SCHEME OF WORK:
WEEK TOPIC
1. Child development- (a) Stages of child development. (b) Factors that influence child development. (c) Conditions necessary for child development.
2. Child care- (a) Different types of care required by a child. (b) Common childhood ailments. (c) Immunization.
3. Family budget- (a) meaning of family budget. (b) Importance of family budget. (c) Factors to consider in preparing family budget. (d) Procedures for preparing family budget. (e) Preparation of a personal budget.
4-7. Revision & mock examination.
8-12. BECE/JSC examination.
3RD TERM
Week 1
TOPIC: CHILD DEVELOPMENT.
CONTENT: 1. Stages of child development.
2. Factors that influence child development and conditions necessary for child
development.
Sub-Topic 1: Stages of child development.
Growth is an increase in the physical size of the whole body. Therefore a child grows in size, height and weight. It is measured in metres and kilograms.
Development is an increase in skill and complexity of function. A child is developing when he/she makes progress in what he/she does with his/her mind and body. Children develop at different rates. Some may be fast and others slow.
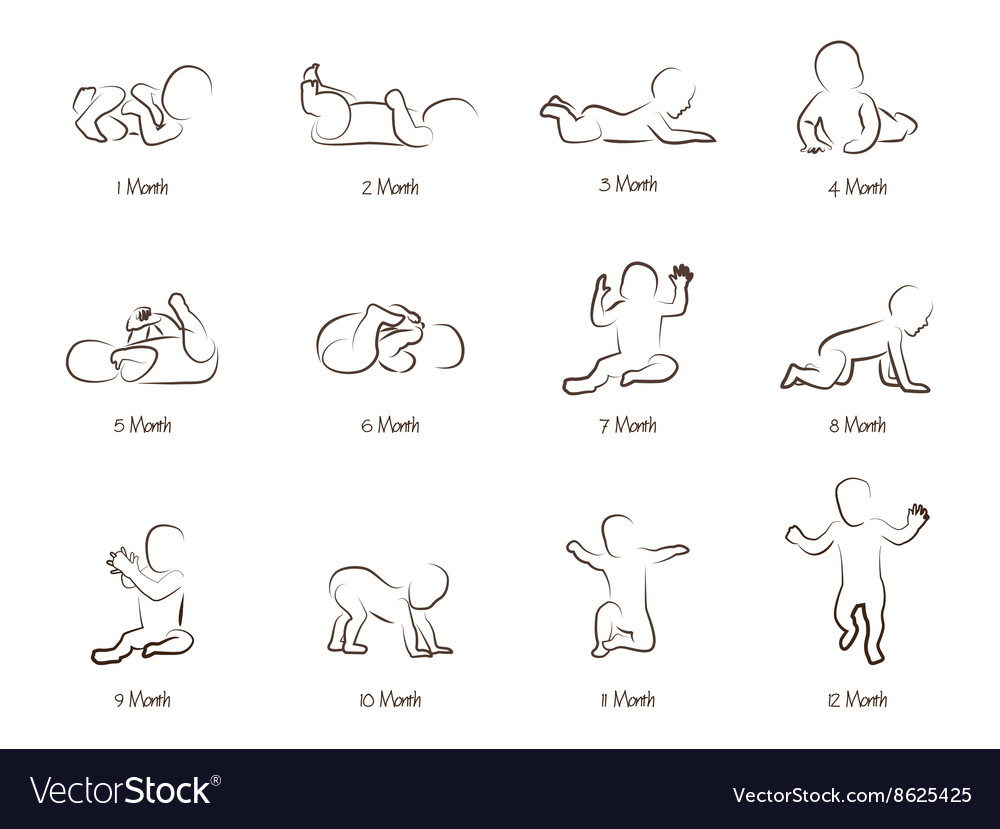

Ages ....................Development
1st month – Head sags needs support.
Hands tightly curled or fisted.
Sleeps most of the time, feeds and cries.

2nd month - Weaves arms about when lying on his back.
Turn head towards direction of sounds.
Have a regular routine such as sleeping all night.
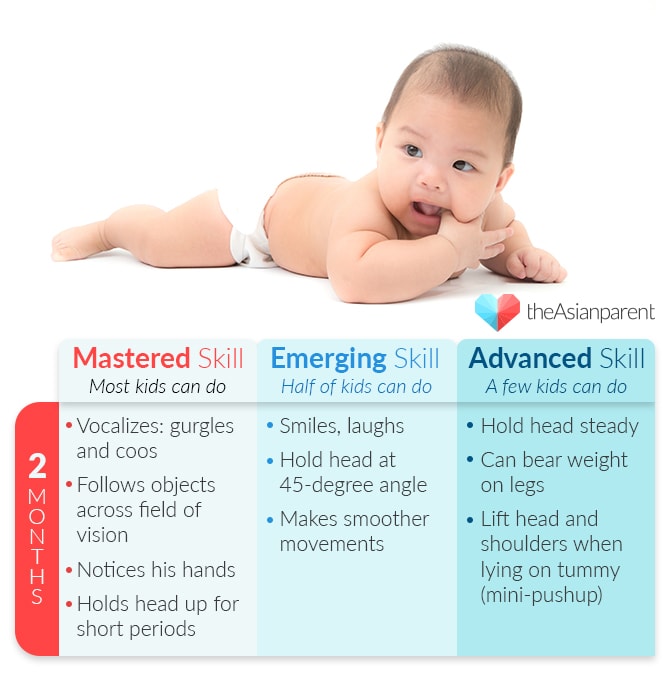
3rd month - Looks at people and follows their movements.
Hearing is fairly developed.
Smiles and enjoys colours and light.
Can hold head up slightly.
Hold an object placed in his hand e:g a rattle.

4th month – Hold head erect. Smiles and shows excitement.
Eyes can follow moving objects slowly.
Can reach for his toes.

5th month- Reaches for an object.
Puts everything within reach into the mouth.
Sits with slight support.
Becomes selective in taste.
Birth- weight may be doubled.

6th month – Birth – weight doubled.
Recognizes constant members of the family.
Sits without support.
Hands and eyes work more together.
Starts teething (milk teeth)

7th-8th month- Transfers objects from one hand to the other.
Begins to associate words with people, ideas or objects.
Uses toys freely.
Sits confidently and crawls.

9th-12th month- Understands some words and can say very few.
Birth-weight triples.
Crawls very well, stands holding on to objects.
Gradually stands unaided
Takes first steps.
More teeth appear

Evaluation:
1. Define growth
2. What is development?
3. Enumerate the four stages in child development.
Reading Assignment:
Home Economics New Concepts for Nigerian Jnr. Secondary Schools Book 3. Popoola o. o. (Mrs.) Pgs.118-121.
Sub–Topic 2: FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE CHILD DEVELOPMENT AND CONDITIONS
NECESSARY FOR CHILD DEVELOPMENT.
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE DEVELOPMENT
There are two major factors that influence development:
(i) Heredity
(ii) Environment
Heredity- The tendency for a parent to transfer his/her characteristics to his/her child such as colour of skin, eyes, noses, etc. The units which bear heredity in our body cells are called GENES.
Environment – It includes everything that is outside the child e.g. Love and care he/she receives, the family, feeding, toys, home surrounding, clothing, shelter, etc.

