SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of last term's work.
2. Man in space
- Space travel
- Gravitational pull.
3. Our disappearing forest.
- Mature forest are almost non-existence in West Africa today due to human activities.
- Unreached deserts.
- Other fuels used for cooking.
- Maintaining our weather.
- Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle.
4. Controlling the weather.
- Human interference with weather.
- Simple weather conditions
- Temperature, humidity and pressure.
5. Family life education
- Implication of teenage pregnancy
- Myths and facts about pregnancy.
6-13 Revision and JSCE
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Electrical Energy: (a) Concept of electron flow, (b) Circuits
series and parallel (c) Ammeter and voltmeter (d) House circuit:
fuse and circuit breaker,(e) Electric meter- reading and billing.
2. Radioactivity: Meaning of radioactivity; radioactive
elements; Types of radiation and properties; Uses of radioactivity;
Dangers of radioactive rays.
3-6. Intensive Revision of Basic 7-9 work
7. Mock Examination
8-12. Revision and BECE (JSCE) Examination.
3RD TERM
WEEK 1
Man in space

http://www.spacekids.co.uk/spacehistory/
http://www.aerospaceguide.net/space_kids.html
Space travel

http://www.space.com/16159-first-man-in-space.html
http://edition.cnn.com/2012/08/25/us/ne ... index.html
Gravitational pull.
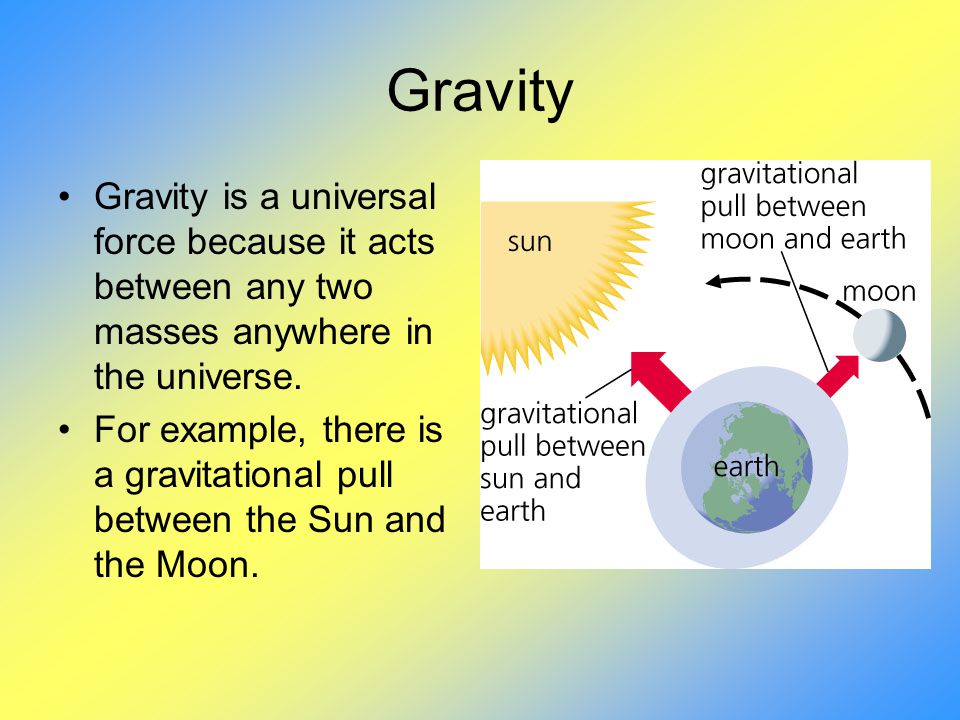
http://idahoptv.org/dialogue4kids/seaso ... /facts.cfm
http://www.physics4kids.com/files/motion_gravity.html
practice test
http://resources.woodlands-junior.kent. ... orces.html
http://www.sciencewithmrnoon.com/physci ... iqz112.htm
http://www.esa.int/esaKIDSen/SEMWWRW797E_q.html
http://funschool.kaboose.com/globe-ride ... -quiz.html
http://www.kidsastronomy.com/fun/quiz.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/newsround/14076541

http://www.spacekids.co.uk/spacehistory/
http://www.aerospaceguide.net/space_kids.html
Space travel

http://www.space.com/16159-first-man-in-space.html
http://edition.cnn.com/2012/08/25/us/ne ... index.html
Gravitational pull.

