3RD TERM
3RD TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Processing and uses of wood
2. Drills and Drilling machines
3. Energy
4. Basic ideas of electricity
5. Electric and magnetic field
6. Basic components of electricity ,electric circuit ,resistors and insulators
7. Definition of voltage, resistance, current and inductance, EMF and capacitors
8. Inter- relations and interaction of electricity and magnetic fields; Coils/ solenoids with examples.
9. Simple Machines.
10. Maintenance
11. Building: types, materials and building construction.
12. Revision
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Basic Electronic Devices; (a) Basic Emission Theory; Simple thermionic, primary emission. Photo-electric emission, cold-cathode and secondary emissions, etc.
2. Basic electronic devices (cont’d); (b) Electronic Devices; semi-conductor, resistors, capacitors, transistors. (i) Uses of Basic Electronic Devices.
3. Types of Building and Materials: (a) Types of building: bungalow, duplex, detached and semi-detached, hut, high rises, skyscrapers, etc.
4. Types of Building and Materials (cont’d): (b) common building materials, cement, sand, gravel, metal plastics, wood, glass, leaves, ceramics, grass, etc. uses of buildings
5. Simple Blue-Print Reading: (a) plan reading and interpretation-Drawing as a language, The language of lines, reading a building plan
6. Simple Blue-Print Reading (cont’d): (b) Identification of Building Components, fittings, sanitary wares, e.g. sink, bath, shower, soak-away, septic tank, sockets, windows, doors, etc.
7. Maintenance: the Concept of Maintenance; the need for maintenance and importance of maintenance.
8. Types of maintenance: (i) Preventive, (ii) Corrective (iii) predictive
9. Practical projects and test.
10. Revision
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Processing and uses of wood
2. Drills and Drilling machines
3. Energy
4. Basic ideas of electricity
5. Electric and magnetic field
6. Basic components of electricity ,electric circuit ,resistors and insulators
7. Definition of voltage, resistance, current and inductance, EMF and capacitors
8. Inter- relations and interaction of electricity and magnetic fields; Coils/ solenoids with examples.
9. Simple Machines.
10. Maintenance
11. Building: types, materials and building construction.
12. Revision
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Basic Electronic Devices; (a) Basic Emission Theory; Simple thermionic, primary emission. Photo-electric emission, cold-cathode and secondary emissions, etc.
2. Basic electronic devices (cont’d); (b) Electronic Devices; semi-conductor, resistors, capacitors, transistors. (i) Uses of Basic Electronic Devices.
3. Types of Building and Materials: (a) Types of building: bungalow, duplex, detached and semi-detached, hut, high rises, skyscrapers, etc.
4. Types of Building and Materials (cont’d): (b) common building materials, cement, sand, gravel, metal plastics, wood, glass, leaves, ceramics, grass, etc. uses of buildings
5. Simple Blue-Print Reading: (a) plan reading and interpretation-Drawing as a language, The language of lines, reading a building plan
6. Simple Blue-Print Reading (cont’d): (b) Identification of Building Components, fittings, sanitary wares, e.g. sink, bath, shower, soak-away, septic tank, sockets, windows, doors, etc.
7. Maintenance: the Concept of Maintenance; the need for maintenance and importance of maintenance.
8. Types of maintenance: (i) Preventive, (ii) Corrective (iii) predictive
9. Practical projects and test.
10. Revision
WEEK 1
TOPIC: REVISION AND BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES
CONTENT:
Basic Emission Theory
Sub-Topic : Basic Emission Theory
What is emission?
Emission is the displacement or dislodgement of electron from a material with the intention of directing such electron to a predetermined position or object. The basic electronic emission occurs when heat, sunlight, electron collision, electromagnetic field and surface bombardment are used to release electron from the metal surface to the vacuum tube.
Electronic Emission
The electronic emission is the process of liberating or emitting free electrons from the metal surface to the vacuum tubes. A vacuum tube is an empty tube in which the air has been completely removed for the purpose of storing liquefied gas.
Methods of Emission
There are four principal methods of liberating electron from the surface of metal:
i. The thermionic emission
ii. The photo-electric emission
iii. The cold-cathode emission
iv. The Secondary emission
i. The Thermionic Emission:
The thermionic Emission is the method by which free electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal by the application of heat energy. Another name for thermionic emission is THE PRIMARY EMISSION.
ii. The Photo-Electric Emission:
This is the method by which free electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal by the application of light or rays of light. It is used in solar panel.
iii. The Cold Cathode Emission or Field Emission:
This is the method by which free electrons are emitted from the surface of metal by the application of magnetic fields or electric field. It is used in the operation of electron microscope.
iv. The Secondary Emission:
This is the method by which electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal by the application of kinetic energy. A stream of moving electrons is called electron.
EVALUATION
1) What is electronic emission?
2) Discuss the following ; thermionic emission, the secondary emission
READING ASSIGNMENT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 11 Pages 92-95
ASSIGNMENT
i. Which of these is an electronic device? (a) a resistor (b) a torch (c) a Walkman (d) an amplifier
ii. The three parts of a transistor are __________,__________ and_______
Sub-Topic 1: BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES (CONT’D)
The basic Electronic devices are the devices which emit and control the movement of electrons in a desirable manner used in generation of electronic appliances.
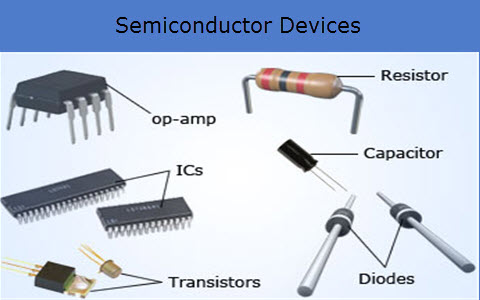
Types of Basic Electronic Devices
i. Semi-conductor
ii. Resistor
iii. Capacitors
iv. Transistors etc
i) Semi Conductors: Semi-conductors are those substances whose electrically conductivity lies between the good conductors (metallic substances) and good insulators (non-metallic substances) E.g. Silicon, Germanium.
Types of Semi Conductors
1. The intrinsic semi-conductor also known as pure semi-conductor
2. The extrinsic semi-conductor also known as impure semi-conductors.
3. Resistor: A Resistor is a device used to control the flow of electric current in an electric circuit or which opposes the flow of electric circuit. The ability of a Resistor to control the flow of electric current is called RESISTANCE. The resistor is measured in Ohms by a device called Ohm meter.
ii) Capacitor:

A capacitor is a piece of a[apparatus designed to store electrical energies in the form of electric charges. An example of capacitor is Condenser or starter in a fluorescent lamp. The capacitors are available in motor vehicles and air conditioner etc.
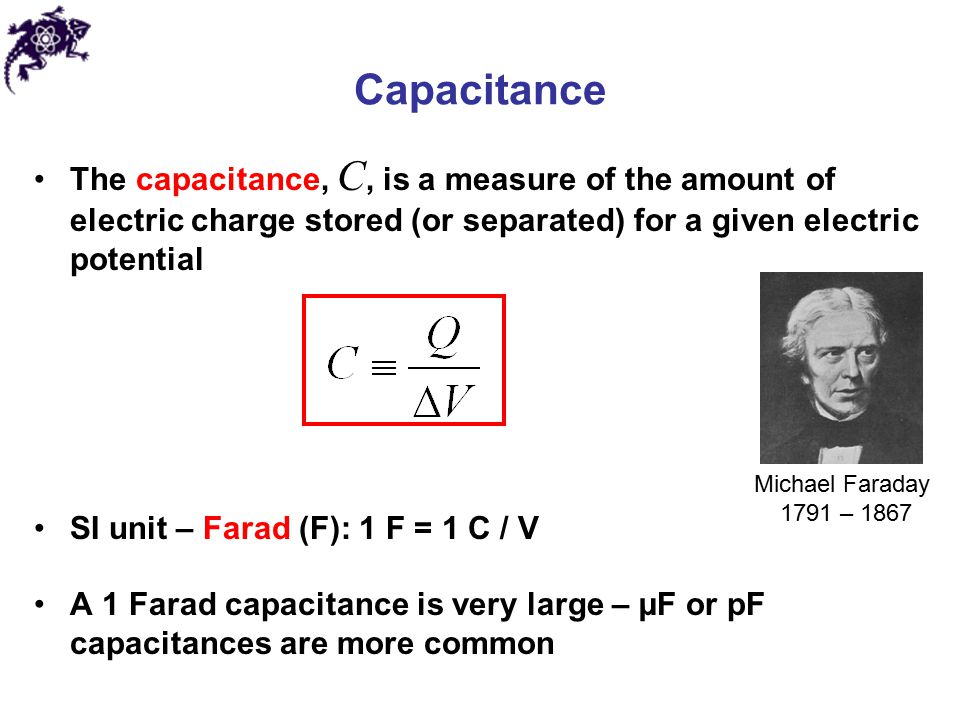
Capacitance: this is a phenomenon which exists when certain parts of an electric circuit are able to store electric charges.
Capacitance (C) = Charge on either plate (Q)/P.d across the plates (V).
The S.I unit of a capacitance is farad (F)
iii) Transistors:
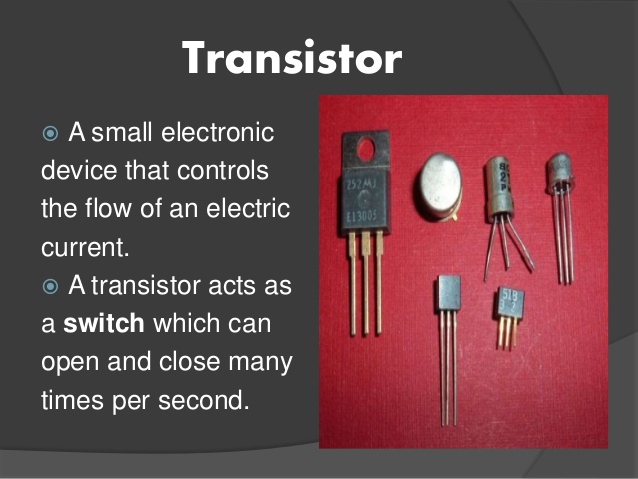
Transistors are semi-conductor materials which are capable of providing amplification in electronic equipment. They are smaller than vacuum tubes; the vacuum tubes control the flow of electron in the airless space while the transistors control the flow of electrons in the semi-conductors materials.
Transistor has three electrodes in terminals
a. The Emitter(E)
b. The Base(B)
c. The Collector(C)
The types of transistors are:
1. The bipolar transistor. E.g. (a) The P-N-P Transistor which are mostly made of Germanium (b) The N-P-N Transistors which are mostly made of silicon
2. The field effect transistor
EVALUATION
1) What is a basic electronic device
2) List 4 types of electronic devices
3) Mention 2 types of transistors
Sub-Topic 2: Uses of Basic Electronic Devices
1. Transistor is used to amplify current. An Amplifier is a circuit that increases the input signal
2. Transistor is used as a sensitive switch
3. Resistor is used to control the current that flows in the bulb
4. Capacitors are used for air conditioning
EVALUATION
1) Mention four uses of electronic devices
2) Identify the following electronic devices:
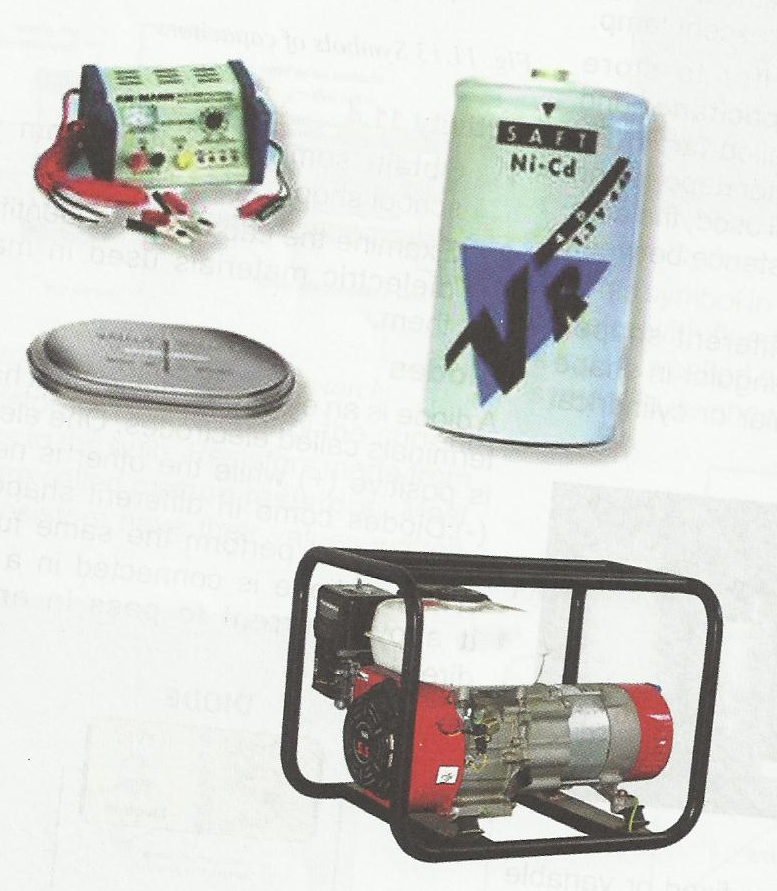

READING ASSIGNMENT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 11 Pages 95 - 103
ASSIGNMENT: Write short notes on the following
1. Semi-conductor
2. Resistor
3. Capacitors
4. Transistors etc.
CONTENT:
Basic Emission Theory
Sub-Topic : Basic Emission Theory
What is emission?
Emission is the displacement or dislodgement of electron from a material with the intention of directing such electron to a predetermined position or object. The basic electronic emission occurs when heat, sunlight, electron collision, electromagnetic field and surface bombardment are used to release electron from the metal surface to the vacuum tube.
Electronic Emission
The electronic emission is the process of liberating or emitting free electrons from the metal surface to the vacuum tubes. A vacuum tube is an empty tube in which the air has been completely removed for the purpose of storing liquefied gas.
Methods of Emission
There are four principal methods of liberating electron from the surface of metal:
i. The thermionic emission
ii. The photo-electric emission
iii. The cold-cathode emission
iv. The Secondary emission
i. The Thermionic Emission:
The thermionic Emission is the method by which free electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal by the application of heat energy. Another name for thermionic emission is THE PRIMARY EMISSION.
ii. The Photo-Electric Emission:
This is the method by which free electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal by the application of light or rays of light. It is used in solar panel.
iii. The Cold Cathode Emission or Field Emission:
This is the method by which free electrons are emitted from the surface of metal by the application of magnetic fields or electric field. It is used in the operation of electron microscope.
iv. The Secondary Emission:
This is the method by which electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal by the application of kinetic energy. A stream of moving electrons is called electron.
EVALUATION
1) What is electronic emission?
2) Discuss the following ; thermionic emission, the secondary emission
READING ASSIGNMENT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 11 Pages 92-95
ASSIGNMENT
i. Which of these is an electronic device? (a) a resistor (b) a torch (c) a Walkman (d) an amplifier
ii. The three parts of a transistor are __________,__________ and_______
Sub-Topic 1: BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES (CONT’D)
The basic Electronic devices are the devices which emit and control the movement of electrons in a desirable manner used in generation of electronic appliances.
Types of Basic Electronic Devices
i. Semi-conductor
ii. Resistor
iii. Capacitors
iv. Transistors etc
i) Semi Conductors: Semi-conductors are those substances whose electrically conductivity lies between the good conductors (metallic substances) and good insulators (non-metallic substances) E.g. Silicon, Germanium.