Areas of development:
Children develop in the following areas:
1. Physical development- It involves development of the physical structures and functions e.g. the brain, muscles, nerves, bones.
2. Mental development- This involves ability to think, understand, solve problems etc.
3. Social development - It includes development of behaviours approved by society or social groups. It enables the child to participate in and enjoy social activities.
4. Emotional development- Emotions involve feelings and how a person expresses such feelings e.g. smiling, crying, frowning, etc. A child develops in the way he/she feels.
5. Moral development – This development shows in behaviour and in how children treat others.

Conditions necessary for child development:
1. Love and care from family.
2. Good nutrition: Children are growing at a rapid rate and need plenty of nutritious foods to help them grow and develop strong, healthy bodies. Their meals must always be balanced.
3. Clothing: They need clothing that is suitable for different weather conditions.
4. Exercise: Children demand plenty of opportunities for exercises. These help them to develop strong bones, muscles and motor skills.
5. Rest: Children bodies need plenty of rest due to their activeness and rapid growth. Good sleep habits promote health and well- being.
6. Medical care: This is necessary for the development of the children.
7. A safe and conducive environment: Safety is needed for children to develop. Therefore parents must provide safe and conducive environment.
8. Good school: When the child has reached school age, the school should provide him with an environment that stimulates his physical, mental, emotional and social abilities.
9. Society; It is a child’s widest environment that helps him to learn those things which the school and home do not teach.

Evaluation:
1. List the two major factors that influence development.
2. An increase in the physical size of the whole body or any of its part.
(a)Health (b) growth (c) development (d) life (e) energy
3. ………. Is measured in metres and kilograms.
(a) Development (b) health (c) life (d) strength (e) growth
4. Development in children follows a definite
(a)Movement (b) style (c) way (d) form (e) pattern
5. An increase in skill and complexity of function is called………..
(a) Energy (b) growth (c) life (d) development (e) life
Assignment:
1. Outline five environmental conditions that are necessary for child development.
2. State any four areas of development.
3. Children develop at ………….
(a) Different rates (b) similar rates (c) a time (d) different times (e) high rates.
4. Development starts from the……………. And spread over the body.
(a) Legs (b) hands (c) mouth (d) eyes (e) head
5. Development is influenced by…………
(a) Heredity and environment (b) heredity only (c) size of clothes (d) environment and food only (e) environment only
6. Which of the following is a tendency for a parent to transfer his/her character to his/her child?
(a) Shelter (b) affection (c) heredity (d) care (e) love
7. A child’s birth weight may be doubled by the age of……
(a) Two months (b) twelve months (c) six months (d) one month (e) twenty months.
CONTENT: 1. Stages of child development.
2. Factors that influence child development and conditions necessary for child
development.
Sub-Topic 1: Stages of child development.
Growth is an increase in the physical size of the whole body. Therefore a child grows in size, height and weight. It is measured in metres and kilograms.
Development is an increase in skill and complexity of function. A child is developing when he/she makes progress in what he/she does with his/her mind and body. Children develop at different rates. Some may be fast and others slow.
Ages ....................Development
1st month – Head sags needs support.
Hands tightly curled or fisted.
Sleeps most of the time, feeds and cries.

2nd month - Weaves arms about when lying on his back.
Turn head towards direction of sounds.
Have a regular routine such as sleeping all night.

3rd month - Looks at people and follows their movements.
Hearing is fairly developed.
Smiles and enjoys colours and light.
Can hold head up slightly.
Hold an object placed in his hand e:g a rattle.

4th month – Hold head erect. Smiles and shows excitement.
Eyes can follow moving objects slowly.
Can reach for his toes.

5th month- Reaches for an object.
Puts everything within reach into the mouth.
Sits with slight support.
Becomes selective in taste.
Birth- weight may be doubled.

6th month – Birth – weight doubled.
Recognizes constant members of the family.
Sits without support.
Hands and eyes work more together.
Starts teething (milk teeth)

7th-8th month- Transfers objects from one hand to the other.
Begins to associate words with people, ideas or objects.
Uses toys freely.
Sits confidently and crawls.

9th-12th month- Understands some words and can say very few.
Birth-weight triples.
Crawls very well, stands holding on to objects.
Gradually stands unaided
Takes first steps.
More teeth appear

Evaluation:
1. Define growth
2. What is development?
3. Enumerate the four stages in child development.
Reading Assignment:
Home Economics New Concepts for Nigerian Jnr. Secondary Schools Book 3. Popoola o. o. (Mrs.) Pgs.118-121.
Sub–Topic 2: FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE CHILD DEVELOPMENT AND CONDITIONS
NECESSARY FOR CHILD DEVELOPMENT.
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE DEVELOPMENT
There are two major factors that influence development:
(i) Heredity
(ii) Environment
Heredity- The tendency for a parent to transfer his/her characteristics to his/her child such as colour of skin, eyes, noses, etc. The units which bear heredity in our body cells are called GENES.
Environment – It includes everything that is outside the child e.g. Love and care he/she receives, the family, feeding, toys, home surrounding, clothing, shelter, etc.

Areas of development:
Children develop in the following areas:
1. Physical development- It involves development of the physical structures and functions e.g. the brain, muscles, nerves, bones.
2. Mental development- This involves ability to think, understand, solve problems etc.
3. Social development - It includes development of behaviours approved by society or social groups. It enables the child to participate in and enjoy social activities.
4. Emotional development- Emotions involve feelings and how a person expresses such feelings e.g. smiling, crying, frowning, etc. A child develops in the way he/she feels.
5. Moral development – This development shows in behaviour and in how children treat others.

Conditions necessary for child development:
1. Love and care from family.
2. Good nutrition: Children are growing at a rapid rate and need plenty of nutritious foods to help them grow and develop strong, healthy bodies. Their meals must always be balanced.
3. Clothing: They need clothing that is suitable for different weather conditions.
4. Exercise: Children demand plenty of opportunities for exercises. These help them to develop strong bones, muscles and motor skills.
5. Rest: Children bodies need plenty of rest due to their activeness and rapid growth. Good sleep habits promote health and well- being.
6. Medical care: This is necessary for the development of the children.
7. A safe and conducive environment: Safety is needed for children to develop. Therefore parents must provide safe and conducive environment.
8. Good school: When the child has reached school age, the school should provide him with an environment that stimulates his physical, mental, emotional and social abilities.
9. Society; It is a child’s widest environment that helps him to learn those things which the school and home do not teach.