http://idahoptv.org/dialogue4kids/seaso ... /facts.cfm
http://www.physics4kids.com/files/motion_gravity.html
practice test
http://resources.woodlands-junior.kent. ... orces.html
http://www.sciencewithmrnoon.com/physci ... iqz112.htm
http://www.esa.int/esaKIDSen/SEMWWRW797E_q.html
http://funschool.kaboose.com/globe-ride ... -quiz.html
http://www.kidsastronomy.com/fun/quiz.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/newsround/14076541
WEEK 2
TOPIC: ELECTRICAL ENERGY
CONTENT: 1. Concept of electron flow.
2. Circuits- series and parallel.
3. Ammeter and Voltmeter.
4. House circuit; fuse and circuit breaker.
5. Electric meter- reading and billing.
PREAMBLE:
We already know various forms of energy. Can you mention them? Today, we are going to learn about Electrical energy in details.
Now, what is electrical energy?
Introduction: We make use of electricity in our towns and some villages, homes; schools etc. electricity is used for lighting, heating and cooling and in our industries. This electrical energy is the energy derived from the flow of electrons which is known as electric current.
How does electron flow, are there types of flow, how and with which device do we measure the flow, what is electrical circuit, how do we prevent the hazards, and read meter and billing system.
CONCEPT OF ELECTRON FLOW
In an electric flow, the current consist of a swarm of moving electrons. What causes electric current to flow is a chemical device called electric cells. Electric do this by producing an electric force which pushes the current along, and current will only flow if there is a complete circuit of conductors, by which the current will leave from one end of the cell and travel round to the other end. The current is the same at any point round the circuit and if the conductor is broken at any point, the current will stop flowing. Note that current flow a negatively charged end to the positively charged end. DEMONSTRATE an activity using unripe orange with zinc and copper plate; repeat the experiment using dilute sulphuric acid in a beaker.
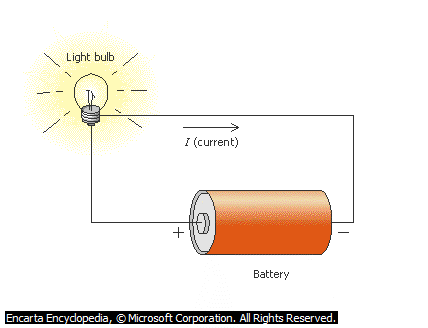
Example of Circuit
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
An electric circuit is a complete path of wires and electrical components through which electric current flows. Electric current can be made to flow from its source through metallic wires, back to their source. Electric current leaves the negatively charged rod of a cell, flows through a wire and then goes back to the cell through the positively charged rod. This complete path is referred to as electric circuit. This is represented by a sketch or symbol on the paper using arrow to indicate the flow of electron.
COMPLETE AND INCOMPLETE CIRCUIT
A circuit is said to be complete if the switch is closed (on), and the bulb will light because it is a closed circuit.
A circuit is said to be incomplete if the switch is opened (off), and the bulb will not light up because the circuit is not completed or closed.
SERIES PARALLEL CIRCUITS
When some components of a circuit are in series, it means that the components are connected end to end. They form a complete loop such that the same current flows through them.
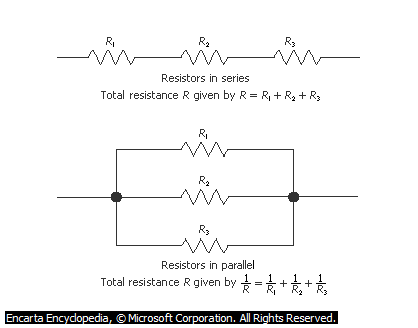
The above diagrams represent the series and parallel circuits
CIRCUIT IN PARALLEL
Components of a circuit are in parallel when the common terminals are connected to common points. Hence, cells are said to in parallel when all the positive terminals of the cells are connected together, and all the negative terminals are connected together. The external electrical component is then connected across the two junctions of the terminals.
1. Calculate the total e.m.f and the internal resistance involved in 3 cells in series with e.m.f of 1.5V and internal resistance 0.5ohms.
2. Assuming a cell in parallel has the same value, calculate the e.m.f and internal resistance.
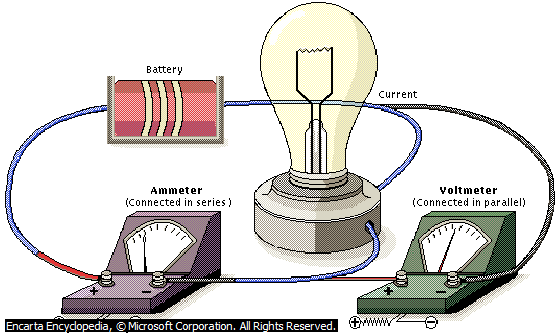
AMMETER AND VOLTMETER
An ammeter is an instrument used to measure electric current. It is always placed in series with the circuit component carrying the current to be measured. An ammeter should have low resistance, so that its introduction into the circuit would not affect the value of the electric current to be measured.
HOUSE CIRCUITS: Fuse and Circuit Breaker
House circuit can be divided into:
i. The lighting circuit
ii. The power circuit
A voltmeter on the other hand is an instrument used to measure the voltage across circuit components through which electric current is flowing. Voltmeters are always connected in parallel within circuit components across which the potential difference is to be measured.
Voltmeters should have high resistance so that when it is introduce into the circuit, current which ought to pass through the circuit component will not be diverted to pass through it and thereby disturbing the circuit.
The Lighting Circuit: The lighting circuit is the network of wires that connect all the bulbs in parallel in a house.
The power circuit: this consists of a complete circuit of three-core cables, which go round the whole house. Three-pin sockets are connected to the circuit at convenient points. Electrical appliances such as TV sets, radio sets, computer sets refrigerators, cooker, etc can be empowered by plugging them into these sockets.
Materials that can be easily seen or used in the house circuit are: Electric sockets and plugs. A typical socket has three holes:
1. The top hole is called the earth ( green or yellow),
2. The hole on the right side is called the live (brown or red)
3. The hole on the left side is called the neutral (blue or black).
FUSE AND CIRCUIT BREAKER
A fuse is a safety device containing a short length of thin conducting wire, which melts and breaks the circuit, if the current exceeds a certain safe value or maximum operating limit.
Circuit Breaker on the other hand works in the same way as the fuse. It is usually placed beside the electric meter such that the current enters it first before going into the meter.
ELECTRIC METER READING AND BILLING
To measure or read electricity consumed in order to bill the consumer accordingly, the standard unit commonly used is the kilowatt/hour.
1 unit of the electric power is the watt
1 watt= 1 volts x 1 ampere
Hence, the electrical meter is a device used for recording the number of units of electrical energy consumed in a house over a period of time.
1KWh = 1000 x 60 x60J
= 3.6 X 10[sup]6[/sup] Joules of energy
The actual cost per unit to electrical energy varies with the nature of the use to which the energy is put.
The PHCN also charges a fixed charge and meter maintenance charge every month. This also varies according to the tariff rate of the consumer.
Example: 1. the tariff rate of a consumer is N4. 00 per unit. The present meter reading is 3760 while the reading was 3648.
a. What is the consumption of the household after one month?
b. If the fixed charge is N30 and the meter maintenance charge is N100. What is the current charge of the consumer?
SOLUTION: i. the consumption of the household is the difference between the present reading and the previous reading.
3760 – 3648 = 112units.
ii. The energy charge of the consumer = 112 x 4. 00 = N448. 00k
Fixed charges = N30
Meter maintenance charge = N100
Current charges = N(448 + 30 + 100) = N578 . 00
EVALUATION/ASSIGNMENT
1. A1600 Watts electric oven is used for 9 hours. Calculate the cost of using the N3. 00 per unit of energy. (Energy Consumed = power x time).What are the functions of the ammeter and voltmeter?
2. Read about Radioactivity in pgs 85- 88 of Basic SC. Made Easy by F. I. Kehinde.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
CONTENT: 1. Concept of electron flow.
2. Circuits- series and parallel.
3. Ammeter and Voltmeter.
4. House circuit; fuse and circuit breaker.
5. Electric meter- reading and billing.
PREAMBLE:
We already know various forms of energy. Can you mention them? Today, we are going to learn about Electrical energy in details.
Now, what is electrical energy?
Introduction: We make use of electricity in our towns and some villages, homes; schools etc. electricity is used for lighting, heating and cooling and in our industries. This electrical energy is the energy derived from the flow of electrons which is known as electric current.
How does electron flow, are there types of flow, how and with which device do we measure the flow, what is electrical circuit, how do we prevent the hazards, and read meter and billing system.
CONCEPT OF ELECTRON FLOW
In an electric flow, the current consist of a swarm of moving electrons. What causes electric current to flow is a chemical device called electric cells. Electric do this by producing an electric force which pushes the current along, and current will only flow if there is a complete circuit of conductors, by which the current will leave from one end of the cell and travel round to the other end. The current is the same at any point round the circuit and if the conductor is broken at any point, the current will stop flowing. Note that current flow a negatively charged end to the positively charged end. DEMONSTRATE an activity using unripe orange with zinc and copper plate; repeat the experiment using dilute sulphuric acid in a beaker.

Example of Circuit
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
An electric circuit is a complete path of wires and electrical components through which electric current flows. Electric current can be made to flow from its source through metallic wires, back to their source. Electric current leaves the negatively charged rod of a cell, flows through a wire and then goes back to the cell through the positively charged rod. This complete path is referred to as electric circuit. This is represented by a sketch or symbol on the paper using arrow to indicate the flow of electron.
COMPLETE AND INCOMPLETE CIRCUIT
A circuit is said to be complete if the switch is closed (on), and the bulb will light because it is a closed circuit.
A circuit is said to be incomplete if the switch is opened (off), and the bulb will not light up because the circuit is not completed or closed.
SERIES PARALLEL CIRCUITS
When some components of a circuit are in series, it means that the components are connected end to end. They form a complete loop such that the same current flows through them.

The above diagrams represent the series and parallel circuits
CIRCUIT IN PARALLEL
Components of a circuit are in parallel when the common terminals are connected to common points. Hence, cells are said to in parallel when all the positive terminals of the cells are connected together, and all the negative terminals are connected together. The external electrical component is then connected across the two junctions of the terminals.
1. Calculate the total e.m.f and the internal resistance involved in 3 cells in series with e.m.f of 1.5V and internal resistance 0.5ohms.
2. Assuming a cell in parallel has the same value, calculate the e.m.f and internal resistance.
AMMETER AND VOLTMETER
An ammeter is an instrument used to measure electric current. It is always placed in series with the circuit component carrying the current to be measured. An ammeter should have low resistance, so that its introduction into the circuit would not affect the value of the electric current to be measured.

