the subject of the sentence is the doer of the action, we say the verb is in the active voice but when the subject of the sentence is the receiver of the action, we say the verb is in the passive voice.
EVALUATION:
Change the following sentences from passive voice to active voice.
i. The car was repaired by the Mechanic.
ii. The book was taken by Miss Biba.
iii. The dinner was cooked by Mrs. Glory.
iv. The letters were delivered by the Postman.
v. The windows were broken by Usher.
vi. The poems were learned by Mary.
vii. The nest was built by a bird.
viii. The ring was stolen by the thief.
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY WRITING
CONTENT: - Expository essays or writings are written in careful and formal language, the type used in formal letters. Such letters does not tolerate the use of shortened forms or slangs. It should be noted that the verb forms used in expository essays are in the present tense form as in descriptive essays.
A MODEL EXPOSITORY ESSAY: THE GAME I LIKE BEST
The game I like best is Football. It is also known as Soccer. It is played between two teams of eleven players each. The game is controlled by the Referee. He is assisted by the Linesman.
Football game is played with football which is a large ball filled with air. It is played on a rectangular area of grass with the edge and parts clearly marked out in white. This area is called the field. On each side of the short side of the field is the goal area. A goal post is made of two upright posts connected at the top with a crossbar. The goal is where each of the team tries to get the ball in order to score a point.
At the beginning of the game, a team occupies one half of the field and faces the other team. There is a goal post behind each team. One player at the team usually stays at the entrance of its goal during the game. His special l duty is to try to prevent the other team from scoring when the Referee blows his whistle to start off the game. All the other players kick or head the ball towards the opponent’s goal. When a point is scored, the Referee blows the whistle, and starts off the game afresh. He also blows the whistle when an infringement of the rules is committed, and metes out the appropriate punishment. Finally he blows the whistle to end the game. And the winner is the team with the highest number of goals.
Note: The paragraphs are organized around the major aspects of the game.
Paragraph 1. The players and officials
2. The Equipment and Facilities needed for the game.
3. The game itself.
Also note the use of present tense verb forms throughout.
EVALUATION; Describe the preparation of your favorite meals.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write a story about two school friends who had a quarrel. Describe what happened, and how the problem was resolved.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: VOWELS /æ/
CONTENT: The vowel /æ/ is articulated with by the front part of the tongue slightly raised to a height above the open position while the lips are spread. The spelling symbols of the word “a’ as in hat,’ ai’ as in the word plait.
Other words where the vowel sounds are found are: bat, than, fail, lag, shall, man, and pen. Evaluation: Make a comparison between the sound (e) as we have in the word (e)bet, then fed all the sound /æ/ as we have in cat, man, can, and pan.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/qVhaIHk88a8?list=PL2BD50C329A9EADA6[/youtube]
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
TOPIC: FEATURE OF A PLAY
CONTENT: A Play has the following features:

The Speaker’s name is printed in capital letters at the beginning of their speech with a colon following the name.
A play may also contain stage directions e.g. (takes her hands). These also appear in Italics and in brackets.
The setting of play may also change from time to time. For example the scene takes place in the morning, in the clearing of the edge of the market. They are put in brackets and italics.
The costumes can be very important for example, Soyinka suggests that Lakunle dressed in old English suit- whereas, Sidi is dressed in traditional clothing. Costumes tell us a lot about the characters.
Other important items, objects or equipment are called props for properties.
The performance features not just the words spoken by the actors but the singing and the dancing as well.
The director of the play decides how, where, the actors should stand and exactly how singing and dancing should be performed.
Sometimes the director may wish to encourage the audience to take part in singing and dancing – this is referred to as audience participation.
EVALUATION:
Read through your recommended text and identify some or all these features discussed above in them.
ASSIGNMENT:
Attempt the food puzzle on page 152 of JEP Exercise 1—17.
ASPECT: VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: SYNONYMS.
