1ST TERM
1ST TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of Last Session's Work
Information and Communication (ICT)
- Basic Electronic Communication System
- Meaning and Nature of ICT
2. Analyze graphically the working principles of G.S.M
- Meaning of internet
- Explanation of its process
3. First Aid and Materials:
- Definition,
- Materials and Measures
4. Uses of Materials:
- Wood
- Metals
5. Uses of Materials:
- Ceramics
- Plastics and Rubber
6. Geometrical Construction:
- Lines: Definition, types and uses
7. Angle: Definition, types and uses
- Bisection and Construction of angles of 90, 45, 60, 30, 15 degrees etc.
8. Circles: Definition, types and parts of a circle
9. Bisection, Construction of tangent and normal to a given circle
10. Bisection of a given line and a given angle:
- Drawing of perpendicular on a straight given line
11. Revision
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of Last Session's Work
Information and Communication (ICT)
- Basic Electronic Communication System
- Meaning and Nature of ICT
2. Analyze graphically the working principles of G.S.M
- Meaning of internet
- Explanation of its process
3. First Aid and Materials:
- Definition,
- Materials and Measures
4. Uses of Materials:
- Wood
- Metals
5. Uses of Materials:
- Ceramics
- Plastics and Rubber
6. Geometrical Construction:
- Lines: Definition, types and uses
7. Angle: Definition, types and uses
- Bisection and Construction of angles of 90, 45, 60, 30, 15 degrees etc.
8. Circles: Definition, types and parts of a circle
9. Bisection, Construction of tangent and normal to a given circle
10. Bisection of a given line and a given angle:
- Drawing of perpendicular on a straight given line
11. Revision
WEEK 1
TOPIC: MEANING OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Define basic electronic communication system.
2. State the full meaning of I.C.T.
3. Define I.C.T.
CONTENT:
BASIC ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION
Electronic communication can be defined as the transmission of data between two or more computer, using a communication channel such as a standard telephone line. The electronic communication is sometimes referred to as data communication or telecommunications.

ICT simply means Information and Communication Technology.
ICT can be defined as the processing of information using all the necessary types of equipments and programs.

APPLICATION OF ICT
The ICT which is the use of computers in communication has affected the following aspect of lines such as education, entertainment, medicine, engineering, manufacturing etc.
EVALUATION
Define Basic Electronic Communication.
State the full meaning of ICT.
Define ICT.
Mention ICT tools.
LESSON 2
TOPIC: COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Explain s communication system.
2. Mention two types of communication systems.
3. Explain the types of communication system.
CONTENT:
A communication system consists of a computer or terminal, communications equipment that sends data, a communication channel, communications equipment that receives data and another computer. Communication software is also required.
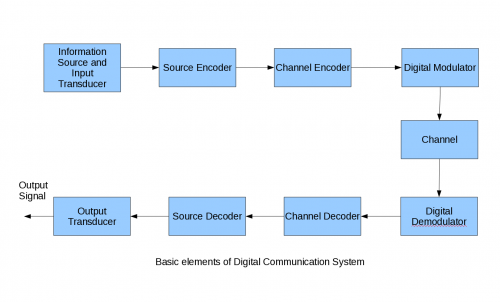
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEM SIGNALS
Computer equipment is designed to process data as:
1. Analogue communication system
2. Digital communication system
Analogue communication system is the electronic communication system such as telephone, equipment designed to carry only voice transmission, which is composed of continuous electrical wave. Examples of analogue systems are telephone box, television set with knob, clock or watch etc.
Digital communication system is the electronic communication system designed to process data as digital signals which are individual electrical pulses that represent the bits that are grouped together in bytes. It is a series of the numbers one i.e. 1s and zeros i.e. 0s. Examples of digital systems are digital watch, mobile phone, digital camera, remote controlled TV etc.
EVALUATION:
Explain communication system.
Mention types of communication system.
Explain types of communication system
Mention examples of digital and analogue communication system.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write 10 examples each of digital and analogue communication system.
further studies
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/four-typ ... ation.html
http://www.slideshare.net/tayyabsheikhg ... n-17110305
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ignal.html
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ogies.html
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ssing.html
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ssing.html
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-the-di ... ystems.htm#
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Define basic electronic communication system.
2. State the full meaning of I.C.T.
3. Define I.C.T.
CONTENT:
BASIC ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION
Electronic communication can be defined as the transmission of data between two or more computer, using a communication channel such as a standard telephone line. The electronic communication is sometimes referred to as data communication or telecommunications.

ICT simply means Information and Communication Technology.
ICT can be defined as the processing of information using all the necessary types of equipments and programs.

APPLICATION OF ICT
The ICT which is the use of computers in communication has affected the following aspect of lines such as education, entertainment, medicine, engineering, manufacturing etc.
EVALUATION
Define Basic Electronic Communication.
State the full meaning of ICT.
Define ICT.
Mention ICT tools.
LESSON 2
TOPIC: COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Explain s communication system.
2. Mention two types of communication systems.
3. Explain the types of communication system.
CONTENT:
A communication system consists of a computer or terminal, communications equipment that sends data, a communication channel, communications equipment that receives data and another computer. Communication software is also required.

TYPES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEM SIGNALS
Computer equipment is designed to process data as:
1. Analogue communication system
2. Digital communication system
Analogue communication system is the electronic communication system such as telephone, equipment designed to carry only voice transmission, which is composed of continuous electrical wave. Examples of analogue systems are telephone box, television set with knob, clock or watch etc.

