1ST TERM
1ST TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Speech Work: Introduction to Speech (Organs of Speech); Structure: Parts of speech – Nouns (Position/Functions of Noun in a given passage); Adjectives Comprehension/Vocabulary Development Reading Skill/Writing Skill (Developing Reading and Writing Skills) Composition: Writing Outline, Literature: Introduction to Literature (Functions/Purpose)
2. Speech Work: Vowels – Introduction to Monophthongs (Examples), Structure: Verbs – Position/Functions of Verbs (in
a given passage) Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Reading for Main ideas, Composition: Types of Composition (Narrative, Descriptive, Argumentative and Expository). Literature: Genres of Literature (Definition of Genres with related texts)
3. Speech Work: Vowels /|/and/i:/ Structure: Adverbials (Frequency, Manner, Intensifiers) Comprehension/Vocabulary Development: Reading for Supporting ideas. Composition: Elements of Composition – Introduction, Body, Conclusion; Stages of writing Literature: Prose (Types of Prose e.g. Narrative, Descriptive, etc.)
4. Speech Work: Vowels /e/ and /æ/: Structure: Tenses (Present, Past and Future) Making sentences with tenses. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development: Writing Skill – Reading to answer specific Questions. Composition/Letter Writing – Introduction/Types of Letters (Formal and Informal)
5. Speech Work: Vowel /a:/ Structure: Conjunctions and Prepositions, Comprehension/Vocabulary Development; Writing Skill-Reading to Answer Specific Questions // Composition: Letter Writing – Format/Features of Letters – Informal Letters, Literature: Folktales – African and Non-African tales.
6. Speech Work: /כ/ and /כ/: Structure: Tenses – Present (making sentences with the present tenses) Comprehensive /Vocabulary Development: Writing Skill (more on developing writing skills) Composition: Letter writing: Guided Writing – Informal Letters Literature: folktales- Features/Themes of Folktales (didactic, entertainment, magical, etc.).
7. Speech Work: Consonants – Introduction (examples) Comprehension/Vocabulary Development.: Reading Skill: (Intensive Reading); Writing Skill - Giving specific answers. Structure: Tenses: Past tenses (making sentences with the Past tenses) Composition: Narrative Composition (Features/Outline Guided Composition).
8. Speech Work: Consonant/p/and/b/ Comprehension/Vocabulary Development.: Writing Skill Giving Specific answers Structure: Tenses: Future Tenses (making sentences with the future tenses) Composition: Descriptive composition (Features/ outline guided composition) Literature: Introduction to figures of Speech (Simile, Metaphor); Recommended Texts.
9. Speech Work: Consonants/t/and/d/ Structure: Tenses and Adverbials: Making sentences with Tenses and Adverbials Comprehension. Vocabulary Development: Reading and Writing Skills (Cont’d). Composition: More on Narrative and Descriptive Compositions (Arrangement of ideas in logical sequence; Development of ideas/outline to full) Literature; prose: Features of prose – plot characterization, style, setting, theme. Reading recommended texts.
10. Revision.
WEEK TOPIC
1. Speech Work: Introduction to Speech (Organs of Speech); Structure: Parts of speech – Nouns (Position/Functions of Noun in a given passage); Adjectives Comprehension/Vocabulary Development Reading Skill/Writing Skill (Developing Reading and Writing Skills) Composition: Writing Outline, Literature: Introduction to Literature (Functions/Purpose)
2. Speech Work: Vowels – Introduction to Monophthongs (Examples), Structure: Verbs – Position/Functions of Verbs (in
a given passage) Comprehension/Vocabulary Development. Reading for Main ideas, Composition: Types of Composition (Narrative, Descriptive, Argumentative and Expository). Literature: Genres of Literature (Definition of Genres with related texts)
3. Speech Work: Vowels /|/and/i:/ Structure: Adverbials (Frequency, Manner, Intensifiers) Comprehension/Vocabulary Development: Reading for Supporting ideas. Composition: Elements of Composition – Introduction, Body, Conclusion; Stages of writing Literature: Prose (Types of Prose e.g. Narrative, Descriptive, etc.)
4. Speech Work: Vowels /e/ and /æ/: Structure: Tenses (Present, Past and Future) Making sentences with tenses. Comprehension/Vocabulary Development: Writing Skill – Reading to answer specific Questions. Composition/Letter Writing – Introduction/Types of Letters (Formal and Informal)
5. Speech Work: Vowel /a:/ Structure: Conjunctions and Prepositions, Comprehension/Vocabulary Development; Writing Skill-Reading to Answer Specific Questions // Composition: Letter Writing – Format/Features of Letters – Informal Letters, Literature: Folktales – African and Non-African tales.
6. Speech Work: /כ/ and /כ/: Structure: Tenses – Present (making sentences with the present tenses) Comprehensive /Vocabulary Development: Writing Skill (more on developing writing skills) Composition: Letter writing: Guided Writing – Informal Letters Literature: folktales- Features/Themes of Folktales (didactic, entertainment, magical, etc.).
7. Speech Work: Consonants – Introduction (examples) Comprehension/Vocabulary Development.: Reading Skill: (Intensive Reading); Writing Skill - Giving specific answers. Structure: Tenses: Past tenses (making sentences with the Past tenses) Composition: Narrative Composition (Features/Outline Guided Composition).
8. Speech Work: Consonant/p/and/b/ Comprehension/Vocabulary Development.: Writing Skill Giving Specific answers Structure: Tenses: Future Tenses (making sentences with the future tenses) Composition: Descriptive composition (Features/ outline guided composition) Literature: Introduction to figures of Speech (Simile, Metaphor); Recommended Texts.
9. Speech Work: Consonants/t/and/d/ Structure: Tenses and Adverbials: Making sentences with Tenses and Adverbials Comprehension. Vocabulary Development: Reading and Writing Skills (Cont’d). Composition: More on Narrative and Descriptive Compositions (Arrangement of ideas in logical sequence; Development of ideas/outline to full) Literature; prose: Features of prose – plot characterization, style, setting, theme. Reading recommended texts.
10. Revision.
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Introduction to speech (Organs of Speech)
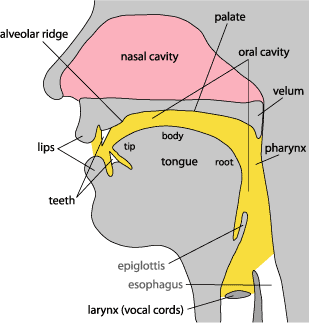
The organs of speech are the parts of human body used in speech production. The organs of speech include: lungs, vocal cords, trachea, larynx, the velum, soft palate, hard palate, alveolar ridge, nasal cavity, teeth, lips and the tongue.
The process of speech production starts from the lungs which serve as the ‘power house’ from which the airstream flows. The tongue may be described as the most active articulator because it moves and come in contact with other organs of speech, create a total or partial obstruction during the production of English consonants.
EVALUATION
1. Define organs of speech
2. List ten (10) organs of speech
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Parts of Speech-Nouns
SUB-TOPIC: Functions of Nouns in a given passage.
Nouns are names of persons, places, animals, and ideas . The word noun is derived from the Latin word “nomen” meaning name. Examples are John, Abuja, tiger, chair, honesty, courage, happiness etc.
Position of Noun
Nouns can take either subject or object position. Subject is the performer of the action in a sentence while object is the receiver of the action in a sentence.
i. Shade is my friend.
ii. The pencil belongs to me.
In the sentences above” Shade” and “pencil” take the subject position.
i. The hunter killed a snake.
ii. I took the book
In the above sentences,” snake” and” book” take the object position.
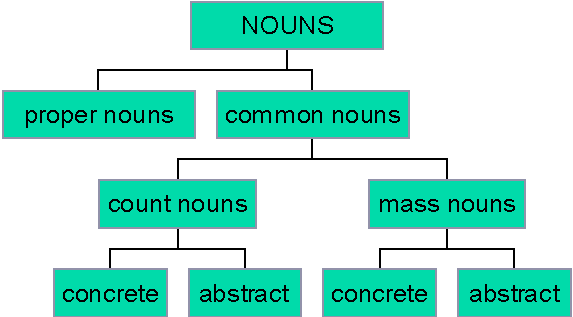
Classes of Nouns: Nouns in English can be classified into the following:
1. Proper Nouns: These refer to the names of particular persons, animals, places or things.
Persons: Sola, Ngozi, Bala, Asuquo etc
Animals: Bingo, Jack, Lucky( names of dogs) etc
Places: London, Lagos, Port Harcourt, Abuja, Calabar, Enugu,
Days/months: Monday, Tuesday, December, July etc
Organizations: Oceanic Bank, Pen-Write Academy, Assemblies of God
Subjects: Mathematics, Christian Religious Studies
Natural features: River Niger , Mount Everest, Lake Chad.
NOTE: Proper nouns always begin with capital letters.

2. Common Nouns: These are general names for persons, animals, places and things that share the same characteristics. Examples include: boy, dog, village, ruler, and city.

3. Concrete Nouns: These refer to materials, persons, objects, things or substances that have physical forms. They are tangible nouns e.g. car, spoon, fork etc.

4. Abstract Nouns: These are names of entities that have no physical forms; that is, those nouns that are immaterial e.g. peace, hope, love, kindness, honesty, etc.
5. Collective Nouns: These are nouns that name or refer to groups or a collection of people, animals or things as unified entities e.g. audience, army, choir, team, committee, etc.



Functions of Nouns:
Generally, nouns perform five major functions:
1. Subject of a verb
John likes fish.
Yahaya swims in the pool always
2. Object of a verb
John kills fishes every day.
The old man praised Banjo.
3. Complement of a Subject
My name is Tina.
Schools are goldmines.
4. Complement of a preposition
I take great delight in sports.
Naturally, all human beings sleep at night.
5. Complement of an Object
We call the bad boy Ogidi.
They crowned him king.
EVALUATION:
i. What is a noun?
ii. Give three classes of noun with two examples each.
iii. State the two positions of noun with relevant examples.
ASSIGNMENT:
Underline the nouns in this passage.
Immediately after the evening meal, when the problems were over, my father bade his friends farewell and I went to sit under the verandah of his hut; I went and sat near him. I began by questioning him in a roundabout manner, as all children do, and on every subject under the sun. Finally, unable to restrain myself any longer, I asked:
“Father, what is that little snake that comes to visit you?”
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Ngozi and Emeka

The passage narrates how Ngozi and Emeka (the twins) grew tall. They were sometimes taken to the town to see their aunt. Then, one day when the twins were nine years old, they went to live with their aunt in the town.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 1.2.2; pages 3-4.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 1.2. 3 and 1.2.4; pages 4-5.

LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Writing Outline
An outline is a statement of relevant points to the topic before the actual writing is done. It is wise to jot down the points, ideas and thoughts that could be developed to meet the goals of the writing exercise. Ideas and points come through thinking and brainstorming. The ideas jotted should then be arranged orderly following a logical pattern.

Illustration of an Outline Form for a Class Essay
Topic: My First Day in High School
Preparation for the journey.
Departure from home.
Events on the way to school.
Arrival at the registration point.
Activities at the registration centre.
Meeting of new friends in the hostel.
Orientation exercise for the new students.
Experience at the dining hall.
Mood at end of the day.

EVALUATION: Write an outline on the topic ‘My Ideal School’
ASSIGNMENT:
Write an essay on the topic ‘My First Day in High School’. Your essay should not be less than 200 words.
LESSON 5
Literature:
TOPIC: Introduction to Literature (functions and purpose).
What is Literature? Literature is a mirror of life. Literature is a tool used to look at the ills of life and aim at correcting it. And that is why literature is a mirror of life.

The functions of literature
The following are some of the major functions of literature:
1. It is for entertainment. That is, the different types of literature such as prose, drama and poetry, entertains.
2. It educates, that is, it is a medium through which the author passes across his believe to the reader.
3. Literature is didactic. It teaches moral lessons through whichever form it takes(drama, poetry and prose).
The purposes of literature among many others are:
It is a vehicle for social change. Through literature, social vices can be corrected.
It is a means of acquiring more vocabularies.
It creates reading interest.
Literature provides guiding principles of life.
It serves as information base.
It describes reality of life.
It is a means of maintaining culture of the people.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Vengeance by Ayo Olaosebikan, Act 1 scene 1,2 and 3
Chike and the riverThe drummer boy
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Introduction to speech (Organs of Speech)

The organs of speech are the parts of human body used in speech production. The organs of speech include: lungs, vocal cords, trachea, larynx, the velum, soft palate, hard palate, alveolar ridge, nasal cavity, teeth, lips and the tongue.
The process of speech production starts from the lungs which serve as the ‘power house’ from which the airstream flows. The tongue may be described as the most active articulator because it moves and come in contact with other organs of speech, create a total or partial obstruction during the production of English consonants.
EVALUATION
1. Define organs of speech
2. List ten (10) organs of speech
LESSON 2
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Parts of Speech-Nouns
SUB-TOPIC: Functions of Nouns in a given passage.
Nouns are names of persons, places, animals, and ideas . The word noun is derived from the Latin word “nomen” meaning name. Examples are John, Abuja, tiger, chair, honesty, courage, happiness etc.
Position of Noun
Nouns can take either subject or object position. Subject is the performer of the action in a sentence while object is the receiver of the action in a sentence.
i. Shade is my friend.
ii. The pencil belongs to me.
In the sentences above” Shade” and “pencil” take the subject position.
i. The hunter killed a snake.
ii. I took the book
In the above sentences,” snake” and” book” take the object position.

Classes of Nouns: Nouns in English can be classified into the following:
1. Proper Nouns: These refer to the names of particular persons, animals, places or things.
Persons: Sola, Ngozi, Bala, Asuquo etc
Animals: Bingo, Jack, Lucky( names of dogs) etc
Places: London, Lagos, Port Harcourt, Abuja, Calabar, Enugu,
Days/months: Monday, Tuesday, December, July etc
Organizations: Oceanic Bank, Pen-Write Academy, Assemblies of God
Subjects: Mathematics, Christian Religious Studies
Natural features: River Niger , Mount Everest, Lake Chad.
NOTE: Proper nouns always begin with capital letters.

2. Common Nouns: These are general names for persons, animals, places and things that share the same characteristics. Examples include: boy, dog, village, ruler, and city.


3. Concrete Nouns: These refer to materials, persons, objects, things or substances that have physical forms. They are tangible nouns e.g. car, spoon, fork etc.

4. Abstract Nouns: These are names of entities that have no physical forms; that is, those nouns that are immaterial e.g. peace, hope, love, kindness, honesty, etc.

5. Collective Nouns: These are nouns that name or refer to groups or a collection of people, animals or things as unified entities e.g. audience, army, choir, team, committee, etc.



Functions of Nouns:
Generally, nouns perform five major functions:
1. Subject of a verb
John likes fish.
Yahaya swims in the pool always
2. Object of a verb
John kills fishes every day.
The old man praised Banjo.
3. Complement of a Subject
My name is Tina.
Schools are goldmines.
4. Complement of a preposition
I take great delight in sports.
Naturally, all human beings sleep at night.
5. Complement of an Object
We call the bad boy Ogidi.
They crowned him king.
EVALUATION:
i. What is a noun?
ii. Give three classes of noun with two examples each.
iii. State the two positions of noun with relevant examples.
ASSIGNMENT:
Underline the nouns in this passage.
Immediately after the evening meal, when the problems were over, my father bade his friends farewell and I went to sit under the verandah of his hut; I went and sat near him. I began by questioning him in a roundabout manner, as all children do, and on every subject under the sun. Finally, unable to restrain myself any longer, I asked:
“Father, what is that little snake that comes to visit you?”
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Ngozi and Emeka

The passage narrates how Ngozi and Emeka (the twins) grew tall. They were sometimes taken to the town to see their aunt. Then, one day when the twins were nine years old, they went to live with their aunt in the town.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 1.2.2; pages 3-4.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 1.2. 3 and 1.2.4; pages 4-5.

LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Writing Outline
An outline is a statement of relevant points to the topic before the actual writing is done. It is wise to jot down the points, ideas and thoughts that could be developed to meet the goals of the writing exercise. Ideas and points come through thinking and brainstorming. The ideas jotted should then be arranged orderly following a logical pattern.

Illustration of an Outline Form for a Class Essay
Topic: My First Day in High School
Preparation for the journey.
Departure from home.
Events on the way to school.
Arrival at the registration point.
Activities at the registration centre.
Meeting of new friends in the hostel.
Orientation exercise for the new students.
Experience at the dining hall.
Mood at end of the day.

EVALUATION: Write an outline on the topic ‘My Ideal School’
ASSIGNMENT:
Write an essay on the topic ‘My First Day in High School’. Your essay should not be less than 200 words.
LESSON 5
Literature:
TOPIC: Introduction to Literature (functions and purpose).
What is Literature? Literature is a mirror of life. Literature is a tool used to look at the ills of life and aim at correcting it. And that is why literature is a mirror of life.