Types of Semi Conductors
1. The intrinsic semi-conductor also known as pure semi-conductor
2. The extrinsic semi-conductor also known as impure semi-conductors.
3. Resistor: A Resistor is a device used to control the flow of electric current in an electric circuit or which opposes the flow of electric circuit. The ability of a Resistor to control the flow of electric current is called RESISTANCE. The resistor is measured in Ohms by a device called Ohm meter.
ii) Capacitor:

A capacitor is a piece of a[apparatus designed to store electrical energies in the form of electric charges. An example of capacitor is Condenser or starter in a fluorescent lamp. The capacitors are available in motor vehicles and air conditioner etc.
Capacitance: this is a phenomenon which exists when certain parts of an electric circuit are able to store electric charges.
Capacitance (C) = Charge on either plate (Q)/P.d across the plates (V).
The S.I unit of a capacitance is farad (F)

iii) Transistors:

Transistors are semi-conductor materials which are capable of providing amplification in electronic equipment. They are smaller than vacuum tubes; the vacuum tubes control the flow of electron in the airless space while the transistors control the flow of electrons in the semi-conductors materials.
Transistor has three electrodes in terminals
a. The Emitter(E)
b. The Base(B)
c. The Collector(C)
The types of transistors are:
1. The bipolar transistor. E.g. (a) The P-N-P Transistor which are mostly made of Germanium (b) The N-P-N Transistors which are mostly made of silicon
2. The field effect transistor

EVALUATION
1) What is a basic electronic device
2) List 4 types of electronic devices
3) Mention 2 types of transistors
Sub-Topic 2: Uses of Basic Electronic Devices
1. Transistor is used to amplify current. An Amplifier is a circuit that increases the input signal
2. Transistor is used as a sensitive switch
3. Resistor is used to control the current that flows in the bulb
4. Capacitors are used for air conditioning
EVALUATION
1) Mention four uses of electronic devices
2) Identify the following electronic devices:

READING ASSIGNMENT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 11 Pages 95 - 103
ASSIGNMENT: Write short notes on the following
1. Semi-conductor
2. Resistor
3. Capacitors
4. Transistors etc.
WEEK 2
MAIN TOPIC : Processing of wood (Revised)
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the steps in the processing of wood
(2) Explain the steps in processing of wood
CONTENT
The steps in processing of wood includes:-
Felling of tree
Wood conversion
Wood seasoning
Wood preservation
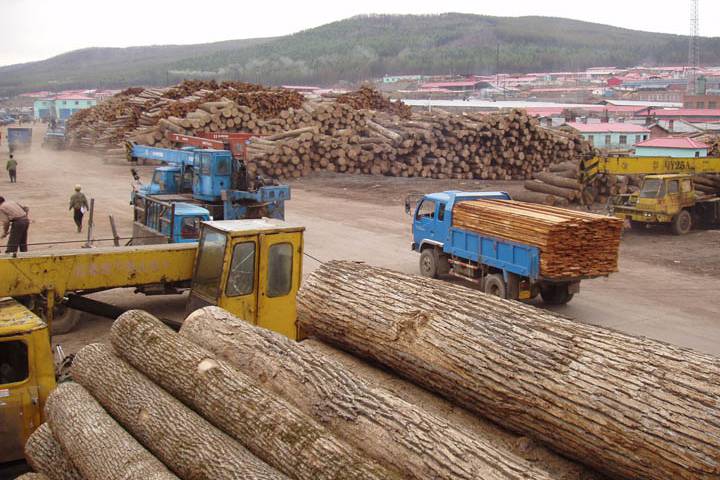

Felling of tree:- simply means cutting down of tree. Felling of trees is carried out with the use of chain saw. In Nigeria Felling of tree is carried out in two places:-
I. Forest Reserve area : a reserved place by government where trees are planted, to cut down tree in this place the timber contractor will pay an amount called OTV out turn volume it means that they will pay for the volume of trees they take.
II. Free Area:- this is an area outside the Forest area e.g. farmland. To cut down tree in this area the amount paid is called Tariff which is paid to the government to obtain permit to cut the tree.
Wood conversion:-is the process of splitting the log into marketable sizes. There are two methods of wood conversion
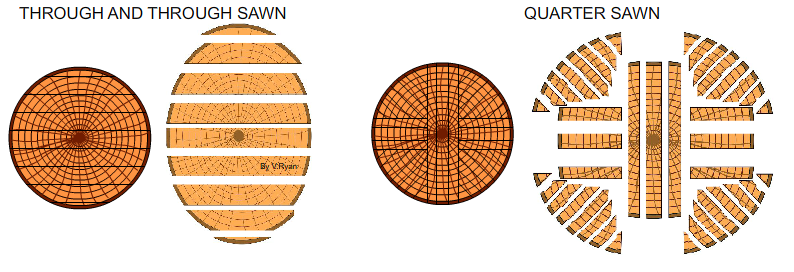
a. Plain sawn or tangential method or through and through method
b. Quarter sawn.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the steps in processing of wood
Explain felling of tree and wood conversion
further studies
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-tree-fe ... #slideshow
http://www.technologystudent.com/joints/forest3a.html
LESSON 34
MAIN TOPIC: Woodwork practice
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Simple woodwork joint
REFERENCE BOOK: Introductory technology for Junior Secondary Schools bk2. Introductory technology textbook for JSS by P.O Olawehinmi
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the student should be able to:
a. Define joinery
b. Mention the classes of woodwork joint
c. Mention examples of joint
CONTENT: Woodwork
Joints are essential in any wooden cabinet and there are different types of joint the choice of a joint depends on the type of cabinet or object to be made.
Joinery: is the art and skill of assembling and fastening two or more pieces of wood together.
Classes of woodwork joint
a. Widening joint

b. Angle or bon joint

c. Framing joint
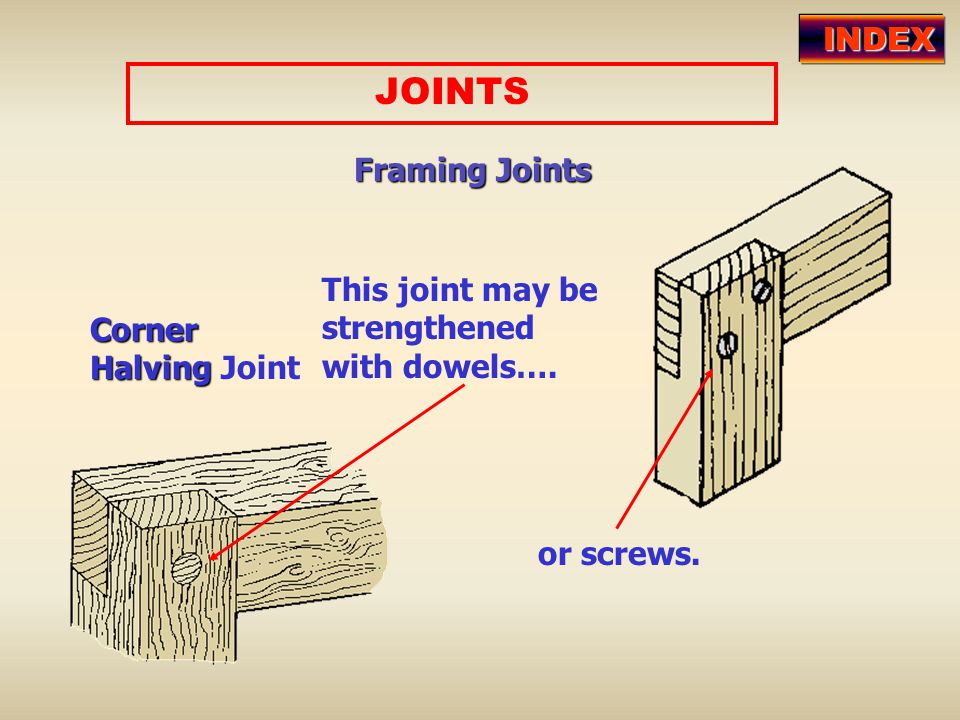
Example of joint
a. Butt joint
b. Halving joint
c. Tongue and groove joint
d. Dovetail joint
e. Bridle joint etc
EVALUATION
a. Define joinery
b. Mention and explain the classes of woodwork joint
c. Mention different types of joint
ASSIGNMENT
Draw all the types of joint
further studies
http://woodworking.about.com/od/joinery ... g_Wood.htm
http://www.popularwoodworking.com/techniques/joinery
http://www.bespokehouse.co.uk/joinery1.jpg
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://home.howstuffworks.com/power-tool-quiz1.htm
http://quiz.thefullwiki.org/Woodworking_joints
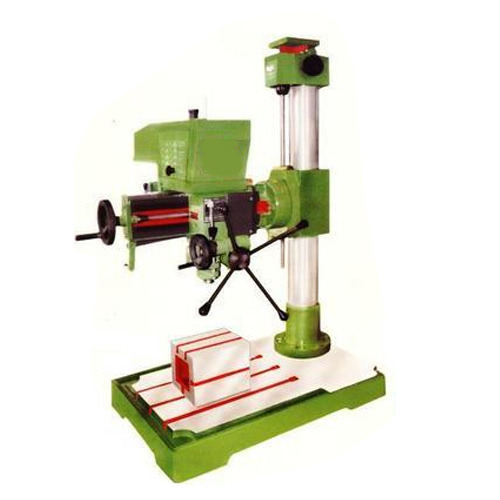
MAIN TOPIC : Drill and drilling machine
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Drilling machine
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define drilling
(2) mention the drilling machine
CONTENT
Drilling is the act of making cylindrical holes in Metal. Drilling is carried out with the use of Drilling machine and drills. This operation is called Drilling.
DRILLING MACHINES
A drilling machine is made to hold a drill and turn it in order to cut a hole in a piece of metal and other materials.
TYPES OF DRILLING MACHINES
1. Hand drilling machines (manual)
2. Hand drilling machine (electrical)
3. Sensitive drilling machine (bench)
4. Sensitive drilling machine (floor)
5. Multiple spindle drilling machine
6. Radial drilling machine
7. Back-geared drilling machine
Hand drilling machine (manual): this machine is always used for light work. To operate this machine, one hand is used to hold it against the work and the other to turn its crank.
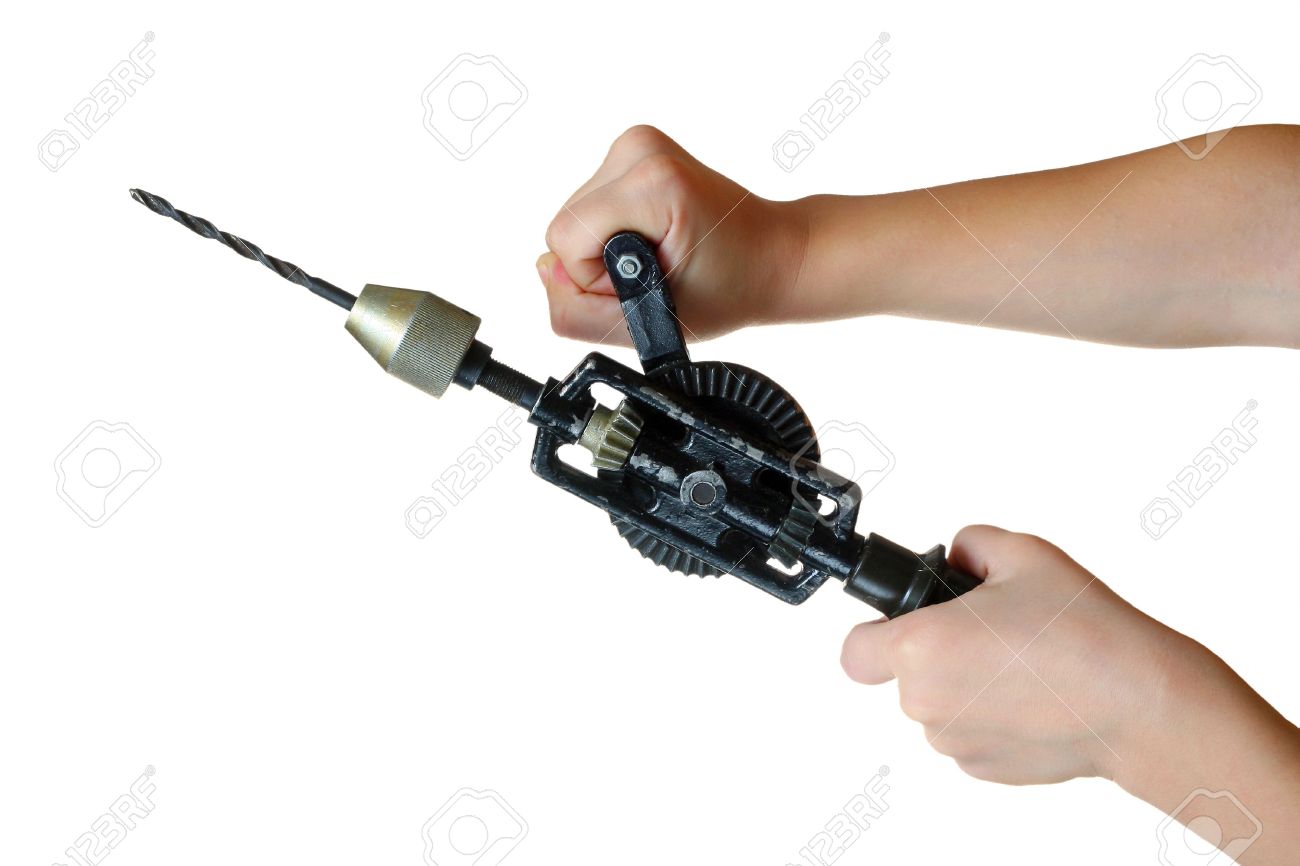
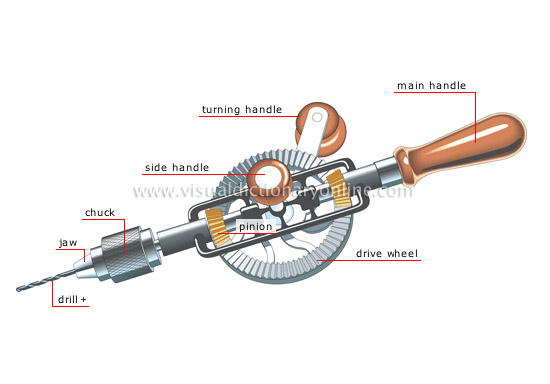