Digital communication system is the electronic communication system designed to process data as digital signals which are individual electrical pulses that represent the bits that are grouped together in bytes. It is a series of the numbers one i.e. 1s and zeros i.e. 0s. Examples of digital systems are digital watch, mobile phone, digital camera, remote controlled TV etc.

EVALUATION:
Explain communication system.
Mention types of communication system.
Explain types of communication system
Mention examples of digital and analogue communication system.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write 10 examples each of digital and analogue communication system.
further studies
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/four-typ ... ation.html
http://www.slideshare.net/tayyabsheikhg ... n-17110305
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ignal.html
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ogies.html
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ssing.html
http://simple-telecom.blogspot.com/2008 ... ssing.html
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-the-di ... ystems.htm#
WEEK 2
TOPIC: THE WORKING PRINCIPLE OF GSM
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention GSM transmission media.
2. State the full meaning of GSM.
CONTENT:
The global system of mobile communication (GSM) is a technological development over the communication via overhead lines as in old NITEL system. The GSM does not use overhead lines but mast. Mast is a tall metal with in aerial that sends and receive communication signal.
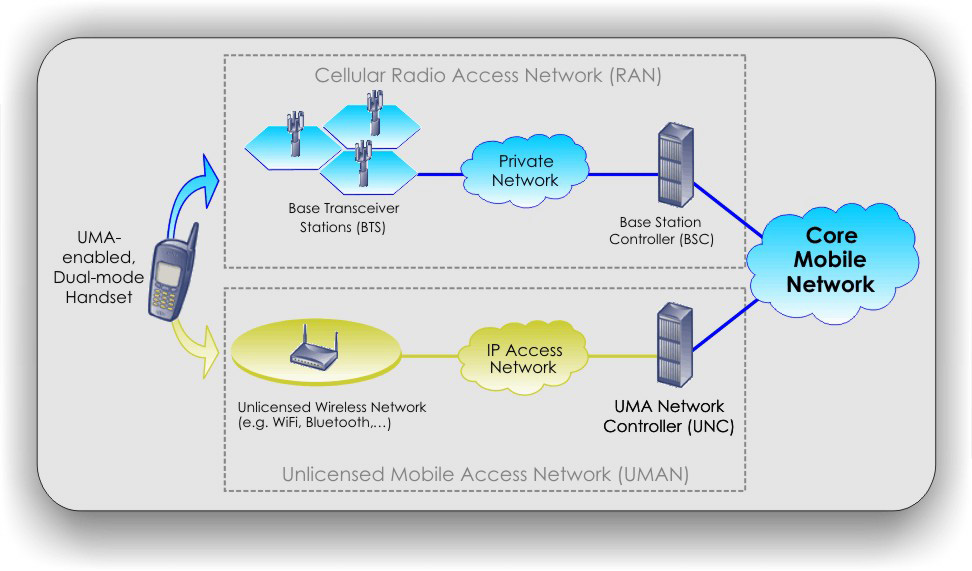
GSM TRANSMISSION MEDIA
Transmission media are the physical materials or other means used to9 establish a communication channel. There are two transmission media.
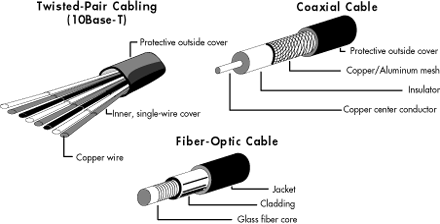
1. Physical cabling media: this includes twisted-pair cable coaxial cable and fibre-optic cable.
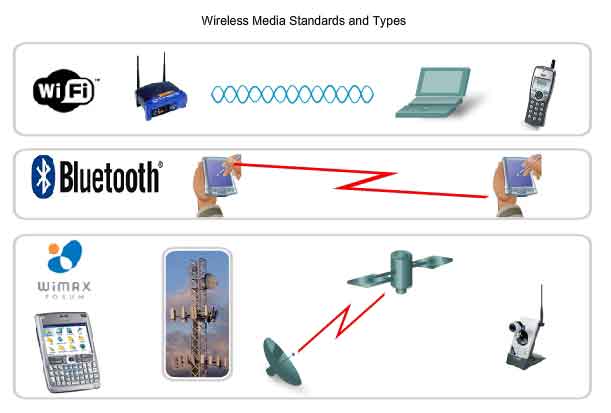
2. Wireless media.
EVALUATION
What is the full meaning of GSM.
Why is GSM better than the old NITEL system.
Mention the GSM transmission media.
Further Studies 1
LESSON 4
TOPIC: WORKING PRINCIPLE OF GSM
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the components of GSM transmission.
2. Explain GSM transmission principle.
CONTENT:
The components of GSM transmission are:
(a) Local antenna
(b) Mast
(c) MTSO (mobile telephone switching office)
(d) Telephone (mobile phone)
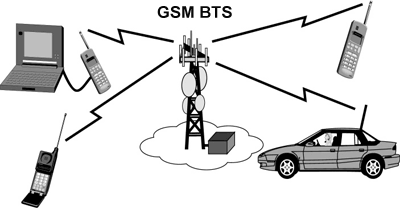
WORKING PRINCIPLE
A GSM telephone uses radio waves to communicate with a local antenna assigned to a specific geographical area called mast. Each mast range from one to ten miles in width and uses between 50 and 75 radio channels. When a call is made from a GSM telephone, the signal is picked up by the nearest GSM antenna. The antennas are located in masts from one to ten miles wide. The GSM antenna relays the signal to the mobile telephone switching office (MTSO) which directs the call to the receiver, when the call is being made to a conventional telephone, the signal enters the regular telephone system lines through which it will get to the telephone.
EVALUATION:
Mention the components of GSM transmission.
Explain the working principle of a GSM.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write briefly on the working principle of the internet.
further studies
http://cellphones.about.com/od/phoneglossary/g/gsm.htm
http://freewimaxinfo.com/gsm-technology.html
http://www.4gamericas.org/index.cfm?fus ... tionid=242
watch video
[youtube]https://youtu.be/ieSQDmp-nlY[/youtube]
practice test
http://quiz.thefullwiki.org/GSM
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz2 ... 38530.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention GSM transmission media.
2. State the full meaning of GSM.
CONTENT:
The global system of mobile communication (GSM) is a technological development over the communication via overhead lines as in old NITEL system. The GSM does not use overhead lines but mast. Mast is a tall metal with in aerial that sends and receive communication signal.