The functions of literature
The following are some of the major functions of literature:
1. It is for entertainment. That is, the different types of literature such as prose, drama and poetry, entertains.
2. It educates, that is, it is a medium through which the author passes across his believe to the reader.
3. Literature is didactic. It teaches moral lessons through whichever form it takes(drama, poetry and prose).
The purposes of literature among many others are:
It is a vehicle for social change. Through literature, social vices can be corrected.
It is a means of acquiring more vocabularies.
It creates reading interest.
Literature provides guiding principles of life.
It serves as information base.
It describes reality of life.
It is a means of maintaining culture of the people.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Vengeance by Ayo Olaosebikan, Act 1 scene 1,2 and 3
Chike and the riverThe drummer boy
WEEK 2
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Vowels
SUB-TOPIC: Introduction to monophthongs
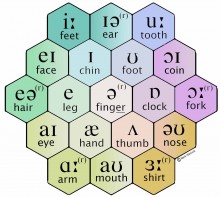
There are forty-four sound segments in English, comprising twenty vowels and twenty-four consonants. Vowel sounds are the sounds produced without any obstruction in the vocal cords.
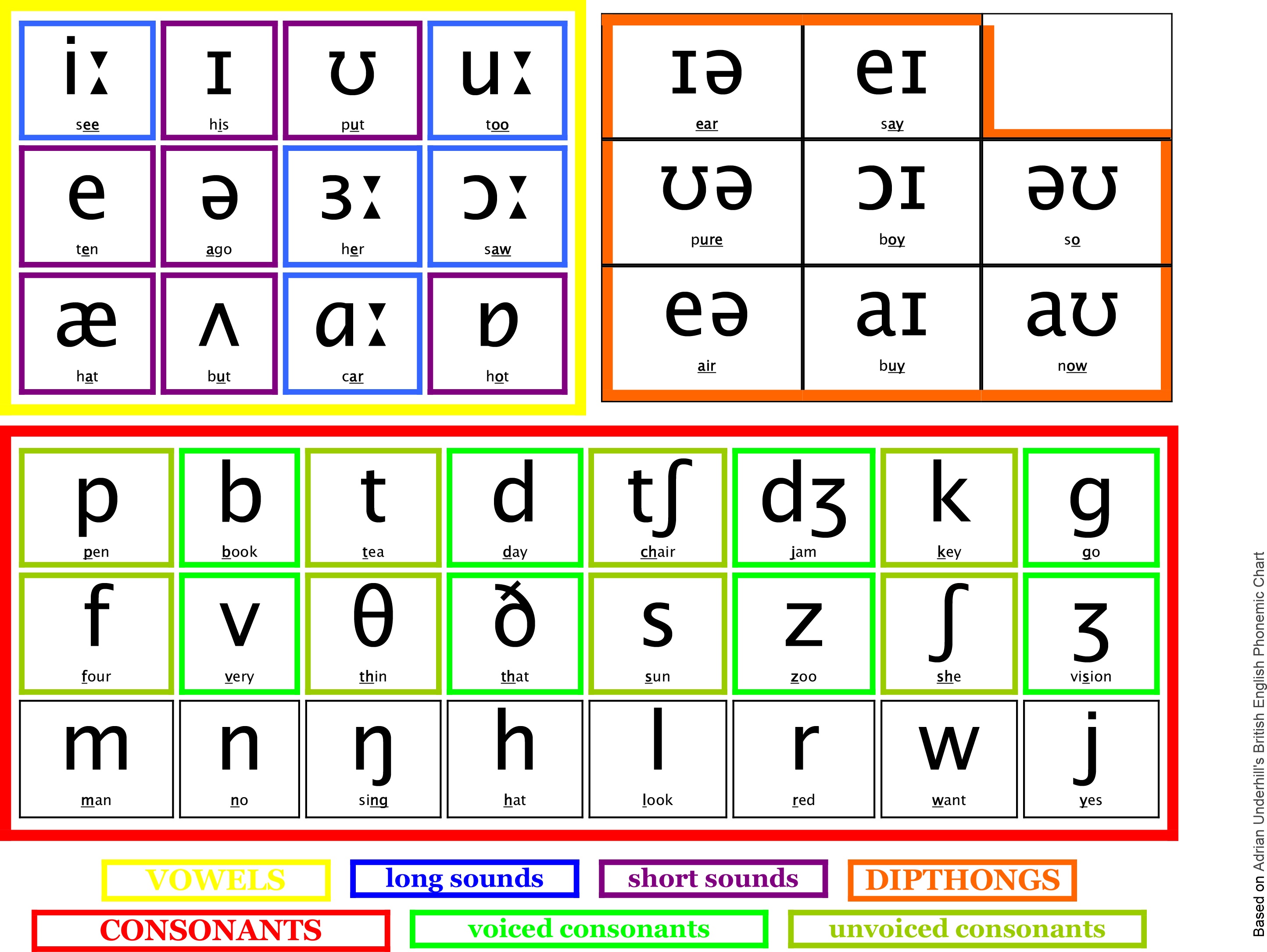
The vowels in English are classified into two main groups: pure vowels (also called monophthongs) and diphthongs. The pure vowels are sub-classified into short vowels and long vowels. These pure vowels are listed below with examples of words where they occur:
1. /i: / e.g. beat, seat, neat, feet.
2. /I/ e.g. bit, sit nymph, village.
3. /e/ e.g. bed, bread, said, bury.
4. // e.g. cat, lack, pack, rat.
5. /a: / e.g. car, dart, calm, heart.
6. /ᴐ/ e.g. pot, what, gone, wash.
7. /ᴐ:/ e.g. war, pork, saw, bought.
8. /u/ e.g. put, foot, book, could.
9. /u: / e.g. pool, blue, screw, shoe.
10. /Ʌ/ e.g. cut, come, blood, country.
11. /з:/ e.g. first, purse, earn, bird.
12. /Ә/ e.g. about, baker, sailor, teacher.
EVALUATION
1. What is a vowel sound?
2. State the classification of monophthongs.
3. Write out five monophthongs with two examples each.
ASSIGNMENT: Identify the vowel sounds underlined in the following words:
I. Weapon
II. Storm
III. Mother
IV. Hunt
V. First
LESSON 2
SUBJECT: English Language
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Functions of Verb
A verb is an action word. For example: sing, eat, jump, sleep, read, make etc.

A verb expresses an action or a state of its subject; it says what people do or act. Verbs are the most important words in a sentence. The predicate of a sentence must contain a verb. It acts as the predicator in the sentence. Verb comes from the Latin word ‘verbum’ which means action word.
If the subject of a sentence is singular, the verb is singular, e.g. The boy is running.
If the subject of sentence is plural, the verb is plural, e.g. The boys are running.
The following are examples of verbs: is, am, are, was, dance, sing, fight, kill, ask, and sleep.

EVALUATION: Fill in the gaps with suitable verbs, chosen from the list below:
Carrying, opened, kicking, writes, live.
1. The woman is _____ a basket of oranges on her head.
2. Ade is ______ the ball with his right foot.
3. Mary ________ letters with pencil every day.
4. My brother _____ the door for the dog to go in.
5. We ______ in a small village.
ASSIGNMENT: Brighter Grammar book 1, Exercise A, pages 35; questions 1-20.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Emeka Quarrels with a Town Boy
The passage narrates how the town boys were rough and tried to bully Emeka. The details follow immediately with the story of how the town boy picked a quarrel with Emeka.

EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 2.2.2; pages 13-15.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 2.2. 3 and 2.2.4; pages 15-16.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Types of Composition
The following types of essay can be identified;
1. Narrative essay
2. Descriptive essay
3. Argumentative essay
4. Expository essay.

1. Narrative Essay: This is a type of essay that tells a story or give account of what has happened. It could be true or made up yourself. It is the past tense form of verbs that are used.
2. Descriptive Essay: It is one that is written to give the reader a mental picture of a person, an object or a place. The composition should be written in such a way that the reader will have a good picture of the person, place or object in his mind. E.g. ”Describe your school compound for someone who has not been there”.
3 Argumentative / Persuasive Essay: It is a composition written to argue that an opinion is superior to some other opinion. It is an essay written to persuade the reader to accept one opinion and reject some other opinion. It is commonly called Debate E.g. “Dry Season is Preferable to Rainy Season in Nigeria”
4. Expository Essay: It is a composition that describes how something is done, planned or organized, made, how something works etc. E.g. “Describe how your favourite meal is prepared”, or ” The Game I like best”.
EVALUATION
1. Mention four types of essay.
2. Explain the features of narrative essay.
LESSON 5
Literature
TOPIC: Genres of literature
The genres of literature are the forms of literature that we have. And these genres are : drama, prose and poetry. The teacher should give examples of the drama and prose textbooks being used.
Genres are often divided into sub-genres. Literature, for instance, is divided into three basic kinds of literature, the classic genres of Ancient Greece, poetry, drama, and prose. Poetry may then be subdivided into epic, lyric, and dramatic. Subdivisions of drama include foremost comedy and tragedy, while e.g. comedy itself has sub-genres, including farce, comedy of manners, burlesque, satire, and so on.
Dramatic poetry, instance, might include comedy, tragedy, melodrama, and mixtures like tragicomedy. This parsing into sub-genres can continue: "comedy" has its own genres, including, for example, comedy of manners, sentimental comedy, burlesque comedy, and satirical comedy.
Drama: Fruit of honesty, Vengeance, Asabe
Prose: The Ambitious Village Boy, Oliver Twist,
Poetry: Twinkle Twinkle Little Star,
Evaluation:
1. What is genres of literature?
2. Mention the genres of literature.
ASSIGNMENT:
A. From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that has the same vowel sound as the one represented by the letter(s) underlined.
1. alone A. heater B. back C. plank D. crawl
2. says A. say B. said C. day D. days
3. coup A. book B. cough C. curve D. who
B. Identify the part of speech underlined in the following sentences.
4. The dogs bark occasionally.
A. noun B. verb C. adverb D. adjective
5. She did the work badly.
A. verb B. adjective C. adverb D. noun
READING ASSIGNMENT: Read and summarize, Vengeance Act 2 Scene i-v, not more than ten lines.
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Vowels
SUB-TOPIC: Introduction to monophthongs
There are forty-four sound segments in English, comprising twenty vowels and twenty-four consonants. Vowel sounds are the sounds produced without any obstruction in the vocal cords.

The vowels in English are classified into two main groups: pure vowels (also called monophthongs) and diphthongs. The pure vowels are sub-classified into short vowels and long vowels. These pure vowels are listed below with examples of words where they occur:
1. /i: / e.g. beat, seat, neat, feet.
2. /I/ e.g. bit, sit nymph, village.
3. /e/ e.g. bed, bread, said, bury.
4. // e.g. cat, lack, pack, rat.
5. /a: / e.g. car, dart, calm, heart.
6. /ᴐ/ e.g. pot, what, gone, wash.
7. /ᴐ:/ e.g. war, pork, saw, bought.
8. /u/ e.g. put, foot, book, could.
9. /u: / e.g. pool, blue, screw, shoe.
10. /Ʌ/ e.g. cut, come, blood, country.
11. /з:/ e.g. first, purse, earn, bird.
12. /Ә/ e.g. about, baker, sailor, teacher.
EVALUATION
1. What is a vowel sound?
2. State the classification of monophthongs.
3. Write out five monophthongs with two examples each.
ASSIGNMENT: Identify the vowel sounds underlined in the following words:
I. Weapon
II. Storm
III. Mother
IV. Hunt
V. First
LESSON 2
SUBJECT: English Language
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Verbs
SUB-TOPIC: Functions of Verb
A verb is an action word. For example: sing, eat, jump, sleep, read, make etc.

A verb expresses an action or a state of its subject; it says what people do or act. Verbs are the most important words in a sentence. The predicate of a sentence must contain a verb. It acts as the predicator in the sentence. Verb comes from the Latin word ‘verbum’ which means action word.
If the subject of a sentence is singular, the verb is singular, e.g. The boy is running.
If the subject of sentence is plural, the verb is plural, e.g. The boys are running.
The following are examples of verbs: is, am, are, was, dance, sing, fight, kill, ask, and sleep.

EVALUATION: Fill in the gaps with suitable verbs, chosen from the list below:
Carrying, opened, kicking, writes, live.
1. The woman is _____ a basket of oranges on her head.
2. Ade is ______ the ball with his right foot.
3. Mary ________ letters with pencil every day.
4. My brother _____ the door for the dog to go in.
5. We ______ in a small village.
ASSIGNMENT: Brighter Grammar book 1, Exercise A, pages 35; questions 1-20.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Emeka Quarrels with a Town Boy
The passage narrates how the town boys were rough and tried to bully Emeka. The details follow immediately with the story of how the town boy picked a quarrel with Emeka.

EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 2.2.2; pages 13-15.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 2.2. 3 and 2.2.4; pages 15-16.
LESSON 4
ASPECT: Composition
TOPIC: Types of Composition
The following types of essay can be identified;
1. Narrative essay
2. Descriptive essay
3. Argumentative essay
4. Expository essay.

1. Narrative Essay: This is a type of essay that tells a story or give account of what has happened. It could be true or made up yourself. It is the past tense form of verbs that are used.
2. Descriptive Essay: It is one that is written to give the reader a mental picture of a person, an object or a place. The composition should be written in such a way that the reader will have a good picture of the person, place or object in his mind. E.g. ”Describe your school compound for someone who has not been there”.
3 Argumentative / Persuasive Essay: It is a composition written to argue that an opinion is superior to some other opinion. It is an essay written to persuade the reader to accept one opinion and reject some other opinion. It is commonly called Debate E.g. “Dry Season is Preferable to Rainy Season in Nigeria”
4. Expository Essay: It is a composition that describes how something is done, planned or organized, made, how something works etc. E.g. “Describe how your favourite meal is prepared”, or ” The Game I like best”.
EVALUATION
1. Mention four types of essay.
2. Explain the features of narrative essay.
LESSON 5
Literature
TOPIC: Genres of literature
The genres of literature are the forms of literature that we have. And these genres are : drama, prose and poetry. The teacher should give examples of the drama and prose textbooks being used.

Genres are often divided into sub-genres. Literature, for instance, is divided into three basic kinds of literature, the classic genres of Ancient Greece, poetry, drama, and prose. Poetry may then be subdivided into epic, lyric, and dramatic. Subdivisions of drama include foremost comedy and tragedy, while e.g. comedy itself has sub-genres, including farce, comedy of manners, burlesque, satire, and so on.
Dramatic poetry, instance, might include comedy, tragedy, melodrama, and mixtures like tragicomedy. This parsing into sub-genres can continue: "comedy" has its own genres, including, for example, comedy of manners, sentimental comedy, burlesque comedy, and satirical comedy.
Drama: Fruit of honesty, Vengeance, Asabe
Prose: The Ambitious Village Boy, Oliver Twist,
Poetry: Twinkle Twinkle Little Star,
Evaluation:
1. What is genres of literature?
2. Mention the genres of literature.
ASSIGNMENT:
A. From the words lettered A to D, choose the word that has the same vowel sound as the one represented by the letter(s) underlined.
1. alone A. heater B. back C. plank D. crawl
2. says A. say B. said C. day D. days
3. coup A. book B. cough C. curve D. who
B. Identify the part of speech underlined in the following sentences.
4. The dogs bark occasionally.
A. noun B. verb C. adverb D. adjective
5. She did the work badly.
A. verb B. adjective C. adverb D. noun
READING ASSIGNMENT: Read and summarize, Vengeance Act 2 Scene i-v, not more than ten lines.
WEEK 3
LESSON 1
SPEECH WORK:
Vowels /I/ and / i:/
CONTENT:
/I/ This sound is a short vowel sound .It is pronounced with the front part of the tongue. It is found in :kit, lip, zip, pit, pick, knit, ship.
/I/
i------y-------e--------ie-------a
sit----nymph—--pretty---ladies---village
fifth—-rhythm—-wicked—--cities--private
rich---symbol—-careless-parties--manage
trick—-lynx----houses---carries--savage
/i:/ This sound is a long vowel sound .It is pronounced as ee’.
/i:/
ee----ea-----e--------i
free--meat—-peter--margarine
bee---sea---we-----machine
tree--beat—-he-----police
need--leaf—-these--kerosine
ie-----ei-----ey-----uay
chief—-seize—-key----Quay
field--receive
thief--deceive
piece--ceiling
The examples are in the following words: seat, beat, peak, feet, sheep, neat, heel.
Revision Questions( objectives)
(1) Which of these words has the sounds below
/I/ ( A) keg, (B) beat (C) pit (D) bed
(2)/I:/( A) ten,(B) tea,(C)ship (D)kit
THEORY
(1) Give three examples of words with this sound/ i/
(2) Give three examples of words with this sound/ i:/
https://youtu.be/5jX-ORMBCFo
LESSON 2 & 3
STRUCTURE/GRAMMAR
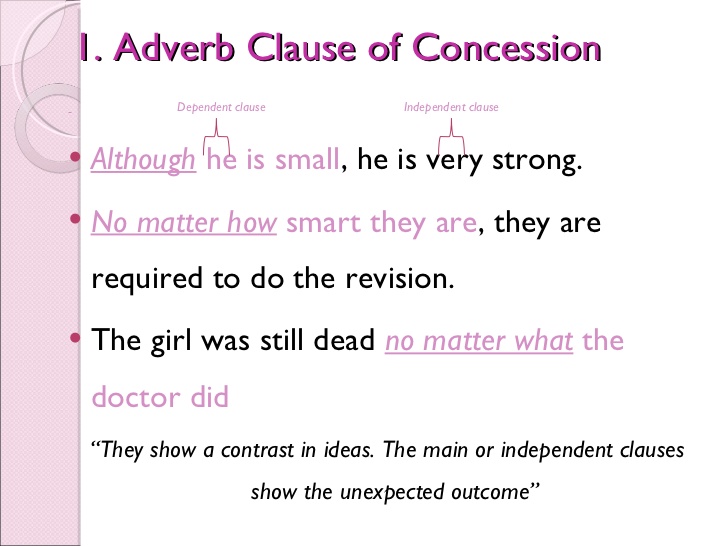
TOPIC: ADVERBS & ADVERBIALS
CONTENT: Adverbs are the words that tell us more about verbs. It gives additional information about verbs. Adverbials are other group of words functioning as an adverb.
e.g
He walks slowly - adverb of manner
He walks as a lady - adverbial phrase of manner
He walks as if he is a lady - adverbial clause of manner

There are various types of adverbs. Thus:
Adverb of Time: This tells us about a particular time that an action takes place. It answers the question when? E.g: early, late, today, tomorrow ,next week etc.
(a)The students came early
(b)I will see you tomorrow.

