3RD TERM
3RD TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of last term's work
2. Technology of appliances based on conversion of one energy to
another:
- Chemical to Electrical
- Electrical to Mechanical
3. Principles of operation of A.C. Motor:
- Electrical fan, shaver, blender
- Washing machine, loud speaker etc.
4. Principles of evaporation leading to cooling by refrigerants
- Working principles of refrigerator
5. Working principles of :
- Generators
- Bicycles and dynamos
6. Transmission of electricity:
- Low frequency
- High frequency
7. Distribution and utilization of electricity:
- Basic principles of house wiring, conduit, surface and trucking
- Power rating appliances
8. Site Preparation.
- Definition, tools
- Classification of tools/plants used for site preparation.
9. Setting out:
- Definition, tools used during setting out,
- Excavation/timbering
10. Simple Maintenance of Domestic Appliances:
- Furniture
- Kitchen wares e.g. pots, cutlery and knives, etc.
11. Simple maintenance of domestic appliances.
- Electronics e.g. radio, television
- Other appliances e.g. refrigerator, fans, pressing iron, electric kettles and air conditioners.
12 Revision
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of Second Term Work
2. Metal work Hand tools: Marking out tools; surface plates, scriber, odd-leg calipers. Etc. Measuring Tools and Gauges: steel rule, protractors, etc. Driving Tools; punches, screw drivers, spanners, etc. cutting tools; chisels, files etc.
3. Energy Based Technological Appliances: (a) principles of operation of processing iron, electric kettle, cookers and water heaters, gas lamps, gas and kerosene cookers, charcoal pressing iron.
4. Energy Based Technological Appliances: (b) principle of evaporation leading to cooling by refrigerants. Operation of compressors responsible for the circulation of refrigerants.
5. Energy Based Technological Appliances: (c) principles of operation of electric fan grinder. (d) Working principle of generators, bicycles, dynamos.
6. Transmission of Electricity: (a) Transmission: low frequency, high frequency (b) distribution (c) Utilization (d) Materials and Equipment: Transformers, cables, insulators, separators, fuses, etc.
7. Building-site Preparation: (a) Hand tools for site preparation- cutlasses, axe, hoses, diggers, etc. (b) Mechanical Plants: Reciprocating chain saw, bulldozer, pay loader, etc. (c) techniques of grubbing out roots, leveling the soil and exterminating termites
8. Setting out Materials: (a) building plans, pegs, lines, builder’s square, plumb, hammer, profile, etc. (b) setting out display setting out materials, names and their uses. (students are to be taken out to a building site to watch and document what they see, to be discussed later in class)
9. Simple Maintenance: (a) simple maintenance methods- cleaning, dusting, washing, oiling, replacement of damaged parts, etc. (b) care of common goods- (i) kitchen wares, pots, cutlery and knives. (ii) Electronic appliances; e.g. radio, television, etc. (iii) other appliances; refrigerator, fans, pressing iron, electric kettles, air conditioners, etc.
10. Practical projects.
11. Revision.
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of last term's work
2. Technology of appliances based on conversion of one energy to
another:
- Chemical to Electrical
- Electrical to Mechanical
3. Principles of operation of A.C. Motor:
- Electrical fan, shaver, blender
- Washing machine, loud speaker etc.
4. Principles of evaporation leading to cooling by refrigerants
- Working principles of refrigerator
5. Working principles of :
- Generators
- Bicycles and dynamos
6. Transmission of electricity:
- Low frequency
- High frequency
7. Distribution and utilization of electricity:
- Basic principles of house wiring, conduit, surface and trucking
- Power rating appliances
8. Site Preparation.
- Definition, tools
- Classification of tools/plants used for site preparation.
9. Setting out:
- Definition, tools used during setting out,
- Excavation/timbering
10. Simple Maintenance of Domestic Appliances:
- Furniture
- Kitchen wares e.g. pots, cutlery and knives, etc.
11. Simple maintenance of domestic appliances.
- Electronics e.g. radio, television
- Other appliances e.g. refrigerator, fans, pressing iron, electric kettles and air conditioners.
12 Revision
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of Second Term Work
2. Metal work Hand tools: Marking out tools; surface plates, scriber, odd-leg calipers. Etc. Measuring Tools and Gauges: steel rule, protractors, etc. Driving Tools; punches, screw drivers, spanners, etc. cutting tools; chisels, files etc.
3. Energy Based Technological Appliances: (a) principles of operation of processing iron, electric kettle, cookers and water heaters, gas lamps, gas and kerosene cookers, charcoal pressing iron.
4. Energy Based Technological Appliances: (b) principle of evaporation leading to cooling by refrigerants. Operation of compressors responsible for the circulation of refrigerants.
5. Energy Based Technological Appliances: (c) principles of operation of electric fan grinder. (d) Working principle of generators, bicycles, dynamos.
6. Transmission of Electricity: (a) Transmission: low frequency, high frequency (b) distribution (c) Utilization (d) Materials and Equipment: Transformers, cables, insulators, separators, fuses, etc.
7. Building-site Preparation: (a) Hand tools for site preparation- cutlasses, axe, hoses, diggers, etc. (b) Mechanical Plants: Reciprocating chain saw, bulldozer, pay loader, etc. (c) techniques of grubbing out roots, leveling the soil and exterminating termites
8. Setting out Materials: (a) building plans, pegs, lines, builder’s square, plumb, hammer, profile, etc. (b) setting out display setting out materials, names and their uses. (students are to be taken out to a building site to watch and document what they see, to be discussed later in class)
9. Simple Maintenance: (a) simple maintenance methods- cleaning, dusting, washing, oiling, replacement of damaged parts, etc. (b) care of common goods- (i) kitchen wares, pots, cutlery and knives. (ii) Electronic appliances; e.g. radio, television, etc. (iii) other appliances; refrigerator, fans, pressing iron, electric kettles, air conditioners, etc.
10. Practical projects.
11. Revision.
WEEK 1
MAIN TOPIC : Technology of Appliances
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Energy conversion
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) mention different forms of energy
(2) explain the technology of appliance based on conversion of energy
CONTENT
TECHNOLOGY OF APPLIANCES
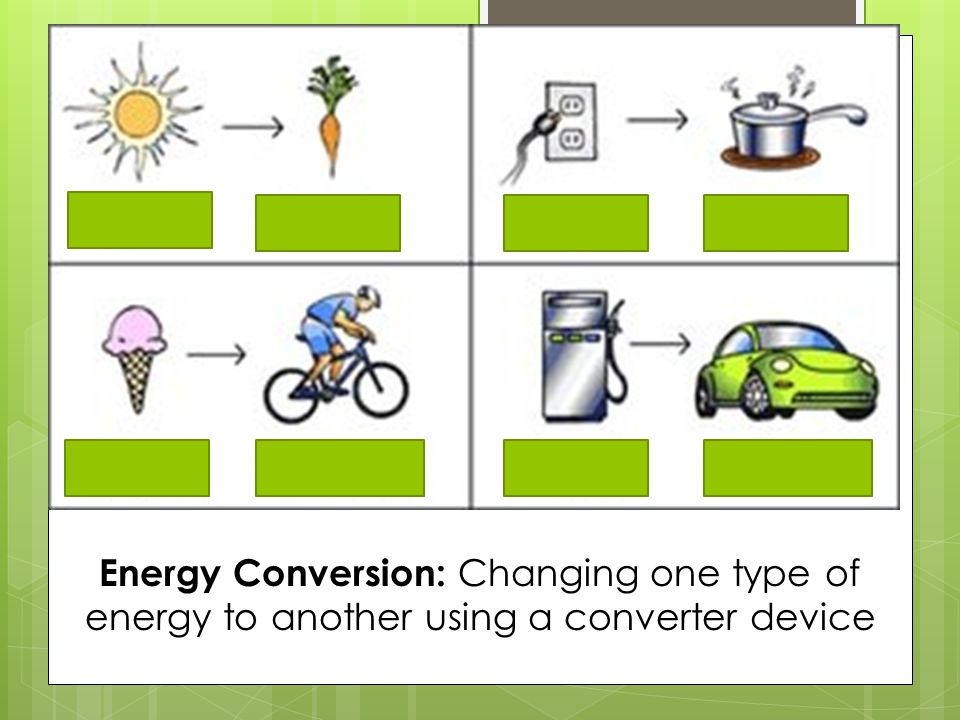
The technology of all appliances is based on the conversion of energy from one form to another. The reason for the conversion is that not all forms of energy are in the appropriate form for our use. At certain time, it is necessary, as well as convenient to convert an available form of energy into a form that is suitable for our use.
CONVERSION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY INTO HEAT ENERGY
Electrical energy can easily be converted into heat by making a current flow through a resistance. A resistance wire especially made to effect conversion of electrical energy into heat is called a heating element. Heating elements are employed in electric cooker, electric pressing irons, kettles and toaster.