GSM TRANSMISSION MEDIA
Transmission media are the physical materials or other means used to9 establish a communication channel. There are two transmission media.
1. Physical cabling media: this includes twisted-pair cable coaxial cable and fibre-optic cable.

2. Wireless media.

EVALUATION
What is the full meaning of GSM.
Why is GSM better than the old NITEL system.
Mention the GSM transmission media.
Further Studies 1
LESSON 4
TOPIC: WORKING PRINCIPLE OF GSM
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the components of GSM transmission.
2. Explain GSM transmission principle.
CONTENT:
The components of GSM transmission are:
(a) Local antenna
(b) Mast
(c) MTSO (mobile telephone switching office)
(d) Telephone (mobile phone)

WORKING PRINCIPLE
A GSM telephone uses radio waves to communicate with a local antenna assigned to a specific geographical area called mast. Each mast range from one to ten miles in width and uses between 50 and 75 radio channels. When a call is made from a GSM telephone, the signal is picked up by the nearest GSM antenna. The antennas are located in masts from one to ten miles wide. The GSM antenna relays the signal to the mobile telephone switching office (MTSO) which directs the call to the receiver, when the call is being made to a conventional telephone, the signal enters the regular telephone system lines through which it will get to the telephone.
EVALUATION:
Mention the components of GSM transmission.
Explain the working principle of a GSM.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write briefly on the working principle of the internet.
further studies
http://cellphones.about.com/od/phoneglossary/g/gsm.htm
http://freewimaxinfo.com/gsm-technology.html
http://www.4gamericas.org/index.cfm?fus ... tionid=242
watch video
[youtube]https://youtu.be/ieSQDmp-nlY[/youtube]
practice test
http://quiz.thefullwiki.org/GSM
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz2 ... 38530.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
WEEK 3
TOPIC: FIRST AID MATERIALS
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Define first aid.
2. State reasons for first aid treatment.
CONTENT:
FIRST AID TREATMENT
First aid can be defined as the simple medical treatment given to somebody before the arrival of the doctor or before the person is taken to the hospital.
The first aid box is a box made of plastic or wood or metal and contains all the materials that are needed for first aid care.
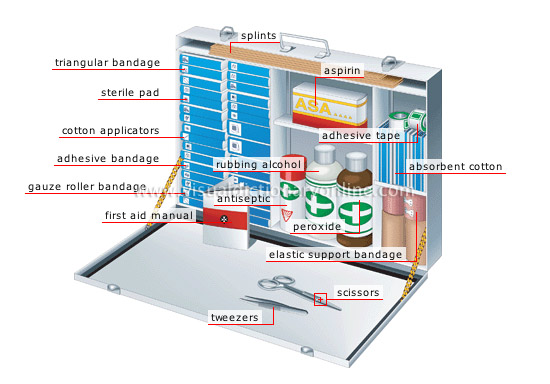
REASONS FOR FIRST AID TREATMENT
The main objective of first aid is toward saving one's life by;
1. Preventing injuries from becoming worse.
2. Arresting bleeding.
3. Assisting the medical personnel with information.
4. Relieving pains.
First aid treatment is primarily used to take care of accident and injury in the workshop.
EVALUATION:
Define first aid treatment.
State reasons for first aid treatment.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 10 materials that can be found in first aid box.
further studies
http://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/category.aspx?CategoryID=72
http://www.medindia.net/patients/firstaid.asp
http://firstaid.webmd.com/
LESSON 6
TOPIC: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FIRST AID PERSONNEL
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. List the characteristics of first aid personnel.
2. Mention at least ten first aid materials and state their functions.
CONTENT:
The person administering the first aid should posses the following characteristics.
1. Must be sympathetic and caring without sentiment.
2. Must be able to take decisions.
3. Must be cheerful and gentle.
4. Must be knowledgeable.
5. Must be resourceful.
6. Must be confident.
FIRST AID MATERIALS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
1. Scissors: for cutting bandages, plasters and for holding cotton wool.
2. Plasters: for covering wound e.g. elastoplasts.
3. Cotton wool: foe cleaning and treating wound.
4. Forceps: for holding cotton wool to clean wounds.
5. Methylated spirit: for cleaning and disinfecting a wound and to quicken blood clotting.
Others are: antiseptics, embrocation, glucose, safety pins, iodine, razor blade, sterile guaze, record book and biro, hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate.