Adverb of place :This type of adverb tells us the exact place where the action takes place. It answers the question where?.Eg: here, there, inside, outside, indoor, outdoor etc .
(a)They slept here.
(b)Tell that boy to go there.

Adverb of manner: This kind of adverb describes how the action is being carried out. It answers the question how? Eg: slowly, quickly , hard, loudly, quietly, secretly, fast.etc
(a)The boy ran quickly
( b)The old man walks slowly.

Adverbial of condition: This is a conditional adverb. It starts with: if, unless, except, in as much as etc.
(a)The students will pass the examination if they study hard.
(b)If there is enough time we shall have our meeting today.

Adverb of frequency: This adverb tells us about how often an action or event takes place. Eg always, frequently, often, normally, regularly, rarely, occasionally etc
(a)He comes to school regularly.
(b)They always go home.
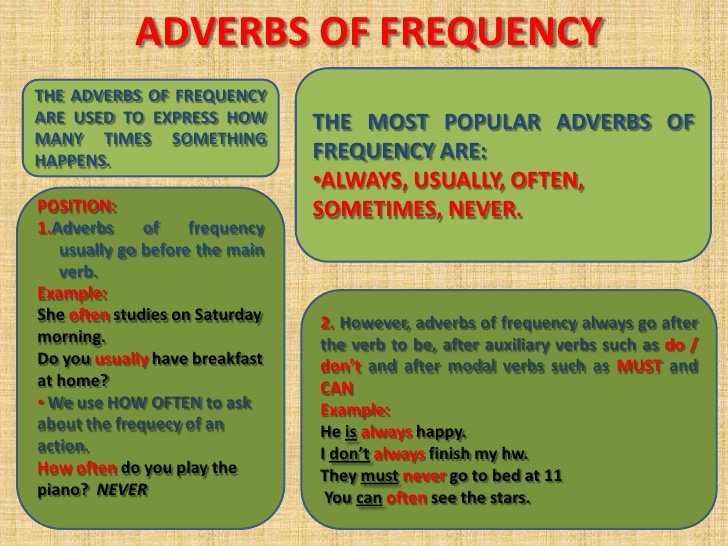
Adverb/adverbial of reason: This type of adverb tells us about reason why an action is being carried out. Eg.
(a)He passed because he worked hard.
(b)The girl failed because she was lazy.


Adverb of purpose: This tells us about the purpose for which the action was carried out. Eg He ran so fast so that he could win a gold medal.
Intensifiers: These are words that make other words stronger, larger. Eg very, too, much, fairly, so, highly, totally.
The house is very big.
The house is big. (without intensifier)
It is so good.
It is good. (without intensifier)
Let your light so shine.

Further Studies
REVISION QUESTIONS
Identify the class of word underlined below.
(1)The man opens the door of his house early.(A) verb (B) noun (C)adverb (D)adjective
(2)The boy quietly enter the room.(A)Adverb (B) pronoun (C) noun
(D)verb
Choose the right option to fill in the gaps bellow
(3)_________you work very hard you may not be able to finish it.
(A)Unless (B) But (C) And ( D) Because
(4) He will come back ______.(A) because (B) but (C)later (D) unless.
(5)He came ______at the right time. (A)their (B)then (C) there (D) thou.
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
LESSON 4
READING COMPREHENSION :
Obika ( Intensive English book 1 page 26-27)

Look at the following opening sentences of these paragraphs in the story:
Obika was one of the handsomest young men in Umuaro…
But two things spoilt Obika.
Not very long ago Obika had come very close indeed to committing murder.
These are topic sentences in the story. You can find more about a story by reading topic sentences first.
Then when you read ,you will see how naturally the details fall in place.
LESSON 5
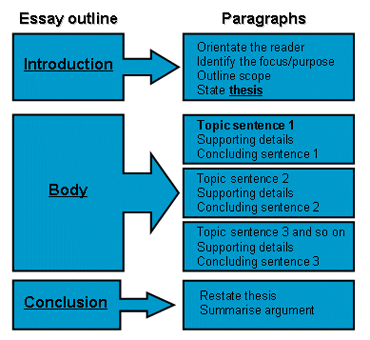
COMPOSITON: ELEMENTS OF COMPOSITION
Introduction:
This is the opening part of the composition. It introduces the content of the composition. It can be in form of proverb or illustration. It prepares the mind of the reader ahead of the main points of the composition.
Content/Body:
The body is the main purpose of writing. The points must be clearly developed and must be logically and sequentially discussed. It must be illustrated in different ways.
Conclusion:
The conclusion is the summary part of the composition. It should be concluded after the points have been fully discussed.
TYPES OF PROSE
(A)Narrative: This tells us about the past event. It involves the use of past tense verbs.
(B) Descriptive :This gives detail description of event, situation, and personalities .The language of description must be clear.
(C)Argumentative: This gives room for logical reasoning on a particular topic the stand must be taken before conclusion. The language must be formal. There is no room for the use of foul language.
(D)Expository: This deals with exposing the methods, procedures and steps of doing things. There is need to state the steps in chronological and sequential order.
THEORY
1(a)What is an adverb? (b) List five types of adverb with two examples each.
2(a)What are the elements of composition? (b)List the types of prose/composition.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
SPEECH WORK:
Vowels /I/ and / i:/

CONTENT:
/I/ This sound is a short vowel sound .It is pronounced with the front part of the tongue. It is found in :kit, lip, zip, pit, pick, knit, ship.
/I/
i------y-------e--------ie-------a
sit----nymph—--pretty---ladies---village
fifth—-rhythm—-wicked—--cities--private
rich---symbol—-careless-parties--manage
trick—-lynx----houses---carries--savage
/i:/ This sound is a long vowel sound .It is pronounced as ee’.
/i:/
ee----ea-----e--------i
free--meat—-peter--margarine
bee---sea---we-----machine
tree--beat—-he-----police
need--leaf—-these--kerosine
ie-----ei-----ey-----uay
chief—-seize—-key----Quay
field--receive
thief--deceive
piece--ceiling
The examples are in the following words: seat, beat, peak, feet, sheep, neat, heel.
Revision Questions( objectives)
(1) Which of these words has the sounds below
/I/ ( A) keg, (B) beat (C) pit (D) bed
(2)/I:/( A) ten,(B) tea,(C)ship (D)kit
THEORY
(1) Give three examples of words with this sound/ i/
(2) Give three examples of words with this sound/ i:/
https://youtu.be/5jX-ORMBCFo
LESSON 2 & 3
STRUCTURE/GRAMMAR
TOPIC: ADVERBS & ADVERBIALS
CONTENT: Adverbs are the words that tell us more about verbs. It gives additional information about verbs. Adverbials are other group of words functioning as an adverb.
e.g
He walks slowly - adverb of manner
He walks as a lady - adverbial phrase of manner
He walks as if he is a lady - adverbial clause of manner

There are various types of adverbs. Thus:
Adverb of Time: This tells us about a particular time that an action takes place. It answers the question when? E.g: early, late, today, tomorrow ,next week etc.
(a)The students came early
(b)I will see you tomorrow.

Adverb of place :This type of adverb tells us the exact place where the action takes place. It answers the question where?.Eg: here, there, inside, outside, indoor, outdoor etc .
(a)They slept here.
(b)Tell that boy to go there.

Adverb of manner: This kind of adverb describes how the action is being carried out. It answers the question how? Eg: slowly, quickly , hard, loudly, quietly, secretly, fast.etc
(a)The boy ran quickly
( b)The old man walks slowly.

Adverbial of condition: This is a conditional adverb. It starts with: if, unless, except, in as much as etc.
(a)The students will pass the examination if they study hard.
(b)If there is enough time we shall have our meeting today.

Adverb of frequency: This adverb tells us about how often an action or event takes place. Eg always, frequently, often, normally, regularly, rarely, occasionally etc
(a)He comes to school regularly.
(b)They always go home.

Adverb/adverbial of reason: This type of adverb tells us about reason why an action is being carried out. Eg.
(a)He passed because he worked hard.
(b)The girl failed because she was lazy.


Adverb of purpose: This tells us about the purpose for which the action was carried out. Eg He ran so fast so that he could win a gold medal.
Intensifiers: These are words that make other words stronger, larger. Eg very, too, much, fairly, so, highly, totally.
The house is very big.
The house is big. (without intensifier)
It is so good.
It is good. (without intensifier)
Let your light so shine.


Further Studies
REVISION QUESTIONS
Identify the class of word underlined below.
(1)The man opens the door of his house early.(A) verb (B) noun (C)adverb (D)adjective
(2)The boy quietly enter the room.(A)Adverb (B) pronoun (C) noun
(D)verb
Choose the right option to fill in the gaps bellow
(3)_________you work very hard you may not be able to finish it.
(A)Unless (B) But (C) And ( D) Because
(4) He will come back ______.(A) because (B) but (C)later (D) unless.
(5)He came ______at the right time. (A)their (B)then (C) there (D) thou.
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
LESSON 4
READING COMPREHENSION :
Obika ( Intensive English book 1 page 26-27)

Look at the following opening sentences of these paragraphs in the story:
Obika was one of the handsomest young men in Umuaro…
But two things spoilt Obika.
Not very long ago Obika had come very close indeed to committing murder.
These are topic sentences in the story. You can find more about a story by reading topic sentences first.
Then when you read ,you will see how naturally the details fall in place.

LESSON 5
COMPOSITON: ELEMENTS OF COMPOSITION
Introduction:
This is the opening part of the composition. It introduces the content of the composition. It can be in form of proverb or illustration. It prepares the mind of the reader ahead of the main points of the composition.
Content/Body:
The body is the main purpose of writing. The points must be clearly developed and must be logically and sequentially discussed. It must be illustrated in different ways.
Conclusion:
The conclusion is the summary part of the composition. It should be concluded after the points have been fully discussed.

TYPES OF PROSE
(A)Narrative: This tells us about the past event. It involves the use of past tense verbs.
(B) Descriptive :This gives detail description of event, situation, and personalities .The language of description must be clear.
(C)Argumentative: This gives room for logical reasoning on a particular topic the stand must be taken before conclusion. The language must be formal. There is no room for the use of foul language.
(D)Expository: This deals with exposing the methods, procedures and steps of doing things. There is need to state the steps in chronological and sequential order.
THEORY
1(a)What is an adverb? (b) List five types of adverb with two examples each.
2(a)What are the elements of composition? (b)List the types of prose/composition.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
WEEK 4
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Vowel /e/ and /æ /
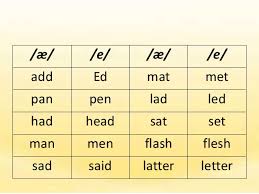
/e/ This is a short vowel sound. It is found in these words bellow:
Ten, bed, pet, keg, pen, shed, men, net, peg etc.
e-----ea-----a-----ie-----u-----ai
met---dead---any---friend-bury--said
red---read---many
bed---breath-Thames
help--instead

/æ/ This sound also is a short vowel sound. It is found in:
Man, cap, map, tap, lad, lap, cat, mad etc.
a-----ai
ram---plait
lamb
gnat
[youtube]https://youtu.be/NavmTDkd8Z8[/youtube]
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/rnpvR-urO-E[/youtube]
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2 & 3
STRUCTURE/GRAMMAR:
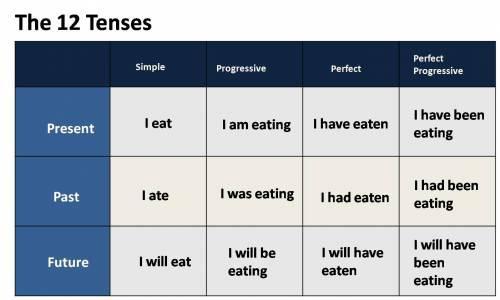
TENSES
Tenses are ways by which we can express ourselves based on time that the events take place. In other words, tenses show time of an action in a sentence. The verb plays very important role in tenses.
TENSE AND ASPECTS
Tense is related to verbs only and it is not the same as time. It is the change that takes place in the form of the verb to indicate time. On this basis, there are two basic changes that occur in verb i.e. present time indication and past time
indication. We can say therefore that there are two tenses in English.
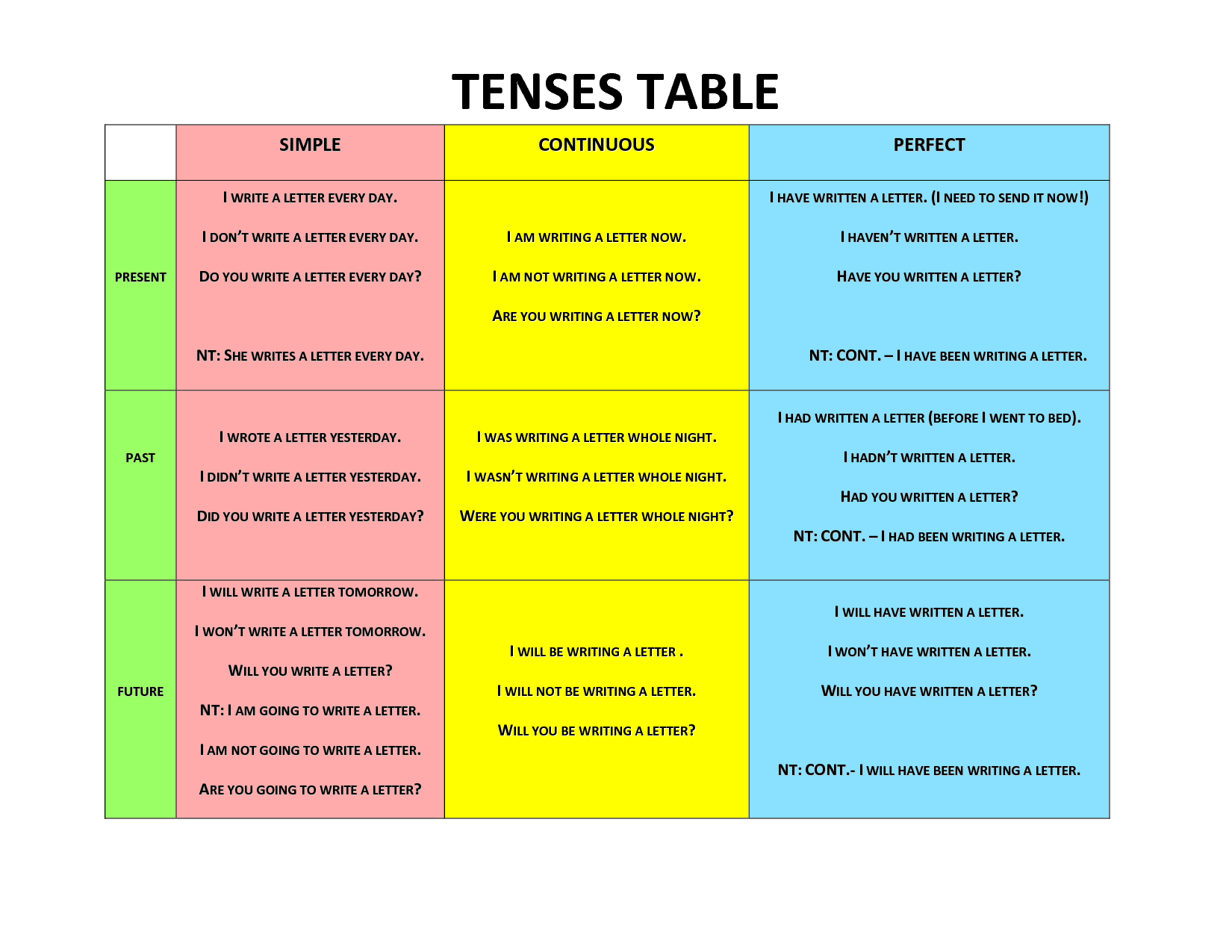
Present Tense:
Apart from the forms of the verb BE, the only change in the form of the verb to indicate the present time is
the addition of the ‘s’ morpheme when using the 3rd person singular numbers as subject. The present tense is said to be simple when the verb form is a single word.
e.g.
I sleep-----He sleeps
We sleep----She sleeps----They sleep
You sleep---It sleeps
Changes with the verb BE are as follows
I am a student----------He is a student
We are students---------She is a student
You are a student-------It is a student…
You are students--------They are students
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
These are the events that take place everyday or that stand as truth.
(1 ) The sun shines.
(2) She cooks on Sundays.
(3) Ade studies in a secondary school .
(4) I love pets.
(5) He loves pets
(6) Bisi goes to school every day.
(7) I go to school early.
(8) You come to our house every Thursday.
(9) She comes to visit her friend on Sundays.
(10) I do my assignment on weekends.
Note: Singular verbs go with singular nouns and plural verbs with plural nouns.
Exceptions are ‘I’ and ‘you’ which go with plural verbs.
Examples:
1. They play in the field on Saturdays.
2. Paul and Silas pray every day.
3. I sing a new song when I am happy.
4. You like oranges.
i. The present tense is used to express habitual activity. For example:
She drinks tea everyday.
ii. It is used to express a future action. For example:
The President arrives in Lagos next week.
iii. It is used to run commentaries. For example:
Okocha passes to Kanu and Kanu to Taribo, he dribbles one, two, three, a shot and it is a goal!
iv. It is used to write headlines in newspapers. For examples:
Bank executives go to jail
The simple present tense appears in the following forms;
(a) Habitual Present:
Expressing a habit or habitual action
I:
We:
You: ---eat everyday
They:
He:
She: ---eats everyday
It:
(b) Universal Present:
Expressing a truism i.e a statement that is acceptable as a general truth.
The sun rises in the East
The earth is spherical.
God is able
Fire is hot
Men are mortals
(c) Present Action:
Expressing an action, a process or state right now.
He owns ten houses.
They know what they do.
I understand you.
(d) Spontaneous Present:
Expressing an action that is taking place under the speaker's nose and the speaker reporting it as it is happening, for instance, in a football commentary.
e.g. Okocha passes the ball
The goalkeeper catches it
He dribbles the opponent
They score three goals.
PAST TENSE
These are events or situations that happened in the past.
This is the form of the verb indicating the time before now which begins from the last second to eternity. What happens only a second ago will be expressed in the past tense and what happened a million years ago will be expressed in the past tense.
e.g.
He just stopped breathing – 1 second ago.
Jesus died and resurrected over 2000 years ago.


