TOPIC: HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS
Content: i. Electronic counting devices and modern computer: William Bill Gate, Philip Emeagwali, John Von Neuman etc
ii. Generation of Computers – First, second, third, fourth and fifth generations.
Sub-Topic: Electronic counting devices and modern computer: William Bill Gate, Philip Emeagwali, John Von Neuman
William Bill Gate
Bill H.W. Gates is the founder and the chairman of Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft is a software services and solution industry and the fastest growing company in the PC industry. Bill Gate is the richest businessman in the world today.
He was born on October 28, 1955 to the family of William H. Gates II (father), who was a Seattle attorney and his late mother Mary Gates was a schoolteacher. He grew in Seattle with his sisters.
He entered Harvard University as a freshman in 1973 and was dropped out of Harvard to create what eventually becomes Microsoft. While at Harvard, Gate developed a version of programming language BASIC for the first microcomputer. His foresight and vision for personal computing has been the central to the success of Microsoft and the software industry. He was guided by a belief that the computer would be a valuable tool on every desktop and in every home; he therefore began to develop software for personal computers.
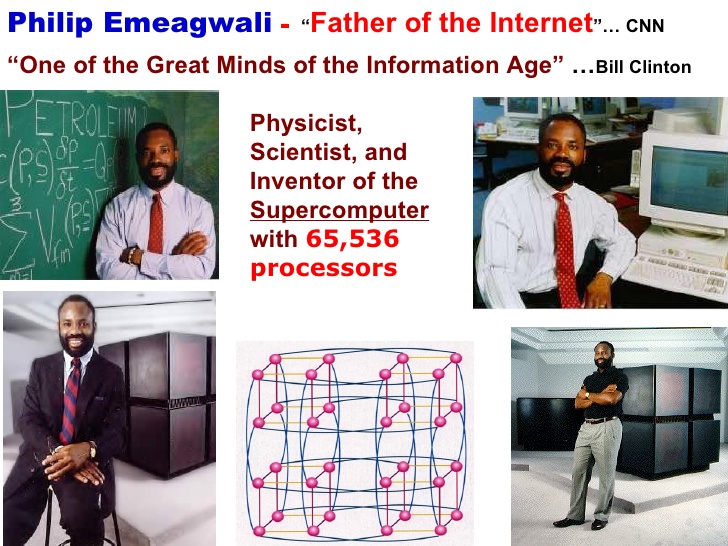
 Philip Emeagwali
Philip Emeagwali
He is a Nigerian, a pride of Africa and the Black race was born on August 23, 1954 in Akure and now base in the US. In April 1967, he was displaced from school due to the civil war which claimed the lives over 50,000 Igbo indigenes.
Philip was determined and by 1973, he earned his first diploma from the University of London through self study and subsequently got a scholarship to Oregon State University. This marked the beginning of his fine career. Philip Emeagwali has received more than 100 prizes, awards and honours.
He applied the power of networked computers to the analysis of oil field services. In the 1980’s, he worked on advanced formulas in networked computers. This achievement led him to win the Gordon Bell Super Computing prize in 1989. Apart from this, he has won several awards including a 1998 Distinguished Scientist Award from the World Bank.
Sub-Topic 2: Generation of Computers – First, second, third, fourth and fifth generations.
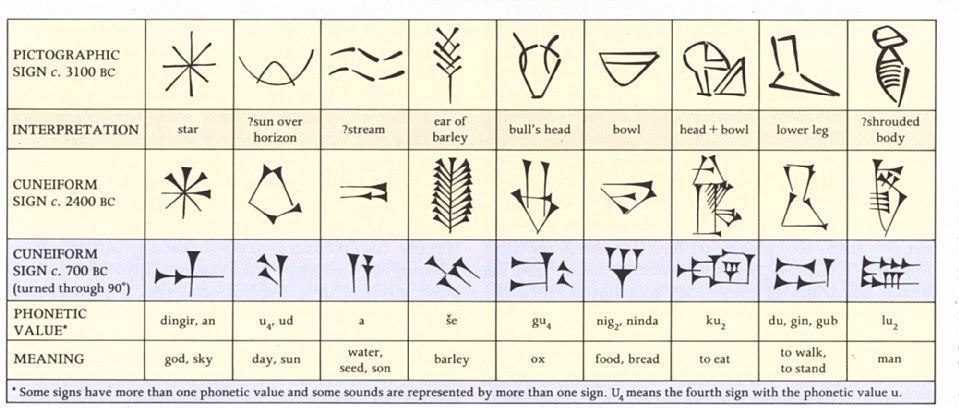
GENERATIONS OF COMPUTER:
Generation of computers are the developmental stages that the computer has gone through. There are 5 generations of computers and their accompanying innovations.