Hand drilling machine (electrical): this is a portable hand drilling machine which can be used in any part of the workshop. It is powered electrically.
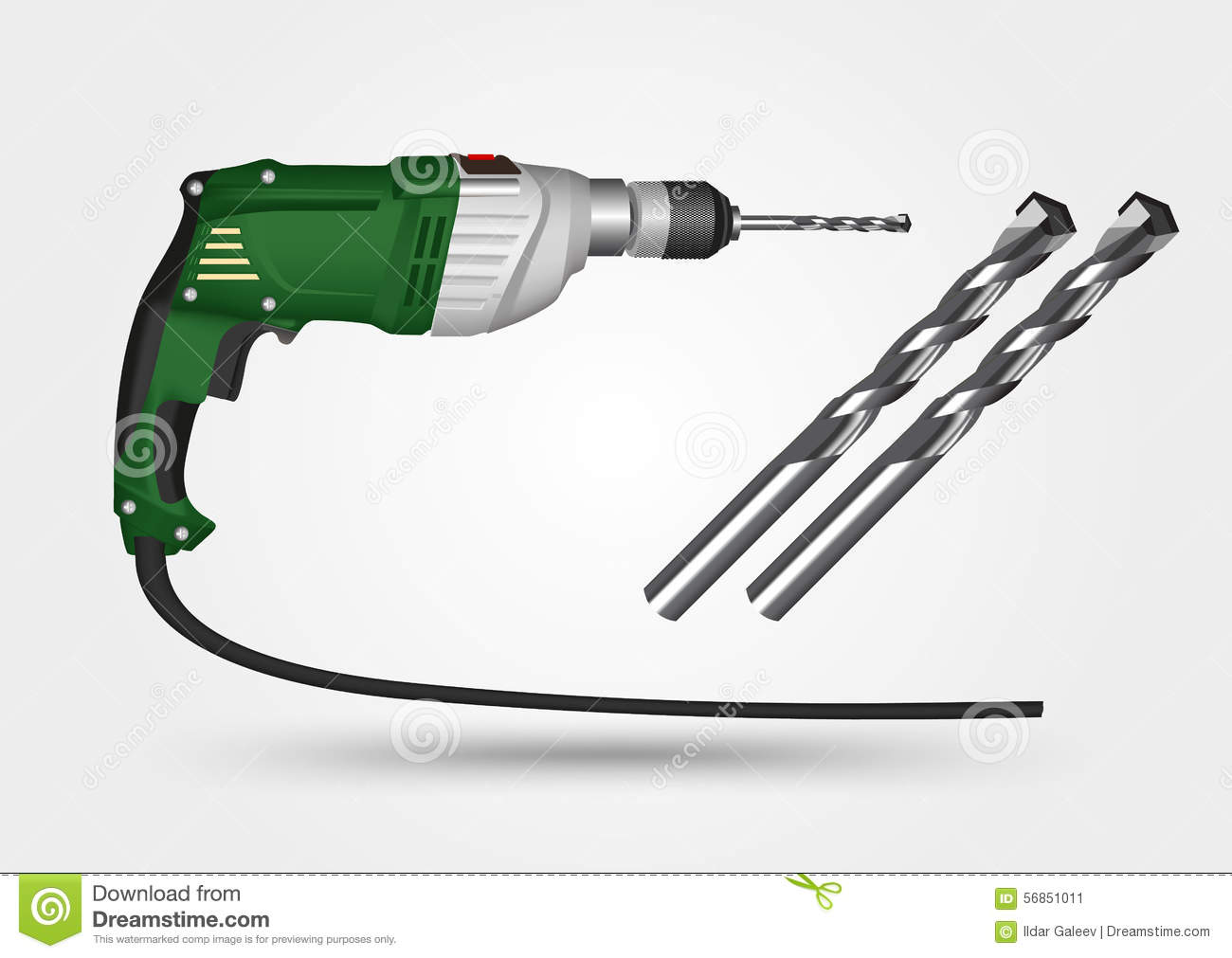

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define drilling
Mention types of drilling machines
further studies
http://www.drillmachine.biz/?gclid=CPTm ... tAodaQwAVg
LESSON 36
MAIN TOPIC : Drills and Drilling machines
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Drills
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) describe the types of drilling machines
(2) mention and state the functions of types of drills
CONTENT
Types of drilling machines
Sensitive drilling machine (bench):
This type of machine is also used for light work, It is used for making holes between 1mm to 18mm. The main difference between this machine and the electrical hand drilling machine is that the bench type is fixed to work bench.
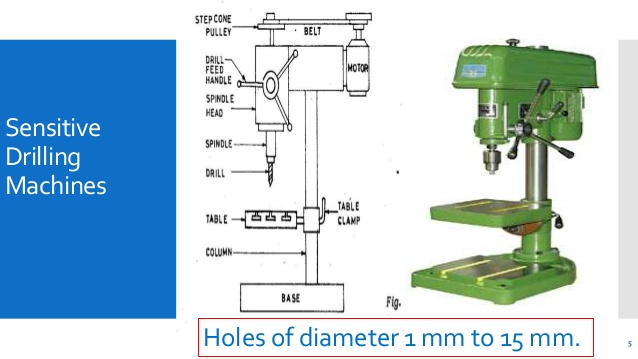
Sensitive drilling machine (floor):
The difference between the bench and the floor type of sensitive drilling machine is that the length of the main column of that of floor type is longer than that of the bench type.

Multiple spindle drilling machine:
There are two types of this machine, it can be bench or floor type. It has a spindle which can accommodate multiple drills if one of the space for drill is empty it will not work. It is useful in mass production.

Radial Drilling machine is designed for big and heavy jobs. The arm on which the spindle is mounted is moveable this arm can be rotated to left or right of the table. The arm of this machine is called radial arm.

[youtube]https://youtu.be/UVUBeNPtgeM[/youtube]
Back geared drilling machine. In construction this machine is like sensitive drilling machine but is more power and longer. It has a back gear for changing the speed. It can be fed manually and automatically. Since it can be fed automatically it larger the one used in the sensitive drilling machine.

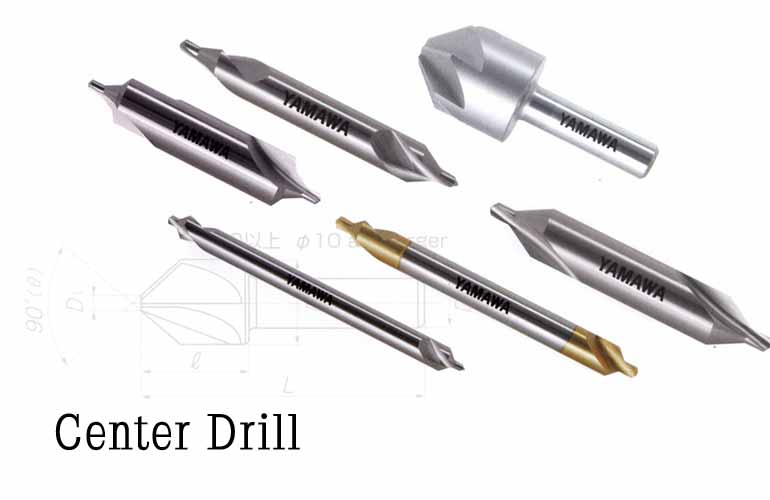
TYPES OF DRILLS
1. Twist drill

2. Flat drill
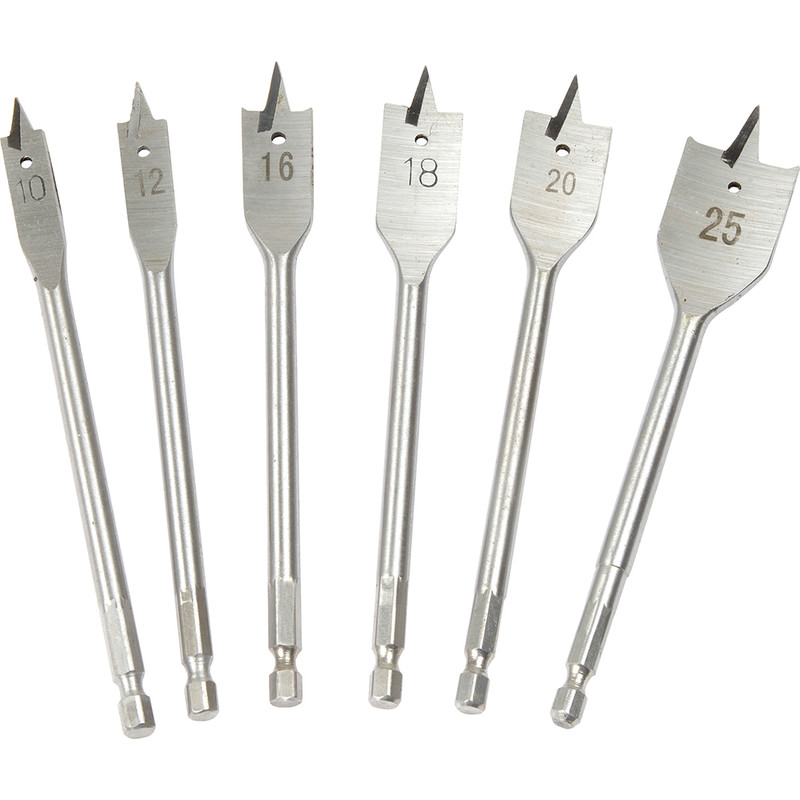

3. Straight fluted drill

4. Countersink drill

5. Centre drill or combination drill


[youtube]https://youtu.be/SrPmvP9Zulg[/youtube]
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe types of drilling machine
Mention different types of drill
ASSIGNMENT: Draw all the types of drilling machine
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the steps in the processing of wood
(2) Explain the steps in processing of wood
CONTENT
The steps in processing of wood includes:-
Felling of tree
Wood conversion
Wood seasoning
Wood preservation

Felling of tree:- simply means cutting down of tree. Felling of trees is carried out with the use of chain saw. In Nigeria Felling of tree is carried out in two places:-
I. Forest Reserve area : a reserved place by government where trees are planted, to cut down tree in this place the timber contractor will pay an amount called OTV out turn volume it means that they will pay for the volume of trees they take.
II. Free Area:- this is an area outside the Forest area e.g. farmland. To cut down tree in this area the amount paid is called Tariff which is paid to the government to obtain permit to cut the tree.
Wood conversion:-is the process of splitting the log into marketable sizes. There are two methods of wood conversion

a. Plain sawn or tangential method or through and through method
b. Quarter sawn.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the steps in processing of wood
Explain felling of tree and wood conversion
further studies
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-tree-fe ... #slideshow
http://www.technologystudent.com/joints/forest3a.html
LESSON 34
MAIN TOPIC: Woodwork practice
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Simple woodwork joint
REFERENCE BOOK: Introductory technology for Junior Secondary Schools bk2. Introductory technology textbook for JSS by P.O Olawehinmi
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the student should be able to:
a. Define joinery
b. Mention the classes of woodwork joint
c. Mention examples of joint
CONTENT: Woodwork
Joints are essential in any wooden cabinet and there are different types of joint the choice of a joint depends on the type of cabinet or object to be made.
Joinery: is the art and skill of assembling and fastening two or more pieces of wood together.
Classes of woodwork joint
a. Widening joint

b. Angle or bon joint

c. Framing joint

Example of joint
a. Butt joint
b. Halving joint
c. Tongue and groove joint
d. Dovetail joint
e. Bridle joint etc

EVALUATION
a. Define joinery
b. Mention and explain the classes of woodwork joint
c. Mention different types of joint
ASSIGNMENT
Draw all the types of joint
further studies
http://woodworking.about.com/od/joinery ... g_Wood.htm
http://www.popularwoodworking.com/techniques/joinery
http://www.bespokehouse.co.uk/joinery1.jpg
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://home.howstuffworks.com/power-tool-quiz1.htm
http://quiz.thefullwiki.org/Woodworking_joints
MAIN TOPIC : Drill and drilling machine
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Drilling machine
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define drilling
(2) mention the drilling machine
CONTENT
Drilling is the act of making cylindrical holes in Metal. Drilling is carried out with the use of Drilling machine and drills. This operation is called Drilling.
DRILLING MACHINES
A drilling machine is made to hold a drill and turn it in order to cut a hole in a piece of metal and other materials.
TYPES OF DRILLING MACHINES
1. Hand drilling machines (manual)
2. Hand drilling machine (electrical)
3. Sensitive drilling machine (bench)
4. Sensitive drilling machine (floor)
5. Multiple spindle drilling machine
6. Radial drilling machine
7. Back-geared drilling machine
Hand drilling machine (manual): this machine is always used for light work. To operate this machine, one hand is used to hold it against the work and the other to turn its crank.


Hand drilling machine (electrical): this is a portable hand drilling machine which can be used in any part of the workshop. It is powered electrically.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define drilling
Mention types of drilling machines
further studies
http://www.drillmachine.biz/?gclid=CPTm ... tAodaQwAVg
LESSON 36
MAIN TOPIC : Drills and Drilling machines
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Drills
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) describe the types of drilling machines
(2) mention and state the functions of types of drills
CONTENT
Types of drilling machines
Sensitive drilling machine (bench):
This type of machine is also used for light work, It is used for making holes between 1mm to 18mm. The main difference between this machine and the electrical hand drilling machine is that the bench type is fixed to work bench.

Sensitive drilling machine (floor):
The difference between the bench and the floor type of sensitive drilling machine is that the length of the main column of that of floor type is longer than that of the bench type.

Multiple spindle drilling machine:
There are two types of this machine, it can be bench or floor type. It has a spindle which can accommodate multiple drills if one of the space for drill is empty it will not work. It is useful in mass production.

Radial Drilling machine is designed for big and heavy jobs. The arm on which the spindle is mounted is moveable this arm can be rotated to left or right of the table. The arm of this machine is called radial arm.

[youtube]https://youtu.be/UVUBeNPtgeM[/youtube]
Back geared drilling machine. In construction this machine is like sensitive drilling machine but is more power and longer. It has a back gear for changing the speed. It can be fed manually and automatically. Since it can be fed automatically it larger the one used in the sensitive drilling machine.

