TOPIC: MANAGEMENT REQUIREMENT IN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY.
CONTENTS: i. Housing and Feeding
ii. Hygiene and Medication
iii. Rearing of Farm animals to maturity
SUB-TOPIC 1: HOUSING AND FEEDING
For effective production of farm animals, it is important to have convenient and durable buildings, good feeds and equipments.
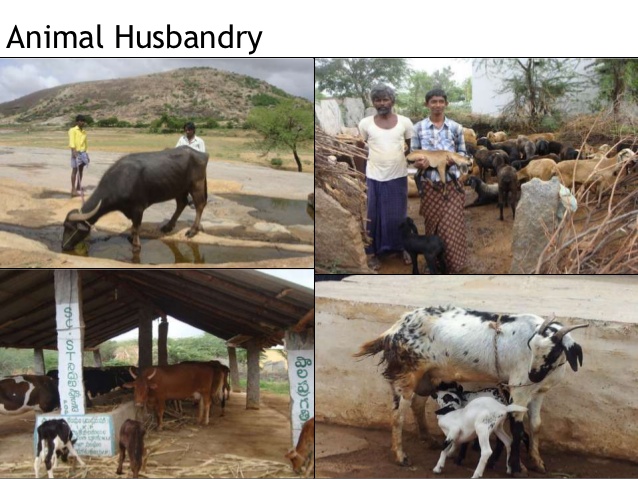
HOUSING: Ruminants such as cattle, sheep and goats do not require special housing. However, under intensive system, they are provided with barns, sheds/shelter and fences to protect them from adverse weather conditions such as severe cold, heat, wind and rain; it also protect them from thieves, straying and keep the incidence of pests and diseases at barest minimum.
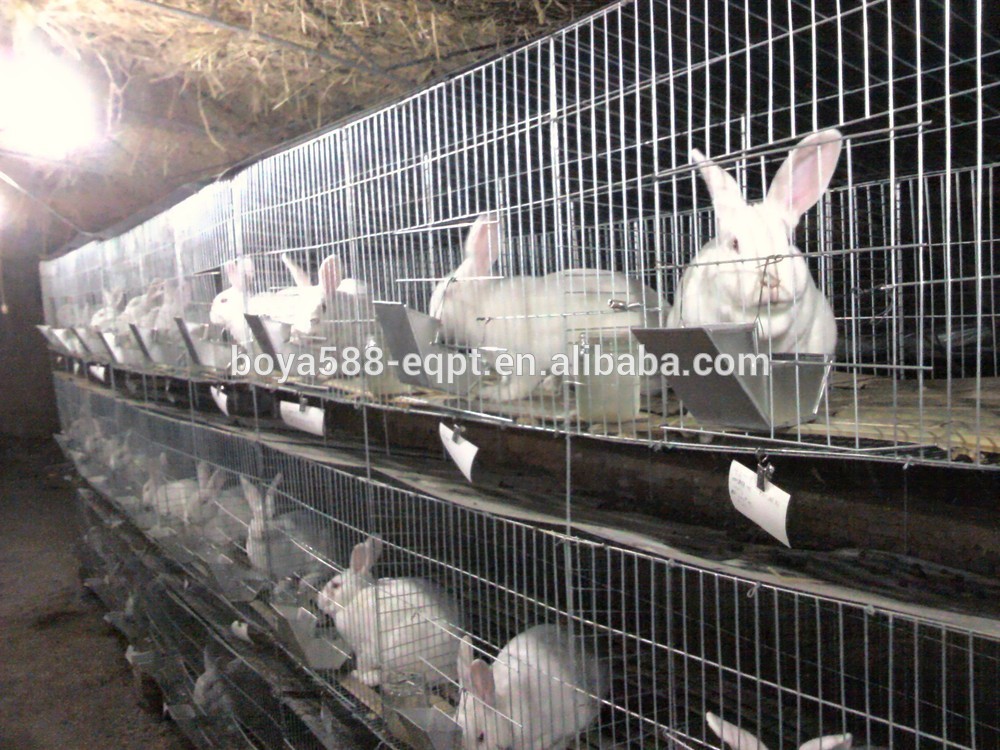
Non-ruminant animals such as pig, poultry etc require well-built houses of which floor are made of concrete (to control internal parasites) and roof made of iron or asbestos sheet. There are three types of housing in pig management. They are farrowing house, breeding house and fattening house. For poultry, we have brooder house for rearing chicks, growers’ house for raising growers and deep litter/battery cages for rearing growers and layers respectfully. In rabbit management, well-ventilated and properly lighted houses called hutches (constructed of wire mesh, wood or both) are provided to keep them from cold, wind, heat and rain.