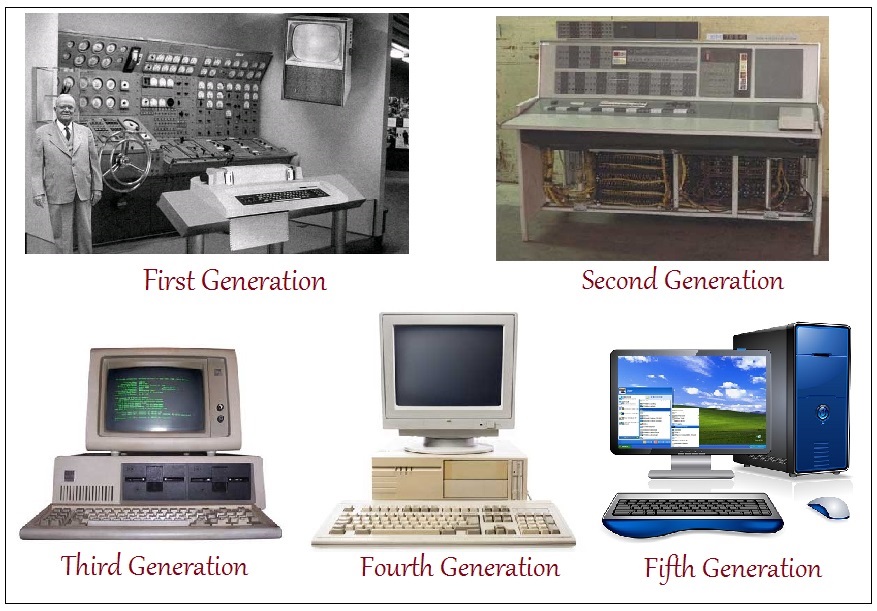
1ST GENERATION
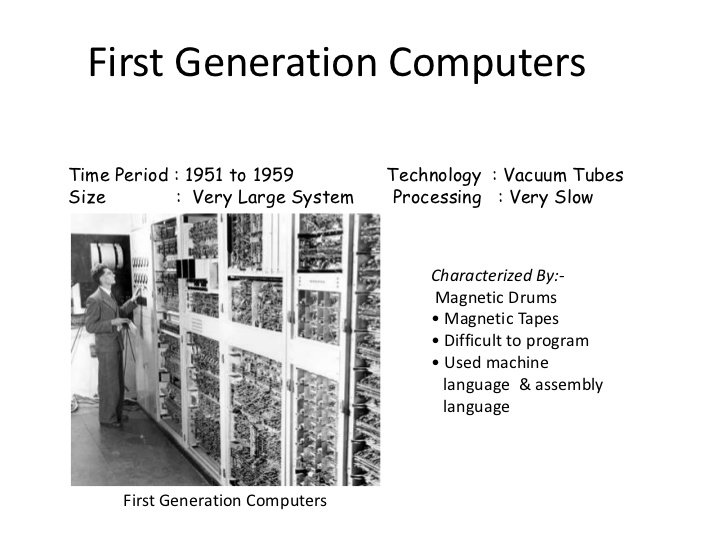
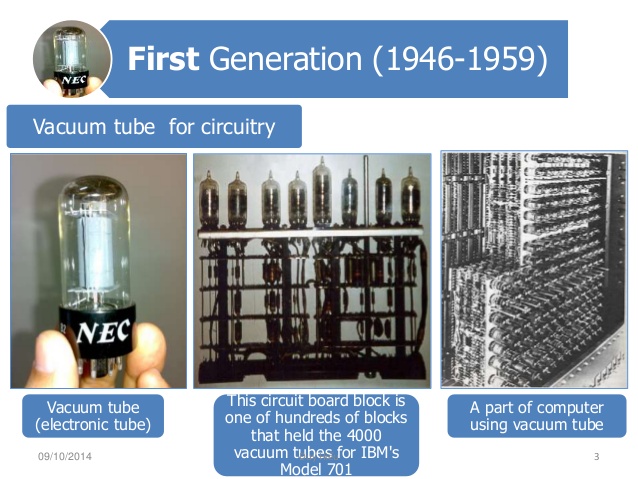
First generation computers were those manufactured between 1946 and 1960. The computers used the stored program concept. First generation computers were associated with the vacuum tubes or valves technology.