TYPES OF DRILLS
1. Twist drill

2. Flat drill

3. Straight fluted drill

4. Countersink drill

5. Centre drill or combination drill


[youtube]https://youtu.be/SrPmvP9Zulg[/youtube]
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe types of drilling machine
Mention different types of drill
ASSIGNMENT: Draw all the types of drilling machine
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
WEEK 4
MAIN TOPIC: Glues and Abrasive
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Glues (Adhesive)
REFERENCES BOOKS:
1. Introductory technology for Junior Secondary Schools bk2.
2. Introductory technology textbook for JSS by P.O Olawehinmi
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Define Adhesive
b. Mention the three(3) classes of adhesive
CONTENT: Adhesive
An adhesive is any substance capable of holding or bonding two or other pieces of materials together. Adhesive are also known as GLUES. They have been in use for over 3,000years for fixing of joints permanently, veneering, furniture construction etc

Class of Adhesive
a. Protein adhesive. E.g animal glue, soya bean glue, blood albumen etc
b. Synthetic resin adhesive: e.g. Urea, melamine, exp oxide - based resin glues etc
c. Contact adhesive e.g. Erostik, Bostik, Araldite etc

EVALUATION:
a. Define adhesive
b. State the uses of adhesive
c. Mention the classes of adhesive
ASSIGNMENT
Write the short note on abrasive
further studies
http://solutions.3m.com/wps/portal/3M/e ... 0818&rt=c3
http://www.adhesiveandglue.com/
http://www.michaels.com/Glue-Adhesives/ ... lt,sc.html
LESSON 38
MAIN TOPIC: Glues and Abrasive
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Abrasive
REFERENCES BOOKS:
1. Introductory technology for Junior Secondary Schools bk2.
2. Introductory technology textbook for JSS by P.O Olawehinmi
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Define Abrasive
b. State the three(3) basic things to know about coated abrasives
c. Mention abrasive materials

CONTENT: Abrasives
Abrasives are papers or cloth coated with hard minerals producing multi-point cutting edges that wear away the surfaces of other materials by rubbing. Abrasives are used for smoothing the surface of materials such as wood and metal.
The process of using abrasive is called SANDING.
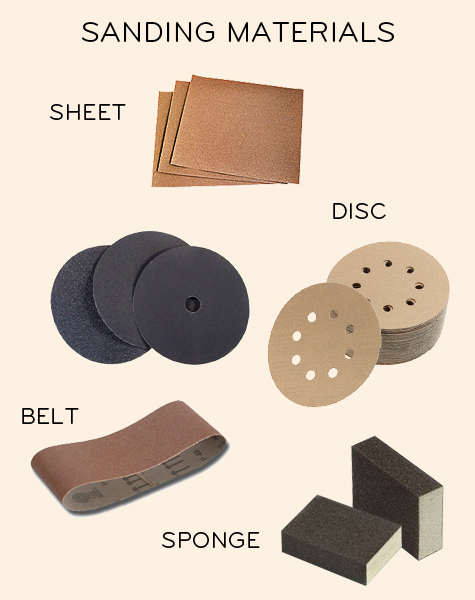

There are three classes of sanding
a. Sanding before finish
b. Sanding the intermediate coats
c. Wet sanding of finished coats
There are three(3) things to know about the coated abrasive. These are:
a. The type of minerals used for the coated abrasive
b. The type of backing
c. The type of bond
There are several type of minerals used in coated abrasive, they are glass, flint, energy, gamet, silicon carbide and aluminium oxide.

EVALUATION
a. Define abrasive
b. State the basic things to know about coated abrasive
c. Mention the classes of sanding
d. Mention the abrasive minerals
ASSIGNMENT
Write out ten(10) uses of metal.
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coated_abrasive
https://www.fepa-abrasives.org/abrasive-products
http://www.popularwoodworking.com/techn ... nding_wood
http://www.familyhandyman.com/DIY-Proje ... r/View-All
http://www.askwoodman.com/2010/06/12/im ... odworkers/
http://www.generalfinishes.com/retail-p ... on-sanding
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Glues (Adhesive)
REFERENCES BOOKS:
1. Introductory technology for Junior Secondary Schools bk2.
2. Introductory technology textbook for JSS by P.O Olawehinmi
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Define Adhesive
b. Mention the three(3) classes of adhesive
CONTENT: Adhesive
An adhesive is any substance capable of holding or bonding two or other pieces of materials together. Adhesive are also known as GLUES. They have been in use for over 3,000years for fixing of joints permanently, veneering, furniture construction etc

Class of Adhesive
a. Protein adhesive. E.g animal glue, soya bean glue, blood albumen etc
b. Synthetic resin adhesive: e.g. Urea, melamine, exp oxide - based resin glues etc
c. Contact adhesive e.g. Erostik, Bostik, Araldite etc

EVALUATION:
a. Define adhesive
b. State the uses of adhesive
c. Mention the classes of adhesive
ASSIGNMENT
Write the short note on abrasive
further studies
http://solutions.3m.com/wps/portal/3M/e ... 0818&rt=c3
http://www.adhesiveandglue.com/
http://www.michaels.com/Glue-Adhesives/ ... lt,sc.html
LESSON 38
MAIN TOPIC: Glues and Abrasive
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Abrasive
REFERENCES BOOKS:
1. Introductory technology for Junior Secondary Schools bk2.
2. Introductory technology textbook for JSS by P.O Olawehinmi
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Define Abrasive
b. State the three(3) basic things to know about coated abrasives
c. Mention abrasive materials

CONTENT: Abrasives
Abrasives are papers or cloth coated with hard minerals producing multi-point cutting edges that wear away the surfaces of other materials by rubbing. Abrasives are used for smoothing the surface of materials such as wood and metal.
The process of using abrasive is called SANDING.

There are three classes of sanding
a. Sanding before finish
b. Sanding the intermediate coats
c. Wet sanding of finished coats
There are three(3) things to know about the coated abrasive. These are:
a. The type of minerals used for the coated abrasive
b. The type of backing
c. The type of bond
There are several type of minerals used in coated abrasive, they are glass, flint, energy, gamet, silicon carbide and aluminium oxide.

EVALUATION
a. Define abrasive
b. State the basic things to know about coated abrasive
c. Mention the classes of sanding
d. Mention the abrasive minerals
ASSIGNMENT
Write out ten(10) uses of metal.
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coated_abrasive
https://www.fepa-abrasives.org/abrasive-products
http://www.popularwoodworking.com/techn ... nding_wood
http://www.familyhandyman.com/DIY-Proje ... r/View-All
http://www.askwoodman.com/2010/06/12/im ... odworkers/
http://www.generalfinishes.com/retail-p ... on-sanding
WEEK 5
TOPIC: TYPES OF BUILDING AND MATERIALS
CONTENT: i. Types of Buildings
ii. Identification of Building by Materials
Sub-Topic I: Types of building
A building is a structure which is designed by the architects or draughtsmen and built for the purpose of providing shelter for human beings.
Building can also be identified through their construction design. The types of buildings are: bungalow, duplex, detached and semi-detached, hut, high-rise, skyscrapers etc
(a) Bungalows:- These are buildings that are only at the ground floor
(b) Duplex: - Is a compact storey building, roofed at the first floor and only designed to locate the sitting room, dining room, the kitchen and guest room with their conveniences are located at the first floor.
(c) Detached: A residential building standing alone
(d) Semi-detached or terraced building: Are series of unit buildings along a line joined together with common dividing walls
(e) Skyscrapers: A very tall storey buildings with many floors.
(f) Hut:- This a small unit and usually round in shape and covered thatch

EVALUATION
1. What is a building
2. Mention 3 types of building you know
Sub-Topic 2: Identification of Buildings by Materials
Buildings are identified by the types of materials with which they are erected.
(1) Mud Buildings: These are erected with loamy or clayed soil which has been properly treated to plastic nature.
(2) Brick Building: Bricks are molded from dried mortar (a mixture of cement, sand and lime and at times clay burnt in a kiln. There two types of Brick Building:
(a) The Sun dried bricks
(b) The fire burnt bricks (Red bricks)
(3) Sand Crete Building: This is made from the mixture of cement and sand. The blocks are used to erect buildings
(4) Wood Building: These are erected with logs timber or plywood
EVALUATION
Mention ways through which you can identify buildings by the building materials
ASSIGNMENT
1. …………………..buildings that are only at the ground floor
2. ……………………. tall storey buildings with many floors.
3. …………….small unit and usually round in shape and covered thatch
4. ………………are erected with loamy or clayed soil which has been properly treated to plastic nature.
5. ……………………… This is made from the mixture of cement and sand. The blocks are used to erect buildings
Reading Assignment: Students should read about types of building materials and uses of building. NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School I Chapter 12 Pages 104 - 107
TOPIC: TYPES OF BUILDINGS AND MATERIALS (cont’d)
CONTENT: I. Common building materials
II. Uses of Buildings
Sub-Topic I: Common Building Materials
The common Building Materials are:
(1) Sand:- This is the most common building materials. The two types of sand used in building construction are soft sand and sharp sand.
(2) Gravel:- This is a constituent of concrete which is used in building construction. There are two types of gravel;
(a) Pebbles:- These are small stones excavated from pits or rover bails
(b) Granite chippings:- These are chipping of blasted granite stones generally collected in grade sizes
(3) Cement:- This is a finely powdered, manufactured substance consisting of gypsum plaster or Portland cement that hardens adheres after being mixed with water. It is an essential materials in building construction.
(4) Wood:- is a natural products that forms the trunk of trees which is used as a material for building construction. They are used to produce wooden doors and windows and are also as roof and ceiling structures.
(5) Loaves and grasses:- are not commonly used nowadays but were good roof covering materials in the past.
(6) Glass:- for windows, doors and sometimes walls of modern buildings.
(7) Plastic and Ceramics for sewage pipes for draining waste
TYPES OF BUILDINGS
Buildings are generally classified according to their uses. The following are different types of buildings:
1. Residential buildings are houses we live in
2. Commercial buildings or stalls are those buildings where buying and selling activities are done
3. School buildings are buildings where teaching and learning take place
4. Hospital buildings are buildings where healthcare services are rendered
5. Hostel buildings are where hospitality is given. That is where strangers and visitors are taken care of.
6. Office buildings are buildings where people do their office work
7. Church/mosque buildings are buildings where religious activities are performed.

EVALUATION
List 5 types of Building Materials
Sub-Topic 2: Uses of building
1. Shelter
2. Privacy
3. Protection
4. Comfort
5. Security
EVALUATION
1. List 5 building materials
2. Name 3 uses of buildings
Reading Assignment
Students should read about Simple Blueprint Reading NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School I Chapter 13 Pages 108 - 109
Assignment
Objective:
1) ______ is one of the common building materials except (a) cement (b) wood (c) chair (d) wood
2) ____ is erected with loamy or clay soil (a) mud building (b) brick building (c) Sand Crete building (d) wood buildings
Essay
1. Differentiate between a bungalow and a duplex
2. List five building materials required for walling
CONTENT: i. Types of Buildings
ii. Identification of Building by Materials
Sub-Topic I: Types of building
A building is a structure which is designed by the architects or draughtsmen and built for the purpose of providing shelter for human beings.
Building can also be identified through their construction design. The types of buildings are: bungalow, duplex, detached and semi-detached, hut, high-rise, skyscrapers etc
(a) Bungalows:- These are buildings that are only at the ground floor
(b) Duplex: - Is a compact storey building, roofed at the first floor and only designed to locate the sitting room, dining room, the kitchen and guest room with their conveniences are located at the first floor.
(c) Detached: A residential building standing alone
(d) Semi-detached or terraced building: Are series of unit buildings along a line joined together with common dividing walls
(e) Skyscrapers: A very tall storey buildings with many floors.
(f) Hut:- This a small unit and usually round in shape and covered thatch

EVALUATION
1. What is a building
2. Mention 3 types of building you know
Sub-Topic 2: Identification of Buildings by Materials
Buildings are identified by the types of materials with which they are erected.
(1) Mud Buildings: These are erected with loamy or clayed soil which has been properly treated to plastic nature.
(2) Brick Building: Bricks are molded from dried mortar (a mixture of cement, sand and lime and at times clay burnt in a kiln. There two types of Brick Building:
(a) The Sun dried bricks
(b) The fire burnt bricks (Red bricks)
(3) Sand Crete Building: This is made from the mixture of cement and sand. The blocks are used to erect buildings
(4) Wood Building: These are erected with logs timber or plywood
EVALUATION
Mention ways through which you can identify buildings by the building materials
ASSIGNMENT
1. …………………..buildings that are only at the ground floor
2. ……………………. tall storey buildings with many floors.
3. …………….small unit and usually round in shape and covered thatch
4. ………………are erected with loamy or clayed soil which has been properly treated to plastic nature.
5. ……………………… This is made from the mixture of cement and sand. The blocks are used to erect buildings
Reading Assignment: Students should read about types of building materials and uses of building. NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School I Chapter 12 Pages 104 - 107
TOPIC: TYPES OF BUILDINGS AND MATERIALS (cont’d)
CONTENT: I. Common building materials
II. Uses of Buildings
Sub-Topic I: Common Building Materials
The common Building Materials are:
(1) Sand:- This is the most common building materials. The two types of sand used in building construction are soft sand and sharp sand.
(2) Gravel:- This is a constituent of concrete which is used in building construction. There are two types of gravel;
(a) Pebbles:- These are small stones excavated from pits or rover bails
(b) Granite chippings:- These are chipping of blasted granite stones generally collected in grade sizes
(3) Cement:- This is a finely powdered, manufactured substance consisting of gypsum plaster or Portland cement that hardens adheres after being mixed with water. It is an essential materials in building construction.
(4) Wood:- is a natural products that forms the trunk of trees which is used as a material for building construction. They are used to produce wooden doors and windows and are also as roof and ceiling structures.
(5) Loaves and grasses:- are not commonly used nowadays but were good roof covering materials in the past.
(6) Glass:- for windows, doors and sometimes walls of modern buildings.
(7) Plastic and Ceramics for sewage pipes for draining waste
TYPES OF BUILDINGS
Buildings are generally classified according to their uses. The following are different types of buildings:
1. Residential buildings are houses we live in
2. Commercial buildings or stalls are those buildings where buying and selling activities are done
3. School buildings are buildings where teaching and learning take place
4. Hospital buildings are buildings where healthcare services are rendered
5. Hostel buildings are where hospitality is given. That is where strangers and visitors are taken care of.
6. Office buildings are buildings where people do their office work
7. Church/mosque buildings are buildings where religious activities are performed.

EVALUATION
List 5 types of Building Materials
Sub-Topic 2: Uses of building
1. Shelter
2. Privacy
3. Protection
4. Comfort
5. Security
EVALUATION
1. List 5 building materials
2. Name 3 uses of buildings
Reading Assignment
Students should read about Simple Blueprint Reading NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School I Chapter 13 Pages 108 - 109
Assignment
Objective:
1) ______ is one of the common building materials except (a) cement (b) wood (c) chair (d) wood
2) ____ is erected with loamy or clay soil (a) mud building (b) brick building (c) Sand Crete building (d) wood buildings
Essay
1. Differentiate between a bungalow and a duplex
2. List five building materials required for walling
WEEK 6
MAIN TOPIC : Basic ideas of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Matter
REFERENCE BK : Basic Technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. define matter
II. explain molecule
CONTENT
Basic ideas of electricity
Basic ideas of electricity deals with the sciences leading with the use of radio, television, fans etc.
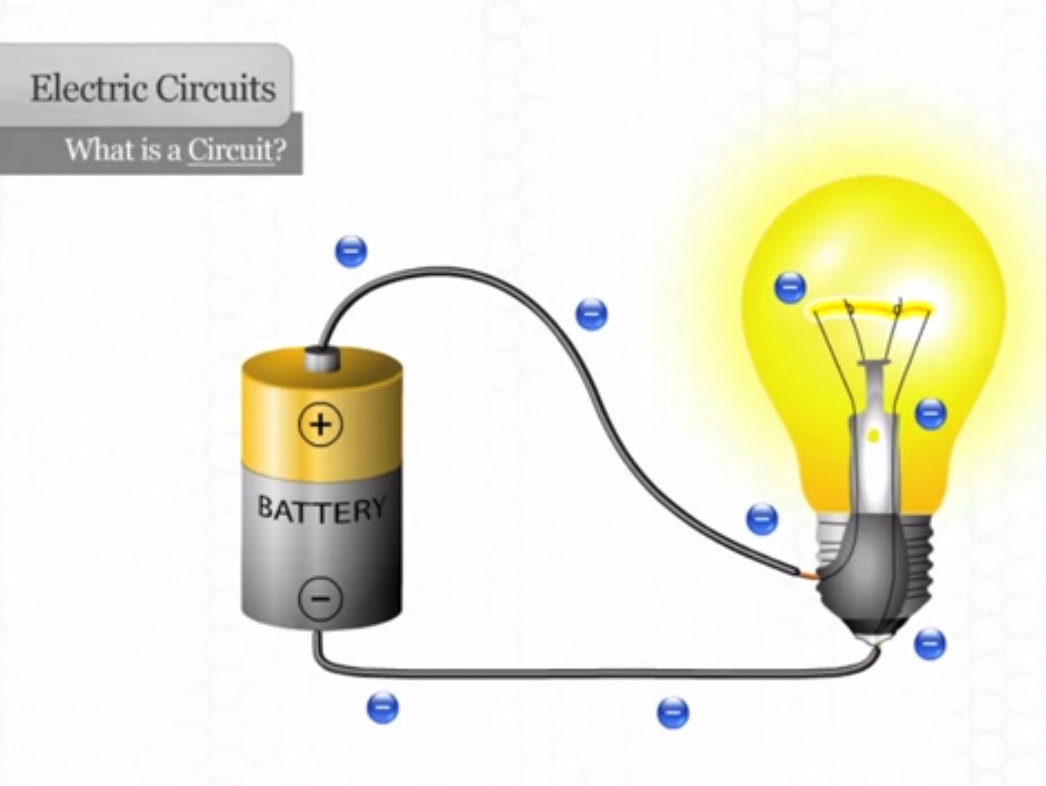
Electric current is the flow of electron in a conductor.
Conductors are materials that allow free flow of electron or electric charges. Examples are copper, aluminum, brass etc.
Insulators are materials that do not allow free flow of electric. They are called also called poor conductors .Examples of insulators are Rubber, Dry wood, Dry cloth etc
Matter is anything that has weight and occupies space. All materials including living things which occupy a space and have weight are examples of matter. All matter is made up of different combination of atom which forms the molecules of the matter. There are about 100 different kinds of atom and all are called Element.