EVALUATION:
List the characteristics of first aid personnel.
Mention and state the functions of first aid materials
further studies
http://www.education.gov.uk/schools/pup ... -personnel
http://www.deir.qld.gov.au/workplace/su ... /index.htm
practice test
http://pediatrics.about.com/cs/quizzes/ ... aid_qz.htm
http://www.allforkidsindia.com/FirstAid ... dQuiz.aspx
http://www.redcross.org.uk/What-we-do/F ... e-the-quiz
http://health.howstuffworks.com/skin-ca ... d-quiz.htm
http://www.abc.net.au/health/quizzestoo ... ZuMAaK1EiU
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Define first aid.
2. State reasons for first aid treatment.
CONTENT:
FIRST AID TREATMENT
First aid can be defined as the simple medical treatment given to somebody before the arrival of the doctor or before the person is taken to the hospital.
The first aid box is a box made of plastic or wood or metal and contains all the materials that are needed for first aid care.

REASONS FOR FIRST AID TREATMENT
The main objective of first aid is toward saving one's life by;
1. Preventing injuries from becoming worse.
2. Arresting bleeding.
3. Assisting the medical personnel with information.
4. Relieving pains.
First aid treatment is primarily used to take care of accident and injury in the workshop.
EVALUATION:
Define first aid treatment.
State reasons for first aid treatment.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 10 materials that can be found in first aid box.
further studies
http://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/category.aspx?CategoryID=72
http://www.medindia.net/patients/firstaid.asp
http://firstaid.webmd.com/
LESSON 6
TOPIC: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FIRST AID PERSONNEL
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. List the characteristics of first aid personnel.
2. Mention at least ten first aid materials and state their functions.
CONTENT:
The person administering the first aid should posses the following characteristics.
1. Must be sympathetic and caring without sentiment.
2. Must be able to take decisions.
3. Must be cheerful and gentle.
4. Must be knowledgeable.
5. Must be resourceful.
6. Must be confident.
FIRST AID MATERIALS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
1. Scissors: for cutting bandages, plasters and for holding cotton wool.
2. Plasters: for covering wound e.g. elastoplasts.
3. Cotton wool: foe cleaning and treating wound.
4. Forceps: for holding cotton wool to clean wounds.
5. Methylated spirit: for cleaning and disinfecting a wound and to quicken blood clotting.
Others are: antiseptics, embrocation, glucose, safety pins, iodine, razor blade, sterile guaze, record book and biro, hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate.

EVALUATION:
List the characteristics of first aid personnel.
Mention and state the functions of first aid materials
further studies
http://www.education.gov.uk/schools/pup ... -personnel
http://www.deir.qld.gov.au/workplace/su ... /index.htm
practice test
http://pediatrics.about.com/cs/quizzes/ ... aid_qz.htm
http://www.allforkidsindia.com/FirstAid ... dQuiz.aspx
http://www.redcross.org.uk/What-we-do/F ... e-the-quiz
http://health.howstuffworks.com/skin-ca ... d-quiz.htm
http://www.abc.net.au/health/quizzestoo ... ZuMAaK1EiU
WEEK 4
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIAL (WOOD)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the two classes of wood.
2. State the uses of wood.
CONTENT:
Wood can be classified into softwood and hardwood. The softwood trees grow in the colder regions of the world while the hardwood trees grow in the warmer climates i.e. the temperate and tropical regions.
Softwood: The following are examples of softwood
(1) Yellow pine: it is commonly used for internal joinery. It is obtained from Canada and North Eastern United States.

(2) Red wood: it is used for building construction e.g. for rafters, joists, windows, flooring etc. it is found in Scotland. It is reddish brown in colour.


(3) White wood (Spruse): it is used for general interior work e.g. packing cases, it is found in United Kingdom and the United States.

(4) Western Red Cedar: very light and soft, it has numerous functions because of its resistance to decay and insects. It is found in Britain, Columbia.

(5) Douglass Fir: for general construction and for making plywood. Found in British Columbia.


EVALUATION:
Mention the two classes of wood.
Mention examples of softwood.
Enumerate the uses of softwood.
further studies
http://www.piecesofwood.com/woods.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_wo ... onifers.29
http://woodmagic.vt.edu/kids/daily/
http://permaculturenews.org/2012/04/21/ ... -wood-ash/
LESSON 9
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIAL (HARDWOOD)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention examples of hardwood.
2. State the uses of hardwood.
CONTENT:
The following are examples of hardwood and their uses:
(a) Agba: is suitable for all interior joinery, is found in West Africa, it is a reliable wood and easy to work on. It is yellow pink in colour.


(b) African Walnut: it is golden brown in colour and if for all type of interior joinery. It is also found in West Africa.

(c) African Mahogany: for shop fitting, general cabinet work, etc. the wood is used for a variety of work. There are various varieties of this wood e.g. Sapele and Gabor Mahogany.

(d) Teak: dark brown in colour. It is used for bench tops in science laboratories and for various furniture works. It is an oily wood highly resistant to moisture and acids.

(e) Ash: pale in colour, used for tool handles, shaft and cars.

(f) English Oak: dark brown in colour, for furniture, flooring and constructional work.
Others are Birch and Beech.

EVALUATION:
Mention examples of hardwood.
State the uses of hardwood.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 10 uses of wood.
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_wo ... osperms.29
http://mff.dsisd.net/Balance/UseWood.htm
http://woodmagic.vt.edu/kids/
practice test
http://www.coedbrynoer.co.uk/Quiz-on-pr ... e-past.php
http://woodmagic.vt.edu/kids/woodid/quiz.htm
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the two classes of wood.
2. State the uses of wood.
CONTENT:
Wood can be classified into softwood and hardwood. The softwood trees grow in the colder regions of the world while the hardwood trees grow in the warmer climates i.e. the temperate and tropical regions.
Softwood: The following are examples of softwood
(1) Yellow pine: it is commonly used for internal joinery. It is obtained from Canada and North Eastern United States.