CHARACTERISTICS:
They were very bulky and heavy.
They measured between 50 – 100ft long and about 80ft high.
The computers weighed up to 200 tons and occupied 3000 cubic ft.
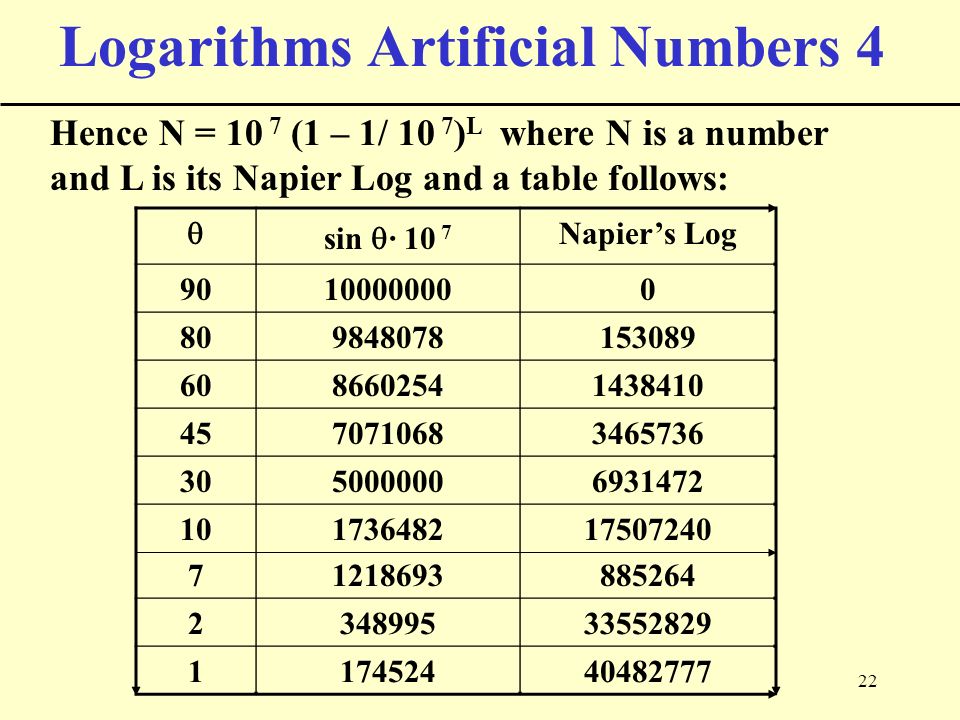
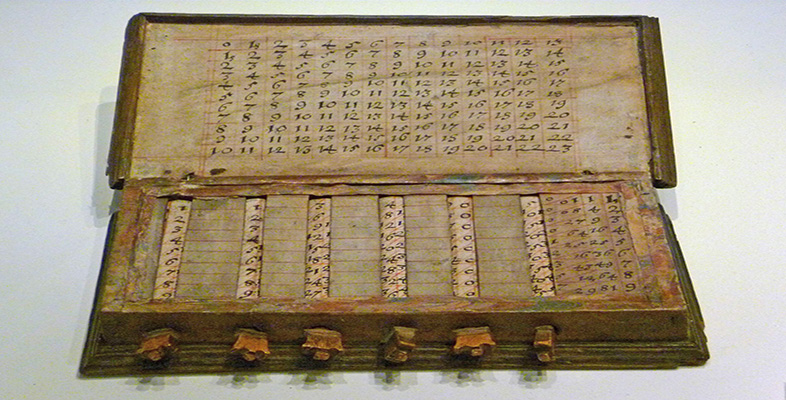
They used vacuum tubes to store and process data.
Examples of first generation computers are ENIAC, EDSAC, and UNIVAC.
PROBLEMS OF FIRST GENERATION COMPUTERS
1. The vacuum tubes also generated a lot of heat. Therefore they needed a cooling system.
2ND GENERATION TRANSISTOR
Second generation computers were developed between 1960 and 1964. The computers used transistors. The transistor was invented by William Shockley in 1948. Magnetic tapes were used for storage.