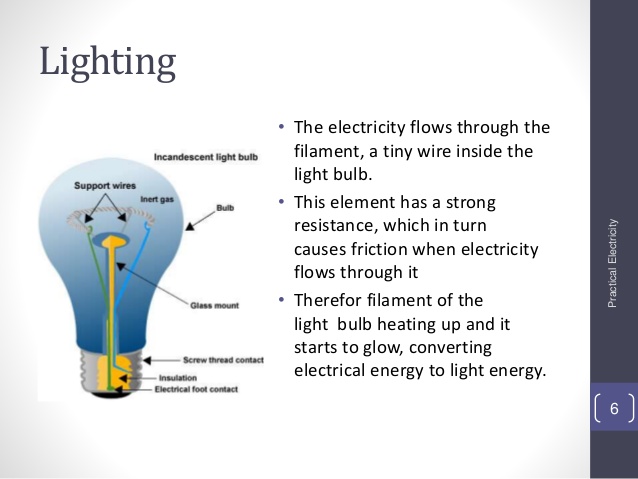
CONVERSION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY INTO LIGHT ENERGY
In conversion of electrical energy to light certain metals, for example tungsten, apart from becoming hot when electric current flows through them, emits a lot of light as well. These are used in lamp filaments.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention all the forms of energy
Explain the conversion of energy from electrical t o light, heat and sound
LESSON 37
MAIN TOPIC : Technology of appliance
SPECIFIC TOPIC : conversion of energy
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1)explain conversion of nuclear energy into electrical energy
(2)explain conversion of heat energy to electrical energy
CONTENT
CONVERSION OF NUCLEAR ENERGY TO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
The heat provided by the nuclear reactor arises as a result of nuclear reaction called fission. When rod of radioactive element uranium excite one another in a reactor tank, huge amount of heat is released which is converted into steam that is now used to drive a generator that generate electricity.

CONVERSION OF HEAT INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
When two ends of wires made of dissimilar metals are joined together rand heat is applied at the junction, an E.M.F is generated. This device which converts heat energy into electrical energy is called THERMOCOUPLE.
The electrical energy which generated is called THERMOELECTRIC ENERGY.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Explain the conversion of energy from nuclear to electrical energy
Explain the conversion of energy from heat energy to electrical energy
TOPIC: ENERGY BASED TECHNOLOGICAL APPLIANCES
CONTENTS
1) Energy and Forms of Energy
2) Principles of operation of pressing iron, Electric kettle, Cookers and Water heaters, Gas lamps, Gas and Kerosene cookers, Charcoal pressing iron.
SUB-TOPIC I: ENERGY AND FORMS OF ENERGY
Energy is said to be the ability to do work and it is measured in joules. Many of our home appliances are operated using Energy. Therefore those appliances that use energy for their operations are energy based technological appliances. We have also learned that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can only be transformed (converted) from one form to another.
These are various forms of energy:
1. Electrical energy
2. Heat Energy
3. Mechanical Energy
4. Chemical Energy
5. Light Energy etc.
Electrical energy can be converted into Heat energy, Mechanical energy to Electrical energy, Chemical energy to Heat energy, Heat energy to Mechanical energy.
The sources of electric energy include the following:
The sources of chemical energy include the following:

EVALUATION
1. Differentiate between the various forms of energy
2. Mention three appliances that convert chemical energy to heat energy.
SUB-TOPIC II: PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION OF PRESSING IRON, ELECTRIC KETTLE, COOKERS AND WATER HEATERS, ELECTRIC FANS.
The operational principle of pressing iron, electric kettle, cookers and water heaters follows the same pattern. They have the same resistance-wire called element.
THE ELECTRIC PRESSING IRON: The operation of the electric pressing iron begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the element; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity, the heat developed also heat the sole plate by radiation. The iron is then used to press the rough clothes.
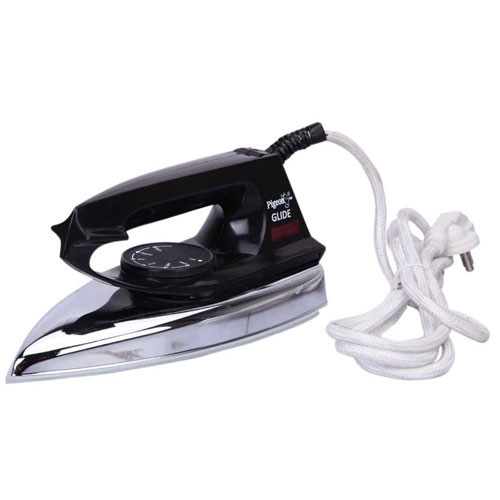

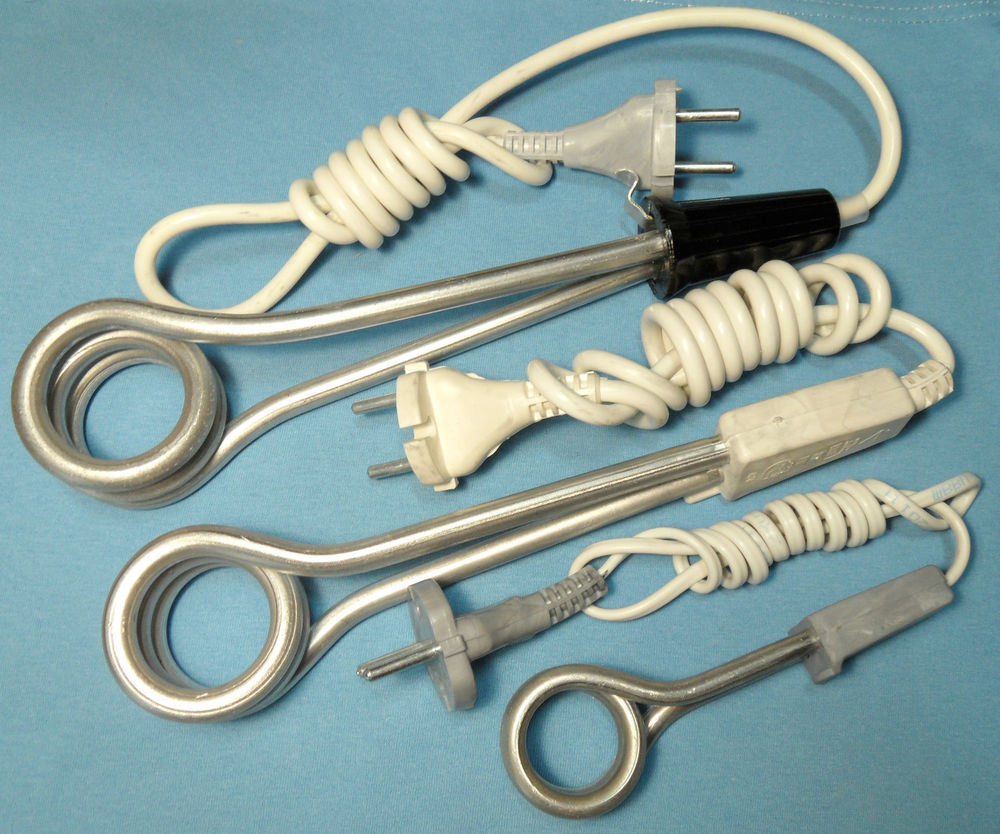
THE ELECTRIC KETTLE: The operation of the electric kettle also begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the element; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity, the heat developed heat up the water in the kettle.

THE ELECTRIC COOKER: The operation of the electric cooker is similar, it begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the Nickel-Chrome high resistance wire (element) concealed in the magnesium oxide tube; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity. The electric cooker heats up quickly, and it is then used for cooking.