Evaluation:
1. List the two major factors that influence development.
2. An increase in the physical size of the whole body or any of its part.
(a)Health (b) growth (c) development (d) life (e) energy
3. ………. Is measured in metres and kilograms.
(a) Development (b) health (c) life (d) strength (e) growth
4. Development in children follows a definite
(a)Movement (b) style (c) way (d) form (e) pattern
5. An increase in skill and complexity of function is called………..
(a) Energy (b) growth (c) life (d) development (e) life
Assignment:
1. Outline five environmental conditions that are necessary for child development.
2. State any four areas of development.
3. Children develop at ………….
(a) Different rates (b) similar rates (c) a time (d) different times (e) high rates.
4. Development starts from the……………. And spread over the body.
(a) Legs (b) hands (c) mouth (d) eyes (e) head
5. Development is influenced by…………
(a) Heredity and environment (b) heredity only (c) size of clothes (d) environment and food only (e) environment only
6. Which of the following is a tendency for a parent to transfer his/her character to his/her child?
(a) Shelter (b) affection (c) heredity (d) care (e) love
7. A child’s birth weight may be doubled by the age of……
(a) Two months (b) twelve months (c) six months (d) one month (e) twenty months.
Week 2
TOPIC: CHILD CARE.
CONTENT: 1. Different types of care required by a child.
2. Common childhood ailments and Immunization.
Sub-Topic 1: DIFFERENT TYPES OF CARE REQUIRED BY A CHILD.
The care given to a baby influences his/her development. A baby, needs love, warmth, food, clothing etc.
GOOD NUTRITION
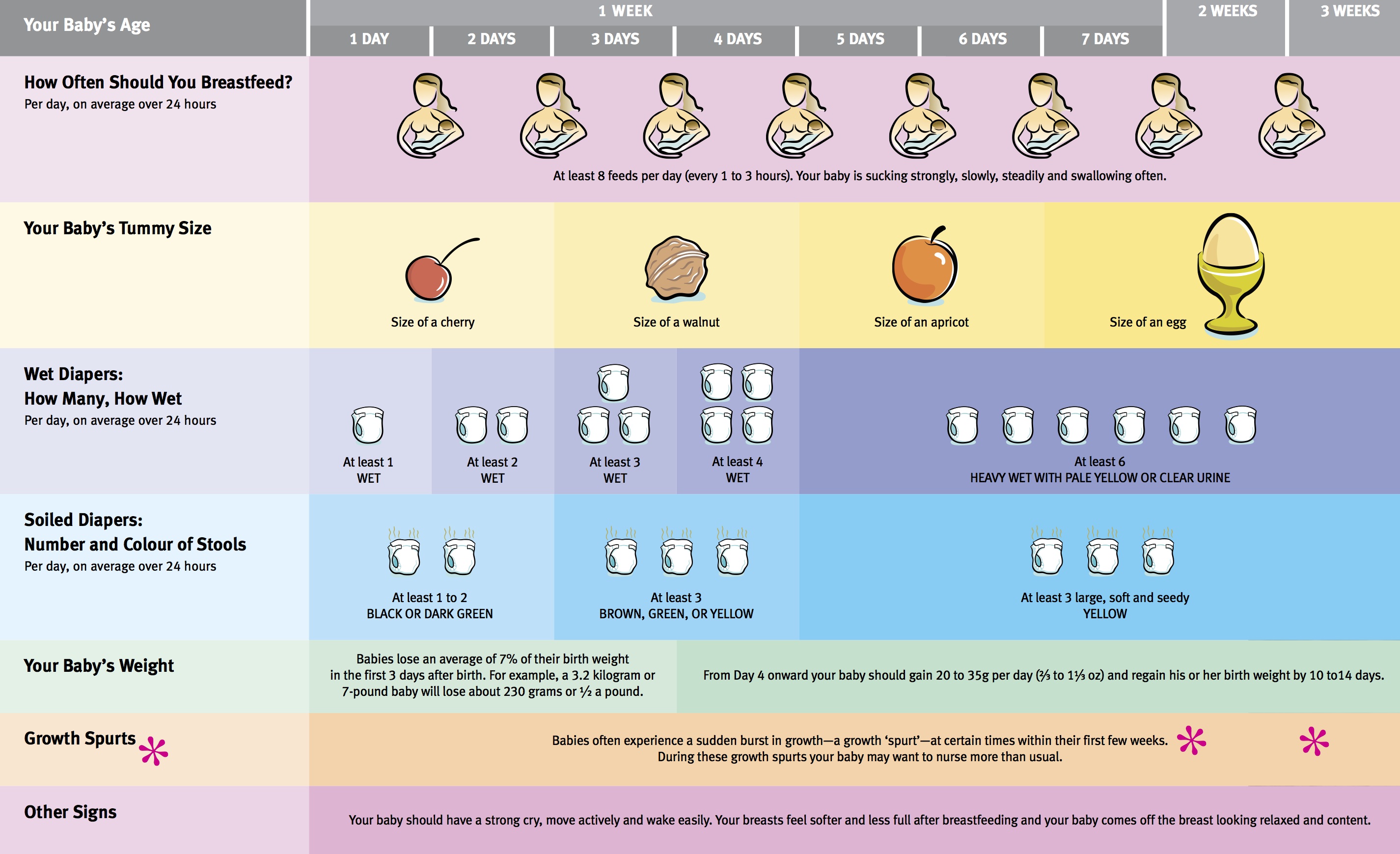
The child needs good food that can promote growth and development. A baby can be fed by the use of feeding either by the breast or bottle. The breast milk is the best. Suitable semi- solid foods (cereals) are introduced as baby grows.
Breast feeding (natural feeding)
This can be started immediately after birth. A baby can be fed exclusively on breast milk from birth to six months.

Colostrums
Colostrums is the first milk produced in the first few days by a nursing mother. Yellowish in colour, it helps to clear the baby’s first sticky stool called
meconium.
Advantages of breast feeding
1. Breast milk contains all the nutrients needed by a baby more than any other food.
2. It contains antibodies which protect the child against disease infection.
3. It is sterile and free from disease germs.
4. It prevents constipation.
5. It is cheaper than artificial feeding.
6. It brings mother and child very close.
7. It is produced in the right temperature.
8. It is easily digested and absorbed by the baby.
9. It does not require any elaborate preparation.
10. Breast–feeding helps some mothers to protect themselves against another pregnancy
Guidelines for breast feeding
The mother has to:
1. Wash her hands and clean her breast before feeding the baby.
2. Sit comfortably and carry the baby close to herself.
3. Hold the breast properly and away from the baby’s nose.
4. Let the baby feed at both breasts, one at a time.
5. Wind the baby at the end of the feeding.
6. Clean nipples brassiere always.
Weaning is the process of introducing the baby gradually to foods other than milk. Suitable weaning foods are cereals, root, fruit juice/drink, peas and beans, animal source (egg, fish, milk etc), vegetables.
Artificial or bottle feeding
This is the process of feeding a baby with artificial milk, often through the feeding bottle.

Disadvantages of bottle-feeding
1. It is expensive.
2. The milk can be contaminated by disease germs.
3. Constipation is common with bottle-fed babies.
4. It does not contain antibodies.
5. It requires elaborate preparation and sterilization unit
Bathing the baby
The baby’s skin is delicate. It should not be allowed to get dirty.
Materials needed for baby’s bath.
1. Baby’s bath tub
2. Large soft for covering
3. Small towel for drying the baby’s skin.
4. Face towel
5. Soft sponge
6. Baby’s comb and brush
7. Baby’s oil, cream or lotion and powder.
8. Clean clothes for dressing baby after bath.