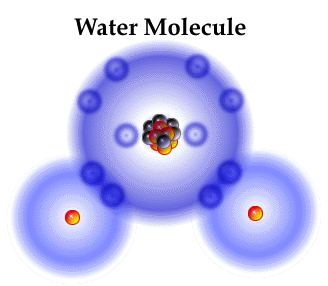
Molecule is the name given to the smallest part of matter which if further broken down will lose its original state.
molecule of water
Molecules are compounds made up of specific combinations of atoms. Familiar substances may theoretically be divided into single molecules, as modeled here, but no further. Like a strict recipe in which atoms are the ingredients, each molecule has a chemical formula. If any ingredients are subtracted or changed, the molecule becomes something completely different.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
What is matter
Explain molecules and how electricity is conducted
further studies
http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html
http://www.neok12.com/States-of-Matter.htm
http://scienceforkids.kidipede.com/chem ... ecules.htm
http://www.ducksters.com/science/molecules.php
LESSON 40
MAIN TOPIC : Basic ideas of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Atom
REFERENCE BK : Basic Technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. define atom
II. mention the components of an atom
III. draw the structure of an atom
CONTENT
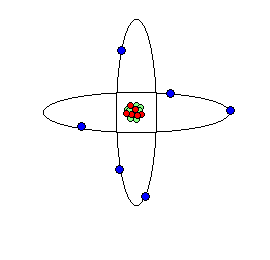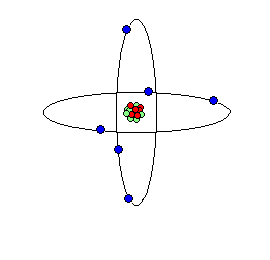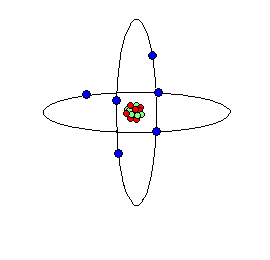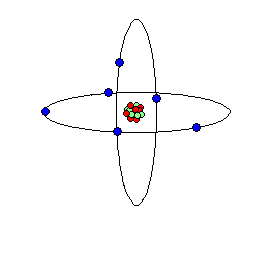
Atom is the result of breaking down the molecule of any matter beyond its original component. Atom under certain conditions breakdown and shoot out smaller particles of matter called electrons. This electron carries a negative charge of electricity. In all atoms the negatively charged electrons circle round their positively charged nucleus at a distance from the nucleus. The nucleus of any atom contains a number of proton each carrying a positive (+ve) charge of electricity along with a number of particles carrying a charge, which are called neutrons
An atom comprises of nucleus, proton, neutron and electron.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
define atom and explains the structure of an atom
mention examples of matter
further studies
http://www.kidskonnect.com/subjectindex ... atoms.html
http://kidsactivitiesblog.com/7833/atom-for-kids
http://scienceforkids.kidipede.com/chemistry/atoms/
http://www.ducksters.com/science/the_atom.php
http://www.sciencekidsathome.com/scienc ... _atom.html
practice test
http://chemistry.about.com/library/week ... omquiz.htm
http://chemistry.about.com/library/week ... noquiz.htm
http://www.mcwdn.org/chemist/atom/atomquiz.html
http://www.chem4kids.com/extras/quiz_at ... index.html
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Matter
REFERENCE BK : Basic Technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. define matter
II. explain molecule
CONTENT
Basic ideas of electricity
Basic ideas of electricity deals with the sciences leading with the use of radio, television, fans etc.

Electric current is the flow of electron in a conductor.
Conductors are materials that allow free flow of electron or electric charges. Examples are copper, aluminum, brass etc.

Insulators are materials that do not allow free flow of electric. They are called also called poor conductors .Examples of insulators are Rubber, Dry wood, Dry cloth etc
Matter is anything that has weight and occupies space. All materials including living things which occupy a space and have weight are examples of matter. All matter is made up of different combination of atom which forms the molecules of the matter. There are about 100 different kinds of atom and all are called Element.

Molecule is the name given to the smallest part of matter which if further broken down will lose its original state.
molecule of water
Molecules are compounds made up of specific combinations of atoms. Familiar substances may theoretically be divided into single molecules, as modeled here, but no further. Like a strict recipe in which atoms are the ingredients, each molecule has a chemical formula. If any ingredients are subtracted or changed, the molecule becomes something completely different.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
What is matter
Explain molecules and how electricity is conducted
further studies
http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html
http://www.neok12.com/States-of-Matter.htm
http://scienceforkids.kidipede.com/chem ... ecules.htm
http://www.ducksters.com/science/molecules.php
LESSON 40
MAIN TOPIC : Basic ideas of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Atom
REFERENCE BK : Basic Technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. define atom
II. mention the components of an atom
III. draw the structure of an atom
CONTENT
Atom is the result of breaking down the molecule of any matter beyond its original component. Atom under certain conditions breakdown and shoot out smaller particles of matter called electrons. This electron carries a negative charge of electricity. In all atoms the negatively charged electrons circle round their positively charged nucleus at a distance from the nucleus. The nucleus of any atom contains a number of proton each carrying a positive (+ve) charge of electricity along with a number of particles carrying a charge, which are called neutrons
An atom comprises of nucleus, proton, neutron and electron.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
define atom and explains the structure of an atom
mention examples of matter
further studies
http://www.kidskonnect.com/subjectindex ... atoms.html
http://kidsactivitiesblog.com/7833/atom-for-kids
http://scienceforkids.kidipede.com/chemistry/atoms/
http://www.ducksters.com/science/the_atom.php
http://www.sciencekidsathome.com/scienc ... _atom.html
practice test
http://chemistry.about.com/library/week ... omquiz.htm
http://chemistry.about.com/library/week ... noquiz.htm
http://www.mcwdn.org/chemist/atom/atomquiz.html
http://www.chem4kids.com/extras/quiz_at ... index.html
WEEK 7
MAIN TOPIC : Electric and magnetic
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Electric Field
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define magnetic field
II. Describe a magnet
III. Mention types of magnet
CONTENT
A magnet is a metallic object made of steel that has the property of attracting other metallic objects.

Magnetism is the ability of a magnet to attract magnetic substance.
There are three types of magnet.
1. Permanent magnet
2. Temporary magnet
3. Electromagnet
There are two poles in a magnet the North Pole and The south pole
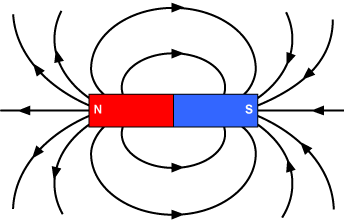
Electric Field: Is the region around a magnet where a magnet force felt. Magnetic field is always represented with a line of flow which is called magnetic flux . Magnetic flux encounter less opposition through a magnetic material such as iron than through a non magnetic material such as glass and copper.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe a magnet
Mention types of magnet
Define magnetic field
further studies
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefacts/magnets.html
http://www.physics4kids.com/files/elec_ ... field.html
http://www.superchargedscience.com/ar/magnet-123.htm
http://www.howstuffworks.com/magnet.htm
http://library.thinkquest.org/28682/eng ... /text.html
http://www.neok12.com/Magnetism.htm
http://www.school-for-champions.com/sci ... netism.htm
practice test
http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junio ... /magnetism
http://www.mcwdn.org/Physics/MagnetQuiz.html
http://www.first4magnets.com/magnet-quiz-304-c.asp
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Electric field
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define electric field
II. State the principle of electric field
CONTENT
ELECTRIC FIELD
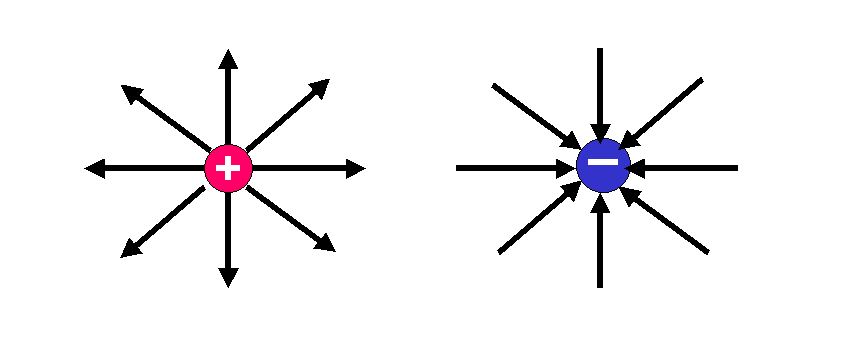
Electric field is the space around a charged body in which another charged body has a force exerted upon it. If a positively charged body is brought close to another charged body , it experiences a force which is known as electric force. The shape of and distribution of and electric field is represented by lines of electric flux which shows the direction of some typical electric field.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define electric field
Explain the principle of electric field
further studies
http://kidsresearchexpress-2.blogspot.c ... ields.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefac ... icity.html
http://kids.niehs.nih.gov/explore/pollute/emf.htm
http://www.kids.esdb.bg/electricity.html
LESSON 43
MAIN TOPIC : Components of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Resistance, Voltage and Current
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define electric circuit
II. Mention the types of electric circuit
CONTENT
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
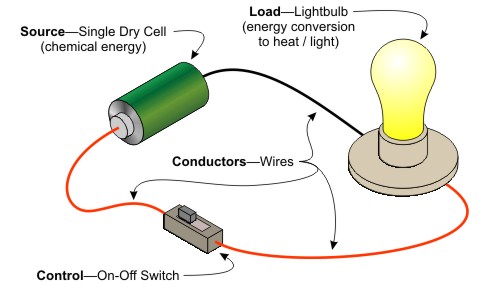
Electric circuit is the closed path of electricity .Is the channel through which electricty flows to where they will be used in terms of heat, sound etc.
TYPES OF ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
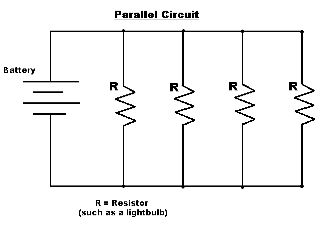
Parallel and series circuit
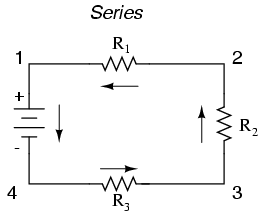
COMPONENT OF ELECTRICITY
The major components of electricity are
1. Resistance
2. Voltage
3. Current
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electricity. The unit of measuring resistance is ohms. The instrument for measuring resistance is called ohmmeter. The device that enables resistance is called resistor. Resistance of a resistor depends
1) The cross sectional area of the material
2) The length of the material
3) The resistivity of the material
4) The ambient temperature of the material
Voltage is the force that drives electric current in an electric circuit, the unit of voltage is volts. The other name for voltage is called electromotive force it can also be called potential difference, the instrument for measuring voltage is called voltmeter.
Current is the flow of charges in an electric conductor. The unit of measuring current is called Ampere and the instrument for measuring current is Ammeter.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define electric circuit
Explain all the components of electric circuit
further studies
http://idahoptv.org/dialogue4kids/seaso ... /facts.cfm
http://www.explainthatstuff.com/electricity.html
http://www.ducksters.com/science/static_electricity.php
http://kids.discovery.com/tell-me/curio ... cuits-work
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/curio ... ctures.htm
practice test & experiments
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... cuits.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... ctors.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... rials.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/experiment ... icity.html
http://www.firstschoolyears.com/science ... tyquiz.swf
http://resources.woodlands-junior.kent. ... /elec.html
http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/scie ... iz771.html
MAIN TOPIC : Inter- relations and interaction of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Working Principle of washing machine
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define magnetism
(2)explain the inter relation between electricity and magnetism
CONTENT
A relationship between electricity and magnetism was discovered in 1819 by a gentle man called Oersted. Another scientist called Ampere studied this observation and explain that a magnetic field exists around every current carrying conductor. He also explained that further that the magnetic field associated with the current must encircle the conduct. This relationship is called Electromagnetism. Many devices such as Amplify, Grinder, Generator, Telephone, microphones and loudspeakers are among few devices that use this principle for their operation. The basic principle of this electromagnetism is that Electric current flow will always produce some form of magnetism.
Magnetism is the ability of a material to attract another material.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
explains the relationship between magnet and electricity
further studies
http://www.kids.esdb.bg/faraday.html
http://library.thinkquest.org/12632/ele ... etism.html
http://www.neok12.com/Electromagnetism.htm
watch video
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d_aTC0iKO68
LESSON 45
MAIN TOPIC : Inter- relations and interaction of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Working principle of an electric bell
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Explain the principle of electric bell
(2)Draw a simple circuit of an electric bell.
CONTENT
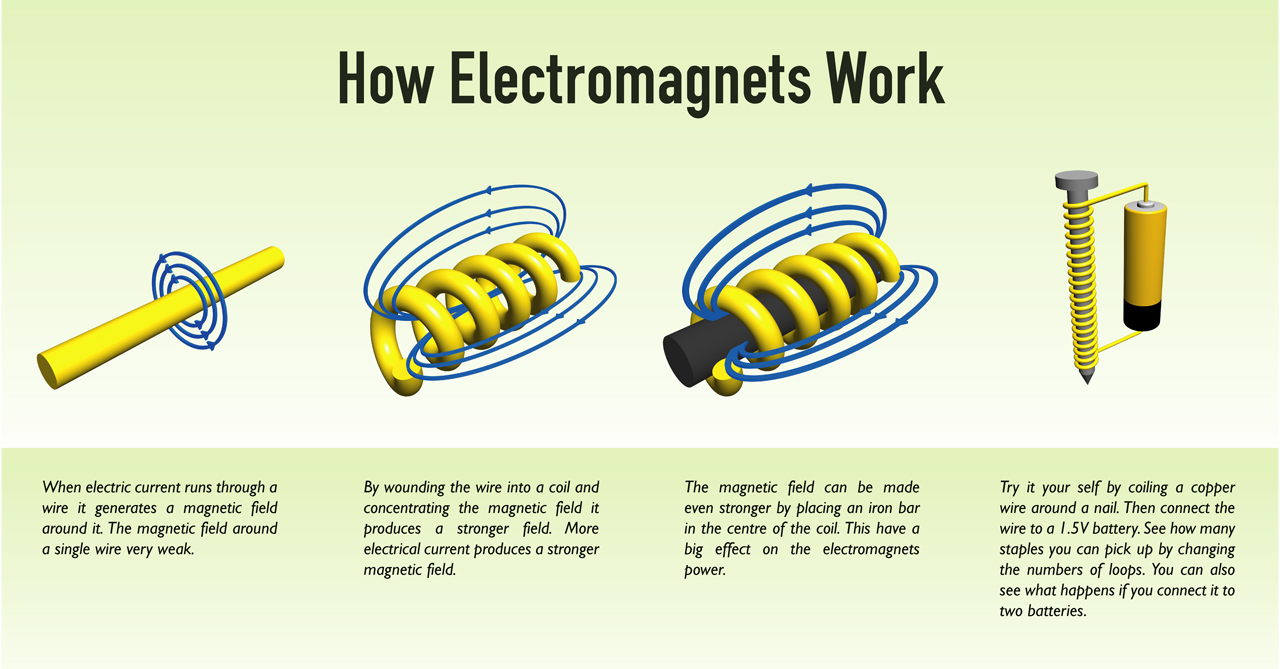
Electromagnet is a device in which a core of magnetic material is encircled by a coil of wire carrying an electric current, e.g. a coil wound round a soft iron or steel core.
Solenoid is a special purpose electromagnet designed for specific function. A solenoid is a coil of wire (usually insulated wire) consisting of many turns in one or more layers, wound on to moveable iron core.
Action of simple electric Bell
By pressing the bell button, a current flows from the positive terminal of the battery through the coil of the solenoid the along spring SS and the armature A, across the contact at C, through the closed switch of the negative terminal of the battery . The core of the solenoid becomes a temporary magnet, attracts the armature and causes the hammer attached to the armature to strike the bell. At the same time this movement of the armature will open the contact at C and break the circuit. The core immediately loses their magnetism and consequently their attraction on the armature. The spring SS returns the armature to its initial position. But since the press of the bell is on the process repeat itself.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
explain the relationship between magnet and electricity
explains solenoid and electromagnet
further studies
http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_are_the_ ... ctric_bell
http://harphys.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/bell.jpg
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/scien ... evision/4/
http://www.coolmagnetman.com/magsolen.htm
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/top ... ctromagnet
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... rbell3.htm
http://www.onlinephys.com/magnetism.html
practice test
http://wps.prenhall.com/chet_halderman_ ... index.html
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz2 ... b09c0.html
http://www.funtrivia.com/newflash/trivia.cfm?qid=259321
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Electric Field
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define magnetic field
II. Describe a magnet
III. Mention types of magnet
CONTENT
A magnet is a metallic object made of steel that has the property of attracting other metallic objects.