HOUSE CIRCUITS: Fuse and Circuit Breaker
House circuit can be divided into:
i. The lighting circuit
ii. The power circuit
A voltmeter on the other hand is an instrument used to measure the voltage across circuit components through which electric current is flowing. Voltmeters are always connected in parallel within circuit components across which the potential difference is to be measured.
Voltmeters should have high resistance so that when it is introduce into the circuit, current which ought to pass through the circuit component will not be diverted to pass through it and thereby disturbing the circuit.
The Lighting Circuit: The lighting circuit is the network of wires that connect all the bulbs in parallel in a house.
The power circuit: this consists of a complete circuit of three-core cables, which go round the whole house. Three-pin sockets are connected to the circuit at convenient points. Electrical appliances such as TV sets, radio sets, computer sets refrigerators, cooker, etc can be empowered by plugging them into these sockets.
Materials that can be easily seen or used in the house circuit are: Electric sockets and plugs. A typical socket has three holes:
1. The top hole is called the earth ( green or yellow),
2. The hole on the right side is called the live (brown or red)
3. The hole on the left side is called the neutral (blue or black).
FUSE AND CIRCUIT BREAKER
A fuse is a safety device containing a short length of thin conducting wire, which melts and breaks the circuit, if the current exceeds a certain safe value or maximum operating limit.
Circuit Breaker on the other hand works in the same way as the fuse. It is usually placed beside the electric meter such that the current enters it first before going into the meter.
ELECTRIC METER READING AND BILLING
To measure or read electricity consumed in order to bill the consumer accordingly, the standard unit commonly used is the kilowatt/hour.
1 unit of the electric power is the watt
1 watt= 1 volts x 1 ampere
Hence, the electrical meter is a device used for recording the number of units of electrical energy consumed in a house over a period of time.
1KWh = 1000 x 60 x60J
= 3.6 X 10[sup]6[/sup] Joules of energy
The actual cost per unit to electrical energy varies with the nature of the use to which the energy is put.
The PHCN also charges a fixed charge and meter maintenance charge every month. This also varies according to the tariff rate of the consumer.
Example: 1. the tariff rate of a consumer is N4. 00 per unit. The present meter reading is 3760 while the reading was 3648.
a. What is the consumption of the household after one month?
b. If the fixed charge is N30 and the meter maintenance charge is N100. What is the current charge of the consumer?
SOLUTION: i. the consumption of the household is the difference between the present reading and the previous reading.
3760 – 3648 = 112units.
ii. The energy charge of the consumer = 112 x 4. 00 = N448. 00k
Fixed charges = N30
Meter maintenance charge = N100
Current charges = N(448 + 30 + 100) = N578 . 00
EVALUATION/ASSIGNMENT
1. A1600 Watts electric oven is used for 9 hours. Calculate the cost of using the N3. 00 per unit of energy. (Energy Consumed = power x time).What are the functions of the ammeter and voltmeter?
2. Read about Radioactivity in pgs 85- 88 of Basic SC. Made Easy by F. I. Kehinde.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3
Practice Test 4
WEEK 3
TOPIC: RADIOACTIVITY
CONTENT: 1. Brief History of Radioactivity
2. Properties and Characteristics of Radiation
3. Uses of Radioactivity
Sub-Topic 1: Brief History of Radioactivity
MEANING OF RADIOACTIVITY: This means the natural dissipation of radioactive element by half after every specific number of years or period of time say 20 years etc. The nuclei of certain elements are not stable, hence they disintegrate and simultaneously emit certain kinds of radiation, and in the process, change into nuclei of other elements. This phenomenon is known as radioactivity.
Definition of Radioactivity: Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei by the emission of subatomic particles called alpha particles and beta particles, or of electromagnetic rays called x-rays and gamma rays.
BRIEF HISTORY OF RADIOACTIVITY
The phenomenon of radioactivity was discovered in 1896 by the French Physicist by name Antoine Henri Becquerel when he observed that the element of Uranium can blacken a photographic plate, although separated from it by glass or black paper. Some few years later, Marie and Pierre Curie husband and wife showed that thorium, polonium, and radium also produce these rays.
SOME RADIOACTIVE ELEMENTS
Uranium
Thorium
Polonium
Radium
Helium
Nitrogen
Vanadium.
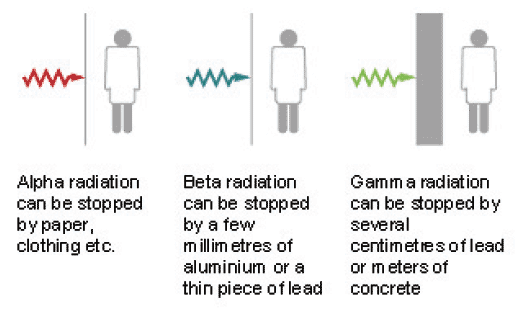
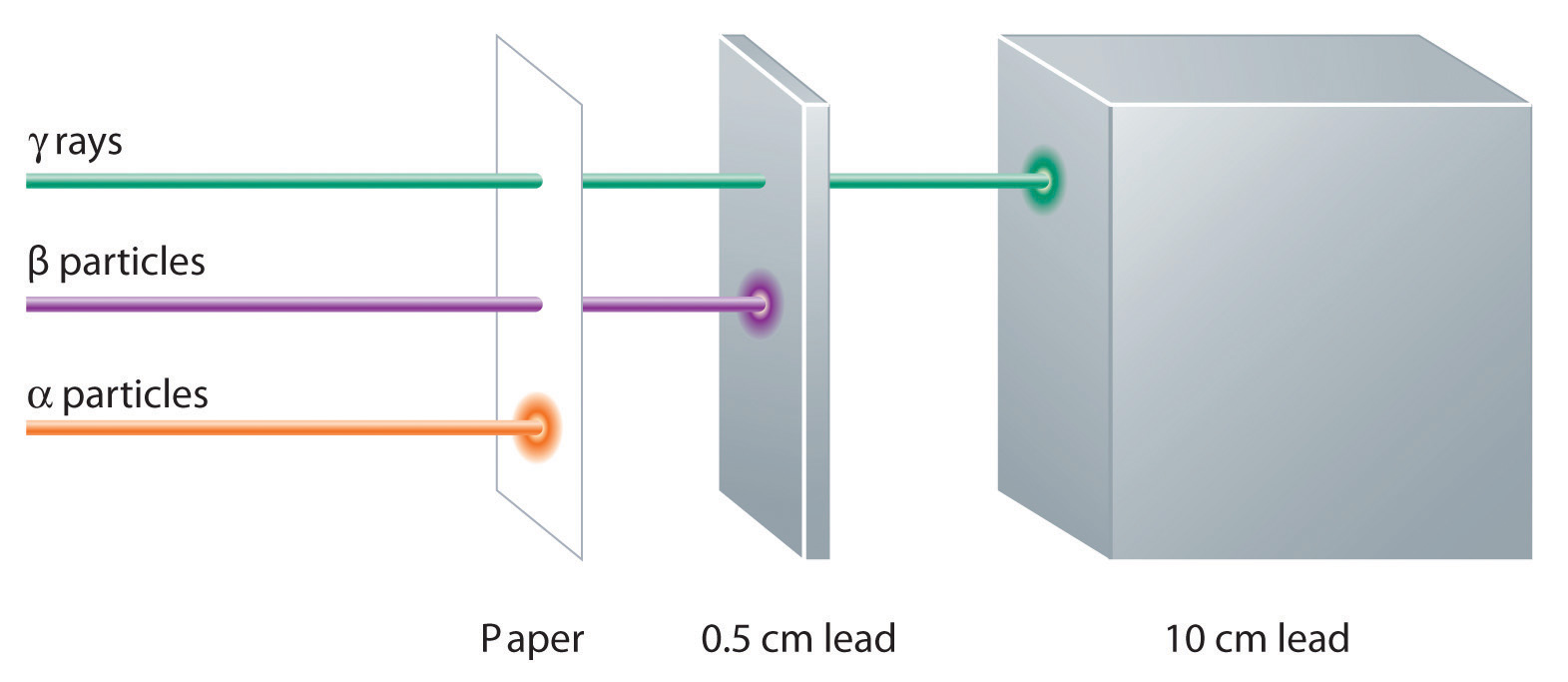
TYPES OF RADIATION
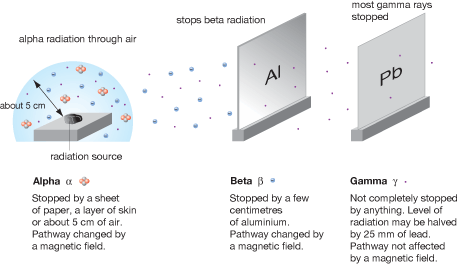
They are basically three (3) different kinds of radiation namely:
Alpha rays α
Beta rays β
Gamma rays γ
These are the invisible ray produced by the radioactive elements; that is what we refer to as radiation.
Note that X-RAY is not part of the basic three (3) rays above.
Three types of radiation
Gamma Rays
ALPHA RAYS
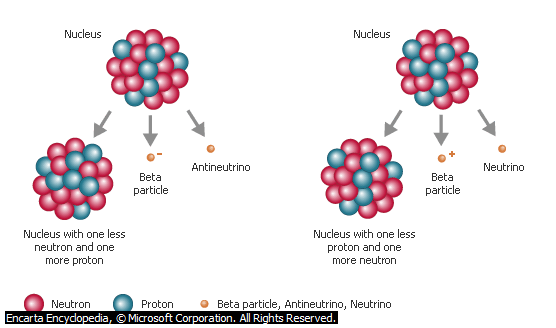
BETA RAYS
Sub-Topic 2: PROPERTIES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF RADIATION
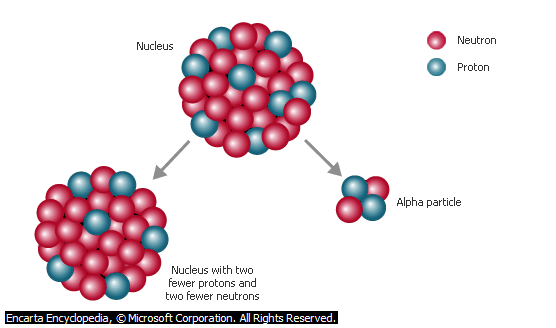
ALPHA RAYS
1. They are positively charged.
2. They nuclei of helium atoms.
3. They contain two protons, two neutrons and electrons.
4. They have a mass of about 4 units on the scale of 12C.
5. They are fast moving.
BETA RAYS
1. They are negatively charged.
2. They moving stream of electrons.
3. They have a charge of -1.
4. They can produce ionization in gases.
5. They can penetrate matter much more than the alpha particles.
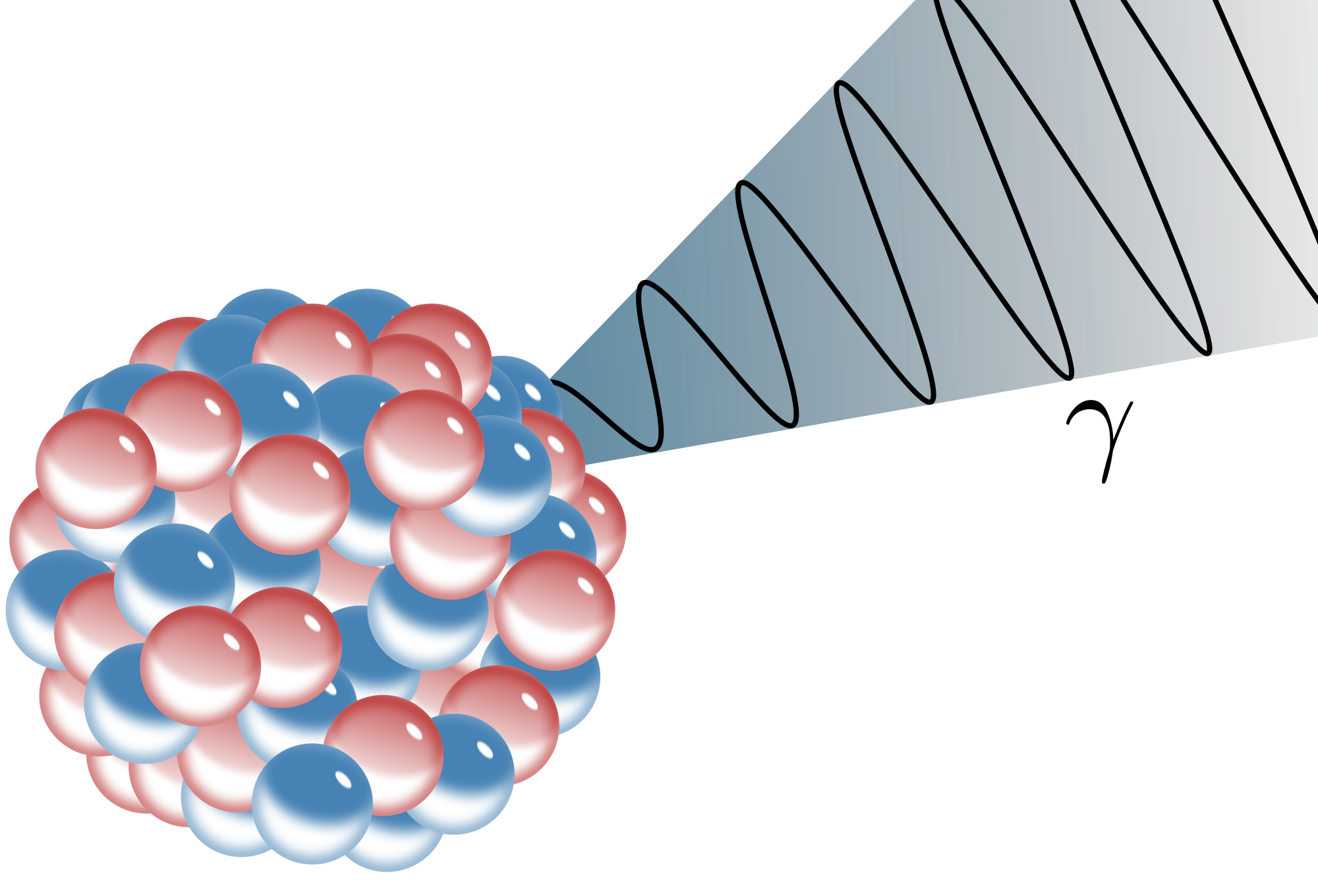
GAMMA RAYS
1. They neutrally charged
2. They are not material particles.
3. They consist of electromagnetic wave of short wavelength.
4. They are more penetrating than Alpha and beta.
5. They can pass through 15cm of lead and even further through other metals.