(2) Red wood: it is used for building construction e.g. for rafters, joists, windows, flooring etc. it is found in Scotland. It is reddish brown in colour.


(3) White wood (Spruse): it is used for general interior work e.g. packing cases, it is found in United Kingdom and the United States.

(4) Western Red Cedar: very light and soft, it has numerous functions because of its resistance to decay and insects. It is found in Britain, Columbia.

(5) Douglass Fir: for general construction and for making plywood. Found in British Columbia.


EVALUATION:
Mention the two classes of wood.
Mention examples of softwood.
Enumerate the uses of softwood.
further studies
http://www.piecesofwood.com/woods.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_wo ... onifers.29
http://woodmagic.vt.edu/kids/daily/
http://permaculturenews.org/2012/04/21/ ... -wood-ash/
LESSON 9
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIAL (HARDWOOD)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention examples of hardwood.
2. State the uses of hardwood.
CONTENT:
The following are examples of hardwood and their uses:
(a) Agba: is suitable for all interior joinery, is found in West Africa, it is a reliable wood and easy to work on. It is yellow pink in colour.


(b) African Walnut: it is golden brown in colour and if for all type of interior joinery. It is also found in West Africa.

(c) African Mahogany: for shop fitting, general cabinet work, etc. the wood is used for a variety of work. There are various varieties of this wood e.g. Sapele and Gabor Mahogany.

(d) Teak: dark brown in colour. It is used for bench tops in science laboratories and for various furniture works. It is an oily wood highly resistant to moisture and acids.

(e) Ash: pale in colour, used for tool handles, shaft and cars.

(f) English Oak: dark brown in colour, for furniture, flooring and constructional work.
Others are Birch and Beech.

EVALUATION:
Mention examples of hardwood.
State the uses of hardwood.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 10 uses of wood.
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_wo ... osperms.29
http://mff.dsisd.net/Balance/UseWood.htm
http://woodmagic.vt.edu/kids/
practice test
http://www.coedbrynoer.co.uk/Quiz-on-pr ... e-past.php
http://woodmagic.vt.edu/kids/woodid/quiz.htm
WEEK 5
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIALS (METAL)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the classes of metal.
2. Highlight the uses of metal.
CONTENT:
Metals can be classified as
1. Ferrous metals

2. Non-ferrous metals

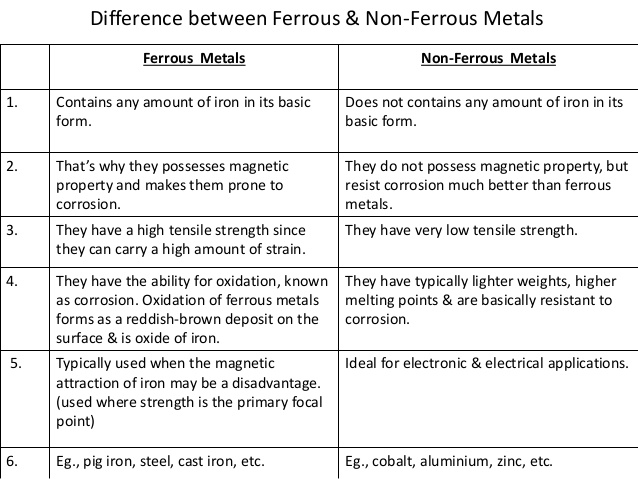
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN FERROUS AND NON-FERROUS METALS
FERROUS METAL................................NON-FERROUS METAL
They contain iron .................................They do not contain iron.
They are magnetic................................They are not magnetic
Examples are cast iron, wrought iron and steel......Examples are aluminium, zinc, and copper.
USES OF METALS
METALS...................PROPERTIES..................................USES
Stainless steel..........It does not rust.........For processing foods and chemicals
Aluminium................Light in weight and does not rust......For manufacturing cooking utensils
High carbon steel ......Shear resistant.............For manufacturing cutting tools, pliers, drills,Punches and hammer heads.
Nichrome (alloy).........Opposes flow of electricity....For manufacturing electrical resistant objects
Mild steel ...................Soft to work on..........Manufacturing of all structural work, bolts,
Non-cutting tools, nuts.
Cast iron....................Wear resistant...........For manufacturing piston rings, cylinder blocks
Uses of Metals
Iron metal is use for making cooking vessels , water boilers , stoves,tools , wires,nails , bolts , electromagnets etc.
Aluminium is very light metal so it is use in making the aircraft bodies.
Copper is most widely use for making electric wires and all things related to electricity
because it is a good conductor of electricity.
Silver is widely use for making jewellery.
Uses of Non-Metals
Phosphorous is used in match-box industry and in fertilizers.
Iodine is used as antiseptic.
Oxygen is essential for all living beings.
Sulphur is used for making fire crackers,gun powder and sulphuric acid.
EVALUATION:
Mention the classes of metal.
Enumerate the differences between the classes of metals.
Highlight the uses of metals.
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2011010 ... etals.html
http://www.themetalinitiative.com/conte ... _of_metal/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... rev4.shtml
http://chestofbooks.com/home-improvemen ... apLjtK1EiU
practice test
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/quizzes/metal.html
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/curio ... s-quiz.htm
http://www.educationquizzes.com/gcse/ch ... d-uses-of/
LESSON 11
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIAL (CERAMIC)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Identify ceramic objects.
2. State the properties of ceramics.
3. Mention the uses of ceramics.
CONTENT:
CERAMICS
Ceramics are objects made of clay and hardened by heat e.g. clay pots, tile, blocks etc.
Ceramics can be identified based on their properties.
The following are the properties of ceramics.
1. Brittleness - ceramics break easily.
2. Heat resistant - ceramics have high melting point.
3. Inorganic materials - ceramics are produced using artificial chemicals.
4. Non-metallic - they are insulators.
5. Hardness - ceramics are hard in shape and appearance.
Other ceramic materials are glass, plasters, clay and cement materials.