Clothing the baby
The baby requires good clothes for protection, warmth, comfort and good appearance. The clothes should be attractive, flat seams should be used. Selection should be on the basis of the weather conditions.

Toys for children
A young baby needs only very few toys like rattles. As he/she needs large toys, such as a push-around toy which can help him to walk or a toy car.
Uses of toys
i. Keep children busy.
ii. Help them to learn
iii. Help them to exercise themselves in different ways.
iv. Make children happy.

Points to consider when choosing toys for children
Children‘s toys should:
1. be safe
2. suit the child’s age
3. be easy to clean
4. have no metal or sharp edges that can injure the child.
5. be strong, durable and simple
6. not be boring to the child

Evaluation:
1. State any four advantages of breast feeding a child.
2. State any four disadvantages of bottle feeding a child.
3. List three points to consider in selecting baby’s clothes.
4. Outline four uses of toys
Reading Assignment:
Home Economics New Concepts for Nigerian Jnr. Secondary Schools Book 3. Popoola o. o. (Mrs.) Pgs.121-129.
Sub – Topic 2: COMMON CHILDHOOD AILMENTS AND IMMUNIZATION.
COMMON AILMENTS IN CHILDREN:
1. Colic is caused by cramps in the intestines of the baby. It causes the baby real discomfort or pains. It is common during the first 3 to 4 months.
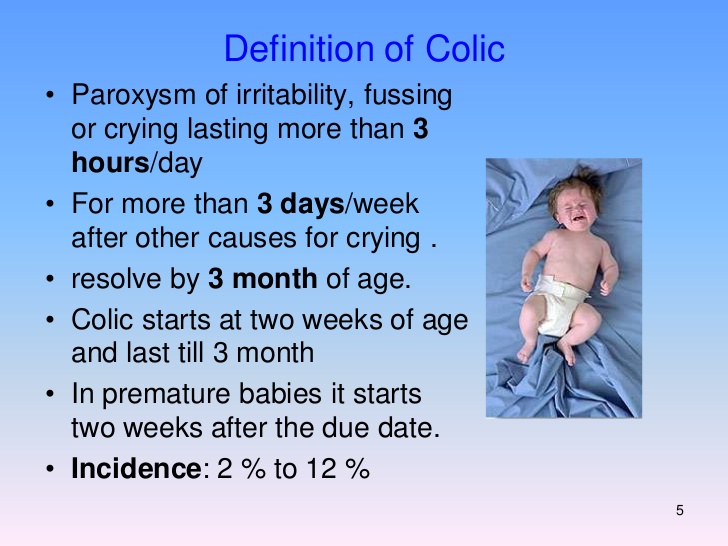
2. Constipation involves the passing of hard stool at long intervals or not passing it all. Constipation could be common with bottle-fed babies.

Treatment
i. Give the child extra water to drink.
ii. Add very small sugar or glucose to his feed.
iii. Serious cases should be taken to doctor.
3. Diarrhea is a sudden increase in the number of bowel movement, especially if they are loose and watery.

Causes are unsuitable diet, overfeeding and infection or disease.
Treatment
i. Give oral Rehydration Therapy (O.R.T) after each stool.
(ORT = 1 level tsp of salt + 10 level tsp of sugar + ½ litre of boiled water)
ii. See the doctor if it persists.
4. Nappy rash – it occurs when a child has rashes in the nappy area. It could be caused by using dirty napkins, leaving soiled napkin on the baby and improper rinsing of baby’s napkin after washing.

Treatment
i. Keep the areas clean.
ii. Expose the area until rashes disappear.
iii. Apply special nappy rash lotions or ointment.
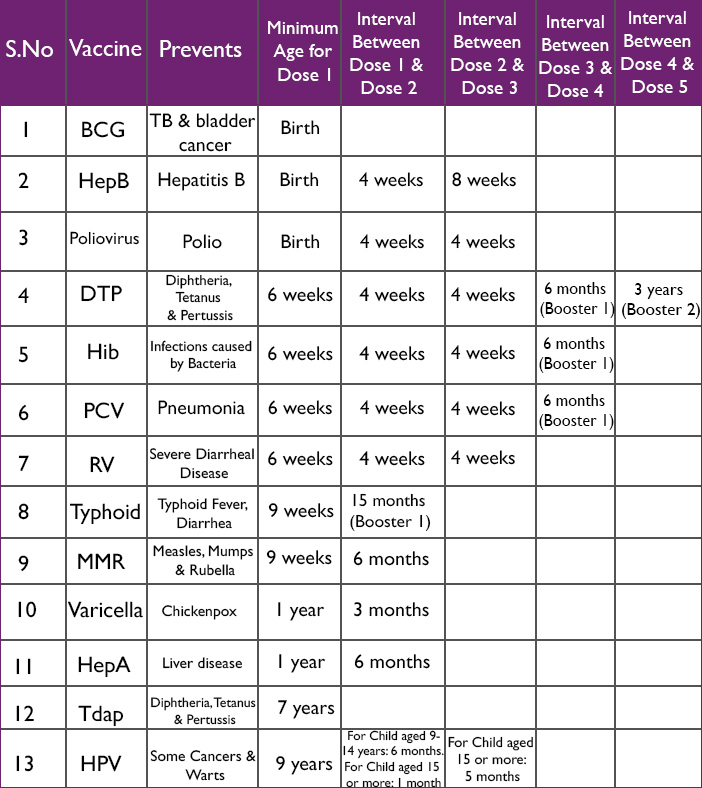
Immunization
It prevents children against diseases. It is administered to protect children from 0-2 years old. Immunization is given to children in infant welfare clinics, immunization centres and hospitals.
1. B. C.G – vaccine protects the body against tuberculosis.
2. Triple vaccine (D.T.P) – mixture of three vaccines- the tetanus, whooping cough and diphtheria vaccines.
3. Polio vaccine – for protection against polio.
4. Smallpox vaccine- to protect against smallpox.
5. Measles – to protect against measles
6. Quadruple vaccine – mixture of four vaccines – diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough and polio vaccines.