X-RAY
This is another radiation discovered by another Scientist Amend Roentgen, because he did not know what this radiation was, he called it X-rays, they are now known to be electromagnetic waves with short wavelengths produced by electrons moving between the inner energy levels of the metal atoms.
X-rays are used in hospitals because although they pass through soft tissue and bones, the rays are absorbed more by the bone structure on a photographic plate.
Sub-Topic 3: USES OF RADIOACTIVITY
1. Gamma rays can be used to destroy cancerous cells.
2. Gamma rays are used in industry for study of defects in metals.
3. For sterilization to kill germs in surgical equipment.
4. Beta and Gamma radiations are used to detect the thickness of pipe, leakages in pipes, etc.
5. A. They are used to induce mutations in plants and animals.
B. Radiation is used in insect and pest control.
6 Radiation is used in dating techniques in determining archeological age of fossil- 146C
7. They are used as tracers.
8. Nuclear energy is used for power generation.
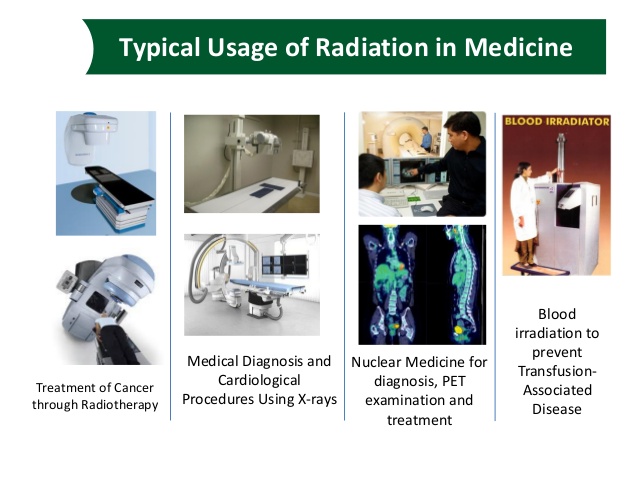
Use of radiation in the hospital
DANGERS IN THE USE OF RADIOACTIVE RAYS
Radioactive substance can be dangerous to the body if one is exposed to radiation for a long time.
1. They have harmful effects on both plants and animals.
2. Small doses of radiation in the treatment of diseases such as cancer cause changes in cell structure.
3. It can lead to infertility.
4. It can damage the skin.
5. Cumulative effects can lead to death.

