TOPIC: NON LIVING THINGS
CONTENT : 1. Examples of non living things; Classification of metals
non metals; Properties of metals and non metals
2. Uses and importance of non living matter
Sub-Topic 1: EXAMPLES OF NON-LIVING THINGS:
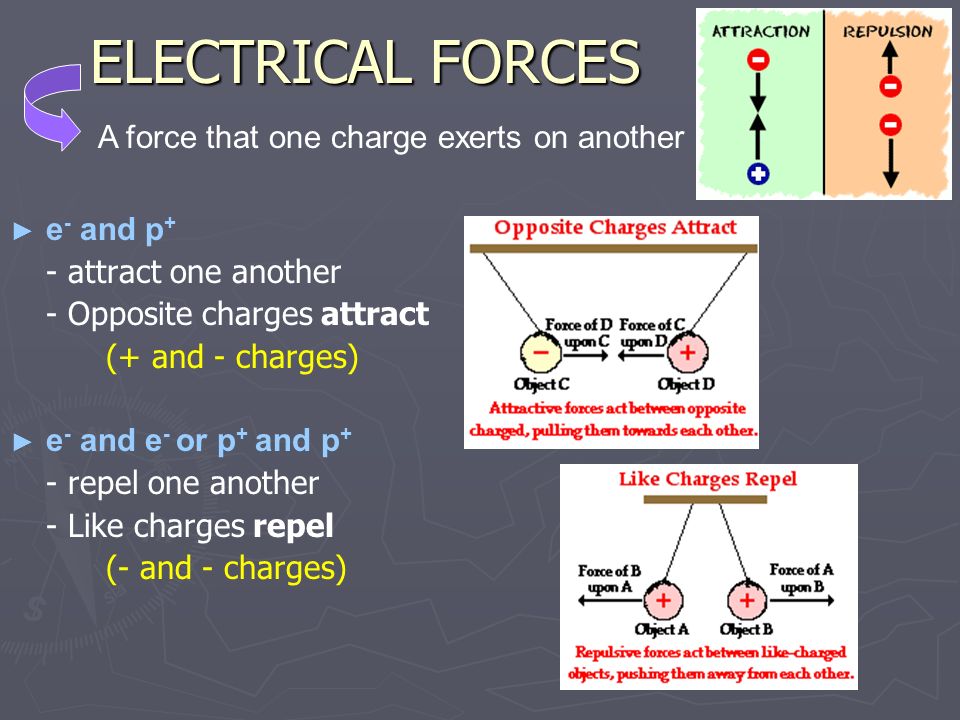
Matter is anything that has weight and occupies space. Matter can be classified into living and non-living things.
Examples of non-living things: many of them could be metals or non-metals.
Metals: examples are copper, iron rod, empty cans, aluminum

Non-metals: examples are plastic, paper, cloth, wood, rubber, sulphur, nitrogen, air, thread, carbon black and diamond.