Time - Immunization
1. At birth - B. C.G.
2. At 2 months – first dose of D.T.P, first dose of polio vaccine.
3. At 3 month – second dose of D.T.P, second dose of polio vaccine.
4. At 4 months – third dose of D. T.P, third dose of polio vaccine.
5. At 9 months – measles vaccine.
Evaluation:
1. State four common ailments in children.
2. Define immunization
3. Briefly describe how O.R.T. can be prepared.
4. State the full meaning of O.R.T.
Assignment:
1. ………. Feeding is the natural way to feed a baby
(a) Bottle (b) breast (c) artificial (d) regular (e) constant
2. The first milk produced by a nursing mother is called
(a) Yellow milk (b) colostrums (c) artificial (d) constant
3. Constipation is common with …………. Babies.
(a) Breast – fed (b) bottle-fed (c) well- fed (d) angry (e) hungry
4. Which of the following contains important antibodies needed by baby?
(a) Cow milk (b) baby’s milk (c) feeding unit (d) breast milk (e) artificial milk
5. The process of introducing a baby gradually to foods other than milk is called………….
(a) Weaving (b) feeding (c)wining (d) warning (e) weaning
6. For the first six months of age ………….. is adequate source of nourishment for a baby.
(a) Pure water (b) white milk (c) breast milk (d) bottled milk (e) artificial milk.
7. Baby’s skin is delicate, it should not be allowed to get
(a) Complex (b) dirty (c) simple (d) hard (e) clean
8. The baby requires good clothes for all except one of the following.
(a) Protection (b) warmth (c) comfort (d) appearance (e) height
9. Baby‘s clothes should not be……………..
(a) Washed (b) ironed (c) starched (d) dried (e) rinsed
10. ……………. Prevents children from disease
(a) Sun (b) air (c) warmth (d) love (e) immunization
11. One of the following is a mixture of three vaccines.
(a) Polio vaccine (b) smallpox vaccine (c) quadruple vaccine (d) triple/DTP vaccine (e) B.C.G. vaccine
12. Which of the following protects children against tuberculosis?
(a) B.C.G. vaccine (b) Immunization (c) quadruple vaccine (d) triple/DTP vaccine (e) smallpox vaccine.
13. Which of the following immunization should be given at birth?
(a) B. C. G. vaccine (b) D.T.P vaccine (c) Triple vaccine (d) smallpox (e) quadruple vaccine.
14. Oral Rehydration Therapy (O.R.T.) is used for the treatment of
(a) Fever (b) constipation (c) colic (d) malaria (e) diarrhea.
CONTENT: 1. Different types of care required by a child.
2. Common childhood ailments and Immunization.
Sub-Topic 1: DIFFERENT TYPES OF CARE REQUIRED BY A CHILD.
The care given to a baby influences his/her development. A baby, needs love, warmth, food, clothing etc.
GOOD NUTRITION
The child needs good food that can promote growth and development. A baby can be fed by the use of feeding either by the breast or bottle. The breast milk is the best. Suitable semi- solid foods (cereals) are introduced as baby grows.
Breast feeding (natural feeding)
This can be started immediately after birth. A baby can be fed exclusively on breast milk from birth to six months.

Colostrums
Colostrums is the first milk produced in the first few days by a nursing mother. Yellowish in colour, it helps to clear the baby’s first sticky stool called
meconium.
Advantages of breast feeding
1. Breast milk contains all the nutrients needed by a baby more than any other food.
2. It contains antibodies which protect the child against disease infection.
3. It is sterile and free from disease germs.
4. It prevents constipation.
5. It is cheaper than artificial feeding.
6. It brings mother and child very close.
7. It is produced in the right temperature.
8. It is easily digested and absorbed by the baby.
9. It does not require any elaborate preparation.
10. Breast–feeding helps some mothers to protect themselves against another pregnancy
Guidelines for breast feeding
The mother has to:
1. Wash her hands and clean her breast before feeding the baby.
2. Sit comfortably and carry the baby close to herself.
3. Hold the breast properly and away from the baby’s nose.
4. Let the baby feed at both breasts, one at a time.
5. Wind the baby at the end of the feeding.
6. Clean nipples brassiere always.

Weaning is the process of introducing the baby gradually to foods other than milk. Suitable weaning foods are cereals, root, fruit juice/drink, peas and beans, animal source (egg, fish, milk etc), vegetables.
Artificial or bottle feeding
This is the process of feeding a baby with artificial milk, often through the feeding bottle.

Disadvantages of bottle-feeding
1. It is expensive.
2. The milk can be contaminated by disease germs.
3. Constipation is common with bottle-fed babies.
4. It does not contain antibodies.
5. It requires elaborate preparation and sterilization unit
Bathing the baby
The baby’s skin is delicate. It should not be allowed to get dirty.
Materials needed for baby’s bath.
1. Baby’s bath tub
2. Large soft for covering
3. Small towel for drying the baby’s skin.
4. Face towel
5. Soft sponge
6. Baby’s comb and brush
7. Baby’s oil, cream or lotion and powder.
8. Clean clothes for dressing baby after bath.

Clothing the baby
The baby requires good clothes for protection, warmth, comfort and good appearance. The clothes should be attractive, flat seams should be used. Selection should be on the basis of the weather conditions.

Toys for children
A young baby needs only very few toys like rattles. As he/she needs large toys, such as a push-around toy which can help him to walk or a toy car.
Uses of toys
i. Keep children busy.
ii. Help them to learn
iii. Help them to exercise themselves in different ways.
iv. Make children happy.

Points to consider when choosing toys for children
Children‘s toys should:
1. be safe
2. suit the child’s age
3. be easy to clean
4. have no metal or sharp edges that can injure the child.
5. be strong, durable and simple
6. not be boring to the child

Evaluation:
1. State any four advantages of breast feeding a child.
2. State any four disadvantages of bottle feeding a child.
3. List three points to consider in selecting baby’s clothes.
4. Outline four uses of toys
Reading Assignment:
Home Economics New Concepts for Nigerian Jnr. Secondary Schools Book 3. Popoola o. o. (Mrs.) Pgs.121-129.
Sub – Topic 2: COMMON CHILDHOOD AILMENTS AND IMMUNIZATION.
COMMON AILMENTS IN CHILDREN:
1. Colic is caused by cramps in the intestines of the baby. It causes the baby real discomfort or pains. It is common during the first 3 to 4 months.

2. Constipation involves the passing of hard stool at long intervals or not passing it all. Constipation could be common with bottle-fed babies.

Treatment
i. Give the child extra water to drink.
ii. Add very small sugar or glucose to his feed.
iii. Serious cases should be taken to doctor.
3. Diarrhea is a sudden increase in the number of bowel movement, especially if they are loose and watery.

Causes are unsuitable diet, overfeeding and infection or disease.
Treatment
i. Give oral Rehydration Therapy (O.R.T) after each stool.
(ORT = 1 level tsp of salt + 10 level tsp of sugar + ½ litre of boiled water)
ii. See the doctor if it persists.
4. Nappy rash – it occurs when a child has rashes in the nappy area. It could be caused by using dirty napkins, leaving soiled napkin on the baby and improper rinsing of baby’s napkin after washing.

Treatment
i. Keep the areas clean.
ii. Expose the area until rashes disappear.
iii. Apply special nappy rash lotions or ointment.
Immunization
It prevents children against diseases. It is administered to protect children from 0-2 years old. Immunization is given to children in infant welfare clinics, immunization centres and hospitals.
1. B. C.G – vaccine protects the body against tuberculosis.
2. Triple vaccine (D.T.P) – mixture of three vaccines- the tetanus, whooping cough and diphtheria vaccines.
3. Polio vaccine – for protection against polio.
4. Smallpox vaccine- to protect against smallpox.
5. Measles – to protect against measles
6. Quadruple vaccine – mixture of four vaccines – diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough and polio vaccines.