THE ELECTRIC WATER HEATER: This is normally mounted on the wall of the bathroom to supply hot water for bathing and for other purposes. Its operation also begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the element; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity, the hot element heats up the cold water in the container. The hot water flows out through the outlet, while the cold water flows in to replace it. This process is repeated continuously.
SUB-TOPIC 2: PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION OF GAS LAMPS, GAS COOKER, KEROSENE COOKER, AND CHARCOAL PRESSING IRON.
The gas lamp, gas cooker, kerosene cooker and charcoal pressing iron are appliances used in converting chemical energy into heat energy. All these operate by converting the chemical energy in a substance called fuel by burning. Burning is a combustion process in which chemical energy is converted into heat energy.
THE GAS LAMP: The fuel flows from the base to the top where it is being ignited. Depending on the quality of flame that is desired, there is a regulator that controls the flow of gas into the burner.
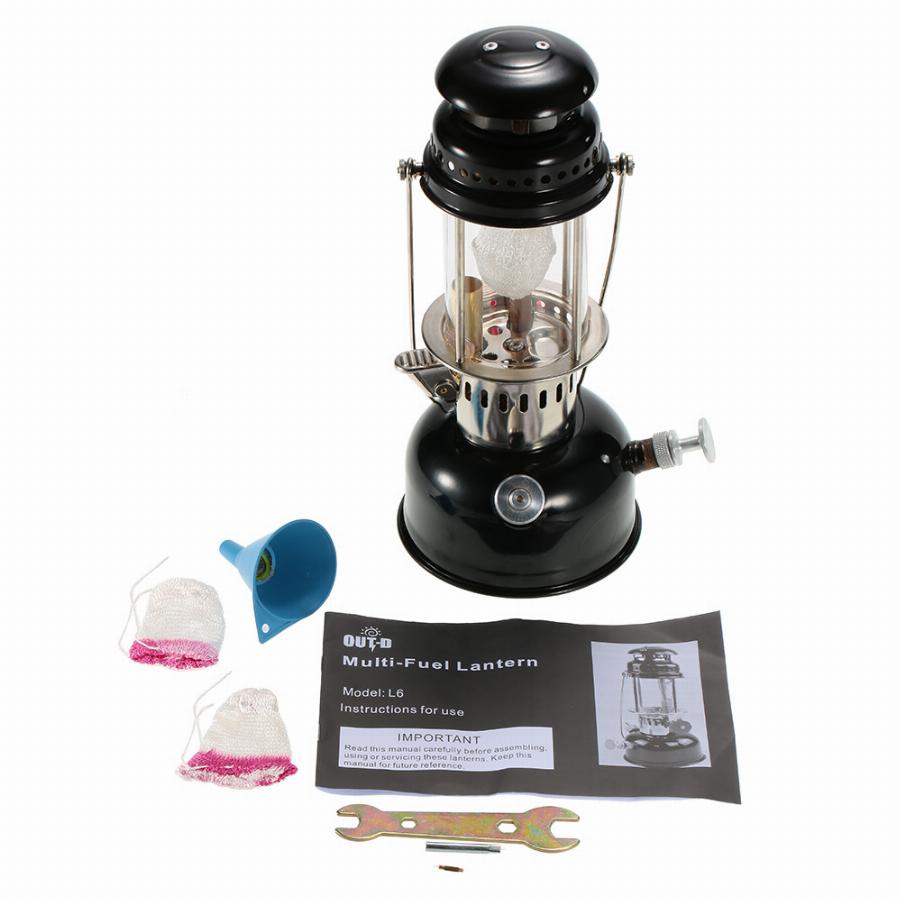

THE GAS COOKER: The gas cooker has burners that have tiny holes on the outer edge through which the fuel gas flows. The heating power of the burner is controlled by a valve along the pipe carrying the gas to the burner.

THE KEROSENE COOKER: in the kerosene stove, the kerosene is put in a container that forms the base of the stove. The kerosene travels in cylindrical cotton materials called a ‘wick` to the heater through a capillary action where it is ignited. The intensity of the flame is adjusted by a control knob which moves the wick up or down, thereby varying the length of the wick that is exposed to the flame.

THE CHARCOAL PRESSING IRON: This is made of cast iron. The pieces of charcoal are put inside the charcoal pressing iron and fire is ignited. The pieces of charcoal are heated in the charcoal pressing iron. The developed heat, heats up the sole plate which is used to press the rough cloth.

EVALUATION
Explain the principle of operation of three electric apparatus.
ASSIGNMENT:
State the uses of the following:
1. Electric pressing iron
2. Electric cooker
3. Electric kettle
4. Gas lamp
READING ASSIGNMENT
NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 2, UBE Edition Chapter 9 Pages 97 – 110 against next lesson
further studies
http://www.eia.gov/kids/index.cfm
http://www.nmsea.org/Curriculum/Primer/ ... energy.htm
http://www.energyeducation.tx.gov/energ ... of_energy/
http://www.eoearth.org/article/Energy?topic=49557#gen2
http://www.teachengineering.org/view_ac ... #procedure
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.thatquiz.org/tq/previewtest? ... 1353924941
http://a4esl.org/q/f/z/zz41mtc.htm
http://www.kubbu.com/student/?i=1&a=176 ... sformation
http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junio ... zes/energy
http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topics/energy/quiz/
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Energy conversion
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) mention different forms of energy
(2) explain the technology of appliance based on conversion of energy
CONTENT
TECHNOLOGY OF APPLIANCES
The technology of all appliances is based on the conversion of energy from one form to another. The reason for the conversion is that not all forms of energy are in the appropriate form for our use. At certain time, it is necessary, as well as convenient to convert an available form of energy into a form that is suitable for our use.

CONVERSION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY INTO HEAT ENERGY
Electrical energy can easily be converted into heat by making a current flow through a resistance. A resistance wire especially made to effect conversion of electrical energy into heat is called a heating element. Heating elements are employed in electric cooker, electric pressing irons, kettles and toaster.

CONVERSION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY INTO LIGHT ENERGY
In conversion of electrical energy to light certain metals, for example tungsten, apart from becoming hot when electric current flows through them, emits a lot of light as well. These are used in lamp filaments.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention all the forms of energy
Explain the conversion of energy from electrical t o light, heat and sound
LESSON 37
MAIN TOPIC : Technology of appliance
SPECIFIC TOPIC : conversion of energy
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1)explain conversion of nuclear energy into electrical energy
(2)explain conversion of heat energy to electrical energy
CONTENT
CONVERSION OF NUCLEAR ENERGY TO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
The heat provided by the nuclear reactor arises as a result of nuclear reaction called fission. When rod of radioactive element uranium excite one another in a reactor tank, huge amount of heat is released which is converted into steam that is now used to drive a generator that generate electricity.

CONVERSION OF HEAT INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
When two ends of wires made of dissimilar metals are joined together rand heat is applied at the junction, an E.M.F is generated. This device which converts heat energy into electrical energy is called THERMOCOUPLE.
The electrical energy which generated is called THERMOELECTRIC ENERGY.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Explain the conversion of energy from nuclear to electrical energy
Explain the conversion of energy from heat energy to electrical energy
TOPIC: ENERGY BASED TECHNOLOGICAL APPLIANCES
CONTENTS
1) Energy and Forms of Energy
2) Principles of operation of pressing iron, Electric kettle, Cookers and Water heaters, Gas lamps, Gas and Kerosene cookers, Charcoal pressing iron.
SUB-TOPIC I: ENERGY AND FORMS OF ENERGY
Energy is said to be the ability to do work and it is measured in joules. Many of our home appliances are operated using Energy. Therefore those appliances that use energy for their operations are energy based technological appliances. We have also learned that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can only be transformed (converted) from one form to another.
These are various forms of energy:
1. Electrical energy
2. Heat Energy
3. Mechanical Energy
4. Chemical Energy
5. Light Energy etc.
Electrical energy can be converted into Heat energy, Mechanical energy to Electrical energy, Chemical energy to Heat energy, Heat energy to Mechanical energy.
The sources of electric energy include the following:

The sources of chemical energy include the following:

EVALUATION
1. Differentiate between the various forms of energy
2. Mention three appliances that convert chemical energy to heat energy.
SUB-TOPIC II: PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION OF PRESSING IRON, ELECTRIC KETTLE, COOKERS AND WATER HEATERS, ELECTRIC FANS.
The operational principle of pressing iron, electric kettle, cookers and water heaters follows the same pattern. They have the same resistance-wire called element.
THE ELECTRIC PRESSING IRON: The operation of the electric pressing iron begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the element; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity, the heat developed also heat the sole plate by radiation. The iron is then used to press the rough clothes.

THE ELECTRIC KETTLE: The operation of the electric kettle also begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the element; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity, the heat developed heat up the water in the kettle.

THE ELECTRIC COOKER: The operation of the electric cooker is similar, it begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the Nickel-Chrome high resistance wire (element) concealed in the magnesium oxide tube; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity. The electric cooker heats up quickly, and it is then used for cooking.

THE ELECTRIC WATER HEATER: This is normally mounted on the wall of the bathroom to supply hot water for bathing and for other purposes. Its operation also begins when the cable is plugged to the electrical socket and then switched on, electric current flows through the element; the electrical energy developed in the element heats it up as a result of the flow of electricity, the hot element heats up the cold water in the container. The hot water flows out through the outlet, while the cold water flows in to replace it. This process is repeated continuously.

SUB-TOPIC 2: PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION OF GAS LAMPS, GAS COOKER, KEROSENE COOKER, AND CHARCOAL PRESSING IRON.
The gas lamp, gas cooker, kerosene cooker and charcoal pressing iron are appliances used in converting chemical energy into heat energy. All these operate by converting the chemical energy in a substance called fuel by burning. Burning is a combustion process in which chemical energy is converted into heat energy.
THE GAS LAMP: The fuel flows from the base to the top where it is being ignited. Depending on the quality of flame that is desired, there is a regulator that controls the flow of gas into the burner.

THE GAS COOKER: The gas cooker has burners that have tiny holes on the outer edge through which the fuel gas flows. The heating power of the burner is controlled by a valve along the pipe carrying the gas to the burner.

THE KEROSENE COOKER: in the kerosene stove, the kerosene is put in a container that forms the base of the stove. The kerosene travels in cylindrical cotton materials called a ‘wick` to the heater through a capillary action where it is ignited. The intensity of the flame is adjusted by a control knob which moves the wick up or down, thereby varying the length of the wick that is exposed to the flame.

THE CHARCOAL PRESSING IRON: This is made of cast iron. The pieces of charcoal are put inside the charcoal pressing iron and fire is ignited. The pieces of charcoal are heated in the charcoal pressing iron. The developed heat, heats up the sole plate which is used to press the rough cloth.

EVALUATION
Explain the principle of operation of three electric apparatus.
ASSIGNMENT:
State the uses of the following:
1. Electric pressing iron
2. Electric cooker
3. Electric kettle
4. Gas lamp
READING ASSIGNMENT
NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 2, UBE Edition Chapter 9 Pages 97 – 110 against next lesson
further studies
http://www.eia.gov/kids/index.cfm
http://www.nmsea.org/Curriculum/Primer/ ... energy.htm
http://www.energyeducation.tx.gov/energ ... of_energy/
http://www.eoearth.org/article/Energy?topic=49557#gen2
http://www.teachengineering.org/view_ac ... #procedure
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.thatquiz.org/tq/previewtest? ... 1353924941
http://a4esl.org/q/f/z/zz41mtc.htm
http://www.kubbu.com/student/?i=1&a=176 ... sformation
http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junio ... zes/energy
http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topics/energy/quiz/
WEEK 2
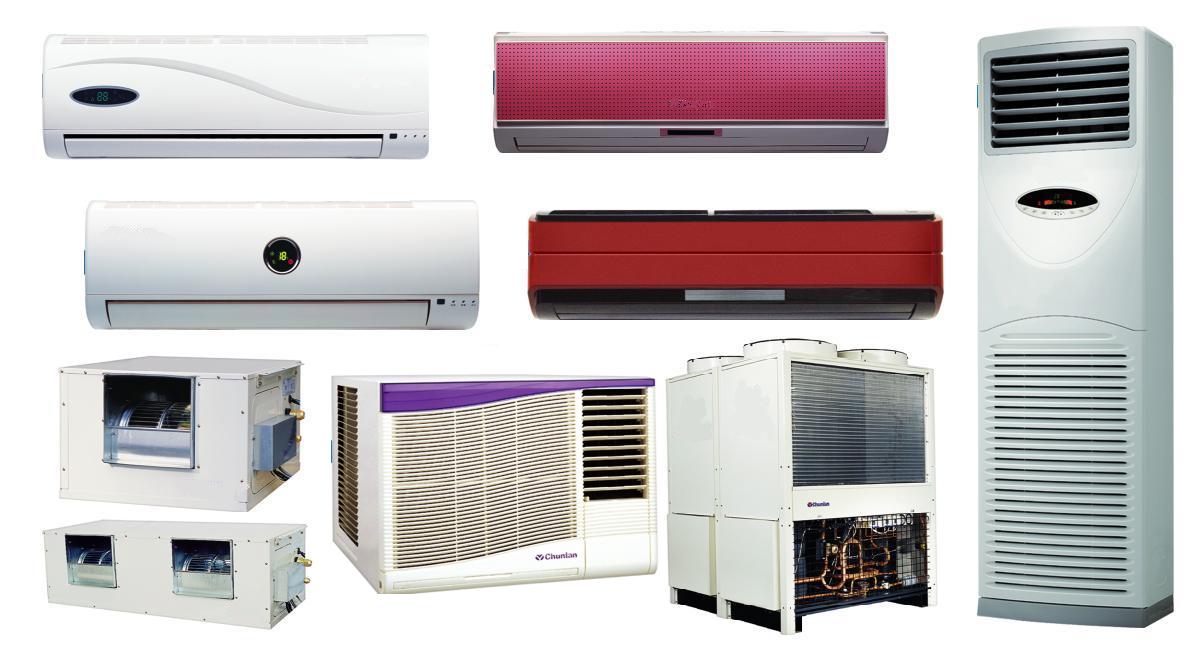
TOPIC: ENERGY BASED TECHNOLOGICAL APPLIANCES.
CONTENTS
(i) TECHNOLOGY OF APPLIANCES BASED ON ELECTRO-MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES
(ii) OPERATION OF A REFRIGERATOR
(iii) OPERATION OF AIR CONDITIONER
SUB-TOPIC 1: TECHNOLOGY OF APPLIANCES BASED ON ELECTRO-MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES.
These are appliances which depend on both electrical and mechanical energies to perform their normal functions. In this group belong refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners. A vital process which takes place while these appliances are being used is called heat transfer.
Heat transfer is the movement of heat energy from one object to another part of the same object. Heat always move from a region of higher temperature to another region of lower temperature. This means that a cold object will gain heat from a warmer object and a hot object will lose heat to a colder object. The reverse is not naturally possible.
In any sustained heat transfer process, at least one or even all the following effects occur:
• EVAPORATION: This is the change of liquid or a solid into a gas. The direct conversion of solid into a gas is called sublimation. The molecules of a substance are always moving as a result, they are said to possess some amount of kinetic energy. Depending on the conditions surrounding the substance, the molecules at its surface may gain enough kinetic energy as to enable them escape into the surrounding space. This is called evaporation.
As the molecules evaporate, they take along with them some amount of energy called latent heat of vaporization, thus creating a net energy loss from the remaining portion of the substance. The consequence is that the temperature of the substance falls. For this reason, evaporation always leads to cooling.
Substances evaporate at different rates. Those which evaporate quickly are called volatile substances. Those which do not evaporate quickly are said to be non – volatile. Volatile substances are of utmost importance in refrigerating and air conditioning systems. In such cases, volatile substances are called refrigerants.
Apart from its use in refrigeration, evaporation is employed in the fractional distillation of crude petroleum into petrol, kerosene, lubricating oils and greases, purification of alcoholic drinks, extraction of sugar cane juices and cooling of the body after perspiration etc.