Classification of metals and non-metals:
Metals has many characteristics which distinguish or differentiate them from non-metals
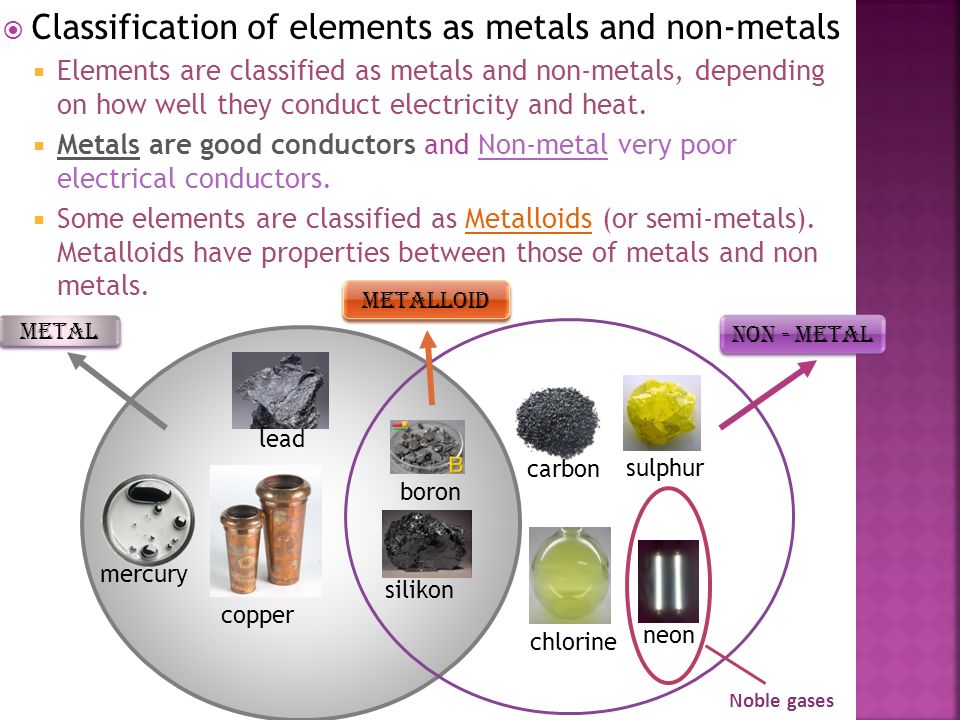
Classification\ properties of metals and non-metals
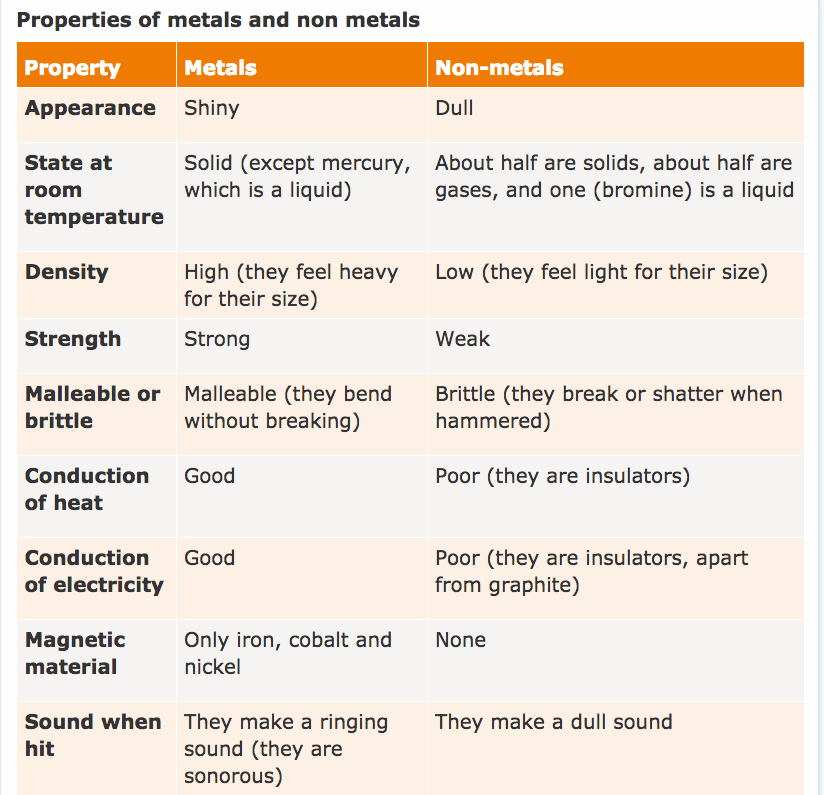
S/No Metals Non-metals
1. Metals are hard Non-metals are soft except diamond
2. Metals can be beaten or hammered into thin sheet i.e. they are malleable Non-metals cannot be hammered i.e. they are brittle
3. Metals are shiny and can be polished i.e. they have metallic lucre Non-metals are not shiny i.e. they have on metallic lucre