Time - Immunization
1. At birth - B. C.G.
2. At 2 months – first dose of D.T.P, first dose of polio vaccine.
3. At 3 month – second dose of D.T.P, second dose of polio vaccine.
4. At 4 months – third dose of D. T.P, third dose of polio vaccine.
5. At 9 months – measles vaccine.

Evaluation:
1. State four common ailments in children.
2. Define immunization
3. Briefly describe how O.R.T. can be prepared.
4. State the full meaning of O.R.T.
Assignment:
1. ………. Feeding is the natural way to feed a baby
(a) Bottle (b) breast (c) artificial (d) regular (e) constant
2. The first milk produced by a nursing mother is called
(a) Yellow milk (b) colostrums (c) artificial (d) constant
3. Constipation is common with …………. Babies.
(a) Breast – fed (b) bottle-fed (c) well- fed (d) angry (e) hungry
4. Which of the following contains important antibodies needed by baby?
(a) Cow milk (b) baby’s milk (c) feeding unit (d) breast milk (e) artificial milk
5. The process of introducing a baby gradually to foods other than milk is called………….
(a) Weaving (b) feeding (c)wining (d) warning (e) weaning
6. For the first six months of age ………….. is adequate source of nourishment for a baby.
(a) Pure water (b) white milk (c) breast milk (d) bottled milk (e) artificial milk.
7. Baby’s skin is delicate, it should not be allowed to get
(a) Complex (b) dirty (c) simple (d) hard (e) clean
8. The baby requires good clothes for all except one of the following.
(a) Protection (b) warmth (c) comfort (d) appearance (e) height
9. Baby‘s clothes should not be……………..
(a) Washed (b) ironed (c) starched (d) dried (e) rinsed
10. ……………. Prevents children from disease
(a) Sun (b) air (c) warmth (d) love (e) immunization
11. One of the following is a mixture of three vaccines.
(a) Polio vaccine (b) smallpox vaccine (c) quadruple vaccine (d) triple/DTP vaccine (e) B.C.G. vaccine
12. Which of the following protects children against tuberculosis?
(a) B.C.G. vaccine (b) Immunization (c) quadruple vaccine (d) triple/DTP vaccine (e) smallpox vaccine.
13. Which of the following immunization should be given at birth?
(a) B. C. G. vaccine (b) D.T.P vaccine (c) Triple vaccine (d) smallpox (e) quadruple vaccine.
14. Oral Rehydration Therapy (O.R.T.) is used for the treatment of
(a) Fever (b) constipation (c) colic (d) malaria (e) diarrhea.
Week 3
TOPIC: FAMILY BUDGET.
CONTENT: 1. Meaning and Importance of family budget.
2. Factors to consider in preparing family budget and Procedures for preparing
family.
Sub-Topic 1: MEANING AND IMPORTANCE OF FAMILY BUDGET
Household / family budget is a plan for future expenditures of a given household. Budgeting is the process of preparing a budget. Good budgeting leads to wise management or use of family income. Family budget assists the family to meet their needs.

Budget -related terms
i. Income: The income of a family includes money which is earned by every member in the family. Sources of family income include salaries, wages, assets, shares, investments, e.g. rents, bonus from insurance policies, gifts, profits etc.
ii. Gross Income: This is the total amount of money from an individual or a family’s income.
iii. Net Income: This is the amount of money that remains after all deductions such as tax, dues, levies etc. have been removed from the gross income.
iv. Money Income: This is the purchasing or buying power of a family at given time. It is the amount of money which the family or individual has at any given time.
v. Expenditure: This is the total amount of money spent to meet the needs of a family in the form of goods and services.
vi. Primary and secondary needs: These are the needs the family spends its income on.
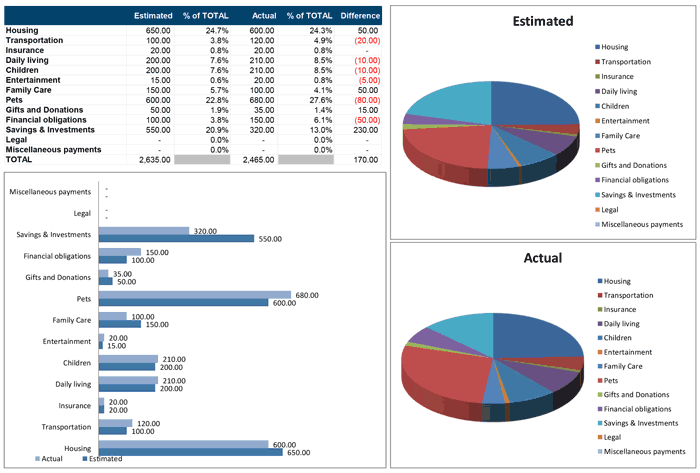
IMPORTANCE OF A FAMILY BUDGET.
1. To serve as a guide in spending.
2. To help to plan within the limits of expenditure
3. It helps to cater for the needs of every member of the family.
4. To prevent unnecessary spending and promote peace, security and stability in the family.
5. It helps the family make wise decisions about their spending.
6. To help the family assess their spending patterns and adjust properly.
7. To help prevent wasteful spending of income.
8. It helps train the children and other members of the family on how to spend money.
9. To help prevent impulsive buying.
10. To help accomplish a long term plan.
EVALUATION:
1. State five reasons why family budget is important.
2. Define household budget.
3. List and explain four budget-related terms.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Home Economics New Concepts for Nigerian Jnr. Secondary Schools Book 3. Popoola o. o. (Mrs.) Pgs.67-71.
Sub – Topic 2: FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN PREPARING FAMILY BUDGET AND PROCEDURES FOR PREPARING.
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN PREPARING FAMILY BUDGET:
1. The family Income: This plays an important role in the family budget.
2. Family needs: These determine the specific goods and services which be budgeted for.
3. Family size: This is the size, age and sex of the family members.
4. Family values: Value is the worth placed on something. This has a great influence on the family budget e.g. a family may value luxury more than education.
5. The season of the year: some food stuffs are more plentiful at certain seasons of the year and scarce at other times.
6. Inflation: This is a continuous increase in the general price level. It makes the family to spend more money on goods and services when it occurs.
7. Locality: This is the area where the family lives. The budget for a family in the rural area is different from that of the urban area e.g. in the area of transportation, available food and type of school etc.