FEEDING: Farm animals require good feeding for optimum production. They need all essential feed nutrients for growth, good health and productivity. Different farm animals require different feeds at different times depending on: a. purpose of production b. digestive system c. age d. cost of feed e. seasons of growth f. stage of growth/development.
Ruminant animals grow well on pasture because of their complex stomach and the presence of bacteria in their rumen which can digest forages. However, concentrate feed and supplements should be given them to improve their production.
Non-ruminant animals on the other hand need concentrate feed because of their simple stomach that cannot digest roughages. Creep feed/pellets, weaners mash, lactating ration, flushing/steaming up, fatteners/finishers mash and breeders mash are examples of concentrates for feeding pigs. Chicks mash, Growers mash, Layers mash, Broilers starter and Broilers finisher are examples of poultry feeds.


FEEDING/REARING EQUIPMENT
CATTLE: These include shade, stock, breeding rack, dipping vat/spraying equipment, calf creep, mineral feeder, scales and silos.
SHEEP/GOAT: These are grain trough, water trough and dipping vat.
POULTRY: Water trough, feeding trough, grit container, dip equipment, brooder, incubators
PIG: Wallow, feeding trough, water trough, brooder.
EVALUATION
1. State three houses for cattle, sheep and goat.
2. The well-ventilated house for rearing rabbit is known as……
3. List five factors that determine feeding of farm animals.
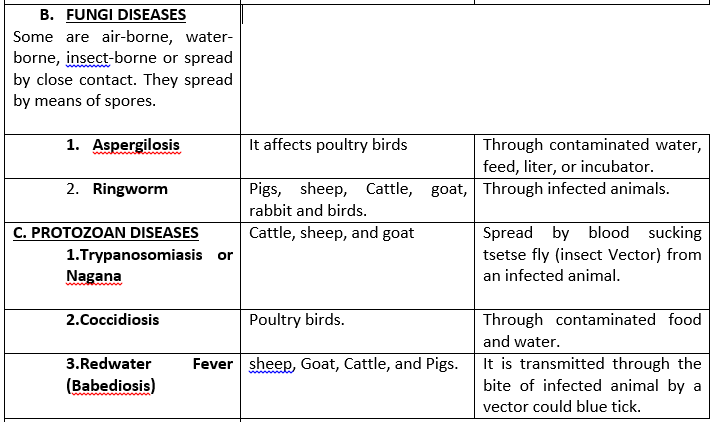
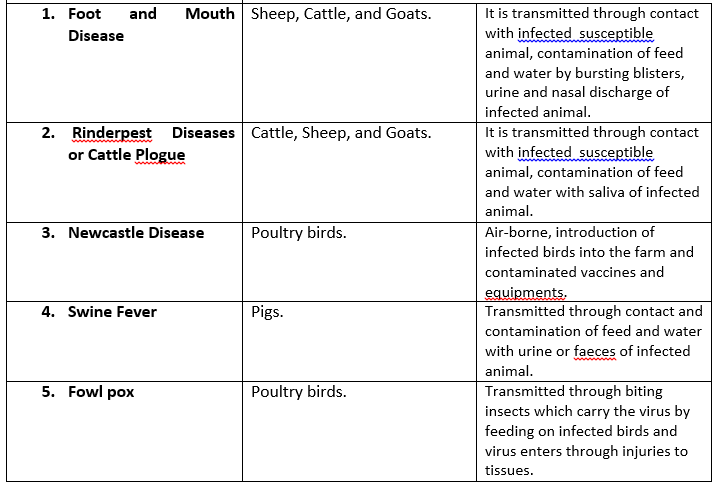
SUB-TOPIC 2: HYGIENE AND MEDICATION
In livestock farming, emphasis is placed on prevention rather than cure/control. This is to prevent economic loss and time wastage. All farm animals should therefore be provided with clean and well-ventilated housing, dry bedding and good feeds. The following are preventive measures to be taken:
1. Animals’ pens, feeding and water troughs should be cleaned daily.
2. Examine the animals regularly for any sign of pests and diseases.
3. Vaccinate the animals at the appropriate time against viral and bacterial diseases.
4. Isolate the sick/diseased animals from the healthy ones.
5. Disinfect the pens at regular interval especially before the arrival of new stock.
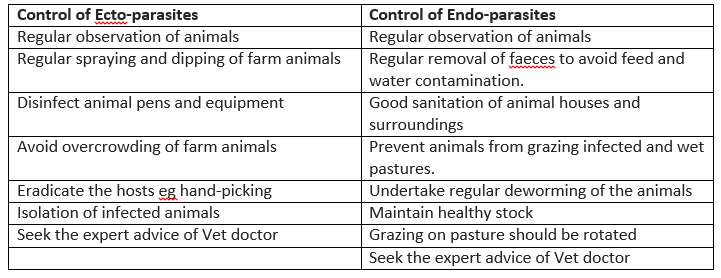
6. Deworm the animals against endo-parasites and delouse/spray them against ecto-parasites.
7. Remove and burn/bury the dead animals.
8. Contact Vet doctor in case of serious disease infection.
9. Remove contaminated feed, beddings and faeces from the pen.
10. Debeak the birds to prevent pecking and egg-sucking.