4. Metals can be drawn into wires i.e. they are ductile They cannot be drawn into wire
5. Metals are heavy in weight i.e. they have high density Non-metals are light i.e. they have low density
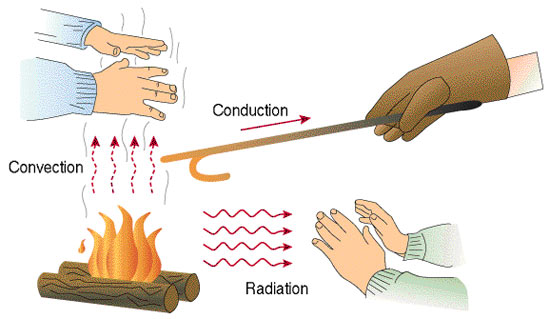
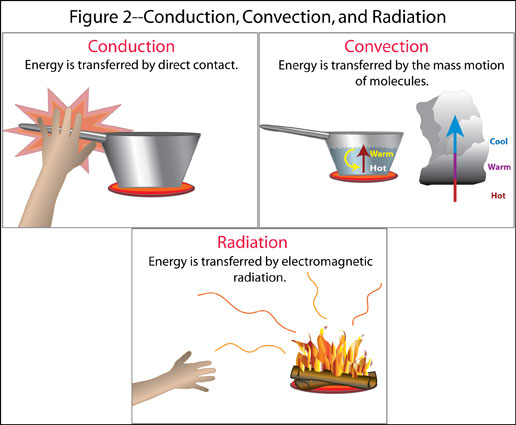
6. Metals are good conductors of heat Non-metals are poor conductors of heat.
7. Metals are good conductors of electricity Non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
8. Metals can rust Non-metals do not rust
9. Metals generally have a high melting point Non-metals have a lower melting point.
Evaluation:
1. Classify the following based on their physical appearance into metals non-metals. Iron, copper, diamond, wood, glass, zinc, carbon, sulphur, paper and Steel.
2. State five properties each of non-metals and metals
Sub-Topic 2: Uses of metals and non-metals
Uses of metals
1. Manufacture of motors vehicles and aero planes
2. For building houses, bridges and water tanks.
3. For construction of ships, roofing sheets and refrigerators.
4. Copper, iron, aluminum, silver, gold e.t.c. can be drawn into wire and used in production of cutleries (e.g. Spoons, Knives, Fork), machetes, hoes, diggers, ornaments (rings, bracelets).
5. For making cooking utensils.
Uses of non-metals
1. Roofing of houses e.g. asbestos, planks
2. Use as insulator for electrical appliances. Help to protect against shock e.g. handle of knife, screwdriver, and rubber for covering flexible wires.
3. For decoration of houses and buildings, furniture (e.g. tables, chairs) etc.
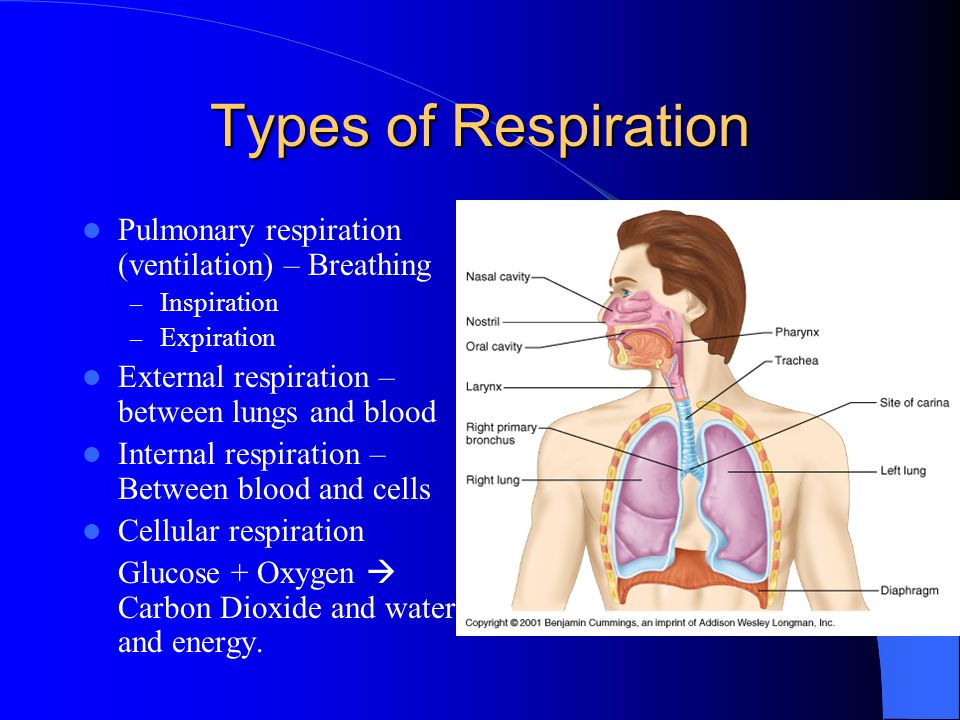
4. Oxygen is used for respiration
5. Carbon is used in torch light batteries
6. Sulphur is used in medicine
7. Chlorine is used for purifying water.
Evaluation:
1. What is matter?
2. Matter can be classified into what? Name them.
3. State the uses of metals and non-metals.
Reading assignment:
Teacher to give assignment from current textbook.