PROCEDURES OR STEPS OR HINTS ON PREPARING FAMILY BUDGETS.
1. List all the family needs (primary and secondary) for the proposed budget.
2. Place the needs according to the family’s priorities e.g. foods, shelter, clothing, education, etc.
3. Give an estimate of the cost of each need giving a higher percentage according to the family priorities.
4. Estimate the total expected income for the budget period.
5. Balance the expenditure with the income. Expenditure should not be more than income.
Budget for Mr and Mrs AB’s family.
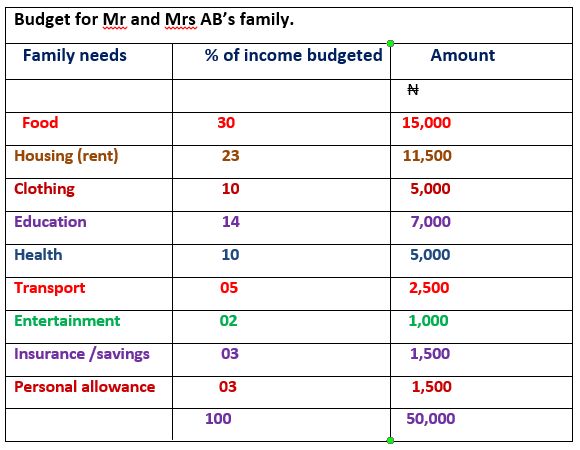
Evaluation:
1. State five steps in preparing a family budget.
2. Outline five factors that influence family budgeting and expenditure.
Assignment:
1. The plan for the future expenditure of a family is called household…………
(a) Plan (b) money (c) expenses (d) budget (e) income
2. The amount of money a family has at a given period is their money………..
(a) income (b) expenses (c) budget (d) power (e) expenditure
3. The total amount of money from a person’s income is his…………………
(a) All income (b) basic income (c) whole income (d) net income (e) gross income.
4. The amount of money that remains after deductions, such as tax and water rate have been removed from income is…………..
(a) Gross income (b) net income (c) partial income (d) whole income
(e) total income.
5. Budget is normally based on……………..
(a) gross income (b) future income (c) net income (d) partial income (e) total income
6. One of the following is not a source of family income.
(a) Salaries (b) wages (c) gifts (d) debts (e) investments.
7. The ………….. needs are important for survival and the family cannot do without
them. (a) secondary (b) tertiary (c) primary (d) total (e) family.
8. The following are given primary needs:
(a) food, clothing , shelter (b) food, shelter, car (c) food, shelter, recreation
(d) food, clothing, vacation (e) food, car, shelter.
9. The ………….. needs are desirable, but the family can do without them.
(a) Community (b) secondary (c) primary (d) family (e) tertiary
10. The practice of buying things not planned for is called…………..
(a) hire purchase (b) impulsive buying (c) wise buying
(d) whole buying (e) basic buying
11. Which of the following may not affect family budget?
CONTENT: 1. Meaning and Importance of family budget.
2. Factors to consider in preparing family budget and Procedures for preparing
family.
Sub-Topic 1: MEANING AND IMPORTANCE OF FAMILY BUDGET
Household / family budget is a plan for future expenditures of a given household. Budgeting is the process of preparing a budget. Good budgeting leads to wise management or use of family income. Family budget assists the family to meet their needs.

Budget -related terms
i. Income: The income of a family includes money which is earned by every member in the family. Sources of family income include salaries, wages, assets, shares, investments, e.g. rents, bonus from insurance policies, gifts, profits etc.
ii. Gross Income: This is the total amount of money from an individual or a family’s income.
iii. Net Income: This is the amount of money that remains after all deductions such as tax, dues, levies etc. have been removed from the gross income.
iv. Money Income: This is the purchasing or buying power of a family at given time. It is the amount of money which the family or individual has at any given time.
v. Expenditure: This is the total amount of money spent to meet the needs of a family in the form of goods and services.
vi. Primary and secondary needs: These are the needs the family spends its income on.

IMPORTANCE OF A FAMILY BUDGET.
1. To serve as a guide in spending.
2. To help to plan within the limits of expenditure
3. It helps to cater for the needs of every member of the family.
4. To prevent unnecessary spending and promote peace, security and stability in the family.
5. It helps the family make wise decisions about their spending.
6. To help the family assess their spending patterns and adjust properly.
7. To help prevent wasteful spending of income.
8. It helps train the children and other members of the family on how to spend money.
9. To help prevent impulsive buying.
10. To help accomplish a long term plan.
EVALUATION:
1. State five reasons why family budget is important.
2. Define household budget.
3. List and explain four budget-related terms.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Home Economics New Concepts for Nigerian Jnr. Secondary Schools Book 3. Popoola o. o. (Mrs.) Pgs.67-71.
Sub – Topic 2: FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN PREPARING FAMILY BUDGET AND PROCEDURES FOR PREPARING.
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN PREPARING FAMILY BUDGET:
1. The family Income: This plays an important role in the family budget.
2. Family needs: These determine the specific goods and services which be budgeted for.
3. Family size: This is the size, age and sex of the family members.
4. Family values: Value is the worth placed on something. This has a great influence on the family budget e.g. a family may value luxury more than education.
5. The season of the year: some food stuffs are more plentiful at certain seasons of the year and scarce at other times.
6. Inflation: This is a continuous increase in the general price level. It makes the family to spend more money on goods and services when it occurs.
7. Locality: This is the area where the family lives. The budget for a family in the rural area is different from that of the urban area e.g. in the area of transportation, available food and type of school etc.

PROCEDURES OR STEPS OR HINTS ON PREPARING FAMILY BUDGETS.
1. List all the family needs (primary and secondary) for the proposed budget.
2. Place the needs according to the family’s priorities e.g. foods, shelter, clothing, education, etc.
3. Give an estimate of the cost of each need giving a higher percentage according to the family priorities.
4. Estimate the total expected income for the budget period.
5. Balance the expenditure with the income. Expenditure should not be more than income.
Budget for Mr and Mrs AB’s family.