Magnetism is the ability of a magnet to attract magnetic substance.
There are three types of magnet.
1. Permanent magnet
2. Temporary magnet
3. Electromagnet
There are two poles in a magnet the North Pole and The south pole

Electric Field: Is the region around a magnet where a magnet force felt. Magnetic field is always represented with a line of flow which is called magnetic flux . Magnetic flux encounter less opposition through a magnetic material such as iron than through a non magnetic material such as glass and copper.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe a magnet
Mention types of magnet
Define magnetic field
further studies
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefacts/magnets.html
http://www.physics4kids.com/files/elec_ ... field.html
http://www.superchargedscience.com/ar/magnet-123.htm
http://www.howstuffworks.com/magnet.htm
http://library.thinkquest.org/28682/eng ... /text.html
http://www.neok12.com/Magnetism.htm
http://www.school-for-champions.com/sci ... netism.htm
practice test
http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junio ... /magnetism
http://www.mcwdn.org/Physics/MagnetQuiz.html
http://www.first4magnets.com/magnet-quiz-304-c.asp
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Electric field
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define electric field
II. State the principle of electric field
CONTENT
ELECTRIC FIELD
Electric field is the space around a charged body in which another charged body has a force exerted upon it. If a positively charged body is brought close to another charged body , it experiences a force which is known as electric force. The shape of and distribution of and electric field is represented by lines of electric flux which shows the direction of some typical electric field.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define electric field
Explain the principle of electric field
further studies
http://kidsresearchexpress-2.blogspot.c ... ields.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefac ... icity.html
http://kids.niehs.nih.gov/explore/pollute/emf.htm
http://www.kids.esdb.bg/electricity.html
LESSON 43
MAIN TOPIC : Components of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Resistance, Voltage and Current
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define electric circuit
II. Mention the types of electric circuit
CONTENT
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
Electric circuit is the closed path of electricity .Is the channel through which electricty flows to where they will be used in terms of heat, sound etc.

TYPES OF ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
Parallel and series circuit


COMPONENT OF ELECTRICITY
The major components of electricity are
1. Resistance
2. Voltage
3. Current
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electricity. The unit of measuring resistance is ohms. The instrument for measuring resistance is called ohmmeter. The device that enables resistance is called resistor. Resistance of a resistor depends
1) The cross sectional area of the material
2) The length of the material
3) The resistivity of the material
4) The ambient temperature of the material
Voltage is the force that drives electric current in an electric circuit, the unit of voltage is volts. The other name for voltage is called electromotive force it can also be called potential difference, the instrument for measuring voltage is called voltmeter.
Current is the flow of charges in an electric conductor. The unit of measuring current is called Ampere and the instrument for measuring current is Ammeter.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define electric circuit
Explain all the components of electric circuit
further studies
http://idahoptv.org/dialogue4kids/seaso ... /facts.cfm
http://www.explainthatstuff.com/electricity.html
http://www.ducksters.com/science/static_electricity.php
http://kids.discovery.com/tell-me/curio ... cuits-work
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/curio ... ctures.htm
practice test & experiments
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... cuits.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... ctors.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactiv ... rials.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/experiment ... icity.html
http://www.firstschoolyears.com/science ... tyquiz.swf
http://resources.woodlands-junior.kent. ... /elec.html
http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/scie ... iz771.html
MAIN TOPIC : Inter- relations and interaction of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Working Principle of washing machine
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define magnetism
(2)explain the inter relation between electricity and magnetism
CONTENT
A relationship between electricity and magnetism was discovered in 1819 by a gentle man called Oersted. Another scientist called Ampere studied this observation and explain that a magnetic field exists around every current carrying conductor. He also explained that further that the magnetic field associated with the current must encircle the conduct. This relationship is called Electromagnetism. Many devices such as Amplify, Grinder, Generator, Telephone, microphones and loudspeakers are among few devices that use this principle for their operation. The basic principle of this electromagnetism is that Electric current flow will always produce some form of magnetism.
Magnetism is the ability of a material to attract another material.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
explains the relationship between magnet and electricity
further studies
http://www.kids.esdb.bg/faraday.html
http://library.thinkquest.org/12632/ele ... etism.html
http://www.neok12.com/Electromagnetism.htm
watch video
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d_aTC0iKO68
LESSON 45
MAIN TOPIC : Inter- relations and interaction of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Working principle of an electric bell
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Explain the principle of electric bell
(2)Draw a simple circuit of an electric bell.
CONTENT
Electromagnet is a device in which a core of magnetic material is encircled by a coil of wire carrying an electric current, e.g. a coil wound round a soft iron or steel core.
Solenoid is a special purpose electromagnet designed for specific function. A solenoid is a coil of wire (usually insulated wire) consisting of many turns in one or more layers, wound on to moveable iron core.