The different forms of the past tense formation have been discussed under Regular and Irregular verbs. A simple past tense
contains a single verb.
(1) I came to school last term.
(2) She ate her food yesterday.
(3) They went to shop.
(4) We slept yesterday.
(5) Akin washed his clothes on Friday.

FUTURE TENSE
This is the expression of future event that has not taken place. It is coming on the way. The two words that we can use to express the future tense are will and shall .Both can be used with I and We.
On the other hand will is used with other pronouns such as: you, she, he, it etc. Eg
(1) I shall travel next week.
(2) We shall meet next year.
(3) He will do it again.
(4) They will pay your money.
(5) She will bring it for us.

There is no change, taking place in the simple form of the verb to express future time, therefore, we do not have a future tense per se but English has a few ways of expressing futurity. Some of which are:
(a) Auxiliary verb construction
(i) Shall + vb + infinite (1st person singular only )
(ii) Will + vb + infinite (all persons) e.g.
I shall try to do my best
She will be here in a moment
(iii)Future orientation in the past(will + perfect)
e.g.
She will have finished her exams by next week
(iv) Will / shall + be + vb + ing + (time) e.g.
I shall / will be doing my best in this test.
(b) Be + going to + verb
(i) Future of present intention
When is Wale going to get married.
(ii) Future of present cause
It is going to rain.
(c) Be + vb + ing + (time)
(i) Future anticipation in the present.
He is travelling tomorrow
(ii) Present continuous / progressive
I am watching that video tonight
(iii) Transition
The Governor is coming to Christ College.
(d) Be + about to + vb
Imminent fulfillment
We are about to leave.
(e) Vb + s
(i) Subordinate conditional clause
What will you do if she marries the chief?
(ii) Immutable event
When is summer?
(iii) Calendar statements
Tomorrow is Friday.
(f) Be + infinitive + vb
(i) Arrangement
They are to be married today
(ii) Command
You are to be here at 10.00am
(iii) Pre-destined future
If you are to succeed, you must work hard.
(g) Vb + s + (time)
She travels tomorrow
The robbers die by hanging
The train leaves at 10.00pm
(h) Wil + shall + vb + time
I will see you next week
She will travel on Monday
We shall meet soon
REVISION QUESTIONS
Choose the right option to complete each of the questions below.
(1) Tunde _________his breakfast daily. (A) take (B) taking (C) takes (D) took
(2 ) I ________to school yesterday. (A) go (B) goes (C) gone (D) went.
(3)The school _________celebrate her founder’s next week.(A) shall (B) will (C) are (D)is
(4) He has_________his assignment. (A) do (B) done (C) does (D) doing.
(5) These ________my friends at school. (A) is (B) her (C) are (D) we.
THEORY ASSIGNMENT
i. What are the uses of the present tense?
ii. Use each of the forms of the present tense in a sentence.
Use the present tense to express five habitual activities of yours and run the commentary of the match between your favourite football club and their opponent.
(1)Write three examples of past simple tense?
(2)Write three examples of present perfect tense?
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
LESSON 4
READING COMPREHENSION
Preparing For A Party (Intensive English Bk 1 Pages 37-39)

Before you read the story , read the following topic sentences :
(a) The house was humming with activities.
(b) The family was preparing for a party.
(c) Our parties never went as we envisaged.
(d) It was almost completely taken over by the animals.
LESSON 5
COMPOSITION
LETTER WRITING:
Letter writing is one of the means of communication in written form. It is continuous writing .The letter contains the address, date, introduction, body, conclusion, and subscript. The two main types of letters we have are: Formal and informal letters.
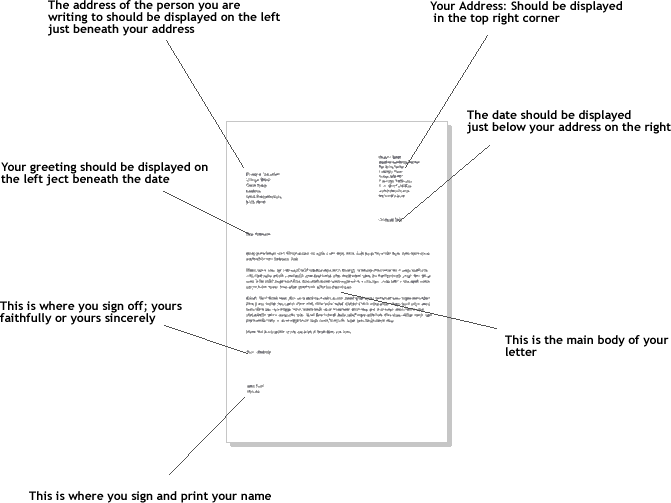
Formal Letter is an official letter that we write to the people in authority or important positions. It contains two addresses. The salutation is Dear Sir/Madam, The letter has a topic or title and the subscription is Yours faithfully with signature and full name. It can be written to people like: President, Minister, Chairman, Principal etc.
Informal letter is the one that we can write to the people that are very close to us. Eg mates, friend, neighbour, brother or sister. It contains one address. The salutation is Dear plus first name. The subscription is Yours sincerely, with First name only without signature.
NOTE: The” Y” of yours should be in capital letter and “s” of sincerely should be in small letter.
REVISION: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option to fill in the gap from options letter A-D
(1) One of the characteristic of informal letter is_____________.( A) two addresses
(B) three addresses ( C) one address (D) two dates.
(2) The letter that we can write to our brother is _________.(A) formal (B) former
(C) informal ( D) abnormal,
(3) The subscription of formal letter is_______. (A) Yours sincerely ( B) yours ever
(C) Yours faithfully ( D) Yours faithful .
(4) The boy wrote ________letter to the Principal of his school.(A) an informal
(B) a formal (C) an informal (D) a friendly.
(5) The one common characteristic of both formal and informal letter is ___________.
(A) address of the writer( B) address of the addressee ( C) title of the letter ( D) signature.
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Vowel /e/ and /æ /
/e/ This is a short vowel sound. It is found in these words bellow:
Ten, bed, pet, keg, pen, shed, men, net, peg etc.
e-----ea-----a-----ie-----u-----ai
met---dead---any---friend-bury--said
red---read---many
bed---breath-Thames
help--instead

/æ/ This sound also is a short vowel sound. It is found in:
Man, cap, map, tap, lad, lap, cat, mad etc.
a-----ai
ram---plait
lamb
gnat
[youtube]https://youtu.be/NavmTDkd8Z8[/youtube]
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/rnpvR-urO-E[/youtube]
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2 & 3
STRUCTURE/GRAMMAR:
TENSES
Tenses are ways by which we can express ourselves based on time that the events take place. In other words, tenses show time of an action in a sentence. The verb plays very important role in tenses.

TENSE AND ASPECTS
Tense is related to verbs only and it is not the same as time. It is the change that takes place in the form of the verb to indicate time. On this basis, there are two basic changes that occur in verb i.e. present time indication and past time
indication. We can say therefore that there are two tenses in English.

Present Tense:
Apart from the forms of the verb BE, the only change in the form of the verb to indicate the present time is
the addition of the ‘s’ morpheme when using the 3rd person singular numbers as subject. The present tense is said to be simple when the verb form is a single word.
e.g.
I sleep-----He sleeps
We sleep----She sleeps----They sleep
You sleep---It sleeps
Changes with the verb BE are as follows
I am a student----------He is a student
We are students---------She is a student
You are a student-------It is a student…
You are students--------They are students

PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
These are the events that take place everyday or that stand as truth.
(1 ) The sun shines.
(2) She cooks on Sundays.
(3) Ade studies in a secondary school .
(4) I love pets.
(5) He loves pets
(6) Bisi goes to school every day.
(7) I go to school early.
(8) You come to our house every Thursday.
(9) She comes to visit her friend on Sundays.
(10) I do my assignment on weekends.
Note: Singular verbs go with singular nouns and plural verbs with plural nouns.
Exceptions are ‘I’ and ‘you’ which go with plural verbs.
Examples:
1. They play in the field on Saturdays.
2. Paul and Silas pray every day.
3. I sing a new song when I am happy.
4. You like oranges.
i. The present tense is used to express habitual activity. For example:
She drinks tea everyday.
ii. It is used to express a future action. For example:
The President arrives in Lagos next week.
iii. It is used to run commentaries. For example:
Okocha passes to Kanu and Kanu to Taribo, he dribbles one, two, three, a shot and it is a goal!
iv. It is used to write headlines in newspapers. For examples:
Bank executives go to jail
The simple present tense appears in the following forms;
(a) Habitual Present:
Expressing a habit or habitual action
I:
We:
You: ---eat everyday
They:
He:
She: ---eats everyday
It:
(b) Universal Present:
Expressing a truism i.e a statement that is acceptable as a general truth.
The sun rises in the East
The earth is spherical.
God is able
Fire is hot
Men are mortals
(c) Present Action:
Expressing an action, a process or state right now.
He owns ten houses.
They know what they do.
I understand you.
(d) Spontaneous Present:
Expressing an action that is taking place under the speaker's nose and the speaker reporting it as it is happening, for instance, in a football commentary.
e.g. Okocha passes the ball
The goalkeeper catches it
He dribbles the opponent
They score three goals.
PAST TENSE
These are events or situations that happened in the past.
This is the form of the verb indicating the time before now which begins from the last second to eternity. What happens only a second ago will be expressed in the past tense and what happened a million years ago will be expressed in the past tense.
e.g.
He just stopped breathing – 1 second ago.
Jesus died and resurrected over 2000 years ago.


The different forms of the past tense formation have been discussed under Regular and Irregular verbs. A simple past tense
contains a single verb.
(1) I came to school last term.
(2) She ate her food yesterday.
(3) They went to shop.
(4) We slept yesterday.
(5) Akin washed his clothes on Friday.

FUTURE TENSE
This is the expression of future event that has not taken place. It is coming on the way. The two words that we can use to express the future tense are will and shall .Both can be used with I and We.
On the other hand will is used with other pronouns such as: you, she, he, it etc. Eg
(1) I shall travel next week.
(2) We shall meet next year.
(3) He will do it again.
(4) They will pay your money.
(5) She will bring it for us.

There is no change, taking place in the simple form of the verb to express future time, therefore, we do not have a future tense per se but English has a few ways of expressing futurity. Some of which are:
(a) Auxiliary verb construction
(i) Shall + vb + infinite (1st person singular only )
(ii) Will + vb + infinite (all persons) e.g.
I shall try to do my best
She will be here in a moment
(iii)Future orientation in the past(will + perfect)
e.g.
She will have finished her exams by next week
(iv) Will / shall + be + vb + ing + (time) e.g.
I shall / will be doing my best in this test.
(b) Be + going to + verb
(i) Future of present intention
When is Wale going to get married.
(ii) Future of present cause
It is going to rain.
(c) Be + vb + ing + (time)
(i) Future anticipation in the present.
He is travelling tomorrow
(ii) Present continuous / progressive
I am watching that video tonight
(iii) Transition
The Governor is coming to Christ College.
(d) Be + about to + vb
Imminent fulfillment
We are about to leave.
(e) Vb + s
(i) Subordinate conditional clause
What will you do if she marries the chief?
(ii) Immutable event
When is summer?
(iii) Calendar statements
Tomorrow is Friday.
(f) Be + infinitive + vb
(i) Arrangement
They are to be married today
(ii) Command
You are to be here at 10.00am
(iii) Pre-destined future
If you are to succeed, you must work hard.
(g) Vb + s + (time)
She travels tomorrow
The robbers die by hanging
The train leaves at 10.00pm
(h) Wil + shall + vb + time
I will see you next week
She will travel on Monday
We shall meet soon

REVISION QUESTIONS
Choose the right option to complete each of the questions below.
(1) Tunde _________his breakfast daily. (A) take (B) taking (C) takes (D) took
(2 ) I ________to school yesterday. (A) go (B) goes (C) gone (D) went.
(3)The school _________celebrate her founder’s next week.(A) shall (B) will (C) are (D)is
(4) He has_________his assignment. (A) do (B) done (C) does (D) doing.
(5) These ________my friends at school. (A) is (B) her (C) are (D) we.
THEORY ASSIGNMENT
i. What are the uses of the present tense?
ii. Use each of the forms of the present tense in a sentence.
Use the present tense to express five habitual activities of yours and run the commentary of the match between your favourite football club and their opponent.
(1)Write three examples of past simple tense?
(2)Write three examples of present perfect tense?
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
LESSON 4
READING COMPREHENSION
Preparing For A Party (Intensive English Bk 1 Pages 37-39)

Before you read the story , read the following topic sentences :
(a) The house was humming with activities.
(b) The family was preparing for a party.
(c) Our parties never went as we envisaged.
(d) It was almost completely taken over by the animals.
LESSON 5
COMPOSITION
LETTER WRITING:
Letter writing is one of the means of communication in written form. It is continuous writing .The letter contains the address, date, introduction, body, conclusion, and subscript. The two main types of letters we have are: Formal and informal letters.

Formal Letter is an official letter that we write to the people in authority or important positions. It contains two addresses. The salutation is Dear Sir/Madam, The letter has a topic or title and the subscription is Yours faithfully with signature and full name. It can be written to people like: President, Minister, Chairman, Principal etc.
Informal letter is the one that we can write to the people that are very close to us. Eg mates, friend, neighbour, brother or sister. It contains one address. The salutation is Dear plus first name. The subscription is Yours sincerely, with First name only without signature.
NOTE: The” Y” of yours should be in capital letter and “s” of sincerely should be in small letter.
REVISION: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option to fill in the gap from options letter A-D
(1) One of the characteristic of informal letter is_____________.( A) two addresses
(B) three addresses ( C) one address (D) two dates.
(2) The letter that we can write to our brother is _________.(A) formal (B) former
(C) informal ( D) abnormal,
(3) The subscription of formal letter is_______. (A) Yours sincerely ( B) yours ever
(C) Yours faithfully ( D) Yours faithful .
(4) The boy wrote ________letter to the Principal of his school.(A) an informal
(B) a formal (C) an informal (D) a friendly.
(5) The one common characteristic of both formal and informal letter is ___________.
(A) address of the writer( B) address of the addressee ( C) title of the letter ( D) signature.
WEEK 5
LESSON 1
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: My Childhood


In this story you are about to read, the opening sentence in paragraph 1 is: Lubwa was a good place in which to live. The details tell what was good about the place:
i. peace and order
ii. examples of kindness
iii. examples of friendliness.
The middle sentence says “I look back upon (my life there) with …thankfulness….” The writer is glad he grew up there.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise5.2.2; pages 48-49.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 5.2. 3, 5.2.3 & 5.2.5; pages 49-51.
LESSON 2 & 3
STRUCTURE: CONJUNCTIONS AND PREPOSITIONS
CONJUNCTIONS

Conjunctions are words used as joiners.
The following are the kinds of conjunctions:
1. Coordinating conjunction
2. Subordinating conjunction
3. Correlative conjunction
1. COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS: AND,OR BUT,
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, clauses of equal status together.
i. They were very rich but very sad
ii. They want John and Tina.
iii. I prefer Shade or Ebele.


A. CORRELATIVE CONJUNCTIONS: These are conjunctions that are used in pairs (i.e. in twos). They are often referred to as correlatives. Among the most common ones are: either…or, neither…and, both…and, not only…but also.
Examples:
i. Both John and Tina are his cousins.
ii. You can either come tomorrow or send someone on Friday.
iii. Neither you nor I am wrong.
iv. Either Segun or his sisters are innocent.
v. Neither the students nor the teacher is right.
vi. Neither the teacher nor the students are right

SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS: Subordinating conjunctions are also known as subordinators. Examples are:
When, although, since, after, unless, yet, until, where etc
Examples:
i. I shall see you when I come back.
ii. You should tell us where you live.
iii. Unless you work hard you may not pass.
iv. While she was working the child sneaked out.


Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
PREPOSITIONS

It shows relationship between two nouns, a noun and a pronoun or two pronouns .e.g. on, by, across, in, inside, beneath, against, over, behind down, upon, off, between etc.
i. The book is on the table.
ii. The book is beneath the table.
iii. The book is leaning against the table.
iv. The book is beside the table.
v. She held the book over the table.