Assignment:
1. State three chemical differences between metal and non-metal.
2. Write five properties of metals.
MAIN TOPIC: Non-living things
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Classification of Non living things
REFERENCE BOOK:
a. Nigerian Basic Science project pupils textbook one by STAN
b. Exam focus, integrated science by Adebayo Begun
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Describe non-living components
b. State the classes of non-living things
CONTENT: Non-living things
Non-living things are things that do not have life. Non living things can be classified according to their properties or characteristics. They may be classified in terms of colour, size, shape, smell, taste and texture. All non-living things are made of matter. Matters can also be grouped in terms of their state that is solid, liquid and gas.
Classification of substances into state, colour, odour, and taste.
Substance.........State...........Colour.................Odour...............Taste
Air.....................Gas..............Colourless...........Odourless..........-
Chlorine............Gas..............Greenish yellow...Irritating............-
Water...............Liquid...........Colourless...........Odourless..........-
Lime juice.........Liquid...........Yellowish.............Fruity smell........Sour
Sulphur............Solid.............Yellow.................Pungent smell.....-
Sand................Solid.............Brown.....................-......................-
EVALUATION
a. Describe non-living things
b. Mention the classes of non-living things
further studies
http://schooltutoring.com/help/classifi ... ng-things/
http://www.glogster.com/umairah/classif ... _view=True
http://www.tutorvista.com/biology/chara ... ing-things#
http://resources.edb.gov.hk/~s1sci/R_S1 ... le-cot.htm
LESSON 55
MAIN TOPIC : Plants and Animals
SUB -TOPIC : Examples and characteristics of plants and animals
REFERENCE BK : Integrated Science for Nigerian Junior Secondary School Book 1 by F O C Ndu, L O Nd
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson student should be able to
1. State ways in which plants is important to human being
2. Mention uses of animals to human being
CONTENT:
EXAMPLES OF PLANTS ARE:-
Carpet grass, Pride of Barbados, Mango tree, Orange tree, Elephant grass, Hibiscus flower, Yellow bush
EXAMPLES OF ANIMALS ARE:-
Sheep, Cow, Rat, Elephant, Grasshopper, Snake, Horse, Sea lion, Monkey, Mouse, Giraffe, Dog, Goat
Characteristics of Plants
1. Plants manufacture their own food through photosynthesis which are called autotrophic
2. Plants have no complex organs for excretion
3. They do not move from one place to another but carry out bending movement
4. Plants grow in length only at the tips of the stems and roots
5. There is no courtship in reproduction
6. Respond to plants is slow only sensitive plants
7. Plants do not have organs for breathing.
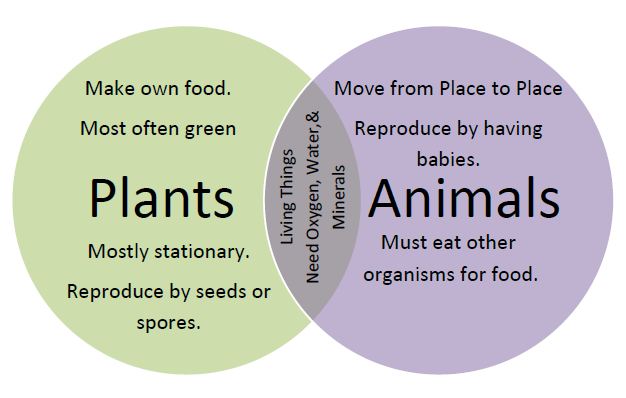
Characteristics of animals
1. Animals move from place to place their own
2. They breathe through complex organs such as lungs and gills
3. They have a complex for excretion
4. They feed on plants or other animals so they are called heterotrophic
5. Growth occurs in all parts of the animals.
6. They respond quickly to changes in the environment.
7. There is usually courtship in reproduction.
EVALUATION / CLASSWORK :
1. Name two examples of plants and animals each besides the one we have mentioned in the class
2. State the characteristics of plants
3. Mention the characteristics of animal
ASSIGNMENT:
1. State uses/importance of the plants
2. Mention uses / importance of the animals
further studies
http://www.learnnext.com/lesson/CBSE-VI ... Things.htm
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/characte ... hings.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... imals.html
http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/ ... -8578.html
practice test
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz139033fec8c0.html
http://www.funtrivia.com/newflash/trivia.cfm?qid=139033