• CONDENSATION: this is the change of a gas into liquid or solid form. It is the opposite of evaporation. Substances condense at different rates. However volatile substances generally condense more readily than non-volatile substances. Apart from refrigeration, a very important natural use of condensation is in the formation of rainfall.


• MELTING: this is the turning of a solid into liquid. An example is the conversion of solid into liquid. An example is the conversion of solid ice into liquid water. Substances melt at different temperature, although each substance melts at a constant temperature called the melting point. The melting point of ice is 00 centigrade. Melting makes it possible to defrost refrigeration system.

• FREEZING: this is the turning of a liquid into a solid. It is the opposite of melting. At the freezing point, the substance loses latent heat.

EVALUATION:
1. What are refrigerants?
2. Explain the following terms:
- Evaporation - condensation
- Melting - freezing
3. Evaporation leads to -----------------------.
4. Non – volatile substances are ------------------------------------------------------------
SUB-TOPIC 2: OPERATION OF A REFRIGERATOR
Refrigeration is the artificial process of removing heat from a substance for the purpose of lowering its temperature. This definition also applies to the process of freezing. The basic aim of refrigeration is to inhibit or prevent entirely the activities of microorganisms and thus preserve food and other materials in which they are present.
A home electric refrigerator is made of five principal parts, namely :
- Storage tank - Expansion device
- Evaporator - Compressor
- Condenser
Compressor-type refrigerator

The process of refrigeration starts from the storage tank which contains the refrigerant that is subjected to high pressure. The most common refrigerant is Freon –12. It’s chemical name is dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2). Freon -12 turns into gas as it enters the evaporator. Because evaporation results in cooling, the evaporator becomes very cold. From the compressor the hot refrigerant circulates in the condenser (an arrangement of winding pipes and fins at the back of the fridge). As the refrigerant circulates in the condenser it loses its heat to the atmosphere. It then flows to the expansion valve where it expands. The expansion process causes the liquid refrigerant to evaporate into gas. Therefore it cools. The cold refrigerant vapor subsequently cools the evaporator as it flows through the pipes in the evaporator. From the evaporator it flows back to the compressor where the process is repeated for as long as the electrical supply is on.