EXERCISE
Underline the conjunctions used in the following sentences. Then identify the type of conjunction (coordinating, correlative, or subordinating) used each case.
1. We may go either on Sunday or on Monday.
2. He not only wrote but also sent some money.
3. Neither the principal nor the Vice-Principal is in the hall now.
4. We saw a man, a woman and a little girl.
5. He came but he didn’t address the gathering.
6. You can see me when you are leaving.
7. She is happy because passed.
8. Both Bimpe and Nkechi look alike.
9. He is small but strong-minded.
10. Come if you like.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
Practice Test 5
Practice Test 6
LESSON 4
Speech work: Vowel /a:/
This is a long vowel which may be described as a back vowel even though it is actually articulated with the part of the tongue between the centre and the back. While the lips are in neutral position, the jaw is fully opened. The usual spelling symbols for /a:/ are given below:
“a” as in pass, father, barrage, class, garage, bath, grass, guava, saga, answer, steadfast etc
“ar” as in cart, mark, bark, mart, dark, part etc
“al” as in palm, calm, balm, psalms, palm, half, qualm,etc
“au” as in laugh, aunt, draught etc.
“ear” as in heart,
“our” as in our
“oi” as in reservoir, chamois, memoir, bourgeois, repertoire
a------ar------ear-----er-------al-----au
pass---arm-----heart---clerk----half---aunt
father-star----hearth—-sergeant-calm---laugh
after—-part---------------------pal
Some people tend to pronounce the long /a: / as if it is the short / æ/ but the difference between the two vowels is clearly illustrated in the following pairs of words:
/ æ/ /a:/
Ban barn
Cat cart
Pat part
Hat heart
Bat bath
As ask
Pack park
Evaluation:
1. Describe how the sound /a: / is produced.
2. List some of the spelling symbols of /a: / and give examples of words realizable with it.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
[youtube]<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/NavmTDkd8Z8" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>[/youtube] [youtube]<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/1F47WdIjn5U" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>[/youtube]
LESSON 5
TOPIC: LITERATURE
SUB- TOPIC:
i. Folktales

ii. African and non African folktales
folktales are often stories of imaginary people that live in the past.
They are sometimes stories of animal kingdom, from which we can draw lessons. They are usually stories that refer to human behaviour as the animal are made to talk and act lke humans. Folktale has a central idea or theme which runs through the story. They often teach a moral lesson.

Read the African and non African folktales in Junior English Today Bk 1 page 49 and 78
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: My Childhood


In this story you are about to read, the opening sentence in paragraph 1 is: Lubwa was a good place in which to live. The details tell what was good about the place:
i. peace and order
ii. examples of kindness
iii. examples of friendliness.
The middle sentence says “I look back upon (my life there) with …thankfulness….” The writer is glad he grew up there.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise5.2.2; pages 48-49.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 5.2. 3, 5.2.3 & 5.2.5; pages 49-51.
LESSON 2 & 3
STRUCTURE: CONJUNCTIONS AND PREPOSITIONS
CONJUNCTIONS

Conjunctions are words used as joiners.
The following are the kinds of conjunctions:
1. Coordinating conjunction
2. Subordinating conjunction
3. Correlative conjunction
1. COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS: AND,OR BUT,
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, clauses of equal status together.
i. They were very rich but very sad
ii. They want John and Tina.
iii. I prefer Shade or Ebele.


A. CORRELATIVE CONJUNCTIONS: These are conjunctions that are used in pairs (i.e. in twos). They are often referred to as correlatives. Among the most common ones are: either…or, neither…and, both…and, not only…but also.
Examples:
i. Both John and Tina are his cousins.
ii. You can either come tomorrow or send someone on Friday.
iii. Neither you nor I am wrong.
iv. Either Segun or his sisters are innocent.
v. Neither the students nor the teacher is right.
vi. Neither the teacher nor the students are right


SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS: Subordinating conjunctions are also known as subordinators. Examples are:
When, although, since, after, unless, yet, until, where etc
Examples:
i. I shall see you when I come back.
ii. You should tell us where you live.
iii. Unless you work hard you may not pass.
iv. While she was working the child sneaked out.


Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
PREPOSITIONS

It shows relationship between two nouns, a noun and a pronoun or two pronouns .e.g. on, by, across, in, inside, beneath, against, over, behind down, upon, off, between etc.
i. The book is on the table.
ii. The book is beneath the table.
iii. The book is leaning against the table.
iv. The book is beside the table.
v. She held the book over the table.

EXERCISE
Underline the conjunctions used in the following sentences. Then identify the type of conjunction (coordinating, correlative, or subordinating) used each case.
1. We may go either on Sunday or on Monday.
2. He not only wrote but also sent some money.
3. Neither the principal nor the Vice-Principal is in the hall now.
4. We saw a man, a woman and a little girl.
5. He came but he didn’t address the gathering.
6. You can see me when you are leaving.
7. She is happy because passed.
8. Both Bimpe and Nkechi look alike.
9. He is small but strong-minded.
10. Come if you like.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
Practice Test 5
Practice Test 6
LESSON 4
Speech work: Vowel /a:/
This is a long vowel which may be described as a back vowel even though it is actually articulated with the part of the tongue between the centre and the back. While the lips are in neutral position, the jaw is fully opened. The usual spelling symbols for /a:/ are given below:
“a” as in pass, father, barrage, class, garage, bath, grass, guava, saga, answer, steadfast etc
“ar” as in cart, mark, bark, mart, dark, part etc
“al” as in palm, calm, balm, psalms, palm, half, qualm,etc
“au” as in laugh, aunt, draught etc.
“ear” as in heart,
“our” as in our
“oi” as in reservoir, chamois, memoir, bourgeois, repertoire
a------ar------ear-----er-------al-----au
pass---arm-----heart---clerk----half---aunt
father-star----hearth—-sergeant-calm---laugh
after—-part---------------------pal

Some people tend to pronounce the long /a: / as if it is the short / æ/ but the difference between the two vowels is clearly illustrated in the following pairs of words:
/ æ/ /a:/
Ban barn
Cat cart
Pat part
Hat heart
Bat bath
As ask
Pack park
Evaluation:
1. Describe how the sound /a: / is produced.
2. List some of the spelling symbols of /a: / and give examples of words realizable with it.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
[youtube]<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/NavmTDkd8Z8" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>[/youtube] [youtube]<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/1F47WdIjn5U" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>[/youtube]
LESSON 5
TOPIC: LITERATURE
SUB- TOPIC:
i. Folktales

ii. African and non African folktales
folktales are often stories of imaginary people that live in the past.
They are sometimes stories of animal kingdom, from which we can draw lessons. They are usually stories that refer to human behaviour as the animal are made to talk and act lke humans. Folktale has a central idea or theme which runs through the story. They often teach a moral lesson.

Read the African and non African folktales in Junior English Today Bk 1 page 49 and 78
WEEK 6
LESSON 1
ASPECT: SPEECH SOUND
Vowel sounds /ᴐ/ and /ᴐ:/
/ ᴐ/: This is a short vowel articulated with the back of the tongue while the jaw is “open”. The lips are rounded for the pronunciation of this vowel and the common spelling symbols are given below:
– o----a----au
sorry was because
pot what sausage
rock quality Austria
long quantity
porridge want
‘o’ as in pot , hot, box, dog, sorry, lock, loss, God, etc
‘a’ as in was, want, wander, what, watch, quantity, quality, quarrel, yatch, etc
‘au’ as in because, austere, sausage, cauliflower, Austria, Australia, laurel, etc
‘ou’ as in trough, cough, etc
‘ow’ as in knowledge, etc
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMJrIzjnmDM[/youtube]
/ ᴐ:/ : This vowel is a long back vowel which is produced by raising the back of the tongue to a height where jaw is between the “half-close” and “half-open” position. The lips are rounded. It is important to remember that / ᴐ:/ is a long vowel which should not be pronounced as if it is similar to the short / ᴐ/. The common spelling symbols are listed below:
or----aw---ou-----au------a
cord law bought daughter all
horse saw thought cause water
for lawn ought caught call
ar----ore---oor—our---oar
war before door four board
quarter store floor court
“al” as in talk
“aw” as in saw,
“ar” as in war,
“oar” as in board,
“or” as in sport,
“ore” as in core,
“oor” as in door,
“ou” as in bought
Pronounce the following pairs of words and pay attention to the difference between the short / ᴐ/ and the long / ᴐ:/.
/ ᴐ/ / ᴐ:/
Cod cord
Cot court
Fox forks
Pot port
Spot sport
Not naught
God gaud
Evaluation:
1. Describe the place of production of the sounds: / ᴐ/ and / ᴐ:/.
2. Give five examples on each of the sounds.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/4CPoq1mnRI4?lis ... D36E1FF870[/youtube] [youtube]https://www.youtube.com/CMc_fES-Dx4[/youtube]
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2 & 3
TOPIC: TENSES
SUBTOPIC: PRESENT TENSE
There are three broad divisions of present tense. They are present simple tense, present continuous tense, present perfect tense.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE:
It is used for actions that take place consistently (every time). They are habitual actions.
EXAMPLES:
I. He comes here often.
II. They come here every weekend.
III. She dances everyday
We can also use the present tense for actions that are being reported as they are happening especially in sports commentary.
i He heads the ball
Ii He passes it to Okocha
Iii Okocha scores.
Present simple tense can be used to express the present condition or state of a person or a thing as in:
I am a teacher .
She is my wife.
We are gentle people.
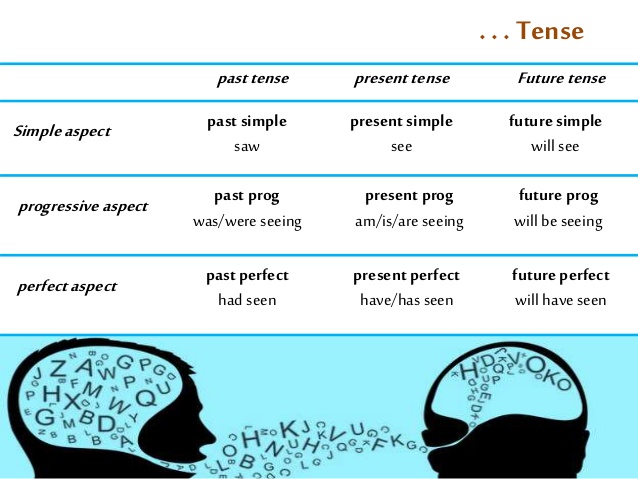
THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
This is used for actions that are taking place at the time we are talking.
Eg Mr Adebayo is teaching us.
I am eating my dinner.
We are going to the church.
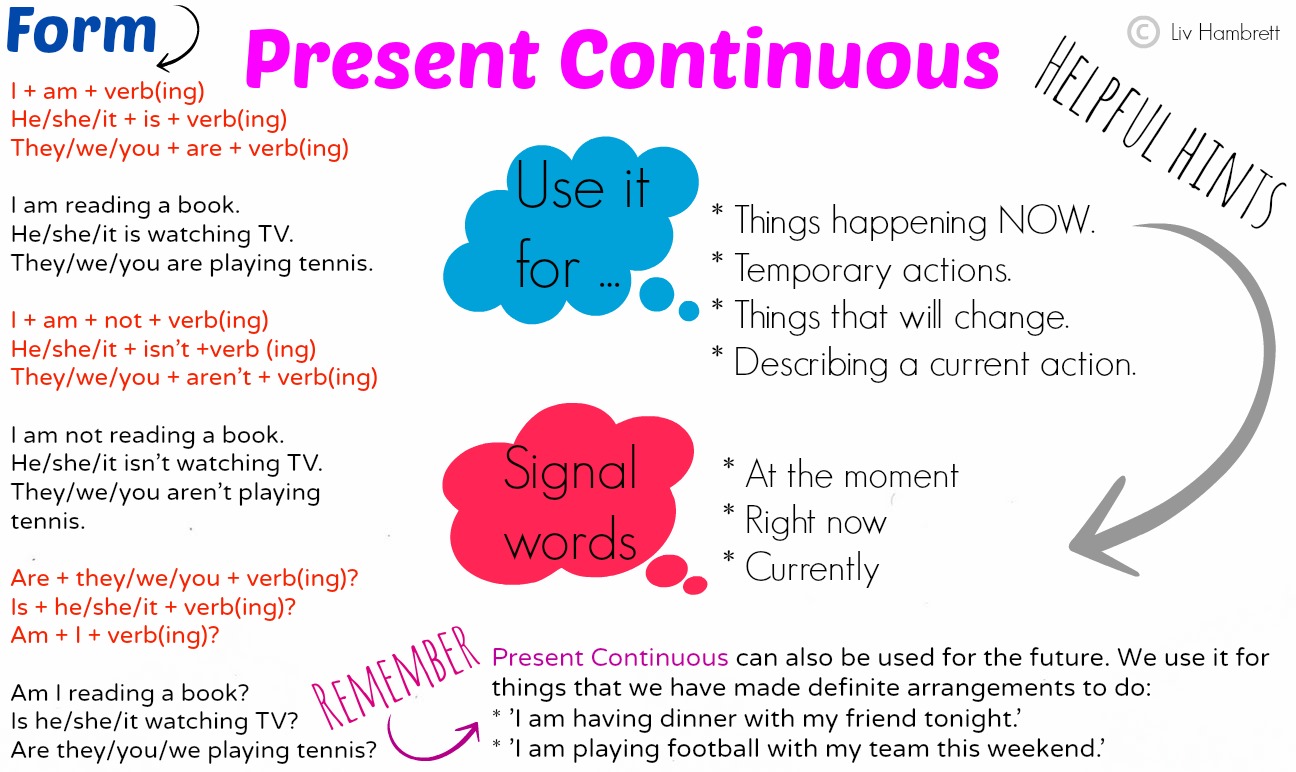
THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE.

This is used to show the action that has just happened.eg
She has just gone out.
We have left the place.
They have just completed the building.
When the event started some time ago and it is still on eg.
I have lived here for ten years
She has taught English for five years.
They have been wise all their lives.
NOTE : We use “have” with the following pronouns: I , We, You and They.
While we use “has” with the pronouns he, she and it.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Further Studies 5
LESSON 4
COMPOSITION
TOPIC: LETTER WRITING
SUB-TOPIC: INFORMAL LETTER
An informal letter is a letter written to any of the following persons: father, mother, brother, sister, uncle, aunt, nephew, niece cousin, in-law, close friend, pen-friend, classmate, neighbour, etc. It requires only one address.
CONTENT
FEATURES OF INFORMAL LETTERS
1. Address of writer (written at the top right-hand corner of your writing sheet of paper)
2. Date (written under the writers address).
3. Opening salutation (e.g; Dear Uncle, Aunt, Brother, Sister, etc).
4. Body(content of the letter)
5. Closing salutation is Yours sincerely, (no signature or surname is allowed.)

EVALUATION
1. Mention 4 features of informal letter.
2. Informal letter has _____ address.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 1
LESSON 5
Reading Comprehension :My childhood(Intensive English book 1 pages 48-50)
The comprehension questions should be attempted.

Assignment.
Write a letter to your parents telling them about your needs in the school and why you need them as they are coming for the visiting day. Your answer should be about 200 words .
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
Practice Test 2
ASPECT: SPEECH SOUND

Vowel sounds /ᴐ/ and /ᴐ:/
/ ᴐ/: This is a short vowel articulated with the back of the tongue while the jaw is “open”. The lips are rounded for the pronunciation of this vowel and the common spelling symbols are given below:
– o----a----au
sorry was because
pot what sausage
rock quality Austria
long quantity
porridge want
‘o’ as in pot , hot, box, dog, sorry, lock, loss, God, etc
‘a’ as in was, want, wander, what, watch, quantity, quality, quarrel, yatch, etc
‘au’ as in because, austere, sausage, cauliflower, Austria, Australia, laurel, etc
‘ou’ as in trough, cough, etc
‘ow’ as in knowledge, etc
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMJrIzjnmDM[/youtube]
/ ᴐ:/ : This vowel is a long back vowel which is produced by raising the back of the tongue to a height where jaw is between the “half-close” and “half-open” position. The lips are rounded. It is important to remember that / ᴐ:/ is a long vowel which should not be pronounced as if it is similar to the short / ᴐ/. The common spelling symbols are listed below:
or----aw---ou-----au------a
cord law bought daughter all
horse saw thought cause water
for lawn ought caught call
ar----ore---oor—our---oar
war before door four board
quarter store floor court
“al” as in talk
“aw” as in saw,
“ar” as in war,
“oar” as in board,
“or” as in sport,
“ore” as in core,
“oor” as in door,
“ou” as in bought
Pronounce the following pairs of words and pay attention to the difference between the short / ᴐ/ and the long / ᴐ:/.
/ ᴐ/ / ᴐ:/
Cod cord
Cot court
Fox forks
Pot port
Spot sport
Not naught
God gaud
Evaluation:
1. Describe the place of production of the sounds: / ᴐ/ and / ᴐ:/.
2. Give five examples on each of the sounds.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/4CPoq1mnRI4?lis ... D36E1FF870[/youtube] [youtube]https://www.youtube.com/CMc_fES-Dx4[/youtube]
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2 & 3
TOPIC: TENSES
SUBTOPIC: PRESENT TENSE
There are three broad divisions of present tense. They are present simple tense, present continuous tense, present perfect tense.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE:
It is used for actions that take place consistently (every time). They are habitual actions.
EXAMPLES:
I. He comes here often.
II. They come here every weekend.
III. She dances everyday
We can also use the present tense for actions that are being reported as they are happening especially in sports commentary.
i He heads the ball
Ii He passes it to Okocha
Iii Okocha scores.
Present simple tense can be used to express the present condition or state of a person or a thing as in:
I am a teacher .
She is my wife.
We are gentle people.

THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
This is used for actions that are taking place at the time we are talking.
Eg Mr Adebayo is teaching us.
I am eating my dinner.
We are going to the church.

THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE.

This is used to show the action that has just happened.eg
She has just gone out.
We have left the place.
They have just completed the building.
When the event started some time ago and it is still on eg.
I have lived here for ten years
She has taught English for five years.
They have been wise all their lives.
NOTE : We use “have” with the following pronouns: I , We, You and They.
While we use “has” with the pronouns he, she and it.


Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Further Studies 5
LESSON 4
COMPOSITION
TOPIC: LETTER WRITING
SUB-TOPIC: INFORMAL LETTER
An informal letter is a letter written to any of the following persons: father, mother, brother, sister, uncle, aunt, nephew, niece cousin, in-law, close friend, pen-friend, classmate, neighbour, etc. It requires only one address.
CONTENT
FEATURES OF INFORMAL LETTERS
1. Address of writer (written at the top right-hand corner of your writing sheet of paper)
2. Date (written under the writers address).
3. Opening salutation (e.g; Dear Uncle, Aunt, Brother, Sister, etc).
4. Body(content of the letter)
5. Closing salutation is Yours sincerely, (no signature or surname is allowed.)