CONTENT: 1. Brief History of Radioactivity
2. Properties and Characteristics of Radiation
3. Uses of Radioactivity
Sub-Topic 1: Brief History of Radioactivity
MEANING OF RADIOACTIVITY: This means the natural dissipation of radioactive element by half after every specific number of years or period of time say 20 years etc. The nuclei of certain elements are not stable, hence they disintegrate and simultaneously emit certain kinds of radiation, and in the process, change into nuclei of other elements. This phenomenon is known as radioactivity.
Definition of Radioactivity: Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei by the emission of subatomic particles called alpha particles and beta particles, or of electromagnetic rays called x-rays and gamma rays.
BRIEF HISTORY OF RADIOACTIVITY
The phenomenon of radioactivity was discovered in 1896 by the French Physicist by name Antoine Henri Becquerel when he observed that the element of Uranium can blacken a photographic plate, although separated from it by glass or black paper. Some few years later, Marie and Pierre Curie husband and wife showed that thorium, polonium, and radium also produce these rays.
SOME RADIOACTIVE ELEMENTS
Uranium
Thorium
Polonium
Radium
Helium
Nitrogen
Vanadium.
TYPES OF RADIATION
They are basically three (3) different kinds of radiation namely:
Alpha rays α
Beta rays β
Gamma rays γ
These are the invisible ray produced by the radioactive elements; that is what we refer to as radiation.
Note that X-RAY is not part of the basic three (3) rays above.


Three types of radiation

Gamma Rays

ALPHA RAYS

BETA RAYS
Sub-Topic 2: PROPERTIES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF RADIATION

ALPHA RAYS
1. They are positively charged.
2. They nuclei of helium atoms.
3. They contain two protons, two neutrons and electrons.
4. They have a mass of about 4 units on the scale of 12C.
5. They are fast moving.
BETA RAYS
1. They are negatively charged.
2. They moving stream of electrons.
3. They have a charge of -1.
4. They can produce ionization in gases.
5. They can penetrate matter much more than the alpha particles.
GAMMA RAYS
1. They neutrally charged
2. They are not material particles.
3. They consist of electromagnetic wave of short wavelength.
4. They are more penetrating than Alpha and beta.
5. They can pass through 15cm of lead and even further through other metals.

X-RAY
This is another radiation discovered by another Scientist Amend Roentgen, because he did not know what this radiation was, he called it X-rays, they are now known to be electromagnetic waves with short wavelengths produced by electrons moving between the inner energy levels of the metal atoms.
X-rays are used in hospitals because although they pass through soft tissue and bones, the rays are absorbed more by the bone structure on a photographic plate.
Sub-Topic 3: USES OF RADIOACTIVITY
1. Gamma rays can be used to destroy cancerous cells.
2. Gamma rays are used in industry for study of defects in metals.
3. For sterilization to kill germs in surgical equipment.
4. Beta and Gamma radiations are used to detect the thickness of pipe, leakages in pipes, etc.
5. A. They are used to induce mutations in plants and animals.
B. Radiation is used in insect and pest control.
6 Radiation is used in dating techniques in determining archeological age of fossil- 146C
7. They are used as tracers.
8. Nuclear energy is used for power generation.

Use of radiation in the hospital
DANGERS IN THE USE OF RADIOACTIVE RAYS
Radioactive substance can be dangerous to the body if one is exposed to radiation for a long time.
1. They have harmful effects on both plants and animals.
2. Small doses of radiation in the treatment of diseases such as cancer cause changes in cell structure.
3. It can lead to infertility.
4. It can damage the skin.
5. Cumulative effects can lead to death.

WEEK 4
Our disappearing forest.
- Mature forest are almost non-existence in West Africa today due to human activities.


https://www.esa.int/esaKIDSen/SEM0YKXJD1E_Earth_0.html
http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topi ... hreats.cfm
http://www.greenpeace.org/international ... g-forests/
- Other fuels used for cooking.
Anything that can burn has been used as fuel for cooking. This includes, but is not limited to:
methane
butane
oil (various grades)
animal fat
cow, yak, buffalo manure
liquid alcohol
solid alcohol
waxes and paraffins
gasoline and kerosene
wood
coal
straw
charcoal
peat
Fuels burned for cooking are usually burned in conditions of plentiful air and low temperatures so the production of CO and NOx is low. Burning of biomass can create organic emissions as volatiles are boiled out of the unburned material. Carbon dioxide emissions are lowest with methane and highest with coal, peat and charcoal.
- Maintaining our weather.
http://www.weatherwizkids.com/weather-wind.htm
http://www.ehow.com/about_5270471_facto ... imate.html
- Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle.
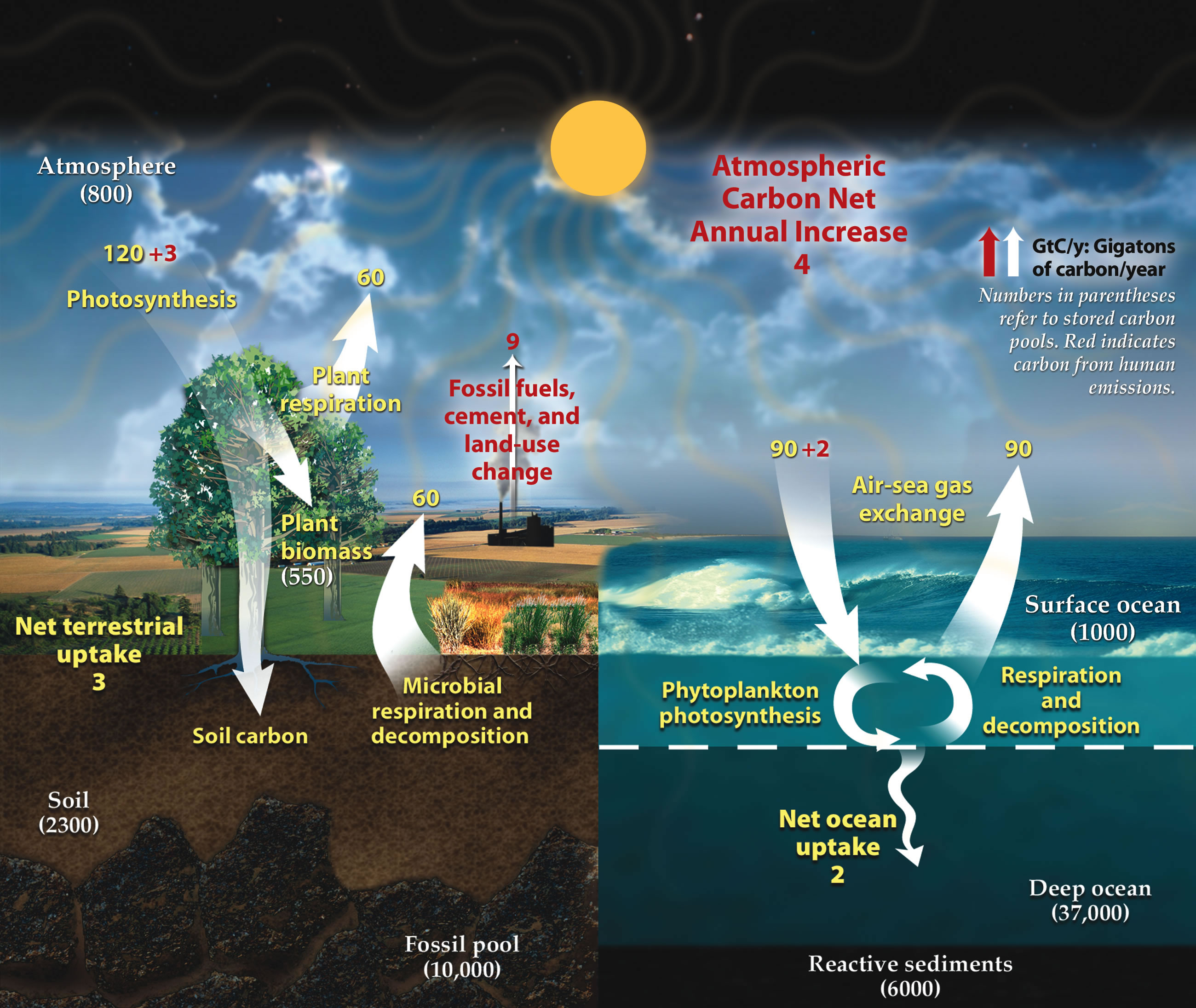
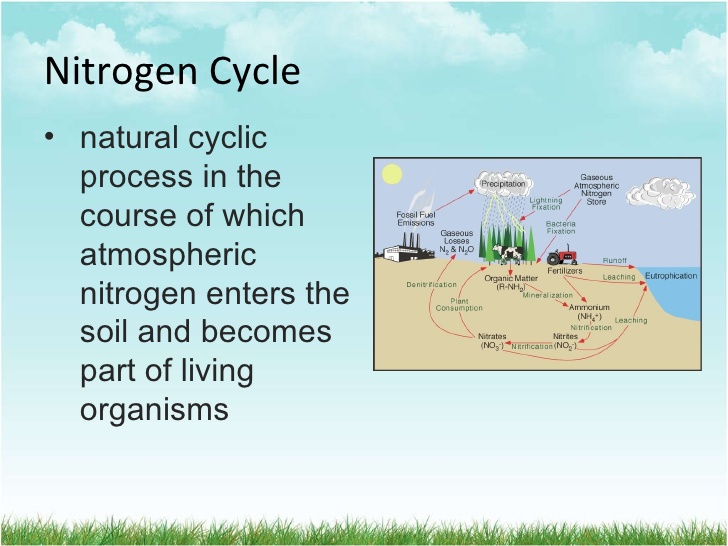
http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-ki ... -cycle.php
http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-ki ... -cycle.php
http://www.ducksters.com/science/ecosys ... _cycle.php
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... rev1.shtml
http://www.etap.org/demo/biology_files/ ... tutor.html
practice test
http://barbers.k12.hi.us/686/quiz.html
http://environment.nationalgeographic.c ... fuel-quiz/
http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topi ... /index.cfm
Controlling the weather.
- Human interference with weather.