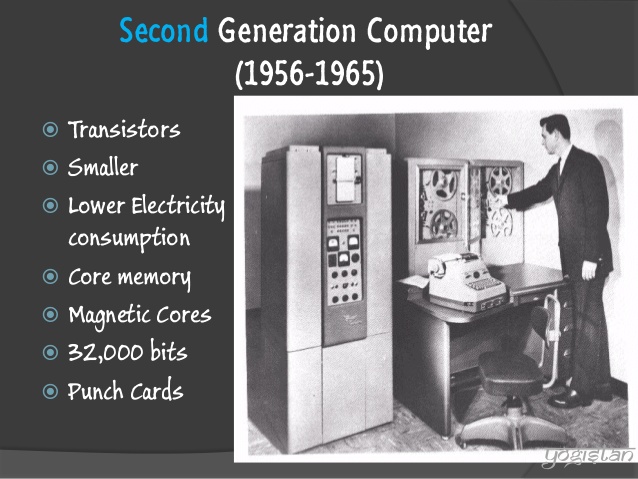
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. They were smaller in size than first generation computers.
2. They occupied smaller space than the first generation computers.
3. Second generation computers used less electricity and generated less heat.
4. The transistors could do all that the vacuum tubes did.
5. The computers were faster and lighter in weight than first generation computers.
Examples of second generation computers are NCR, 315, IBM, 7030.
3RD GENERATION INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Third generation computers were manufactured between 1964 and 1970.
During this period, the integrated circuit was invented.
They were first used in space ships and electronic military equipment.
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. The computers used integrated circuits.
2. They were faster than second generation computers.
3. They were smaller in size and also more powerful.
4. The computers had fast memory access.

4TH GENERATION VERY LARGE INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
The computers were manufactured between 1974 and 1984. One of the most important results of large-scale integration was the introduction of the microprocessor in the fourth generation by an American company – Intel Corporation. A microprocessor is a central processing unit fabricated on a chip. This generation of computers had optical readers and graphic display terminals. The use of floppy diskette as a storage facility was introduced in this generation.
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. The computers were smaller in size.
2. They were very powerful computers.
3. They had high processing speed.
4. They had high storage capacity.
Examples are Intel 4004, Intel 8085, Pentium 1, 2, 3, etc

5TH GENERATION ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
From the 1990s, the fifth generation computers entered into the computer world through the application of fibre optics technology. This generation of computers evolved as a result of the need for computers to take decisions in various circumstances. This generation is witnessing the influx of super microcomputers through artificial intelligence whose main attraction over previous computers is speed and power. Expert systems have the capacity of making decisions and judgements.
These are computers that will be able to mimic many things that so far can only be done by human beings. For example, fifth generation computers will be able to accept spoken word instruction (voice recognition) and assist doctors in carrying out diagnosis.


EVALUATION
1. The fifth generation computers made use of ________________
2. The means by which a computer receives spoken word instruction is called
__________
3. The 3rd generation computers were manufactured between ___ and _____
4. List two characteristics of 3rd generation computers.
5. First generation computers were manufactured between __ and _____
6. One of the problems of the first generation computers was that they generate a lot of _________
7. ________ were used for storage in the 2nd generation computers.
8. List two examples of 2nd Generation computers.
9. What is a microprocessor?
10 . List two software tools developed during the 4th generation.
ASSIGNMENT
1. We have ________ generations of computers.
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
2. The characteristics of first generation computers include the following except ________________
(a) They were very bulky and heavy.
(b) They measured between 50ft and 100ft long.
(c) The computers weighed up to 200 tons and occupied 3000 cubic ft.
(d) They used transistors to store and process data.
3. Fourth generation computers used __________
(a) Vacuum tubes b. Transistors c. Artificial Intelligence
d. Large scale integrated circuits
4. _______ generation computers used fibre optics.
(a) First (b) Second (c) Fourth (d) Fifth
5. Second generation computers were _____ than 3rd generation of computers. (a) Smaller (b) Faster (c) More reliable (d) Slower
THEORY
1. What do we mean by ‘generation of computers’?
2. Compare and contrast the characteristics of the 3rd and 4th generation computers.