EVALUATION
1. Mention 4 features of informal letter.
2. Informal letter has _____ address.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 1
LESSON 5
Reading Comprehension :My childhood(Intensive English book 1 pages 48-50)
The comprehension questions should be attempted.

Assignment.
Write a letter to your parents telling them about your needs in the school and why you need them as they are coming for the visiting day. Your answer should be about 200 words .
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
Practice Test 2
WEEK 7
LESSON 1
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Someone

You cannot read a poem in quite the same way as you read stories. You don’t look for topic sentences, for example. But you look for pictures. Each detail suggests a picture. In this poem, pictures appear every two lines.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise7.2.2; pages 66-68.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises7.2. 3 and 7.3.5; pages68-72.
LESSON 2
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO CONSONANTS
A consonant is a speech sound which is produced with the obstruction of airstream. The obstruction could be ‘partial’ or ‘total’.
There are 24 consonant sounds in English studies. They are:
/p/ /b/ /ʈ/ /d/ /k/ /g/ /ʧ/ /ʤ/ /f/ /v/ /Ө/ /ð/ /s/ /z/ /∫/ /Ӡ/ /h/ /Ɩ/ /r/ /m/ /ŋ/ /j/ /w/ /n/
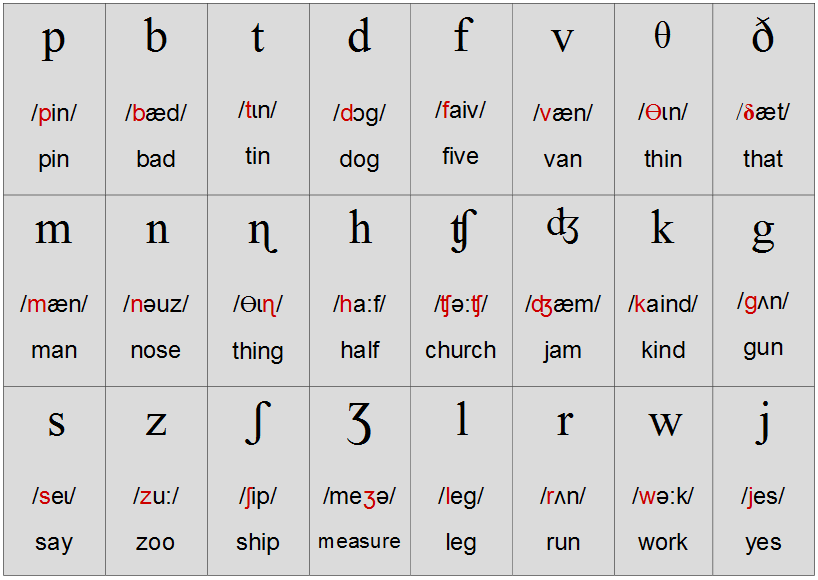
/p/----- put, pat, pot, peg, pit, push, wrapper, pass, place, happen, party
/b/---- but, bet, book, boom, boost, bay, baby, rob, bad, bat, back, abort, about, abide
/ʈ/--- ten, tap, tomb, table, take, tack, track
/d/---- dam, do, cord, draft, powder, advert, kid, deep, dim, divide, diary, dark, middle, paddle
/k/----- kid, kiss, cock, fix, six, choir, chord, require, back, calculate, kit, chasm
/g/ ----- game, goggle, got, gum, gay, guy, example, get, rogue, girl, grow
/ʧ/ ----fetch, match, march, rich, reach, nature, pasture, patch, chain, choice, children, Christ, Christians, character
/ʤ/ ---- gin, joy, edge, badge, jaw, jest, jeep, gem, general, gentle, page, judge, jam, giant
/f/------ tough, fall, phone, elephant, photo, food, fleet, fault
/v/ -------very, nephew, of, value, vice, voice, van, view, prove, visible
/Ө/ ------ thin, think, three, threw, though, length, breath, theatre, theme, thick, thicket, third, thrust
/ð/ ------- the, father, mother, them, that, thine, bathe, then, rather, this, there
/s/ ------- science, class, fast, slow, city, pass, dress, psychology, lace, face, pastor, taste, set
/z/ ------zoo, zoom, lazy, zigzag, zinc, close, rose, represent, reason, candies, laze, raise, zebra, easy
/∫/ ------ chalet, chateau, charade, machine, education, social, palatial, mission, short, sure, passion pressure
/Ӡ/------ garage, measure, treasure, leisure, television, vision, confusion, decision, fusion, pleasure, division, closure, usual
/h/ ----- house, home, harrow, harassment
/Ɩ/------- look, late, life, lake, lift, later, letter, local, lion, low, love, lame, lie
/r/------ robe, right, reflex, run, carry, merry, bright, story, bury, rite, wrong, wrote, radio
/m/------ flame, hammer, man, malt, make, come, mother, magic
/ŋ/------- bang, uncle, bank, sing, long, king, zinc, single, thank
/j/-------- you, yawn, yellow, yam, union, use, yes, university
/w/------ one, wine, when, suite, quit, work, what, where, which, wife
/n/-------- know, night, knight, knowledge, banner
EVALUATION
1.What is consonant?
2.State the classifications of consonant sounds.
ASSIGNMENT
Identify the consonant sounds in the following
Chair, chain, church, chip, match, teacher
LESSON 3 & 4
Aspect: Structure
Topic: Tenses (The Past Tense)
The past tense is sub divided into four sub-topics:
(1) The Simple past tense
(2) The past continuous tense
(3) The past perfect tense
(4) The past perfect continuous tense.
The Simple Past Tense:

This shows that an action started in the past and was completed in the past. It also indicates a past habit which the person being referred to is no more involved
e.g. (1) I worked yesterday.
(2) Olu passed the last stage of the examination last year.
(3)He made his way home.
(4) She sang so beautifully.
(5)I was employed in 1991.
(6)He used to travel home when he was young.
(7)They kept mute over the issue.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
The Past Continuous Tense:

It is used to express the following:
(1) An action that was going on in the past, at a particular time.
(2) That action that was going on in the past but was interrupted by another action.
e.g. (1) I was teaching the students yesterday when the principal sent for me.
(2) While the bus was moving, the woman jumped down.
(3) Ayo and I were reading for our examination this last week.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
The Past Perfect Tense:

It is used to indicate that two or more actions took place in the past but one happened or was completed before the other. The action that happened first is expressed in the past perfect tense while the other action is expressed in the simple past tense.
e.g. (1) The boy had died before help reached him.
(2) By the time I got to the office, Olu had left for the meeting.
(3) The suspect had escaped when the police raised the alarm.
(4) James had alighted by the time we got to the bus –stop.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
The Past perfect Continuous tense:

This is used to show that an action had been completed at a particular time in the past but is being discussed or analyzed at present.
E.g. (1) We had been praying since 1998 before God intervened in 2008
(2) The girl had been writing SSCE for five years before she passed it last year.
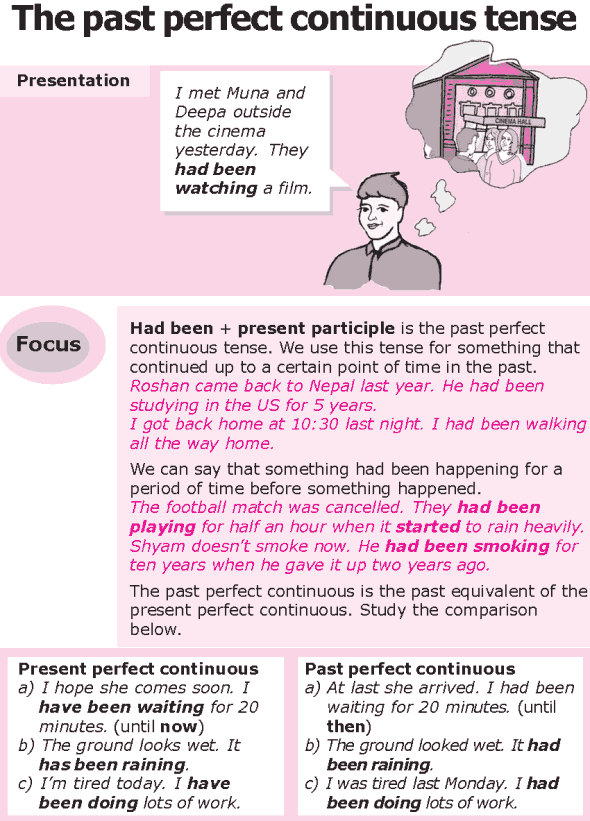
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Evaluation: Choose the correct answer:
i. She ……………. the assignment before I came in.(a)has already finished (b) had already finished(c) have already finished (d) was finishing
ii. The news ………….. before I returned from office that day (a) have been broadcast (b) has been broadcast (c) has been broadcast (d) had been broadcast
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
Practice Test 5
Practice Test 6
Practice Test 7
Practice Test 8
Practice Test 9
Practice Test 10
LESSON 5
Aspect: Continuous Writing
TOPIC: NARRATIVE ESSAY
It is a complete account of a story, an event or incident which the writer experienced or witnessed. A narrative essay is one that requires you to narrate an event, to tell a story or to relate how an incident happened. It is the type that requires relating past events or experienced.

The situations in which writing narrative essays are required include the following:
1) Writing a personal experience
2) Writing the story of another person
3) Giving an action of an incident as an eye-witness
4) Writing a story to illustrate /prove the fact presented by proverb.

USEFUL HINTS ON HOW TO WRITE A GOOD NARRATIVE ESSAY
1. Content
a) Narrative events which are believable, credible and possible, you should make your story appear true
b) You are expected to narrate the events in relevant details so as to give your reader an insight into the events you are narrating
c) Be concerned with the incident or event, the persons involved and the time and place, when the incident happened
2. Organization
a) Write your narrative essay in a lively manner by opening up your essay in separate and interesting paragraph
b) Your paragraphs should be properly developed
3. Expression
a) You are expected to use language that is chatty, friendly, informal and casual
b) Past tense is the normal tense in a narrative essay since the writer is involved in reporting a past experience or incident, he should depend on the use of the past tense.
E.g.
i. I narrowly escaped being attacked by a group of angry people when I was going to my office that faithful day.
ii. The woman realized that reporting the case to the police was not going to be a productive effort since she could not identify any of the robbers
4. Use of reported speech
The writer of a good narrative essay can make his narration more interesting if he can use the reported speech or direct speech appropriately e.g.
I. The manager confirmed that he noticed some strange behavior among the workers who claimed to be loyal.
II. The director general of the company shouted “these wicked souls have ruined the organization”.
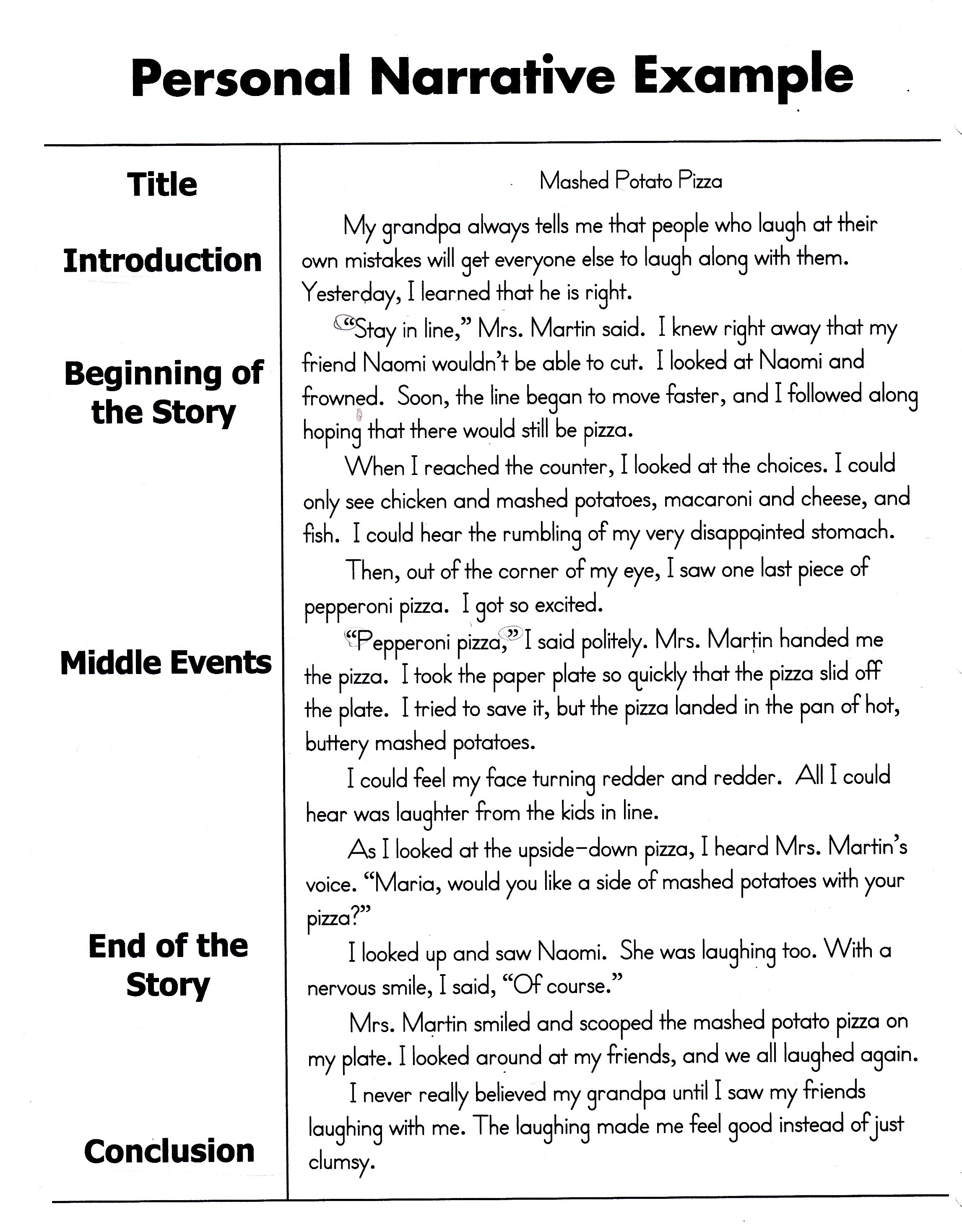
EVALUATION
Which of these essays illustrate a narrative essay?
1)Write an essay arguing for or against the motion
“Polygamy is better than monogamy”
2)Write an essay illustrating a careless loving mother
3)Describe a political leader whose life you cherish
ASSIGNMENT
Write a narrative essay on the topic “My excursion to bar-beach”.
Further Studies
Further Studies
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: Someone

You cannot read a poem in quite the same way as you read stories. You don’t look for topic sentences, for example. But you look for pictures. Each detail suggests a picture. In this poem, pictures appear every two lines.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise7.2.2; pages 66-68.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises7.2. 3 and 7.3.5; pages68-72.
LESSON 2
ASPECT: SPEECH WORK
TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO CONSONANTS
A consonant is a speech sound which is produced with the obstruction of airstream. The obstruction could be ‘partial’ or ‘total’.
There are 24 consonant sounds in English studies. They are:
/p/ /b/ /ʈ/ /d/ /k/ /g/ /ʧ/ /ʤ/ /f/ /v/ /Ө/ /ð/ /s/ /z/ /∫/ /Ӡ/ /h/ /Ɩ/ /r/ /m/ /ŋ/ /j/ /w/ /n/

/p/----- put, pat, pot, peg, pit, push, wrapper, pass, place, happen, party
/b/---- but, bet, book, boom, boost, bay, baby, rob, bad, bat, back, abort, about, abide
/ʈ/--- ten, tap, tomb, table, take, tack, track
/d/---- dam, do, cord, draft, powder, advert, kid, deep, dim, divide, diary, dark, middle, paddle
/k/----- kid, kiss, cock, fix, six, choir, chord, require, back, calculate, kit, chasm
/g/ ----- game, goggle, got, gum, gay, guy, example, get, rogue, girl, grow
/ʧ/ ----fetch, match, march, rich, reach, nature, pasture, patch, chain, choice, children, Christ, Christians, character
/ʤ/ ---- gin, joy, edge, badge, jaw, jest, jeep, gem, general, gentle, page, judge, jam, giant
/f/------ tough, fall, phone, elephant, photo, food, fleet, fault
/v/ -------very, nephew, of, value, vice, voice, van, view, prove, visible
/Ө/ ------ thin, think, three, threw, though, length, breath, theatre, theme, thick, thicket, third, thrust
/ð/ ------- the, father, mother, them, that, thine, bathe, then, rather, this, there
/s/ ------- science, class, fast, slow, city, pass, dress, psychology, lace, face, pastor, taste, set
/z/ ------zoo, zoom, lazy, zigzag, zinc, close, rose, represent, reason, candies, laze, raise, zebra, easy
/∫/ ------ chalet, chateau, charade, machine, education, social, palatial, mission, short, sure, passion pressure
/Ӡ/------ garage, measure, treasure, leisure, television, vision, confusion, decision, fusion, pleasure, division, closure, usual
/h/ ----- house, home, harrow, harassment
/Ɩ/------- look, late, life, lake, lift, later, letter, local, lion, low, love, lame, lie
/r/------ robe, right, reflex, run, carry, merry, bright, story, bury, rite, wrong, wrote, radio
/m/------ flame, hammer, man, malt, make, come, mother, magic
/ŋ/------- bang, uncle, bank, sing, long, king, zinc, single, thank
/j/-------- you, yawn, yellow, yam, union, use, yes, university
/w/------ one, wine, when, suite, quit, work, what, where, which, wife
/n/-------- know, night, knight, knowledge, banner
EVALUATION
1.What is consonant?
2.State the classifications of consonant sounds.
ASSIGNMENT
Identify the consonant sounds in the following
Chair, chain, church, chip, match, teacher
LESSON 3 & 4
Aspect: Structure
Topic: Tenses (The Past Tense)
The past tense is sub divided into four sub-topics:
(1) The Simple past tense
(2) The past continuous tense
(3) The past perfect tense
(4) The past perfect continuous tense.
The Simple Past Tense:

This shows that an action started in the past and was completed in the past. It also indicates a past habit which the person being referred to is no more involved
e.g. (1) I worked yesterday.
(2) Olu passed the last stage of the examination last year.
(3)He made his way home.
(4) She sang so beautifully.
(5)I was employed in 1991.
(6)He used to travel home when he was young.
(7)They kept mute over the issue.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
The Past Continuous Tense:

It is used to express the following:
(1) An action that was going on in the past, at a particular time.
(2) That action that was going on in the past but was interrupted by another action.
e.g. (1) I was teaching the students yesterday when the principal sent for me.
(2) While the bus was moving, the woman jumped down.
(3) Ayo and I were reading for our examination this last week.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
The Past Perfect Tense:

It is used to indicate that two or more actions took place in the past but one happened or was completed before the other. The action that happened first is expressed in the past perfect tense while the other action is expressed in the simple past tense.
e.g. (1) The boy had died before help reached him.
(2) By the time I got to the office, Olu had left for the meeting.
(3) The suspect had escaped when the police raised the alarm.
(4) James had alighted by the time we got to the bus –stop.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
The Past perfect Continuous tense:

This is used to show that an action had been completed at a particular time in the past but is being discussed or analyzed at present.
E.g. (1) We had been praying since 1998 before God intervened in 2008
(2) The girl had been writing SSCE for five years before she passed it last year.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Evaluation: Choose the correct answer:
i. She ……………. the assignment before I came in.(a)has already finished (b) had already finished(c) have already finished (d) was finishing
ii. The news ………….. before I returned from office that day (a) have been broadcast (b) has been broadcast (c) has been broadcast (d) had been broadcast
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
Practice Test 5
Practice Test 6
Practice Test 7
Practice Test 8
Practice Test 9
Practice Test 10
LESSON 5
Aspect: Continuous Writing
TOPIC: NARRATIVE ESSAY
It is a complete account of a story, an event or incident which the writer experienced or witnessed. A narrative essay is one that requires you to narrate an event, to tell a story or to relate how an incident happened. It is the type that requires relating past events or experienced.