http://wiki.answers.com/Q/How_do_humans ... _disasters
http://www.findingdulcinea.com/news/env ... guins.html
- Simple weather conditions
http://www.minecraftforum.net/topic/162 ... e-weather/
- Temperature, humidity and pressure.
http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-ki ... midity.php
http://weather.thefuntimesguide.com/200 ... essure.php
http://www.weather-climate.org.uk/05.php
practice test
http://www.quibblo.com/quiz/bVaZSJ5/Wea ... imate-Quiz
http://www.mcwdn.org/WEATHER/ClimateQuiz.html
http://www.interactivegeography.co.uk/g ... ather.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... imate-quiz
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... ogen-Cycle
http://wps.prenhall.com/esm_mcknight_ph ... index.html
- Mature forest are almost non-existence in West Africa today due to human activities.


https://www.esa.int/esaKIDSen/SEM0YKXJD1E_Earth_0.html
http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topi ... hreats.cfm
http://www.greenpeace.org/international ... g-forests/
- Other fuels used for cooking.
Anything that can burn has been used as fuel for cooking. This includes, but is not limited to:
methane
butane
oil (various grades)
animal fat
cow, yak, buffalo manure
liquid alcohol
solid alcohol
waxes and paraffins
gasoline and kerosene
wood
coal
straw
charcoal
peat
Fuels burned for cooking are usually burned in conditions of plentiful air and low temperatures so the production of CO and NOx is low. Burning of biomass can create organic emissions as volatiles are boiled out of the unburned material. Carbon dioxide emissions are lowest with methane and highest with coal, peat and charcoal.
- Maintaining our weather.

http://www.weatherwizkids.com/weather-wind.htm
http://www.ehow.com/about_5270471_facto ... imate.html
- Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle.


http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-ki ... -cycle.php
http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-ki ... -cycle.php
http://www.ducksters.com/science/ecosys ... _cycle.php
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... rev1.shtml
http://www.etap.org/demo/biology_files/ ... tutor.html
practice test
http://barbers.k12.hi.us/686/quiz.html
http://environment.nationalgeographic.c ... fuel-quiz/
http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topi ... /index.cfm
Controlling the weather.
- Human interference with weather.

http://wiki.answers.com/Q/How_do_humans ... _disasters
http://www.findingdulcinea.com/news/env ... guins.html
- Simple weather conditions

http://www.minecraftforum.net/topic/162 ... e-weather/
- Temperature, humidity and pressure.
http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-ki ... midity.php
http://weather.thefuntimesguide.com/200 ... essure.php
http://www.weather-climate.org.uk/05.php
practice test
http://www.quibblo.com/quiz/bVaZSJ5/Wea ... imate-Quiz
http://www.mcwdn.org/WEATHER/ClimateQuiz.html
http://www.interactivegeography.co.uk/g ... ather.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... imate-quiz
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... ogen-Cycle
http://wps.prenhall.com/esm_mcknight_ph ... index.html
WEEK 5
Family life education
- Implication of teenage pregnancy


http://breezemagazine.blogspot.com/2012 ... fe_31.html
http://www.ourfamilyworld.com/2012/06/1 ... 2-studies/
http://www.livestrong.com/article/86972 ... pregnancy/
http://ischoolsmcgrominez.wordpress.com ... pregnancy/
- Myths and facts about pregnancy.


http://www.welcomebabyhome.com/pregnanc ... _myths.htm
http://kidshealth.org/parent/pregnancy_ ... tales.html
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
http://www.quibblo.com/quiz/4lhqMw/How- ... -Pregnancy
- Implication of teenage pregnancy


http://breezemagazine.blogspot.com/2012 ... fe_31.html
http://www.ourfamilyworld.com/2012/06/1 ... 2-studies/
http://www.livestrong.com/article/86972 ... pregnancy/
http://ischoolsmcgrominez.wordpress.com ... pregnancy/
- Myths and facts about pregnancy.