EVALUATION
1. Why is prevention better than cure?
2. State five preventive measures to be observed in by livestock farmers.
3. Who is the specialist in treating animals’ diseases?
SUB-TOPIC 3: REARING OF FARM ANIMALS TO MATURITY
Rearing is the sum total of all the activities or processes involved in bringing farm animals to maturing. These processes include:
1. For mammals such as cattle, sheep, goat, pig, rabbit etc, rearing involve three major periods
i. Breeding (mating and pregnancy period) to parturition (production of young ones).

ii. Calves/lambs/kids/piglets/kittens to weaning.(Routine management practices like dehorning, tattooing[branding], castration etc) are carried out during this period.

iii. Weaning to finishing/fattening.

2. For non-mammals like poultry, rearing involves
i. Breeding (mating and laying of eggs).
ii. Incubation and candling.
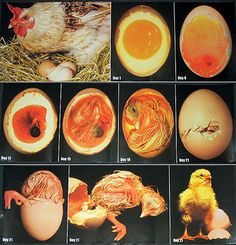
iii. Hatching and sexing.

iv. Brooding.(Rearing of chicks i.e pullet chicks and or broiler chicks in deep litter houses)

v. Grower and finisher stage (Rear in deeper litter houses).

vi. Layers stage (Rear in battery cages).

MATURITY AGE AND MARKET SIZE/WEIGHT OF FARM ANIMALS
Animals Age (months) Weight (kg)
Cattle 12-20 200-360
Sheep 8-12 35-45
Goat 10-14 40-60
Pig 7 60-70
Rabbit 4-6 4-5
Poultry 9-12 weeks 2.5-3
MARKETING OF LIVESTOCK AND LIVESTOCK PRODUCTS
In most West African countries including Nigeria, the Northern part supplies the major quantity of meat consumed by the South. Live animals are slaughtered, dressed and frozen/processed and sold for consumption. The marketing channels are thus: Producer > Middle men (wholesalers and retailers) > Consumers.

EVALUATION
1. Define rearing.
2. Mention three routine management practices you know.
3. State the marketing channels for farm animals and their products in Nigeria.
4. List the processes involved in rearing poultry birds to maturity.
ASSIGNMENT
Junior School Agriculture Workbook 2, chapter 10, No 26-47 by Anthony et al
READING ASSIGNMENT
Junior School Agriculture book 2 chapter 13 pages 165-171by Anthony et al
REFERENCE TEXTS
1. Junior School Agriculture book 2 by Anthony et al
2. Essentials of Agricultural Science for JSS by EC Anie.