The situations in which writing narrative essays are required include the following:
1) Writing a personal experience
2) Writing the story of another person
3) Giving an action of an incident as an eye-witness
4) Writing a story to illustrate /prove the fact presented by proverb.

USEFUL HINTS ON HOW TO WRITE A GOOD NARRATIVE ESSAY
1. Content
a) Narrative events which are believable, credible and possible, you should make your story appear true
b) You are expected to narrate the events in relevant details so as to give your reader an insight into the events you are narrating
c) Be concerned with the incident or event, the persons involved and the time and place, when the incident happened
2. Organization
a) Write your narrative essay in a lively manner by opening up your essay in separate and interesting paragraph
b) Your paragraphs should be properly developed
3. Expression
a) You are expected to use language that is chatty, friendly, informal and casual
b) Past tense is the normal tense in a narrative essay since the writer is involved in reporting a past experience or incident, he should depend on the use of the past tense.
E.g.
i. I narrowly escaped being attacked by a group of angry people when I was going to my office that faithful day.
ii. The woman realized that reporting the case to the police was not going to be a productive effort since she could not identify any of the robbers
4. Use of reported speech
The writer of a good narrative essay can make his narration more interesting if he can use the reported speech or direct speech appropriately e.g.
I. The manager confirmed that he noticed some strange behavior among the workers who claimed to be loyal.
II. The director general of the company shouted “these wicked souls have ruined the organization”.

EVALUATION
Which of these essays illustrate a narrative essay?
1)Write an essay arguing for or against the motion
“Polygamy is better than monogamy”
2)Write an essay illustrating a careless loving mother
3)Describe a political leader whose life you cherish
ASSIGNMENT
Write a narrative essay on the topic “My excursion to bar-beach”.
Further Studies
Further Studies
WEEK 8
LESSON 1
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonants /p/ and /b/
1. /p/ - This is a voiceless bilabial plosive sound. It can be realized at the initial, medial and the final positions.
Examples: pen, peg, paid, leg, keeper, happy, lip, cheap, ship etc.
Note that /p/ is silent when it precedes ‘n’ and some other words like: corps, receipt, psalm, psychiatry, pneumatic, pneumonia etc.
Also, ‘ph’ is pronounced as /f/ and /v/ in certain words such as physics, phobia, phase, Stephen, nephew. Yet, only /p/ is pronounced in ‘shepherd’ while ‘h’ is silent though both combined in the word.
p------pp
paper apple
proper supply
reply apple
stop
/p/ appear the same way in written and spoken form except for the silent p which belongs to other families of sound e.g.
coup, psalm, etc.
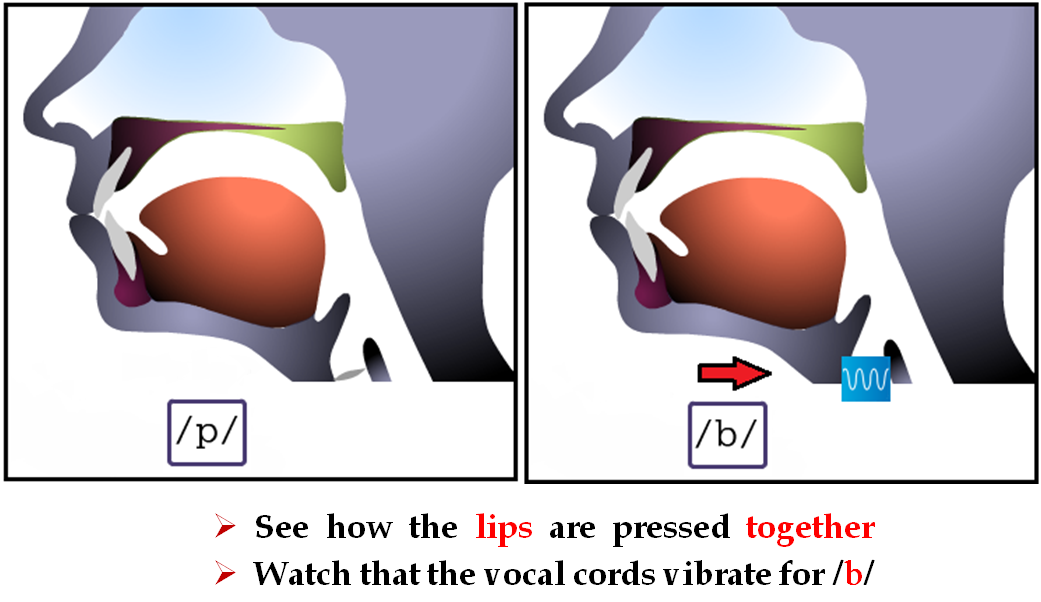
2. /b/ - This consonant, a voiced bilabial plosive, can occur at the initial, medial, and final positions. Its spelling symbols are:
‘b’ – bin, ban, bat, labour, tab, mob, nib.
‘bb’ – babble, blabber, bubble.
Note that ‘b’ is silent when:
a. It precedes‘t’ e.g. debt, doubt, subtle.
b. It succeeds ‘m’ lamb, tomb, bomb, comb, dumb, plumber, climb, plumb, crumb.
However, it is pronounced in chamber, member, timber, timbre, September, November, and December.
/b/ appear the same in written and spoken form except for the silent b which belongs to the /m/ family e.g.
comb, bomb, etc.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/JmsRkAeNCY0[/youtube]
Further Studies
LESSON 2
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: The Mountebank
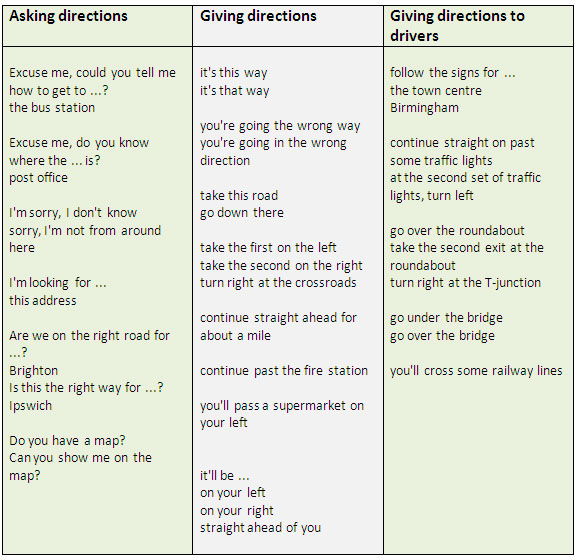
The writer points out the meanings of passages by using “direction words”. When you go to visit a friend for the first time, your friend gives you directions. He tells you:
I. Go up this way
II. Turn left by the market
You will find directions in the story below. Emeka’s aunt gave him many directions. You must follow directions carefully after reading.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 8.2.2; pages 75-78.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 8.2. 3, 8.2.4, 8.3.4 and 8.3.5; pages 78-83.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Descriptive Composition
A descriptive essay is different from narrative essay in the sense that descriptive essay involves describing a scene, person, an object or a place in order to create a vivid picture of it. A descriptive essay demands that one should have the clear picture in one’s mind of what one desires to describe. One is expected to view the scene, person, object or place one is to describe.

USEFUL HINTS ON HOW TO WRITE GOOD DESCRIPTIVE ESSAY
1. CONTENT:
a. You are expected to give a detailed description of what you are asked to describe.
b. Give some ideas of the importance/significance of what you are to describing if you are describing a person; describe the qualities you appreciate in the person.
2. ORGANIZATION:
You are expected to start your description with an introductory paragraph, which should mention the scene, object or person you want to describe, the general features and the outward appearance if you are describing a place. Your introductory paragraph should be followed by detailed description of what you are describing.
3. EXPRESSION:
You are expected to make use of the appropriate words which will best explain your description to your reader.
Example: describing a particular situation. The following paragraph describes a particular situation:
On a fateful Saturday, I slept in my room in an old fashioned building in a dirty area of Lagos, hoping to wake up as early as possible the second day in order to set for the journey I already planned. I was still swimming in my ocean of deep sleep when I heard a knock at my door. I was already shivering thinking that they were armed robbers and had started their “operation”. Actually, fear did not allow me to respond. Later I managed to open the door and I saw Uncle Joe looking dejected. He did not waste any time before announcing that my father had died. I could not control the stream of tears that was rolling from my checks.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 4
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: FIGURE OF SPEECH
1. SIMILE: it is a figure of speech that draws a comparison between two different things, especially a phrase containing the word ‘like’ or ‘as’
e.g.
i. Miracle is as gentle as a dove
ii. Peter is as strong as a lion
iii. Toyosi behaves like a dog
iv. Tope talks like a parrot

[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTSCSSHqH_U[/youtube]
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
2. METAPHOR: it is the direct comparison without the use of ‘like’ or ‘as’

e.g.
i. Tosin is a parrot
ii. Baraka is a lion

Further Studies
3. ASSONANCE: The repletion of the same initial vowel sounds, especially in words that are close together in a poem.

4. ALLITERATION: The repletion of the same initial consonant sounds in a line of poetry.E.g
Wonderful stars
Without you how would the world be.
Further Studies
5. OXYMORON: it is the placing together of two contradictory words side by side.

E.g.
i. The wise fool.
ii. from the dangerous safety of my towers
iii. The legal murder
iv. It is an open secret.
Further Studies
6. PERSONIFICATION: This is giving human attributes/characteristics to non-human beings. e.g.

Love is blind
The trees bow to let the wind pass.
Further Studies
7. HYPERBOLE: This simply means exaggeration.

i. The whole world came for my birthday party.
ii. He had drunk ten gallons of water before he was rescued from drowning.
Further Studies
LESSON 5
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Tenses (Future Tenses)
There are four major divisions of future tense, they are the Simple Future, the Future Continuous, the Future Perfect, and the Future Perfect Continuous.
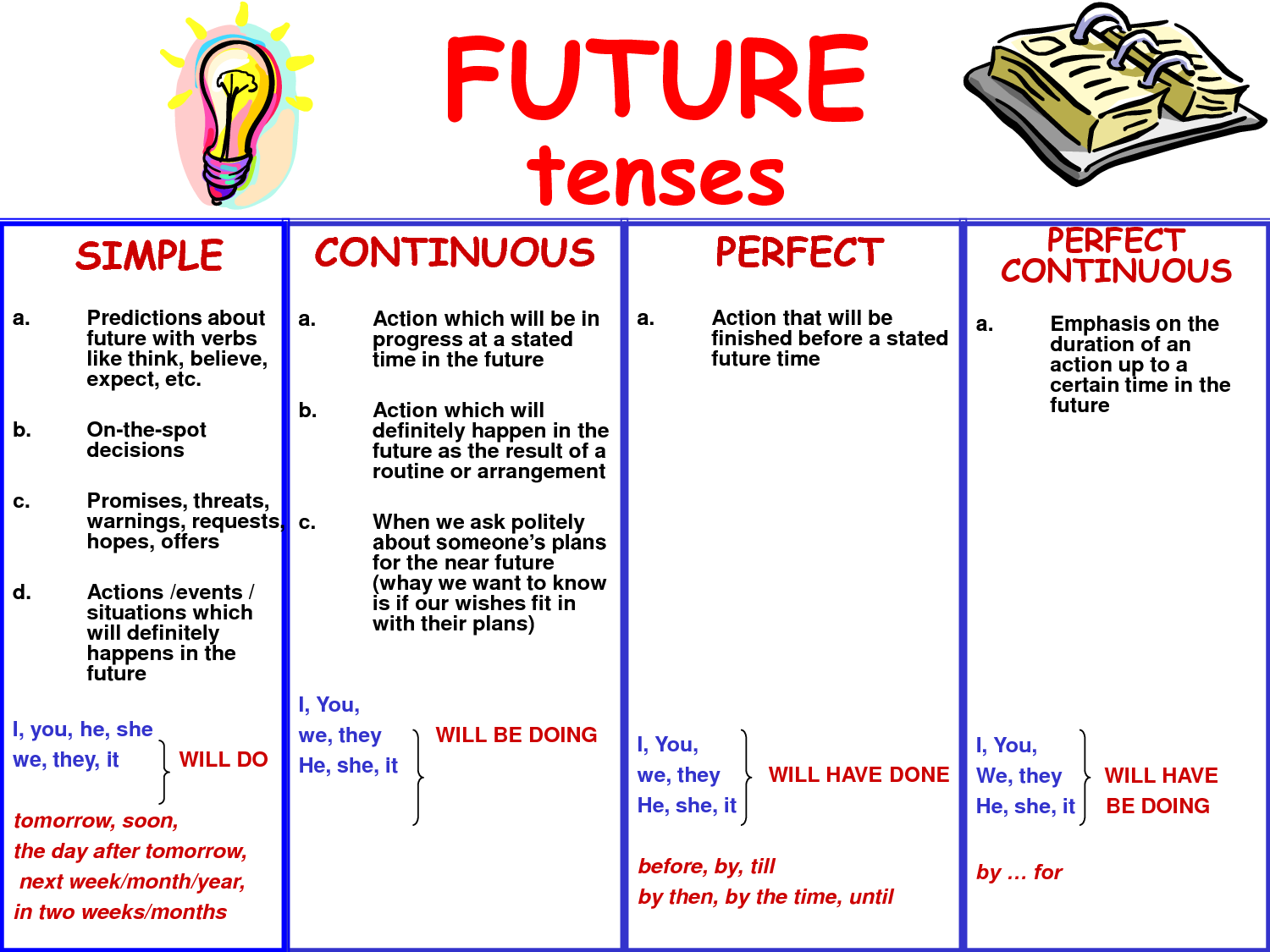
1. The simple future
The Simple Future tense is used to express non-continuous actions which will take place in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Simple Future tense are underlined.
e.g. They will finish the work tomorrow.
He will arrive next Saturday.
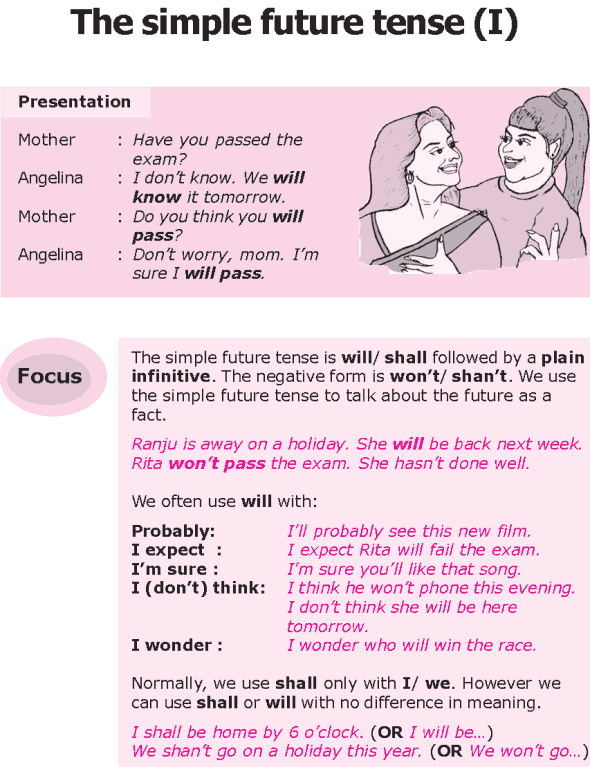
2. The future continuous
The Future Continuous tense is used to express continuous, ongoing actions which will take place in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Future Continuous tense are underlined.
e.g. He will be waiting for us.
They will be arriving tomorrow.
It can be seen that the Future Continuous tense has two auxiliaries. The first auxiliary is will or shall, and the second auxiliary is be.