http://www.welcomebabyhome.com/pregnanc ... _myths.htm
http://kidshealth.org/parent/pregnancy_ ... tales.html
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
http://www.quibblo.com/quiz/4lhqMw/How- ... -Pregnancy
WEEK 6
MODEL QUESTIONS FOR INTENSIVE REVISION FROM BASIC 7 -9.
1. Example 0f plants that store their food in the stems are
(a) plantain, groundnut, and rice. (b) Cocoyam, carrot, and beans. (c) Yam, sugar cane and potato (d) Onion, lettuce, and ginger. (e) Lettuce, cassava and sugar cane.
2. Where excess glucose is stored in the body (a) Pancreas (b) Kidney (c) Bladder (d) Stomach (d) Liver.
3. Where are excess fatty acids stored in the body (a) duodenum (b) under the skin and round the muscle and organs of the body, (c) liver (d) stomach (e) buttocks?
4. Which of the following cannot be stored in the body because they are dangerous to the body (a) fatty acid (b) glycerol (c) glucose (d) enzymes (e) amino acid?
5. Which of these food items, when taken and digested, have as their major end products fatty acids and glycerol (a) bread and yam (b) melon and groundnut (c) beans and plantain (d) fish and meat (e) potato and cassava.
6. When food is absorbed, excess carbohydrate is stored as (a) amylase (b) glycogen (c) fats in the muscle (d)ptyalin (e) insulin.
7. Excess protein is destroyed by which organ (a) stomach (b) pancreas (c) bile (d) liver (e) duodenum.
8. The removal of waste product of digestion from the body is called (a) elimination (b) excretion (c) defecation (d) ingestion (e) digestion.
9. Why is man considered superior to other animals (a) man has brighter eyes (b) man has most efficient nose (c) man has higher intelligence (d) man has a big heart (e) man has efficient hands.
10. The end product of carbohydrate digestion in the alimentary canal is (a) glucose and simple sugar (b) peptides and poly peptides (c) amino acids (d) polysaccharides (e) fatty acid and glycerol.
11. What part of the brain is concerned with balancing (a) cerebrum (b) medulla oblongata (c) cerebellum (d) spinal cord (e) ole fatty lobe?
12. Ability to react to external stimulus is called------- (a) irritability (b) nutrition (c) reproduction (d) growth (e) movement.
13. Which part of the ear is responsible for maintaining balance in the body (a) inner ear (b) external auditory meatus (c) pinna (d) cochlea (e) middle ear?
14. The way we fill after receiving and responding to stimulus is known as (a) sensation (b) involuntary action (c) voluntary action (d) reflex action (e) receptor.
15. Which one of the following is not a reflex action (a) dancing (b) sneezing (c) sweating (d) swallowing (e) coughing?
16. In domestic circuit, electrical appliances and lamps are arranged in parallel across the mains so as to enable (a) the same current to flow through the appliance and the lamp. (b) Maximum energy to be consumed at least cost. (c) Same fuse to be used for the electrical appliances (d) voltage across the appliances not to be affected when the lamps are switched on and off.
17. Electric fuse in domestic wiring system are used to: (a) fuse all the circuits together (b) cut off the main supply if too high a current flow (c) supply electricity to all the electrical appliances (d) prevent electric shock.
18. When connected to 250V, the fuse rating in the plug of an electric device of 1KW is: (a) 4A (b) 2A (c) 5A (d) 3A.
19. An electric meter reading is 76215. If the reading for the previous month is 75900 and 1 unit of energy cost N4 .00, what is the cost of the energy consumed in the period (a) N3, 048 .60 (b) N3, 036. 00 (c) N1, 260. 00 (d) N2, 520 .00.
20. Which of the following is a radioactive element (a) Sodium (b) Calcium (c) Uranium (d) Aluminum?
21. Spontaneous disintegration of the nuclei of an atom is ------- (a) radioactivity (b) decomposity (c) chemical reaction (d) thermal decomposition (e) energy dissolution.
22. The three types of radiation are: i- alpha ii- beta iii- gamma iv- electron. (a) I , ii, and iv. (b) I, ii, and iii (c) ii, iii,and iv (d) I, iii, iv.
23. Which of the following is not a property of the alpha ray? it (a) has a mass of 4 units (b) is positively charged (c) has very powerful ionizing effect (d) has high penetrating power.
24. Which of the following statements is correct (a) Gamma ray has no mass (b) beta ray has a positive charge (c) gamma ray has very powerful ionizing effect (d) alpha ray has no charge.
25. The study of the transfer of traits is: (a) science of traits. (b) Genetics (c) histology (d) traits transfer (e) genealogy.
26. --------------- are responsible for the transfer of traits. (a) Genes (b) trait cell (c) genetics (d) traits (e) pedigree.
27. Which of these is NOT a shared trait (a) skin colour (b) height (c) manner of driving a car (d) albinism (e) walking style?
28. Height is affected by (a) environment alone (b) genes alone (c) environment alone (d) nutrition alone (e) gene and environment.
29. Lack of melanin results in: (a) dark skin (b) light skins (c) no colour (d) yellow colour (e) albinism.
30. The most commonly used blood group is: (a) abc (b) abd (c) abo (d) abs (e)cds.
31. The stone in the gizzard of birds is responsible for food (a) chewing (b)absorption (c) chuming (d) assimilating (e) molding.
32. A substance produces pop sound when a student ignited it. The substance is------- (a) CO2 (b) O2 (c) hydrogen (d) chlorine (e) carbon.
33. Another name for pollutants is -------- (a) environmental politicians (b) environmental officers (c) environmental progressives (d) environmental sanitation (e) environmental hazards.
34. The process of evaporation, cooling and condensation of water is known as: (a) river ways (b) water cycle (c) water condensation (d) rainfall (e) condensation.
35. A connective tissue between two joints is called a ----- (a) cartilage (b) joint (c) tendor (d) ligament (e) bone.
36. The formation of iron iii oxide is called---------- (a) mixture (b) compound (c) rusting (d) colloid (e) neutralization.
37. The bone that protects the brain is called the ----- (a) suture (b) skull (c) humerus (d) femur (e) tibia.
38. Which of the following is not a mammal: (a) crocodile (b) rat (c) cat (d)donkey (e) goat.
39. An oxide of hydrogen is (a) air (b) gas (c) coke (d) water (e) liquid.
40. Which of the following planet is closest to the sun (a) earth (b) mass (c) Saturn (d) Uranus (e) venus?
41. How many metres are there in 5kilometres (a) 0.005 (b) 5.000 (c) 50 .000 (d) 500.000 (e) 5000 .000.
42. The study of organisms in relation to their environment is called--- (a) ecology (b) ecosystem (c) population (d) association (e) community.
43. Which of these is a gas (a) stone (b) iron (c) carbon (d) sulphur (e) hydrogen?
44. The male sex cell is ----- (a) egg (b) ovum (c) sperm (d0 testes (e) scrotum.
45. Alum is an example of ------ salt (a)normal (b) acidic (c) basic (d) double (e) domestic
MODEL ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. List three family trait
2. Differentiate between dominant and recessive trait.
3. List two dominant and recessive traits you know.
4. What is soil erosion
5. List two activities of man that cause erosion
6. State two methods of controlling soil erosion
7. List two causes of flooding in your community.
8. State two effects of flooding on the environment
9. State two methods of preventing flooding.
10. State three human practices influencing bush burning.
11. Discuss two effects of bush burning on the environment.
12. Suggest measures that can be taken minimize bush burning.
13. State two reasons for deforestation.
14. Discuss three effects of deforestation in plants and animals.
15. State two government regulation prohibiting deforestation.
16. Define desertification.
17. Describe the effects desertification on the environment.
18. List three methods of control of desertification.
19. State the location of ozone layer in the atmosphere.
20. What is the importance of ozone layer?
21. List three effects of depletion of ozone layer to the environment.
22. Describe two adverse effects of drug use on youths and the family.
23. Mention two ways in which a youth can maintain a drug-free life.
24. Describe briefly the activities of one national drug control agency.
25. Describe the process of digestion and absorption.
26. Give two reasons why excess protein is harmful to the body.
27. List the forms in which excess foods are stored.
28. List three sense organs and their functions.
29. Mention the parts of the central nervous system.
30. Give two examples of a reflex action.
31. Explain reproductive health.
32. What is the significance of reproductive health?
33. List two sexually transmitted infections.
34. State consequences of STI’s
35. Name three examples of: i- elements, ii- compounds, iii- mixtures.
36. Write the symbol for each of the following: i- Sodium, ii- Copper, iii-Iron iv- Calcium, v-Aluminum.
37. Write the formula for each of the following: i- Water, ii- Zinc chloride iii- Copper chloride, iv- Calcium hydroxide.
38. State four differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures.
39. List four resources obtained from living things.
40. Classify the resources obtained from living things based on: (a) plant sources (b) animal sources.
41. State three economic importance of resources obtained from living things.
42. Name three differences between sandy, loamy and clayey soils.
43. State three uses of soil.