Evaluation:
1. State five steps in preparing a family budget.
2. Outline five factors that influence family budgeting and expenditure.
Assignment:
1. The plan for the future expenditure of a family is called household…………
(a) Plan (b) money (c) expenses (d) budget (e) income
2. The amount of money a family has at a given period is their money………..
(a) income (b) expenses (c) budget (d) power (e) expenditure
3. The total amount of money from a person’s income is his…………………
(a) All income (b) basic income (c) whole income (d) net income (e) gross income.
4. The amount of money that remains after deductions, such as tax and water rate have been removed from income is…………..
(a) Gross income (b) net income (c) partial income (d) whole income
(e) total income.
5. Budget is normally based on……………..
(a) gross income (b) future income (c) net income (d) partial income (e) total income
6. One of the following is not a source of family income.
(a) Salaries (b) wages (c) gifts (d) debts (e) investments.
7. The ………….. needs are important for survival and the family cannot do without
them. (a) secondary (b) tertiary (c) primary (d) total (e) family.
8. The following are given primary needs:
(a) food, clothing , shelter (b) food, shelter, car (c) food, shelter, recreation
(d) food, clothing, vacation (e) food, car, shelter.
9. The ………….. needs are desirable, but the family can do without them.
(a) Community (b) secondary (c) primary (d) family (e) tertiary
10. The practice of buying things not planned for is called…………..
(a) hire purchase (b) impulsive buying (c) wise buying
(d) whole buying (e) basic buying
11. Which of the following may not affect family budget?
Week 4
KEYNOTES
Adolescence The period that lies between the end of childhood to adulthood.
AIDS Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
Adolescent A boy or girl who is passing through the adolescent period.
Ante-natal care The care given to the pregnant woman before the birth of the child. Also called pre-natal care.
Appetizer An optional first course in a meal.
Baking Cooking in an oven or oven-type appliance with dry heat.
Antiperspirants Special products or astringents that reduce the amount of perspiration or sweat a person secretes for several hours.
Balanced diet Is a diet that contains all the food nutrients in the correct quantities for a given individual or group of individuals.
Beverages A liquid for drinking e.g. tea, coffee, fruit juice, mineral waters, milk drinks.
Body posture The way the body parts are held up or carried, when one walks, stands, sits or works.
Bulk purchase The process of buying goods e.g. food, in large quantities at a time.
Conflict A struggle between two or more people who disagree.
Clothing Any article placed on the body in order to protect and/or beautify it, e.g. clothes, Jewelry, make-up, shoes, etc.
Caramelization The Process whereby sugar is converted to caramel.
Colostrum The first milk produced in the first few days by a nursing mother.
Crisis A situation that marks a turning-point, when things cease to go on as usual in the family.
Culture The way of life of a society or a group of people, this is passed on from one generation to another.
Deodorant Substances which can be applied to the skin, to prevent odour from forming on the body, when a person sweats.
Dermis Inner layer of skin.
Disinfectant Substances that kill disease germs.
Drainage system Methods and channels of removing and disposing of liquid waste, e.g dirty water from household.
Family A group of persons who live together and are united by ties of marriage, blood or adoption.
Fabric finish Special treatment given to fabrics after construction.
Floor covering Special material used for covering the floor of a house e.g mats, linoleum, carpets, rugs.
Floor finish The material with which a floor of a house is made e.g. mud, concrete, terrazzo
Foetus An unborn baby developing in the womb.
Frying Process of cooking food in hot oil or fat.
Heredity The tendency for a parent to transfer his/her characteristics to his/her child [offspring].
Hiv Human immunodeficiency virus.
Household budget Plan for future expenditure of a given household.
Immunization The process of protecting a person against diseases by injecting vaccines into the body.
Implusive buying Process of buying things that are not planned for.
Interior decoration The act of beautifying rooms other interior areas of a house.
Inflation The continuous upward movement in general price levels of goods and services.
Layette The complete out-fit of clothing for the new -born baby.
Manicuring Process of caring for the hands and finger nails.
Menstruation The monthly flow of blood from the womb, through the vagina of every woman of child-bearing age.
Menu A plan showing the course that makes up a meal.
Mixed diet A diet that contains two or more of the food nutrients.
Money income The Amount of money which the family has at a given period.
Nuclear family A family made up of a man, his wife and their children.
Ovulation The release of a mature egg or ovum by the ovary of a woman.
Pedicure The process of caring for the legs including toes and nails.
Perishable food The foods that spoil easily.
Post-natal care The care required by a mother after child-birth.
Puberty The short life span of time which marks the beginning of sexual maturity.
Refrigerator Process of keeping food or other things cold, often in refrigerator.
Right A statement showing a natural due, moral claim or legal entitlement.
Steaming Process of cooking food in the steam from boiling water.
Stewing Cooking food slowly or at low heat in a small quantity of water for a long time.
Sibling Children [brothers and sisters] of the same parent.
Value Belief, feeling or idea of what is important, desirable and good.
Ventilation Changing the air in a room often enough to keep it fresh.
Wardrobe The process of planning for the clothing needs of an individual or the entire family.
Warp The yarn of thread that runs lengthwise in a woven fabric.
Weaning The process of gradually introducing a child to other foods apart from milk.
Weft The yarn of thread that runs crosswise in a woven fabric.
Adolescence The period that lies between the end of childhood to adulthood.
AIDS Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
Adolescent A boy or girl who is passing through the adolescent period.
Ante-natal care The care given to the pregnant woman before the birth of the child. Also called pre-natal care.
Appetizer An optional first course in a meal.
Baking Cooking in an oven or oven-type appliance with dry heat.
Antiperspirants Special products or astringents that reduce the amount of perspiration or sweat a person secretes for several hours.
Balanced diet Is a diet that contains all the food nutrients in the correct quantities for a given individual or group of individuals.
Beverages A liquid for drinking e.g. tea, coffee, fruit juice, mineral waters, milk drinks.
Body posture The way the body parts are held up or carried, when one walks, stands, sits or works.
Bulk purchase The process of buying goods e.g. food, in large quantities at a time.
Conflict A struggle between two or more people who disagree.
Clothing Any article placed on the body in order to protect and/or beautify it, e.g. clothes, Jewelry, make-up, shoes, etc.
Caramelization The Process whereby sugar is converted to caramel.
Colostrum The first milk produced in the first few days by a nursing mother.
Crisis A situation that marks a turning-point, when things cease to go on as usual in the family.
Culture The way of life of a society or a group of people, this is passed on from one generation to another.
Deodorant Substances which can be applied to the skin, to prevent odour from forming on the body, when a person sweats.
Dermis Inner layer of skin.
Disinfectant Substances that kill disease germs.
Drainage system Methods and channels of removing and disposing of liquid waste, e.g dirty water from household.
Family A group of persons who live together and are united by ties of marriage, blood or adoption.
Fabric finish Special treatment given to fabrics after construction.
Floor covering Special material used for covering the floor of a house e.g mats, linoleum, carpets, rugs.
Floor finish The material with which a floor of a house is made e.g. mud, concrete, terrazzo
Foetus An unborn baby developing in the womb.
Frying Process of cooking food in hot oil or fat.
Heredity The tendency for a parent to transfer his/her characteristics to his/her child [offspring].
Hiv Human immunodeficiency virus.
Household budget Plan for future expenditure of a given household.
Immunization The process of protecting a person against diseases by injecting vaccines into the body.
Implusive buying Process of buying things that are not planned for.
Interior decoration The act of beautifying rooms other interior areas of a house.
Inflation The continuous upward movement in general price levels of goods and services.
Layette The complete out-fit of clothing for the new -born baby.
Manicuring Process of caring for the hands and finger nails.
Menstruation The monthly flow of blood from the womb, through the vagina of every woman of child-bearing age.
Menu A plan showing the course that makes up a meal.
Mixed diet A diet that contains two or more of the food nutrients.
Money income The Amount of money which the family has at a given period.
Nuclear family A family made up of a man, his wife and their children.
Ovulation The release of a mature egg or ovum by the ovary of a woman.
Pedicure The process of caring for the legs including toes and nails.
Perishable food The foods that spoil easily.
Post-natal care The care required by a mother after child-birth.
Puberty The short life span of time which marks the beginning of sexual maturity.
Refrigerator Process of keeping food or other things cold, often in refrigerator.
Right A statement showing a natural due, moral claim or legal entitlement.
Steaming Process of cooking food in the steam from boiling water.
Stewing Cooking food slowly or at low heat in a small quantity of water for a long time.
Sibling Children [brothers and sisters] of the same parent.
Value Belief, feeling or idea of what is important, desirable and good.
Ventilation Changing the air in a room often enough to keep it fresh.
Wardrobe The process of planning for the clothing needs of an individual or the entire family.
Warp The yarn of thread that runs lengthwise in a woven fabric.
Weaning The process of gradually introducing a child to other foods apart from milk.
Weft The yarn of thread that runs crosswise in a woven fabric.