3. The future perfect
The Future Perfect tense is used to refer to a non-continuous action which will be completed by a certain time in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Future Perfect tense are underlined.
e.g. She will have finished the work by Wednesday.
I will have cleaned the room before the guests arrive.
They will have eaten breakfast by the time he gets up.

In these examples, the use of the Future Perfect indicates that the actions of finishing the work, cleaning the room, and eating breakfast will have been completed before the coming of Wednesday, the arrival of the guests, and his getting up take place.
4. The future perfect continuous
The Future Perfect Continuous tense is used to express a continuous, ongoing action which will be completed by a certain time in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Future Perfect Continuous tense are underlined.
e.g. By next January, she will have been living here for a year.
You will have been traveling a great deal by the time you return home.
He will have been working for ten months by the time he takes his vacation.
In these examples, the use of the Future Perfect Continuous indicates that the continuous, ongoing actions of living, traveling, and working, will have been completed before the events of the coming of January, your returning home, and his taking a vacation, take place.

Summary of the formation of the English future tenses
The following table summarizes the formation of the English future tenses.
Tense Auxiliary Verb Form
Simple Future will (shall) bare infinitive(go)
Future Continuous will (shall) be present participle(going)
Future Perfect will (shall) have past participle(gone)
Future Perfect Continuous will (shall) have been present participle(going)
EVALUATION
Using either the auxiliary shall or the auxiliary will for the first person, fill in the blanks with the Future Continuous of the verbs shown in brackets. For example:
We _______________ you tomorrow. (to see)
We shall be seeing you tomorrow. or We will be seeing you tomorrow.
He _________________ school next year. (to attend)
He will be attending school next year.
1. You _____________________ with us. (to come)
2. It _____________________ warmer. (to grow)
3. They ____________________ new furniture. (to buy)
4. She _____________________ the clock. (to watch)
5. I ____________________ downtown. (to go)
6. You _____________________ the cake. (to cut)
7. They ____________________ the newspaper. (to read)
8. We __________________ the museum. (to visit)
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Further Studies 5
Further Studies 6
Further Studies 7
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonants /p/ and /b/
1. /p/ - This is a voiceless bilabial plosive sound. It can be realized at the initial, medial and the final positions.
Examples: pen, peg, paid, leg, keeper, happy, lip, cheap, ship etc.
Note that /p/ is silent when it precedes ‘n’ and some other words like: corps, receipt, psalm, psychiatry, pneumatic, pneumonia etc.
Also, ‘ph’ is pronounced as /f/ and /v/ in certain words such as physics, phobia, phase, Stephen, nephew. Yet, only /p/ is pronounced in ‘shepherd’ while ‘h’ is silent though both combined in the word.
p------pp
paper apple
proper supply
reply apple
stop
/p/ appear the same way in written and spoken form except for the silent p which belongs to other families of sound e.g.
coup, psalm, etc.

2. /b/ - This consonant, a voiced bilabial plosive, can occur at the initial, medial, and final positions. Its spelling symbols are:
‘b’ – bin, ban, bat, labour, tab, mob, nib.
‘bb’ – babble, blabber, bubble.
Note that ‘b’ is silent when:
a. It precedes‘t’ e.g. debt, doubt, subtle.
b. It succeeds ‘m’ lamb, tomb, bomb, comb, dumb, plumber, climb, plumb, crumb.
However, it is pronounced in chamber, member, timber, timbre, September, November, and December.
/b/ appear the same in written and spoken form except for the silent b which belongs to the /m/ family e.g.
comb, bomb, etc.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/JmsRkAeNCY0[/youtube]
Further Studies
LESSON 2
ASPECT: COMPREHENSION
TOPIC: The Mountebank

The writer points out the meanings of passages by using “direction words”. When you go to visit a friend for the first time, your friend gives you directions. He tells you:
I. Go up this way
II. Turn left by the market
You will find directions in the story below. Emeka’s aunt gave him many directions. You must follow directions carefully after reading.
EVALUATION: Intensive English for Jss1, Exercise 8.2.2; pages 75-78.
ASSIGNMENT: Intensive English for Jss1 Exercises 8.2. 3, 8.2.4, 8.3.4 and 8.3.5; pages 78-83.
LESSON 3
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Descriptive Composition
A descriptive essay is different from narrative essay in the sense that descriptive essay involves describing a scene, person, an object or a place in order to create a vivid picture of it. A descriptive essay demands that one should have the clear picture in one’s mind of what one desires to describe. One is expected to view the scene, person, object or place one is to describe.

USEFUL HINTS ON HOW TO WRITE GOOD DESCRIPTIVE ESSAY
1. CONTENT:
a. You are expected to give a detailed description of what you are asked to describe.
b. Give some ideas of the importance/significance of what you are to describing if you are describing a person; describe the qualities you appreciate in the person.
2. ORGANIZATION:
You are expected to start your description with an introductory paragraph, which should mention the scene, object or person you want to describe, the general features and the outward appearance if you are describing a place. Your introductory paragraph should be followed by detailed description of what you are describing.
3. EXPRESSION:
You are expected to make use of the appropriate words which will best explain your description to your reader.
Example: describing a particular situation. The following paragraph describes a particular situation:
On a fateful Saturday, I slept in my room in an old fashioned building in a dirty area of Lagos, hoping to wake up as early as possible the second day in order to set for the journey I already planned. I was still swimming in my ocean of deep sleep when I heard a knock at my door. I was already shivering thinking that they were armed robbers and had started their “operation”. Actually, fear did not allow me to respond. Later I managed to open the door and I saw Uncle Joe looking dejected. He did not waste any time before announcing that my father had died. I could not control the stream of tears that was rolling from my checks.

Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 4
ASPECT: LITERATURE
TOPIC: FIGURE OF SPEECH
1. SIMILE: it is a figure of speech that draws a comparison between two different things, especially a phrase containing the word ‘like’ or ‘as’
e.g.
i. Miracle is as gentle as a dove
ii. Peter is as strong as a lion
iii. Toyosi behaves like a dog
iv. Tope talks like a parrot

[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTSCSSHqH_U[/youtube]
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
2. METAPHOR: it is the direct comparison without the use of ‘like’ or ‘as’

e.g.
i. Tosin is a parrot
ii. Baraka is a lion

Further Studies
3. ASSONANCE: The repletion of the same initial vowel sounds, especially in words that are close together in a poem.

4. ALLITERATION: The repletion of the same initial consonant sounds in a line of poetry.E.g
Wonderful stars
Without you how would the world be.
Further Studies
5. OXYMORON: it is the placing together of two contradictory words side by side.

E.g.
i. The wise fool.
ii. from the dangerous safety of my towers
iii. The legal murder
iv. It is an open secret.
Further Studies
6. PERSONIFICATION: This is giving human attributes/characteristics to non-human beings. e.g.

Love is blind
The trees bow to let the wind pass.
Further Studies
7. HYPERBOLE: This simply means exaggeration.

i. The whole world came for my birthday party.
ii. He had drunk ten gallons of water before he was rescued from drowning.
Further Studies
LESSON 5
ASPECT: Structure
TOPIC: Tenses (Future Tenses)
There are four major divisions of future tense, they are the Simple Future, the Future Continuous, the Future Perfect, and the Future Perfect Continuous.

1. The simple future
The Simple Future tense is used to express non-continuous actions which will take place in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Simple Future tense are underlined.
e.g. They will finish the work tomorrow.
He will arrive next Saturday.

2. The future continuous
The Future Continuous tense is used to express continuous, ongoing actions which will take place in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Future Continuous tense are underlined.
e.g. He will be waiting for us.
They will be arriving tomorrow.
It can be seen that the Future Continuous tense has two auxiliaries. The first auxiliary is will or shall, and the second auxiliary is be.

3. The future perfect
The Future Perfect tense is used to refer to a non-continuous action which will be completed by a certain time in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Future Perfect tense are underlined.
e.g. She will have finished the work by Wednesday.
I will have cleaned the room before the guests arrive.
They will have eaten breakfast by the time he gets up.

In these examples, the use of the Future Perfect indicates that the actions of finishing the work, cleaning the room, and eating breakfast will have been completed before the coming of Wednesday, the arrival of the guests, and his getting up take place.
4. The future perfect continuous
The Future Perfect Continuous tense is used to express a continuous, ongoing action which will be completed by a certain time in the future. In the following examples, the verbs in the Future Perfect Continuous tense are underlined.
e.g. By next January, she will have been living here for a year.
You will have been traveling a great deal by the time you return home.
He will have been working for ten months by the time he takes his vacation.
In these examples, the use of the Future Perfect Continuous indicates that the continuous, ongoing actions of living, traveling, and working, will have been completed before the events of the coming of January, your returning home, and his taking a vacation, take place.

Summary of the formation of the English future tenses
The following table summarizes the formation of the English future tenses.
Tense Auxiliary Verb Form
Simple Future will (shall) bare infinitive(go)
Future Continuous will (shall) be present participle(going)
Future Perfect will (shall) have past participle(gone)
Future Perfect Continuous will (shall) have been present participle(going)
EVALUATION
Using either the auxiliary shall or the auxiliary will for the first person, fill in the blanks with the Future Continuous of the verbs shown in brackets. For example:
We _______________ you tomorrow. (to see)
We shall be seeing you tomorrow. or We will be seeing you tomorrow.
He _________________ school next year. (to attend)
He will be attending school next year.
1. You _____________________ with us. (to come)
2. It _____________________ warmer. (to grow)
3. They ____________________ new furniture. (to buy)
4. She _____________________ the clock. (to watch)
5. I ____________________ downtown. (to go)
6. You _____________________ the cake. (to cut)
7. They ____________________ the newspaper. (to read)
8. We __________________ the museum. (to visit)
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
Further Studies 5
Further Studies 6
Further Studies 7
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
WEEK 9
LESSON 1
Aspect: Comprehension
Topic: Emeka and the Ring

Intensive English book 1 page 87-88
LESSON 2
Literature: Prose
Features of Prose are:
1. Plot: This is the events that make up the story.
2. Characterizations: These are the people who are portrayed in a book, play or movie.
3. Style: This is whether the author uses short or long sentences; simple or complex sentences.
4. Settings: This refers to the location of the story, that is, where the incident takes place.
5. Theme: The theme refers to the central idea which runs through the story.
Related texts should read for proper teaching of the features of prose.
Evaluation:
What is prose?
Mention features of prose and explain them one by one.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2
TOPIC: TENSES
SUB-TOPIC: Sequence of Tenses and Subjunctive Mood
The convention about how tenses of verbs should appear in the same sentence is stated:

a. If the first verb in a sentence is in present tense, those in other parts of the sentence should also be in the present tense. E.g.
i. Amina says that she is the captain of her team.
ii. He can do it if you permit him.
b. If the first verb in a sentence is in past tense, those in other parts of the sentence should also be in the past tense. E.g.
i. He could have done it if you had permitted him.
ii. Amina said that she was the captain of her team.
SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD:

Usually the verb “were” is a past tense plural form which combines with plural subjects “they” and ”we” . but as a subjunctive to express doubt or uncertainty and imply a negative, the verb “were” can also be shed it’s plural form and combine with singular subjects. I, he, she, or the person’s name as follows:
vi. If I were you I would buy it.
vii. If it were possible I will do it.
viii. If he were wise he would follow the doctors advice.
EVALUATION:
Sequences of Tenses
i. She could have done it if you ----------- him a. will permit b. had permitted c. permit
ii. The lecture ------------- when we arrived a. begin b. begins c. has begun d. had begun
iii. Had I known I would have -------- it a. do b. did c. done
Subjunctive Mood
iv. If I -------- you, I would follow doctor’s advice a. am b. were c. was
v. If Ade ---------- wise, he would stop making a noise a. is b. were c. will be
vi. If he ------------ the captain, he would be proud a. is b. was c. were
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
LESSON 3 & 4
TOPIC : Composition
SUB-TOPIC: Writing Composition on Narrative and Descriptive Essays
Narrative essay tells us about the events that happened in the past.
Steps to take when writing narrative essay
Topic /title of the essay eg. The Day I will Never Forget In My Life.

Brainstorming (before you write, think deeply about the above topic. Some points may be coming to your mind write them down.eg
• The date of that day
• What happened on that day?
• How did it happen?
• Why did it happen?
• Where did it happen?
• What made it unforgettable?
When you are writing, it is necessary to develop each point in paragraph form. Use different kinds of sentences in past tense verbs. Each paragraph should be properly linked together sequentially and chronologically. Do not number the essay.
DESCRIPTIVE ESSAY: Gives vivid description of things ,situation or people that we have known before. The writer should have mental picture of the thing to describe.
Steps to take when writing Descriptive Essay
Title / Topic of the essay eg ( My Best Friend )
Before you start writing , think of what you can write about the topic(brainstorm)
eg
• The name of the person
• His family background
• His parents’ name
• Where we first met.
• How we became friends
• Special qualities in him or her.
Do not itemize the paragraph but it must be properly developed in continuous writing. Use correct form of adjective to describe the object.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
LESSON 5
Literature: Prose
Prose is a written or spoken language that is not in verse form. It can also be defined as long, free written work done in sentences, paragraphs and chapters. In order words prose is a novel.

Features of Prose are:
1. Plot: This is the events that make up the story.
2. Characterizations: These are the people who are portrayed in a book, play or movie.
3. Style: This is whether the author uses short or long sentences; simple or complex sentences.
4. Settings: This refers to the location of the story, that is, where the incident takes place.
5. Theme: The theme refers to the central idea which runs through the story.
Related texts should read for proper teaching of the features of prose.
Evaluation:
What is prose?
Mention features of prose and explain them one by one.
Further Studies
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Aspect: Comprehension
Topic: Emeka and the Ring

Intensive English book 1 page 87-88
LESSON 2
Literature: Prose

Features of Prose are:
1. Plot: This is the events that make up the story.
2. Characterizations: These are the people who are portrayed in a book, play or movie.
3. Style: This is whether the author uses short or long sentences; simple or complex sentences.
4. Settings: This refers to the location of the story, that is, where the incident takes place.
5. Theme: The theme refers to the central idea which runs through the story.
Related texts should read for proper teaching of the features of prose.
Evaluation:
What is prose?
Mention features of prose and explain them one by one.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 2
TOPIC: TENSES
SUB-TOPIC: Sequence of Tenses and Subjunctive Mood
The convention about how tenses of verbs should appear in the same sentence is stated:

a. If the first verb in a sentence is in present tense, those in other parts of the sentence should also be in the present tense. E.g.
i. Amina says that she is the captain of her team.
ii. He can do it if you permit him.
b. If the first verb in a sentence is in past tense, those in other parts of the sentence should also be in the past tense. E.g.
i. He could have done it if you had permitted him.
ii. Amina said that she was the captain of her team.
SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD:

Usually the verb “were” is a past tense plural form which combines with plural subjects “they” and ”we” . but as a subjunctive to express doubt or uncertainty and imply a negative, the verb “were” can also be shed it’s plural form and combine with singular subjects. I, he, she, or the person’s name as follows:
vi. If I were you I would buy it.
vii. If it were possible I will do it.
viii. If he were wise he would follow the doctors advice.
EVALUATION:
Sequences of Tenses
i. She could have done it if you ----------- him a. will permit b. had permitted c. permit
ii. The lecture ------------- when we arrived a. begin b. begins c. has begun d. had begun
iii. Had I known I would have -------- it a. do b. did c. done
Subjunctive Mood
iv. If I -------- you, I would follow doctor’s advice a. am b. were c. was
v. If Ade ---------- wise, he would stop making a noise a. is b. were c. will be
vi. If he ------------ the captain, he would be proud a. is b. was c. were
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
LESSON 3 & 4
TOPIC : Composition
SUB-TOPIC: Writing Composition on Narrative and Descriptive Essays
Narrative essay tells us about the events that happened in the past.
Steps to take when writing narrative essay
Topic /title of the essay eg. The Day I will Never Forget In My Life.

Brainstorming (before you write, think deeply about the above topic. Some points may be coming to your mind write them down.eg
• The date of that day
• What happened on that day?
• How did it happen?
• Why did it happen?
• Where did it happen?
• What made it unforgettable?
When you are writing, it is necessary to develop each point in paragraph form. Use different kinds of sentences in past tense verbs. Each paragraph should be properly linked together sequentially and chronologically. Do not number the essay.
DESCRIPTIVE ESSAY: Gives vivid description of things ,situation or people that we have known before. The writer should have mental picture of the thing to describe.
Steps to take when writing Descriptive Essay
Title / Topic of the essay eg ( My Best Friend )

Before you start writing , think of what you can write about the topic(brainstorm)
eg
• The name of the person
• His family background
• His parents’ name
• Where we first met.
• How we became friends
• Special qualities in him or her.
Do not itemize the paragraph but it must be properly developed in continuous writing. Use correct form of adjective to describe the object.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Further Studies 4
LESSON 5
Literature: Prose
Prose is a written or spoken language that is not in verse form. It can also be defined as long, free written work done in sentences, paragraphs and chapters. In order words prose is a novel.

Features of Prose are:
1. Plot: This is the events that make up the story.
2. Characterizations: These are the people who are portrayed in a book, play or movie.
3. Style: This is whether the author uses short or long sentences; simple or complex sentences.
4. Settings: This refers to the location of the story, that is, where the incident takes place.
5. Theme: The theme refers to the central idea which runs through the story.
Related texts should read for proper teaching of the features of prose.
Evaluation:
What is prose?
Mention features of prose and explain them one by one.
Further Studies
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