USES OF CERAMIC
Ceramics are used for making articles such as:
1. W.C (modern toilet)

2. Portrait

3. Ceramic bakery oven

4. Electric socket

5. T.V screen

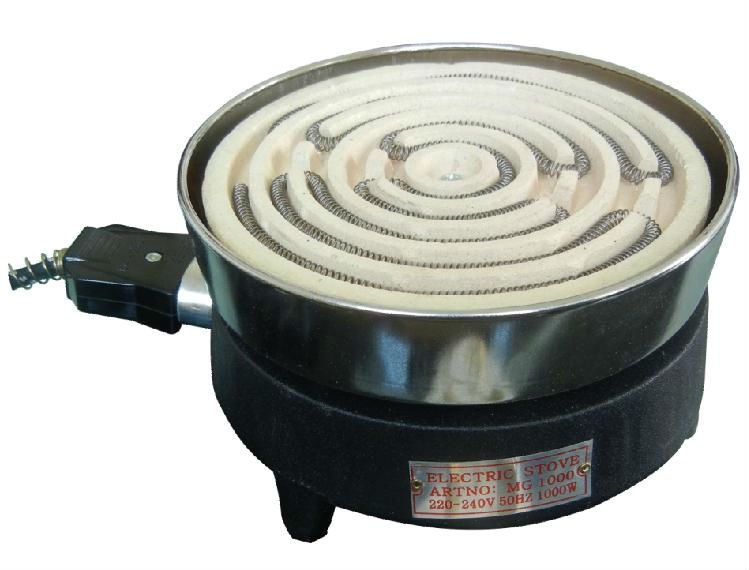
6. Electric stove

7. Concrete or block

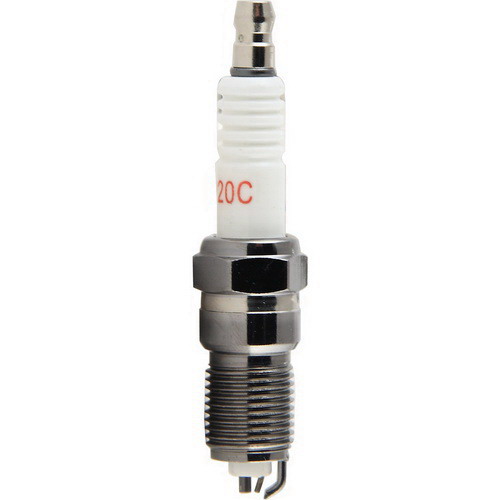
8. Spark plug.

Glass is a type of ceramic that is composed of sand (silica), soda and lime. These major ingredients are mixed and melted to such a temperature that all the gases are given off and a clear liquid is obtained.

FORMS OF GLASS
1. Sheet glass
2. Plate glass
3. Rolled glass
EVALUATION:
State the properties of ceramic.
Mention the use of ceramic.
Mention ceramic materials.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 5 uses of glass.
further studies
http://www.scribd.com/doc/7029380/Chemi ... ss-Ceramic
http://ezinearticles.com/?Ceramics---A- ... id=3268181
practice test
http://quizlet.com/10612249/ceramics-qu ... ash-cards/
http://matse1.matse.illinois.edu/ceramics/quiz.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.flashcardexchange.com/cards/ ... uiz-555297
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the classes of metal.
2. Highlight the uses of metal.
CONTENT:
Metals can be classified as
1. Ferrous metals

2. Non-ferrous metals

DIFFERENCES BETWEEN FERROUS AND NON-FERROUS METALS
FERROUS METAL................................NON-FERROUS METAL
They contain iron .................................They do not contain iron.
They are magnetic................................They are not magnetic
Examples are cast iron, wrought iron and steel......Examples are aluminium, zinc, and copper.

USES OF METALS
METALS...................PROPERTIES..................................USES
Stainless steel..........It does not rust.........For processing foods and chemicals
Aluminium................Light in weight and does not rust......For manufacturing cooking utensils
High carbon steel ......Shear resistant.............For manufacturing cutting tools, pliers, drills,Punches and hammer heads.
Nichrome (alloy).........Opposes flow of electricity....For manufacturing electrical resistant objects
Mild steel ...................Soft to work on..........Manufacturing of all structural work, bolts,
Non-cutting tools, nuts.
Cast iron....................Wear resistant...........For manufacturing piston rings, cylinder blocks
Uses of Metals
Iron metal is use for making cooking vessels , water boilers , stoves,tools , wires,nails , bolts , electromagnets etc.
Aluminium is very light metal so it is use in making the aircraft bodies.
Copper is most widely use for making electric wires and all things related to electricity
because it is a good conductor of electricity.
Silver is widely use for making jewellery.
Uses of Non-Metals
Phosphorous is used in match-box industry and in fertilizers.
Iodine is used as antiseptic.
Oxygen is essential for all living beings.
Sulphur is used for making fire crackers,gun powder and sulphuric acid.