SUB TOPIC 3: OPERATION OF AIR CONDITIONER
An air conditioner is an appliance which is used to control the properties of air within an enclosed space with the purpose of providing human comfort. These physical properties are: temperature control, humidity control, cleanliness of air, circulation of air.
A typical air conditioning system consists of the following parts;
• Expansion valve
• Evaporator
• Blower
• Compressor
• Condenser fan
• Control panel
In air conditioner, the warm room air is drawn over the condenser coils by an evaporator fan through the air filter. The air filter cleanses the air. Heat from the air is transferred to the refrigerant and causes the air to evaporate. In the process, the air is cooled and is returned to the room by the fan.
The cooling process is further enhanced by the action of the condenser coils. These coils are exposed to the cooling stream of outdoor air blown from the second fan. The liquid refrigerant (gas), which has been compressed by the compressor, passes into the evaporator, and the cycle is repeated.
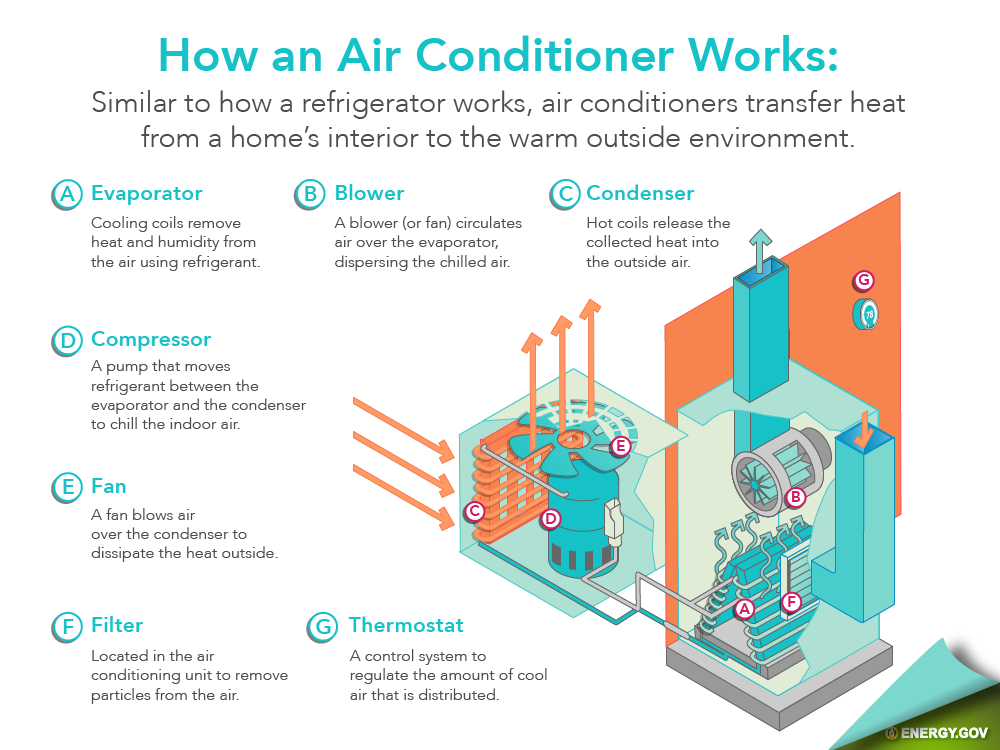
EVALUATION
1. Explain refrigeration cycle.
2. List all the principal parts in a refrigerator
3. What is refrigeration?
4. List any three parts of an air conditioner.
5. Explain the operation of a refrigerator.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Students should read about ‘Energy based Technological Appliances: Principles of operation of electric fan, grinder etc against the next lesson.
TEXT: NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 Chapter 9 pgs 105-109 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Explain the refrigeration cycle.
2. Name three refrigerants. What is the function of a refrigerant?
3. What is the latent heat of vaporization of a substance? How does it play a part in cooling?
4. There are various brands of unit air conditioners in use in Nigeria. Name three of them.
MAIN TOPIC : Principle of cooling effect
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of Air conditioner
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to
I. Define air conditioning
II. Explain the process of air cooling
CONTENT
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning is define as the process of treating air so as to control simultaneously its temperature, humidity, cleanliness and distribution to meet the room requirement of the conditioned space.
Hot weather air conditioning systems, like the one shown here, are used to keep household air from becoming uncomfortably hot, humid, or stale. Air conditioning systems are fairly complex, so they are usually installed as a house is being built. This system involves three separate cycles: the air cycling through the ducts inside the house, the flow of air through the unit outside the house, and the circulation of the refrigerant between the inside and outside units. Air in a duct system passes through a filter to remove dust particles. Then it enters a blower, which sends the air into the evaporator. The hot air vaporizes the refrigerant, which cools the air and transports the heat out of the house. Clean, cool air then passes through the duct system and throughout the house, later returning to be cooled again. The refrigerant is condensed, cooled by outside air, compressed, and then sent back to the evaporator. The cooling system in a small space like a room gives the idea of an air conditioner.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
state the functions of an air conditioner
further studies
http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/how_it_wo ... ioner.html
http://home.howstuffworks.com/ac.htm
http://www.jagbits.com/a26airconditioning.html
practice test
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... s-quiz.htm
http://quizlet.com/18273023/test/
http://webquiz.ilrn.com/ilrn/bca/user/q ... FEC7C312F3
CONTENTS
(i) TECHNOLOGY OF APPLIANCES BASED ON ELECTRO-MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES
(ii) OPERATION OF A REFRIGERATOR
(iii) OPERATION OF AIR CONDITIONER
SUB-TOPIC 1: TECHNOLOGY OF APPLIANCES BASED ON ELECTRO-MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES.
These are appliances which depend on both electrical and mechanical energies to perform their normal functions. In this group belong refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners. A vital process which takes place while these appliances are being used is called heat transfer.
Heat transfer is the movement of heat energy from one object to another part of the same object. Heat always move from a region of higher temperature to another region of lower temperature. This means that a cold object will gain heat from a warmer object and a hot object will lose heat to a colder object. The reverse is not naturally possible.
In any sustained heat transfer process, at least one or even all the following effects occur:
• EVAPORATION: This is the change of liquid or a solid into a gas. The direct conversion of solid into a gas is called sublimation. The molecules of a substance are always moving as a result, they are said to possess some amount of kinetic energy. Depending on the conditions surrounding the substance, the molecules at its surface may gain enough kinetic energy as to enable them escape into the surrounding space. This is called evaporation.
As the molecules evaporate, they take along with them some amount of energy called latent heat of vaporization, thus creating a net energy loss from the remaining portion of the substance. The consequence is that the temperature of the substance falls. For this reason, evaporation always leads to cooling.
Substances evaporate at different rates. Those which evaporate quickly are called volatile substances. Those which do not evaporate quickly are said to be non – volatile. Volatile substances are of utmost importance in refrigerating and air conditioning systems. In such cases, volatile substances are called refrigerants.
Apart from its use in refrigeration, evaporation is employed in the fractional distillation of crude petroleum into petrol, kerosene, lubricating oils and greases, purification of alcoholic drinks, extraction of sugar cane juices and cooling of the body after perspiration etc.

• CONDENSATION: this is the change of a gas into liquid or solid form. It is the opposite of evaporation. Substances condense at different rates. However volatile substances generally condense more readily than non-volatile substances. Apart from refrigeration, a very important natural use of condensation is in the formation of rainfall.