Action of simple electric Bell
By pressing the bell button, a current flows from the positive terminal of the battery through the coil of the solenoid the along spring SS and the armature A, across the contact at C, through the closed switch of the negative terminal of the battery . The core of the solenoid becomes a temporary magnet, attracts the armature and causes the hammer attached to the armature to strike the bell. At the same time this movement of the armature will open the contact at C and break the circuit. The core immediately loses their magnetism and consequently their attraction on the armature. The spring SS returns the armature to its initial position. But since the press of the bell is on the process repeat itself.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
explain the relationship between magnet and electricity
explains solenoid and electromagnet
further studies
http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_are_the_ ... ctric_bell
http://harphys.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/bell.jpg
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/scien ... evision/4/
http://www.coolmagnetman.com/magsolen.htm
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/top ... ctromagnet
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... rbell3.htm
http://www.onlinephys.com/magnetism.html
practice test
http://wps.prenhall.com/chet_halderman_ ... index.html
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz2 ... b09c0.html
http://www.funtrivia.com/newflash/trivia.cfm?qid=259321
WEEK 7
TOPIC: SIMPLE BLUE PRINT READING
CONTENT: 1. Definition of Blue Print
2. Drawing as a language
3. Reading a building plan
Sub-Topic 1: Definition of Blue Print
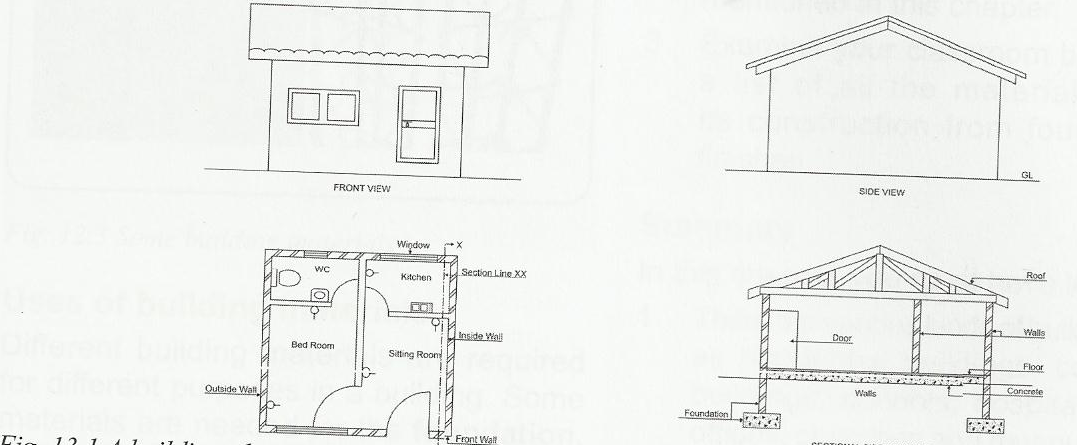
A blue print is a set of approved building drawings necessary to be put in place before construction commences. It is drawn by a draftsman or an architect on transparent paper and later printed on paper. Blue print is the means of communication between the builders and the architects. Blue prints are the complete drawings builders use at their building sites to build. Blue prints are also called working drawings. While the blue print is made by the architect, it is the duty of the builder to interpret it correctly. Mistakes or errors could be too costly; therefore, blue reading requires high-level knowledge of architectural and engineering drawings. It also requires ability to understand measurements and to measure accurately. An example of blueprint is the building plan, shown below:
Sub-Topic II: Drawing As a Language
Technical drawing is a universal language used for communication among technical people. Building design is done by written language in codes and symbols. The language of lines must be under stood first before the understanding of codes and symbols.
Types and Uses of Lines in Technical Drawing:
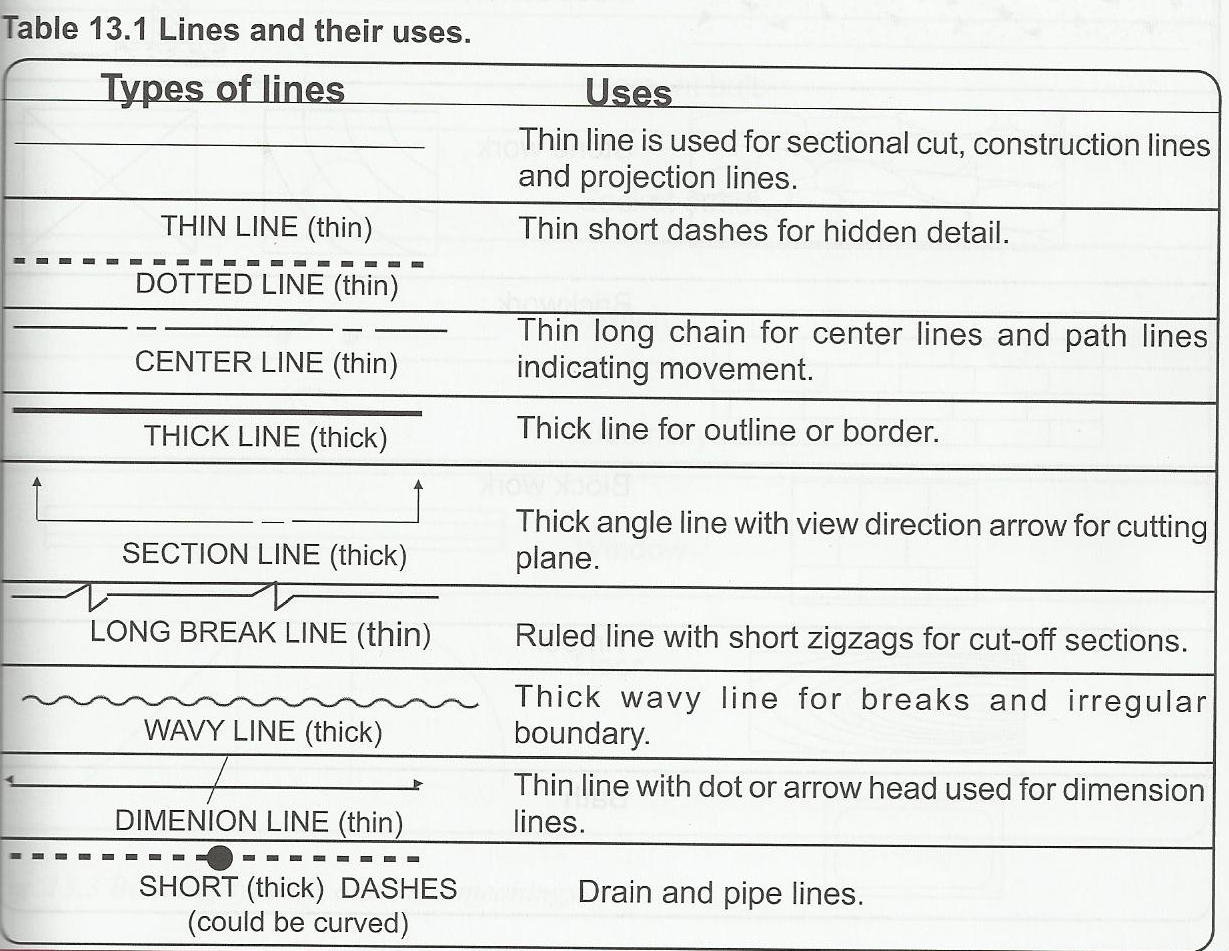
EVALUATION
1. Define the term ‘blue print’
2. Give a brief explanation on the role of an architect in building industry.
3. Thin continuous line is used for ------------- , -------------------- and ---------------------
4. -------------------- is a means of communication among the engineers and technical people
5. Arrow heads are used for --------------------------
Sub-Topic 3: Reading a Building Plan
The drawings prepared for building construction are many. They include:
(i) The Plan: A plan is a section viewed from the top. It is a common method of depicting the internal arrangement of a building in two dimensions.
(ii) Elevations: The front elevation shows how the building looks like when viewed from the front. It reveals the beauty of the building, as well as the back elevation which shows how the structure looks like when viewed from the back. Side views show the appearance of the building from the sides
(iii) Sectional view: This is the projection of a cut when viewed from the plan. This shows some hidden details within the building.
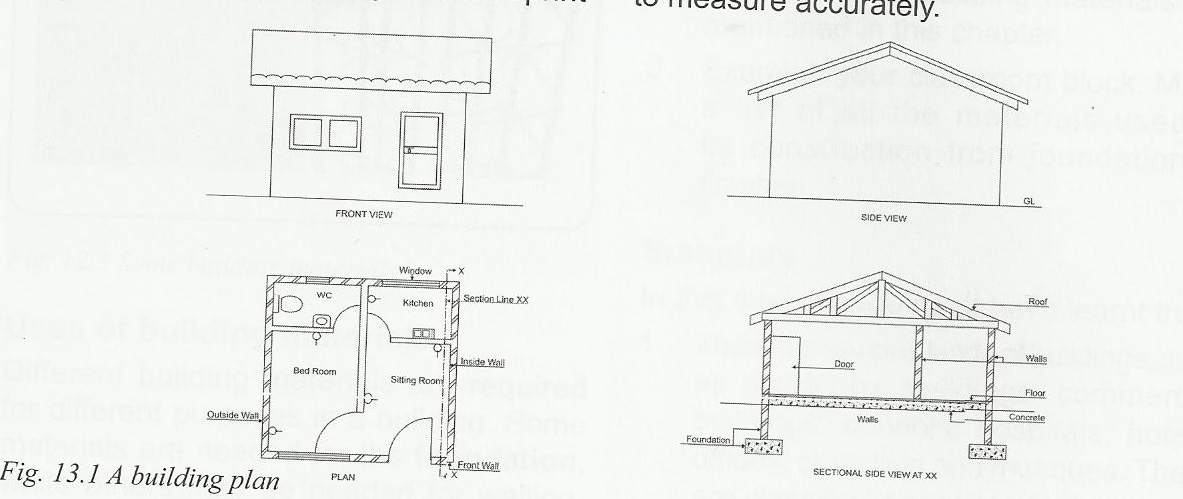
EVALUATION
(a) Why are building drawings necessary?
(b) Mention different types of drawings required for a building and why they are necessary.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about ‘Simple blue print reading-Identification of building components’.
TEXT : NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 1 Chapter 13 Pages 109 - 112.
ASSIGNMENT
Draw the following architectural symbols:
(i) Door
(ii) Window
(iii) Wall
(iv) Water closet
TOPIC: SIMPLE BLUEPRINT READING: IDENTIFICATION OF BUILDING COMPONENTS
CONTENT: 1. Building Symbols and their meanings
2. Building Symbols and their meanings (cont’d)
Sub-Topic I: Building Symbols and their meanings
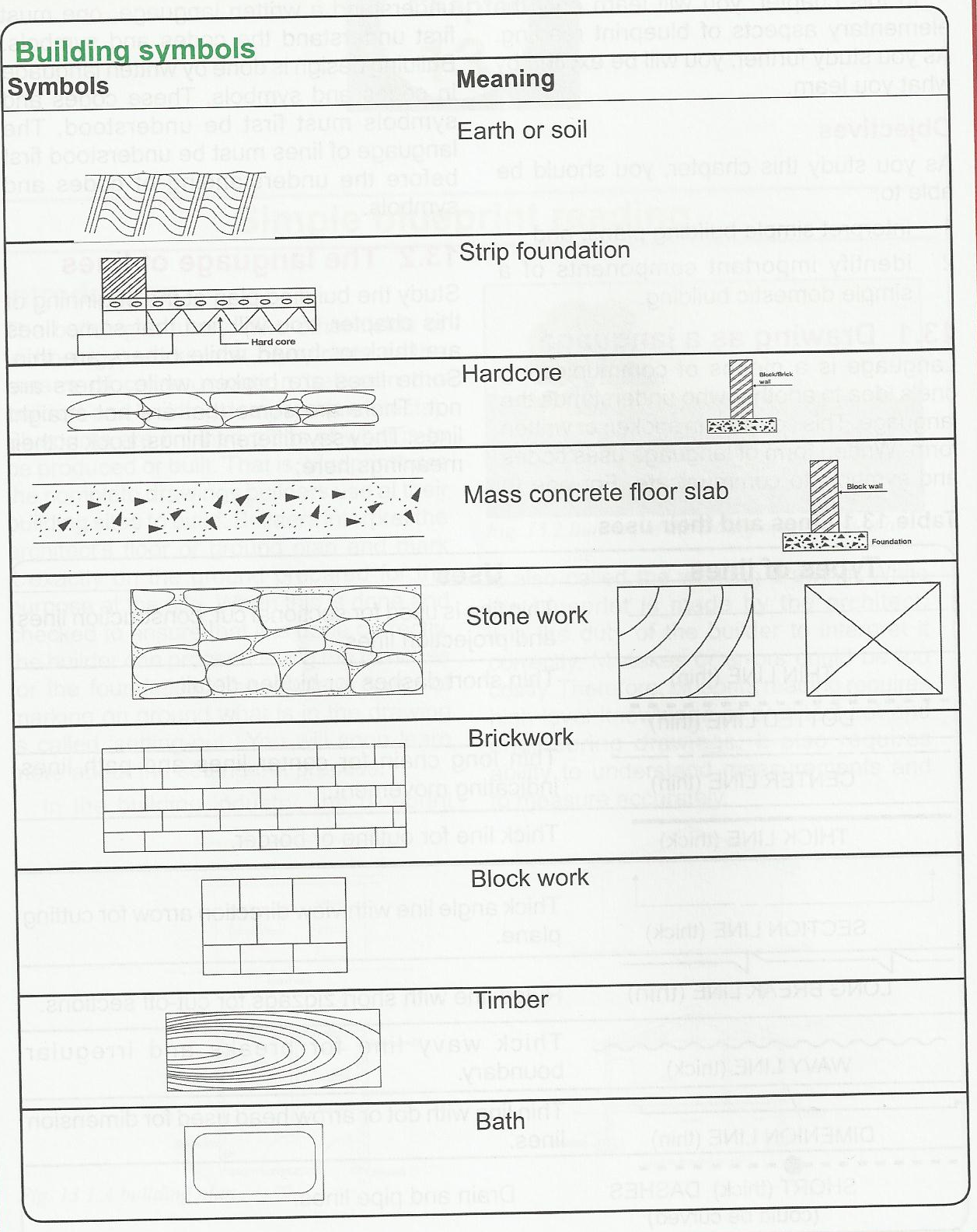
EVALUATION:
List any 5 building components
Sub-Topic 2: Building Symbols and their meanings (cont’d)
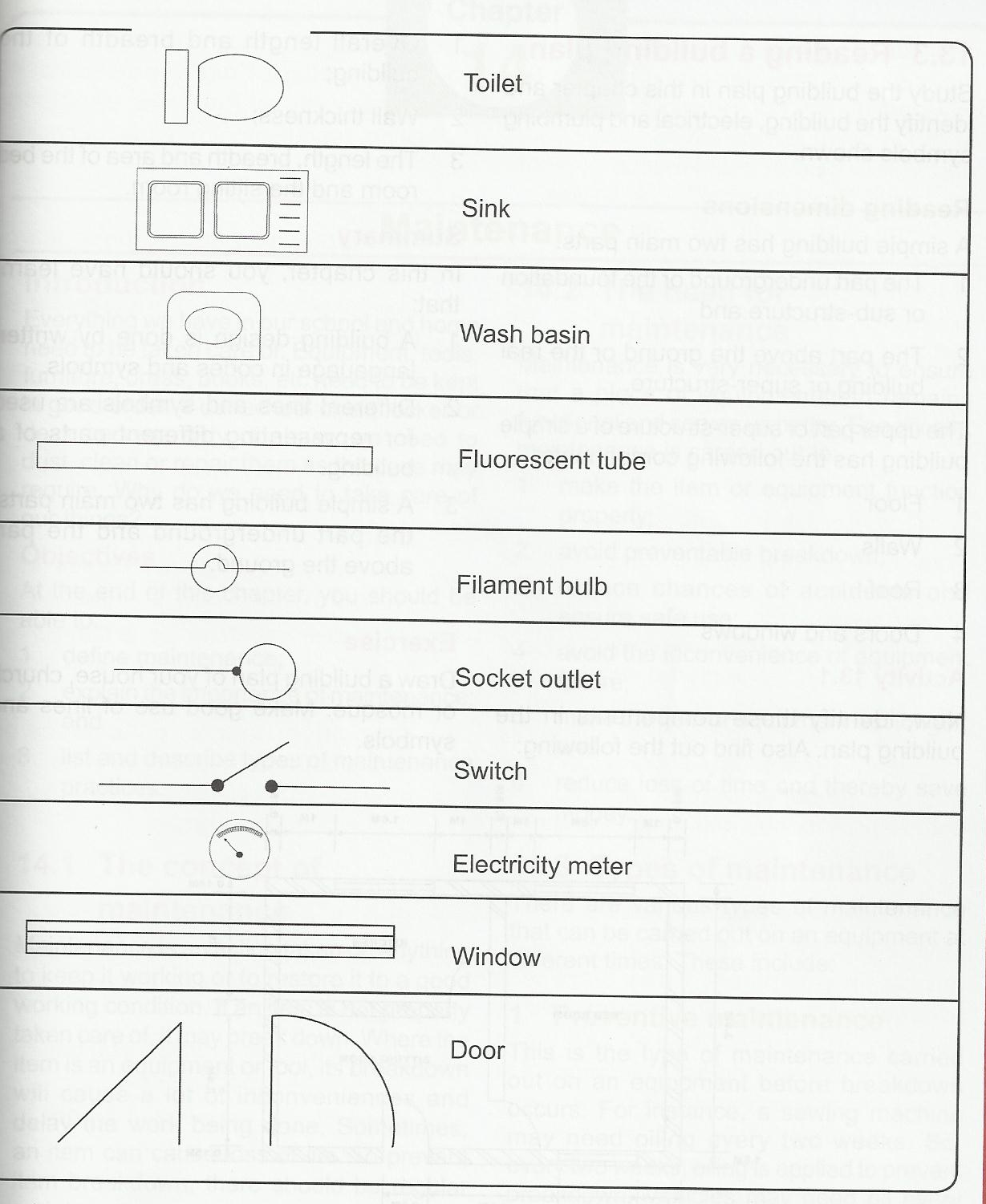
EVALUATION
Draw the symbols of any five building components that you know.
TEXT: NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 1 Chapter 14 pgs 113 – 114 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Draw the following architectural symbols:
(i) Door
(ii) Window
(iii) Wall
(iv) Water closet
2. Draw a hut
3. Study the plan of a one – bedroom building in your text book, pg 112, then draw:
a. The front elevation.
b. The back elevation.
CONTENT: 1. Definition of Blue Print
2. Drawing as a language
3. Reading a building plan
Sub-Topic 1: Definition of Blue Print
A blue print is a set of approved building drawings necessary to be put in place before construction commences. It is drawn by a draftsman or an architect on transparent paper and later printed on paper. Blue print is the means of communication between the builders and the architects. Blue prints are the complete drawings builders use at their building sites to build. Blue prints are also called working drawings. While the blue print is made by the architect, it is the duty of the builder to interpret it correctly. Mistakes or errors could be too costly; therefore, blue reading requires high-level knowledge of architectural and engineering drawings. It also requires ability to understand measurements and to measure accurately. An example of blueprint is the building plan, shown below:

Sub-Topic II: Drawing As a Language
Technical drawing is a universal language used for communication among technical people. Building design is done by written language in codes and symbols. The language of lines must be under stood first before the understanding of codes and symbols.
Types and Uses of Lines in Technical Drawing:

EVALUATION
1. Define the term ‘blue print’
2. Give a brief explanation on the role of an architect in building industry.
3. Thin continuous line is used for ------------- , -------------------- and ---------------------
4. -------------------- is a means of communication among the engineers and technical people
5. Arrow heads are used for --------------------------
Sub-Topic 3: Reading a Building Plan
The drawings prepared for building construction are many. They include:
(i) The Plan: A plan is a section viewed from the top. It is a common method of depicting the internal arrangement of a building in two dimensions.
(ii) Elevations: The front elevation shows how the building looks like when viewed from the front. It reveals the beauty of the building, as well as the back elevation which shows how the structure looks like when viewed from the back. Side views show the appearance of the building from the sides
(iii) Sectional view: This is the projection of a cut when viewed from the plan. This shows some hidden details within the building.

EVALUATION
(a) Why are building drawings necessary?
(b) Mention different types of drawings required for a building and why they are necessary.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about ‘Simple blue print reading-Identification of building components’.
TEXT : NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 1 Chapter 13 Pages 109 - 112.
ASSIGNMENT
Draw the following architectural symbols:
(i) Door
(ii) Window
(iii) Wall
(iv) Water closet
TOPIC: SIMPLE BLUEPRINT READING: IDENTIFICATION OF BUILDING COMPONENTS
CONTENT: 1. Building Symbols and their meanings
2. Building Symbols and their meanings (cont’d)
Sub-Topic I: Building Symbols and their meanings

EVALUATION:
List any 5 building components
Sub-Topic 2: Building Symbols and their meanings (cont’d)

EVALUATION
Draw the symbols of any five building components that you know.
TEXT: NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 1 Chapter 14 pgs 113 – 114 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Draw the following architectural symbols:
(i) Door
(ii) Window
(iii) Wall
(iv) Water closet
2. Draw a hut
3. Study the plan of a one – bedroom building in your text book, pg 112, then draw:
a. The front elevation.
b. The back elevation.
WEEK 8
TOPIC: MAINTENANCE: Concept of and Need for Maintenance
CONTENT: 1. Concept of maintenance
2. Need for maintenance.
Sub-Topic 1: Concept of Maintenance
Maintenance is defined as the work done on any engineering equipment to keep it in good operating condition. Everything we have in our school and home need to be taken care of so that they can serve us better. A driver checks the oil level, radiator water, battery, tyres, brakes etc in his car to see if there is any problem before he hits the road.