CONTENT: Law is a whole system of rules that everyone in a country or society must obey. Words synonymous to law in context are: rules, regulations, decree, legislature, act, ruling, commandment, direction, principle, directive, and bye-law. They are commonly used as in the examples below:
1. It is against the law to drink while driving.
2. The Presidency has issued a decree to stop Okada riding on the Nation’s highways.
3 .The Company’s regulation states that you pay your taxes before any service is rendered to you.
EVALUATION:
Make five sentences with some of the above written law synonyms.
ASPECT: STRUCTURE.
TOPIC: PASSIVE VOICE.
CONTENT:Unlike the active voice where the subject of a sentence is the doer of the action,the passive voice indicates that the subject of the sentence is the receiver of the action described in the given sentence.Below is a list of sentence showimg the active and the passive voice.
ACTIVE VOICE------------------------------------ PASSIVE VOICE.
(1 ) Margaret sang a song. A song was sung by Margaret.
( 2)The Policeman caught the thief. The thief was caught by the Policeman.
( 3 )Did you write this letter? Was the letter written by you?
(4)John answered the questions. The questions were answered by John.
(5 )The boys kicked the ball. The ball was kicked by the boys.
Please note that when the subject changes from singular to plural, then plural verbs are used to realise a correct tense in the sentence. Also note that the subject in the passive sentence is turned to be object in the active voice.
EVALUATION
Change the following statements from active into passive voice.
( A) The cat chased the rat.
(B) Mary hit the ball.
(C) The train was pulled by a powerful engine;
(D )The wind blew two big trees down
(E ) The gardener cleanned up the mess.
(F) Thieves stole his car last night.
(G) Rose has not swept the room yet.
(H) Nobody took the temperature of the boy.
(I) They boiled the yam for too long.
(J )Somebody else did that.
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY WRITING
CONTENT: PROPER STORY WRITING
In the examination, you may be given a choice of several topics. Our advice is that you choose a topic that is most familiar to you. Narrative or descriptive topics are easier. Normally you will be required to write not less than 200-250 words. We advise you to get use to writing within that constraint as examiners may ignore anything written exceeding the number of words allowed.
In writing an expository essay, planning and organization are very important. You are advised to follow these fives stages as they will be of great help:
Stage 1 PREPARATION
a—initial thinking or brainstorming
b---minor ideas
c---drawing up the plan
Stage 2 Rough Draft
Stage 3 Making Improvements
Stage 4 Final Draft
Stage 5 Check For Corrections
EVALUATION: Write a composition of not less than 200 words describing how your local community has developed over the past few years.
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: DIPHTHONGS (A REVISION).
CONTENT: The word diphthongs is said to be a Greek word meaning double sound. Diphthongs are vowel sounds but differ from pure vowels because their articulation involves a glide from one vowel quality to the other.
There are eight diphthongs in English and their phonetic symbols indicate the initial and final vowels represented in the articulation. Below are a list of the eight English diphthongs:
/ei/: As in pay, again
/ǝu/: As in go, home
/ai/: As in rice, kite
/au/: As in cow, house
/ↄi/: As in toy voice
/iǝ/: As in ear, here
/eǝ/: As in air, hair
/Ʊe/: As in poor, tour
[youtube]https://youtu.be/d1HZPx8DuDw[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
Choose the word that contains the sounds indicated in the list below
(1) /ei/ (A) Fight (B) Feet (C) Fate (D) Hair (E) Niece
(2) /eə/ (A) Weather (B) Share (C) Here (D) Tyre (E) Afraid
(3) /ai/ (A) Sky (B) Play (C) Make (D) Veil (E) Pail
(4) /iə/ (A) Spare (B) Tired (C) Weather (D) Fear (E) Careful
(5) /ɔi/ (A) Closed (B) Fly (C) Story (D) Noise (E) Quiet
ASPECT: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH.
TOPIC: Reading of recommended text in poetry.
CONTENT: Using already learned literary devices to appreciate the poems.
EVALUATION: Answer relevant questions on the passage to ensure proper understanding of the poem read.
ASSIGNMENT: Write a composition of not less than 200 words describing how your local community has developed over the past few years.