44. What is a solid mineral, name five solid minerals found in Nigeria?
45. Name the states where these minerals can be found.
1. Example 0f plants that store their food in the stems are
(a) plantain, groundnut, and rice. (b) Cocoyam, carrot, and beans. (c) Yam, sugar cane and potato (d) Onion, lettuce, and ginger. (e) Lettuce, cassava and sugar cane.
2. Where excess glucose is stored in the body (a) Pancreas (b) Kidney (c) Bladder (d) Stomach (d) Liver.
3. Where are excess fatty acids stored in the body (a) duodenum (b) under the skin and round the muscle and organs of the body, (c) liver (d) stomach (e) buttocks?
4. Which of the following cannot be stored in the body because they are dangerous to the body (a) fatty acid (b) glycerol (c) glucose (d) enzymes (e) amino acid?
5. Which of these food items, when taken and digested, have as their major end products fatty acids and glycerol (a) bread and yam (b) melon and groundnut (c) beans and plantain (d) fish and meat (e) potato and cassava.
6. When food is absorbed, excess carbohydrate is stored as (a) amylase (b) glycogen (c) fats in the muscle (d)ptyalin (e) insulin.
7. Excess protein is destroyed by which organ (a) stomach (b) pancreas (c) bile (d) liver (e) duodenum.
8. The removal of waste product of digestion from the body is called (a) elimination (b) excretion (c) defecation (d) ingestion (e) digestion.
9. Why is man considered superior to other animals (a) man has brighter eyes (b) man has most efficient nose (c) man has higher intelligence (d) man has a big heart (e) man has efficient hands.
10. The end product of carbohydrate digestion in the alimentary canal is (a) glucose and simple sugar (b) peptides and poly peptides (c) amino acids (d) polysaccharides (e) fatty acid and glycerol.
11. What part of the brain is concerned with balancing (a) cerebrum (b) medulla oblongata (c) cerebellum (d) spinal cord (e) ole fatty lobe?
12. Ability to react to external stimulus is called------- (a) irritability (b) nutrition (c) reproduction (d) growth (e) movement.
13. Which part of the ear is responsible for maintaining balance in the body (a) inner ear (b) external auditory meatus (c) pinna (d) cochlea (e) middle ear?
14. The way we fill after receiving and responding to stimulus is known as (a) sensation (b) involuntary action (c) voluntary action (d) reflex action (e) receptor.
15. Which one of the following is not a reflex action (a) dancing (b) sneezing (c) sweating (d) swallowing (e) coughing?
16. In domestic circuit, electrical appliances and lamps are arranged in parallel across the mains so as to enable (a) the same current to flow through the appliance and the lamp. (b) Maximum energy to be consumed at least cost. (c) Same fuse to be used for the electrical appliances (d) voltage across the appliances not to be affected when the lamps are switched on and off.
17. Electric fuse in domestic wiring system are used to: (a) fuse all the circuits together (b) cut off the main supply if too high a current flow (c) supply electricity to all the electrical appliances (d) prevent electric shock.
18. When connected to 250V, the fuse rating in the plug of an electric device of 1KW is: (a) 4A (b) 2A (c) 5A (d) 3A.
19. An electric meter reading is 76215. If the reading for the previous month is 75900 and 1 unit of energy cost N4 .00, what is the cost of the energy consumed in the period (a) N3, 048 .60 (b) N3, 036. 00 (c) N1, 260. 00 (d) N2, 520 .00.
20. Which of the following is a radioactive element (a) Sodium (b) Calcium (c) Uranium (d) Aluminum?
21. Spontaneous disintegration of the nuclei of an atom is ------- (a) radioactivity (b) decomposity (c) chemical reaction (d) thermal decomposition (e) energy dissolution.
22. The three types of radiation are: i- alpha ii- beta iii- gamma iv- electron. (a) I , ii, and iv. (b) I, ii, and iii (c) ii, iii,and iv (d) I, iii, iv.
23. Which of the following is not a property of the alpha ray? it (a) has a mass of 4 units (b) is positively charged (c) has very powerful ionizing effect (d) has high penetrating power.
24. Which of the following statements is correct (a) Gamma ray has no mass (b) beta ray has a positive charge (c) gamma ray has very powerful ionizing effect (d) alpha ray has no charge.
25. The study of the transfer of traits is: (a) science of traits. (b) Genetics (c) histology (d) traits transfer (e) genealogy.
26. --------------- are responsible for the transfer of traits. (a) Genes (b) trait cell (c) genetics (d) traits (e) pedigree.
27. Which of these is NOT a shared trait (a) skin colour (b) height (c) manner of driving a car (d) albinism (e) walking style?
28. Height is affected by (a) environment alone (b) genes alone (c) environment alone (d) nutrition alone (e) gene and environment.
29. Lack of melanin results in: (a) dark skin (b) light skins (c) no colour (d) yellow colour (e) albinism.
30. The most commonly used blood group is: (a) abc (b) abd (c) abo (d) abs (e)cds.
31. The stone in the gizzard of birds is responsible for food (a) chewing (b)absorption (c) chuming (d) assimilating (e) molding.
32. A substance produces pop sound when a student ignited it. The substance is------- (a) CO2 (b) O2 (c) hydrogen (d) chlorine (e) carbon.
33. Another name for pollutants is -------- (a) environmental politicians (b) environmental officers (c) environmental progressives (d) environmental sanitation (e) environmental hazards.
34. The process of evaporation, cooling and condensation of water is known as: (a) river ways (b) water cycle (c) water condensation (d) rainfall (e) condensation.
35. A connective tissue between two joints is called a ----- (a) cartilage (b) joint (c) tendor (d) ligament (e) bone.
36. The formation of iron iii oxide is called---------- (a) mixture (b) compound (c) rusting (d) colloid (e) neutralization.
37. The bone that protects the brain is called the ----- (a) suture (b) skull (c) humerus (d) femur (e) tibia.
38. Which of the following is not a mammal: (a) crocodile (b) rat (c) cat (d)donkey (e) goat.
39. An oxide of hydrogen is (a) air (b) gas (c) coke (d) water (e) liquid.
40. Which of the following planet is closest to the sun (a) earth (b) mass (c) Saturn (d) Uranus (e) venus?
41. How many metres are there in 5kilometres (a) 0.005 (b) 5.000 (c) 50 .000 (d) 500.000 (e) 5000 .000.
42. The study of organisms in relation to their environment is called--- (a) ecology (b) ecosystem (c) population (d) association (e) community.
43. Which of these is a gas (a) stone (b) iron (c) carbon (d) sulphur (e) hydrogen?
44. The male sex cell is ----- (a) egg (b) ovum (c) sperm (d0 testes (e) scrotum.
45. Alum is an example of ------ salt (a)normal (b) acidic (c) basic (d) double (e) domestic
MODEL ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. List three family trait
2. Differentiate between dominant and recessive trait.
3. List two dominant and recessive traits you know.
4. What is soil erosion
5. List two activities of man that cause erosion
6. State two methods of controlling soil erosion
7. List two causes of flooding in your community.
8. State two effects of flooding on the environment
9. State two methods of preventing flooding.
10. State three human practices influencing bush burning.
11. Discuss two effects of bush burning on the environment.
12. Suggest measures that can be taken minimize bush burning.
13. State two reasons for deforestation.
14. Discuss three effects of deforestation in plants and animals.
15. State two government regulation prohibiting deforestation.
16. Define desertification.
17. Describe the effects desertification on the environment.
18. List three methods of control of desertification.
19. State the location of ozone layer in the atmosphere.
20. What is the importance of ozone layer?
21. List three effects of depletion of ozone layer to the environment.
22. Describe two adverse effects of drug use on youths and the family.
23. Mention two ways in which a youth can maintain a drug-free life.
24. Describe briefly the activities of one national drug control agency.
25. Describe the process of digestion and absorption.
26. Give two reasons why excess protein is harmful to the body.
27. List the forms in which excess foods are stored.
28. List three sense organs and their functions.
29. Mention the parts of the central nervous system.
30. Give two examples of a reflex action.
31. Explain reproductive health.
32. What is the significance of reproductive health?
33. List two sexually transmitted infections.
34. State consequences of STI’s
35. Name three examples of: i- elements, ii- compounds, iii- mixtures.
36. Write the symbol for each of the following: i- Sodium, ii- Copper, iii-Iron iv- Calcium, v-Aluminum.
37. Write the formula for each of the following: i- Water, ii- Zinc chloride iii- Copper chloride, iv- Calcium hydroxide.
38. State four differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures.
39. List four resources obtained from living things.
40. Classify the resources obtained from living things based on: (a) plant sources (b) animal sources.
41. State three economic importance of resources obtained from living things.
42. Name three differences between sandy, loamy and clayey soils.
43. State three uses of soil.
44. What is a solid mineral, name five solid minerals found in Nigeria?
45. Name the states where these minerals can be found.