Evaluation
(1) What is maintenance?
(2) How can we maintain our items?
Sub-Topic 2: Need for maintenance
The following are the reasons or need for the maintenance of any item:
a. To make the equipment function properly
b. To avoid preventable breakdown
c. To reduce chances of accidents and ensure safe use
d. To avoid the inconvenience of equipment failure
e. To make the item last longer ;and
f. To reduce loss of time and thereby save money.
EVALUATION
Why do we need to maintain our equipment?
Text: The students should read more about ‘maintenance’ NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 14 Pages 113 - 114
TOPIC: MAINTENANCE: Importance and Types of Maintenance
CONTENT: i. Importance of Maintenance
ii. Types of Maintenance
Sub-Topic 1: Importance of Maintenance
Maintenance is the work done to keep or restore equipment to an acceptable working standard at a minimum cost. To avoid breakdown, an organization or individual should formulate an appropriate maintenance policy or plan. Maintenance is important so as to save cost and time that may be required for the installation of new equipment to replace the damaged ones. It is also necessary to prevent disappointment and loss of precious opportunities.
EVALUATION
1. Give a brief explanation on maintenance.
2. Why is maintenance necessary?
Sub Topic 2: Types of maintenance
The types of maintenance carried out on machines and equipment are grouped under the following:
(i) Predictive maintenance
(ii) Preventive maintenance
(iii) Corrective maintenance
(i) Predictive maintenance: this is the maintenance carried out using computers and other devices to predict impending breakdowns. Once the predictions are made, necessary remedies are immediately designed and applied to avoid those breakdowns.
Basically, predictive maintenance reduces the amount of other types of maintenance to be carried out on the equipment. However, what is important here is to carry out a routine check on the facilities for the predictive maintenance to ensure that they are still in place and functioning.
(ii) Preventive maintenance: This is the type of maintenance carried out on equipment before breakdown occurs. Typical examples of preventive maintenance are:
• Regular servicing of cars
• Regular oiling or lubricating of moving parts
• Regular painting of corrosive metal
• Regular cleaning of equipment routine checks on lubricants, safety gurds, nuts and bolts, studs, signal indicators.
• Routine checks on level of wears, alignment, tension of belt and chains.
(iii) Corrective maintenance: This involves actions taken to correct or restore broken down equipment to a functional state. The equipment may need a total overhaul and some parts may need to be replaced or repaired, and both require money and time.
EVALUATION
1) Mention the types of maintenance
2) State which of the three types of maintenance we should avoid. Give one reason for your answer
Text: Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools and Colleges Books 1 Page 91-96.
ASSIGNMENT
1) ________ is the most expensive maintenance
2) ________ is necessary in order to keep the machine in operating condition
3) Maintenance is cheaper than repair (a) True (b) False
4) Maintenance does not avoid wastage of money and time (a) True (b) False
5) The maintenance that should be most avoided is ______
Essay Questions:
1) What is maintenance?
2) List three types of maintenance
PRACTICAL PROJECTS AND TESTS
CONTENT: 1. Concept of maintenance
2. Need for maintenance.
Sub-Topic 1: Concept of Maintenance
Maintenance is defined as the work done on any engineering equipment to keep it in good operating condition. Everything we have in our school and home need to be taken care of so that they can serve us better. A driver checks the oil level, radiator water, battery, tyres, brakes etc in his car to see if there is any problem before he hits the road.

Evaluation
(1) What is maintenance?
(2) How can we maintain our items?
Sub-Topic 2: Need for maintenance
The following are the reasons or need for the maintenance of any item:
a. To make the equipment function properly
b. To avoid preventable breakdown
c. To reduce chances of accidents and ensure safe use
d. To avoid the inconvenience of equipment failure
e. To make the item last longer ;and
f. To reduce loss of time and thereby save money.
EVALUATION
Why do we need to maintain our equipment?
Text: The students should read more about ‘maintenance’ NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 14 Pages 113 - 114
TOPIC: MAINTENANCE: Importance and Types of Maintenance
CONTENT: i. Importance of Maintenance
ii. Types of Maintenance
Sub-Topic 1: Importance of Maintenance
Maintenance is the work done to keep or restore equipment to an acceptable working standard at a minimum cost. To avoid breakdown, an organization or individual should formulate an appropriate maintenance policy or plan. Maintenance is important so as to save cost and time that may be required for the installation of new equipment to replace the damaged ones. It is also necessary to prevent disappointment and loss of precious opportunities.
EVALUATION
1. Give a brief explanation on maintenance.
2. Why is maintenance necessary?
Sub Topic 2: Types of maintenance
The types of maintenance carried out on machines and equipment are grouped under the following:
(i) Predictive maintenance
(ii) Preventive maintenance
(iii) Corrective maintenance
(i) Predictive maintenance: this is the maintenance carried out using computers and other devices to predict impending breakdowns. Once the predictions are made, necessary remedies are immediately designed and applied to avoid those breakdowns.
Basically, predictive maintenance reduces the amount of other types of maintenance to be carried out on the equipment. However, what is important here is to carry out a routine check on the facilities for the predictive maintenance to ensure that they are still in place and functioning.
(ii) Preventive maintenance: This is the type of maintenance carried out on equipment before breakdown occurs. Typical examples of preventive maintenance are:
• Regular servicing of cars
• Regular oiling or lubricating of moving parts
• Regular painting of corrosive metal
• Regular cleaning of equipment routine checks on lubricants, safety gurds, nuts and bolts, studs, signal indicators.
• Routine checks on level of wears, alignment, tension of belt and chains.
(iii) Corrective maintenance: This involves actions taken to correct or restore broken down equipment to a functional state. The equipment may need a total overhaul and some parts may need to be replaced or repaired, and both require money and time.
EVALUATION
1) Mention the types of maintenance
2) State which of the three types of maintenance we should avoid. Give one reason for your answer
Text: Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools and Colleges Books 1 Page 91-96.
ASSIGNMENT
1) ________ is the most expensive maintenance
2) ________ is necessary in order to keep the machine in operating condition
3) Maintenance is cheaper than repair (a) True (b) False
4) Maintenance does not avoid wastage of money and time (a) True (b) False
5) The maintenance that should be most avoided is ______
Essay Questions:
1) What is maintenance?
2) List three types of maintenance
PRACTICAL PROJECTS AND TESTS
WEEK 9
Simple Machines
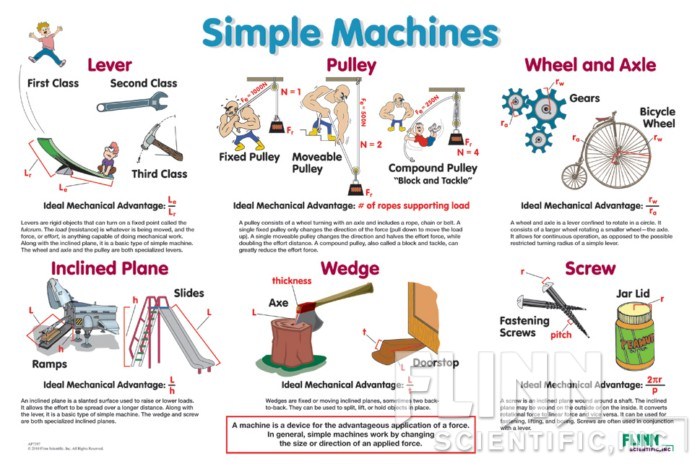
http://www.fi.edu/qa97/spotlight3/
http://www.mikids.com/Smachines.htm
http://www.cosi.org/downloads/activitie ... s/sm1.html
http://legacy.mos.org/sln/Leonardo/Inve ... olbox.html
http://scienceforkids.kidipede.com/physics/machines/
Maintenance
Machine Maintenance and Simple Troubleshooting for a Sewing Machine

1. Machine Maintenance
2. Cleaning • The machine should be carefully cleaned of dust, lint, and thread before it is used and again before it is put away. • Thread, carelessly left, often results in damage to the shuttle and in the blunting of needles.
3. Oiling • Oiling keep the parts working smoothly and without unnecessary wear. • Only a drop of oil once a week may be required.
Places on the sewing machine which require oiling include: – two or more points on the treadle – two points on the band-wheel crank – one point on the band wheel
The head of the machine has many more point which needs to be oiled. • If a more thorough oiling is necessary, the upper thread, presser foot, face plate, slide plate, bobbin, bobbin case, and throat plate should be removed. The shuttle case should then be cleaned and oiled.
The arrows show where the machine is to be oiled
The arrows show where the machine is to be oiled
Caring for the Sewing Machine
Wipe off dust from the exposed parts. 2. Lower or raise the head by holding the arm carefully. 3. With soft cloth, clean the: – tension regulator – take-up lever and thread guides – bobbin case and shuttle – machine surface holes
Do not use detergents for cleaning 5. Using the lint brush, clean the: – feed dog – shuttle (area under the throat plate)
Sew a line of stitching on a scrap material to remove excess oil 7. If there is a need to disassemble some parts, remember how they were placed 8. Replace each part carefully using the correct screwdriver
Lubricate the bottom part of the machine by tilting the machine back and oil parts indicated below 10.Put 2-3 layers of swatches between presser foot and feed dog. Keep the sewing machine in its bed and cover.
Clucking noise. This happens when the top tension is not properly or correctly threaded. Re-thread the upper tension from the thread guide. 2. Stuck balance wheel. This happens when threads tangle around the bobbin. Gently rock the balance wheel back and forth to untangle the thread. Slowly pull out the thread with tweezers.
Puckered stitches. This happens when the point is blunt or bent. Replace needle with a new one.
Machine skip stitches. This is caused by using the wrong size of the needle specified for the kind of fabric being sewn. Make sure you have the right size of the needle. 5. Fabric does not move. This happens when the feed dog is not adjusted to the correct sewing position. Raise the feed dog by turning the feed dog regulator or darning knob. 6. Uneven stitches. This is caused by holding tight or pulling back the fabric while sewing. Hold the fabric lightly as you stitch.
Needle breaks. This happens when the needle strikes the presser foot or around the needle hole. Tighten the presser foot to avoid misaligning the needle, the presser foot and the needle hole.
Thread breaks at the needle eye. This happens when the needle eye is not threaded correctly. Thread the needle properly following the direction of the arrow indicated in the throat plate. The needle must be placed with the needle groove turned toward the side from which the needle is threaded.
Copied from: CJ Fajilan reference books and internet -
http://www.woodshopnews.com/columns-blo ... and-simple
http://www.tapco-europe-tools.com/Care_ ... Video.html
practice test
http://atlantis.coe.uh.edu/archive/scie ... 1/test.htm
http://www.neok12.com/quiz/SIMACH02
http://www.mikids.com/SimpleMachines/smquiz.htm
http://www.edinformatics.com/math_scien ... s_quiz.htm
http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junio ... e-machines
Buildings: Types

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_building_types
http://www.clearybuilding.com/Types.htm
Materials

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_building_materials
https://www.google.com.ng/search?q=buil ... d=0CGYQsAQ
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/curio ... erials.htm
Building Construction


http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... htm#page=9
http://photosofinteriors.com/contact-us ... cture.html
https://www.google.com.ng/search?q=buil ... d=0CGwQsAQ
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.erp.oissel.onac.org/anglais/ ... onquiz.htm
http://archives.library.oregonstate.edu ... /quiz.html
http://uapccd.blogspot.com/2011/10/buil ... -quiz.html

http://www.fi.edu/qa97/spotlight3/
http://www.mikids.com/Smachines.htm
http://www.cosi.org/downloads/activitie ... s/sm1.html
http://legacy.mos.org/sln/Leonardo/Inve ... olbox.html
http://scienceforkids.kidipede.com/physics/machines/
Maintenance
Machine Maintenance and Simple Troubleshooting for a Sewing Machine

1. Machine Maintenance
2. Cleaning • The machine should be carefully cleaned of dust, lint, and thread before it is used and again before it is put away. • Thread, carelessly left, often results in damage to the shuttle and in the blunting of needles.
3. Oiling • Oiling keep the parts working smoothly and without unnecessary wear. • Only a drop of oil once a week may be required.
Places on the sewing machine which require oiling include: – two or more points on the treadle – two points on the band-wheel crank – one point on the band wheel
The head of the machine has many more point which needs to be oiled. • If a more thorough oiling is necessary, the upper thread, presser foot, face plate, slide plate, bobbin, bobbin case, and throat plate should be removed. The shuttle case should then be cleaned and oiled.
The arrows show where the machine is to be oiled
The arrows show where the machine is to be oiled
Caring for the Sewing Machine
Wipe off dust from the exposed parts. 2. Lower or raise the head by holding the arm carefully. 3. With soft cloth, clean the: – tension regulator – take-up lever and thread guides – bobbin case and shuttle – machine surface holes
Do not use detergents for cleaning 5. Using the lint brush, clean the: – feed dog – shuttle (area under the throat plate)
Sew a line of stitching on a scrap material to remove excess oil 7. If there is a need to disassemble some parts, remember how they were placed 8. Replace each part carefully using the correct screwdriver
Lubricate the bottom part of the machine by tilting the machine back and oil parts indicated below 10.Put 2-3 layers of swatches between presser foot and feed dog. Keep the sewing machine in its bed and cover.
Clucking noise. This happens when the top tension is not properly or correctly threaded. Re-thread the upper tension from the thread guide. 2. Stuck balance wheel. This happens when threads tangle around the bobbin. Gently rock the balance wheel back and forth to untangle the thread. Slowly pull out the thread with tweezers.
Puckered stitches. This happens when the point is blunt or bent. Replace needle with a new one.
Machine skip stitches. This is caused by using the wrong size of the needle specified for the kind of fabric being sewn. Make sure you have the right size of the needle. 5. Fabric does not move. This happens when the feed dog is not adjusted to the correct sewing position. Raise the feed dog by turning the feed dog regulator or darning knob. 6. Uneven stitches. This is caused by holding tight or pulling back the fabric while sewing. Hold the fabric lightly as you stitch.
Needle breaks. This happens when the needle strikes the presser foot or around the needle hole. Tighten the presser foot to avoid misaligning the needle, the presser foot and the needle hole.
Thread breaks at the needle eye. This happens when the needle eye is not threaded correctly. Thread the needle properly following the direction of the arrow indicated in the throat plate. The needle must be placed with the needle groove turned toward the side from which the needle is threaded.
Copied from: CJ Fajilan reference books and internet -
http://www.woodshopnews.com/columns-blo ... and-simple
http://www.tapco-europe-tools.com/Care_ ... Video.html
practice test
http://atlantis.coe.uh.edu/archive/scie ... 1/test.htm
http://www.neok12.com/quiz/SIMACH02
http://www.mikids.com/SimpleMachines/smquiz.htm
http://www.edinformatics.com/math_scien ... s_quiz.htm
http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junio ... e-machines
Buildings: Types

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_building_types
http://www.clearybuilding.com/Types.htm
Materials

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_building_materials
https://www.google.com.ng/search?q=buil ... d=0CGYQsAQ
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/curio ... erials.htm
Building Construction


http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... htm#page=9
http://photosofinteriors.com/contact-us ... cture.html
https://www.google.com.ng/search?q=buil ... d=0CGwQsAQ
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.erp.oissel.onac.org/anglais/ ... onquiz.htm
http://archives.library.oregonstate.edu ... /quiz.html
http://uapccd.blogspot.com/2011/10/buil ... -quiz.html