EVALUATION:
Mention the classes of metal.
Enumerate the differences between the classes of metals.
Highlight the uses of metals.
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2011010 ... etals.html
http://www.themetalinitiative.com/conte ... _of_metal/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... rev4.shtml
http://chestofbooks.com/home-improvemen ... apLjtK1EiU
practice test
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/quizzes/metal.html
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/curio ... s-quiz.htm
http://www.educationquizzes.com/gcse/ch ... d-uses-of/
LESSON 11
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIAL (CERAMIC)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Identify ceramic objects.
2. State the properties of ceramics.
3. Mention the uses of ceramics.
CONTENT:
CERAMICS
Ceramics are objects made of clay and hardened by heat e.g. clay pots, tile, blocks etc.
Ceramics can be identified based on their properties.
The following are the properties of ceramics.
1. Brittleness - ceramics break easily.
2. Heat resistant - ceramics have high melting point.
3. Inorganic materials - ceramics are produced using artificial chemicals.
4. Non-metallic - they are insulators.
5. Hardness - ceramics are hard in shape and appearance.
Other ceramic materials are glass, plasters, clay and cement materials.

USES OF CERAMIC
Ceramics are used for making articles such as:
1. W.C (modern toilet)

2. Portrait

3. Ceramic bakery oven

4. Electric socket

5. T.V screen

6. Electric stove

7. Concrete or block

8. Spark plug.

Glass is a type of ceramic that is composed of sand (silica), soda and lime. These major ingredients are mixed and melted to such a temperature that all the gases are given off and a clear liquid is obtained.

FORMS OF GLASS
1. Sheet glass
2. Plate glass
3. Rolled glass
EVALUATION:
State the properties of ceramic.
Mention the use of ceramic.
Mention ceramic materials.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 5 uses of glass.
further studies
http://www.scribd.com/doc/7029380/Chemi ... ss-Ceramic
http://ezinearticles.com/?Ceramics---A- ... id=3268181
practice test
http://quizlet.com/10612249/ceramics-qu ... ash-cards/
http://matse1.matse.illinois.edu/ceramics/quiz.html
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.flashcardexchange.com/cards/ ... uiz-555297
WEEK 6
TOPIC: USES OF MATERIALS (PLASTIC AND RUBBER)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention two types of plastic.
2. Mention uses of plastic.
CONTENT:
PLASTICS
Plastics exhibit both physical and chemical properties which vary according to the different types.

TYPES OF PLASTIC
1. Thermoset or thermosetting

2. Thermoplast

USES OF PLASTICS
Plastics have properties such as low tensile strength and low specific gravity. As a result of some of these properties, they have found wide application in many different fields.
The uses of plastics include
1. Aircrafts and automobile parts: they are used as:
(a) Fuel filters
(b) Insulators
(c) Accelerator and clutch pedal covers etc.
2. Industrial use
(a) Plastic bottles
(b) Containers
(c) Storage bottles etc.
3. Household items such as:
(a) Buckets
(b) Cups
(c) Spoons
(d) Water pipes etc.
EVALUATION:
Mention the types of plastics
State the use of plastics
further studies
http://www.qualitylogoproducts.com/lib/ ... lastic.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... rev3.shtml
http://science.howstuffworks.com/plastic4.htm
http://plasticsmakeitpossible.com/2012/ ... are-there/
practice test
http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/scie ... z6361.html
LESSON 13
TOPIC: GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTION (LINES)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention types of lines.
2. Draw and state the uses of lines.
CONTENT:
LINES
There are different types of lines in Technical Drawing and these lines serve different purposes.
Line is the extension of point when two lines meet at a point they form an angle.
A Straight line is the shortest distance between two points.
TYPES AND USES OF LINES
LINES------------------------------------------------------------USES
Thick Continuous Line ________________________For visible outlines and edges
Thin Continuous Line ________________________For dimension lines, projection lines and construction lines.
Thick Long Chain Lines ____.____. ______ .___ For cutting and viewing planes
Thin Long Chain Line _____.______.____._____ For centre lines
Short Dashes __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ For hidden outlines
Thick Continuous Wavy----------------------------------For short break and boundary lines
Thin Continuous Wavy---------------------------------------For limits of partial views
Thin Ruled Line with Short Zig-Zag------------------------For long break lines
Arrow Head Lines ↔ ---------------------------------Used at the end of dimension lines and for direction.
EVALUATION:
Mention types of lines and state their uses.
Draw the following lines arrowhead, zig-zag, short dashes, thick continuous line, etc.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/im81vHIhZS8[/youtube]
CONSTRUCTON OF PARALLEL LINES
http://www.mathopenref.com/constparallel.html
http://www.mathopenref.com/constperpextpoint.html
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/constructions.html
practice test
http://toolboxes.flexiblelearning.net.a ... tem3_3.htm
http://grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/grammar/ ... m_quiz.htm
http://www.mathchamber.com/geometry_ccs ... unit_3.htm
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention two types of plastic.
2. Mention uses of plastic.
CONTENT:
PLASTICS
Plastics exhibit both physical and chemical properties which vary according to the different types.

TYPES OF PLASTIC
1. Thermoset or thermosetting

2. Thermoplast

USES OF PLASTICS
Plastics have properties such as low tensile strength and low specific gravity. As a result of some of these properties, they have found wide application in many different fields.
The uses of plastics include
1. Aircrafts and automobile parts: they are used as:
(a) Fuel filters
(b) Insulators
(c) Accelerator and clutch pedal covers etc.
2. Industrial use
(a) Plastic bottles
(b) Containers
(c) Storage bottles etc.
3. Household items such as:
(a) Buckets
(b) Cups
(c) Spoons
(d) Water pipes etc.
EVALUATION:
Mention the types of plastics
State the use of plastics
further studies
http://www.qualitylogoproducts.com/lib/ ... lastic.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... rev3.shtml
http://science.howstuffworks.com/plastic4.htm
http://plasticsmakeitpossible.com/2012/ ... are-there/
practice test
http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/scie ... z6361.html
LESSON 13
TOPIC: GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTION (LINES)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention types of lines.
2. Draw and state the uses of lines.
CONTENT:
LINES
There are different types of lines in Technical Drawing and these lines serve different purposes.
Line is the extension of point when two lines meet at a point they form an angle.
A Straight line is the shortest distance between two points.

TYPES AND USES OF LINES
LINES------------------------------------------------------------USES
Thick Continuous Line ________________________For visible outlines and edges
Thin Continuous Line ________________________For dimension lines, projection lines and construction lines.
Thick Long Chain Lines ____.____. ______ .___ For cutting and viewing planes
Thin Long Chain Line _____.______.____._____ For centre lines
Short Dashes __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ For hidden outlines
Thick Continuous Wavy----------------------------------For short break and boundary lines
Thin Continuous Wavy---------------------------------------For limits of partial views
Thin Ruled Line with Short Zig-Zag------------------------For long break lines
Arrow Head Lines ↔ ---------------------------------Used at the end of dimension lines and for direction.
EVALUATION:
Mention types of lines and state their uses.
Draw the following lines arrowhead, zig-zag, short dashes, thick continuous line, etc.
[youtube]https://youtu.be/im81vHIhZS8[/youtube]
CONSTRUCTON OF PARALLEL LINES
http://www.mathopenref.com/constparallel.html
http://www.mathopenref.com/constperpextpoint.html
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/constructions.html
practice test
http://toolboxes.flexiblelearning.net.a ... tem3_3.htm
http://grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/grammar/ ... m_quiz.htm
http://www.mathchamber.com/geometry_ccs ... unit_3.htm
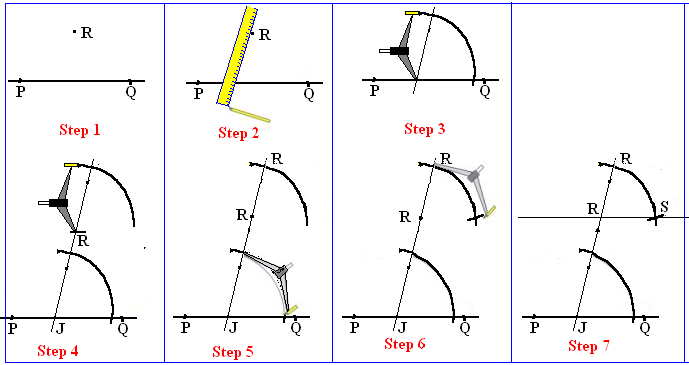
WEEK 7
TOPIC: CONSTRUCTION OF ANGLES
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Draw and bisect a given line.
2. Construct angles 90 and 45.
CONTENT:
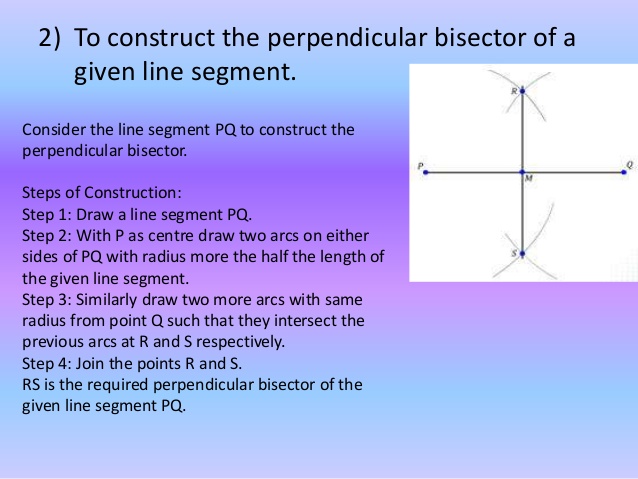
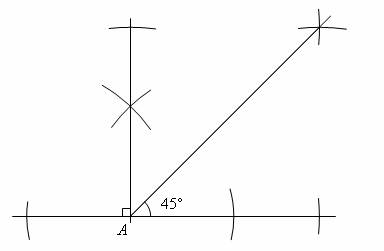
http://www.homeschoolmath.net/teaching/g/angles.php
[youtube]https://youtu.be/5l8bltVe_IE[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
Draw a line of 90mm and bisect it.
Construct the following angles
(a) 90 (b) 45 (c) 22.5
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Draw and bisect a given line.
2. Construct angles 90 and 45.
CONTENT:


http://www.homeschoolmath.net/teaching/g/angles.php
[youtube]https://youtu.be/5l8bltVe_IE[/youtube]
EVALUATION:
Draw a line of 90mm and bisect it.
Construct the following angles
(a) 90 (b) 45 (c) 22.5
WEEK 8
TOPIC
Angle: Definition, types and uses
- Bisection and Construction of angles
(http://www.mathopenref.com/constbisectangle.html)
Angle: Definition, types and uses
- Bisection and Construction of angles
(http://www.mathopenref.com/constbisectangle.html)