• MELTING: this is the turning of a solid into liquid. An example is the conversion of solid into liquid. An example is the conversion of solid ice into liquid water. Substances melt at different temperature, although each substance melts at a constant temperature called the melting point. The melting point of ice is 00 centigrade. Melting makes it possible to defrost refrigeration system.

• FREEZING: this is the turning of a liquid into a solid. It is the opposite of melting. At the freezing point, the substance loses latent heat.

EVALUATION:
1. What are refrigerants?
2. Explain the following terms:
- Evaporation - condensation
- Melting - freezing
3. Evaporation leads to -----------------------.
4. Non – volatile substances are ------------------------------------------------------------
SUB-TOPIC 2: OPERATION OF A REFRIGERATOR
Refrigeration is the artificial process of removing heat from a substance for the purpose of lowering its temperature. This definition also applies to the process of freezing. The basic aim of refrigeration is to inhibit or prevent entirely the activities of microorganisms and thus preserve food and other materials in which they are present.
A home electric refrigerator is made of five principal parts, namely :
- Storage tank - Expansion device
- Evaporator - Compressor
- Condenser
Compressor-type refrigerator

The process of refrigeration starts from the storage tank which contains the refrigerant that is subjected to high pressure. The most common refrigerant is Freon –12. It’s chemical name is dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2). Freon -12 turns into gas as it enters the evaporator. Because evaporation results in cooling, the evaporator becomes very cold. From the compressor the hot refrigerant circulates in the condenser (an arrangement of winding pipes and fins at the back of the fridge). As the refrigerant circulates in the condenser it loses its heat to the atmosphere. It then flows to the expansion valve where it expands. The expansion process causes the liquid refrigerant to evaporate into gas. Therefore it cools. The cold refrigerant vapor subsequently cools the evaporator as it flows through the pipes in the evaporator. From the evaporator it flows back to the compressor where the process is repeated for as long as the electrical supply is on.

SUB TOPIC 3: OPERATION OF AIR CONDITIONER
An air conditioner is an appliance which is used to control the properties of air within an enclosed space with the purpose of providing human comfort. These physical properties are: temperature control, humidity control, cleanliness of air, circulation of air.
A typical air conditioning system consists of the following parts;
• Expansion valve
• Evaporator
• Blower
• Compressor
• Condenser fan
• Control panel
In air conditioner, the warm room air is drawn over the condenser coils by an evaporator fan through the air filter. The air filter cleanses the air. Heat from the air is transferred to the refrigerant and causes the air to evaporate. In the process, the air is cooled and is returned to the room by the fan.
The cooling process is further enhanced by the action of the condenser coils. These coils are exposed to the cooling stream of outdoor air blown from the second fan. The liquid refrigerant (gas), which has been compressed by the compressor, passes into the evaporator, and the cycle is repeated.

EVALUATION
1. Explain refrigeration cycle.
2. List all the principal parts in a refrigerator
3. What is refrigeration?
4. List any three parts of an air conditioner.
5. Explain the operation of a refrigerator.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Students should read about ‘Energy based Technological Appliances: Principles of operation of electric fan, grinder etc against the next lesson.
TEXT: NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 Chapter 9 pgs 105-109 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Explain the refrigeration cycle.
2. Name three refrigerants. What is the function of a refrigerant?
3. What is the latent heat of vaporization of a substance? How does it play a part in cooling?
4. There are various brands of unit air conditioners in use in Nigeria. Name three of them.
MAIN TOPIC : Principle of cooling effect
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of Air conditioner
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to
I. Define air conditioning
II. Explain the process of air cooling
CONTENT
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning is define as the process of treating air so as to control simultaneously its temperature, humidity, cleanliness and distribution to meet the room requirement of the conditioned space.
Hot weather air conditioning systems, like the one shown here, are used to keep household air from becoming uncomfortably hot, humid, or stale. Air conditioning systems are fairly complex, so they are usually installed as a house is being built. This system involves three separate cycles: the air cycling through the ducts inside the house, the flow of air through the unit outside the house, and the circulation of the refrigerant between the inside and outside units. Air in a duct system passes through a filter to remove dust particles. Then it enters a blower, which sends the air into the evaporator. The hot air vaporizes the refrigerant, which cools the air and transports the heat out of the house. Clean, cool air then passes through the duct system and throughout the house, later returning to be cooled again. The refrigerant is condensed, cooled by outside air, compressed, and then sent back to the evaporator. The cooling system in a small space like a room gives the idea of an air conditioner.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
state the functions of an air conditioner
further studies
http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/how_it_wo ... ioner.html
http://home.howstuffworks.com/ac.htm
http://www.jagbits.com/a26airconditioning.html
practice test
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... s-quiz.htm
http://quizlet.com/18273023/test/
http://webquiz.ilrn.com/ilrn/bca/user/q ... FEC7C312F3
WEEK 3
TOPIC: Energy Based Technological appliances (cont’d)
CONTENTS
1. Principles of operation of electric fan, grinder
2. Working principles of generators, bicycles dynamos
Sub-Topic 1: Principles of operation of electric fan, grinder
ELECTRIC FAN
The electric fan converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
The parts of an electric fan are the:
a. Motor which rotates, and carries the blade
b. Blades which circulate the air
c. Guard which prevents contact with the blade (present in table and standing fans)
d. Power plug for supplying electricity to the motor of the fan
e. Switch selector which regulates the speed of rotation of the fan blade.
The electric fan rotates by connecting the fan to the source of electrical energy, when connected, the motor which carries the blades rotates, therefore making the blades. The switch selector helps to increase or lower the speed of rotation of the blades.
The fans should be properly taken care of by regular dusting and greasing, to keep them functioning well.

GRINDER
a. FRUIT GRINDER (BLENDER); The parts of the fruit grinder are as follows:
The housing which contains the motor
The motor
The cup which contains the blades, and houses the fruits to be grinded.
The blades which grinds the fruits
The pulley
The switch
The power plug.
The motor which carries the grinder
The motor which carries the cup rotates the blades as soon as the grinder is connected to a source of electricity and switched on. As the blades rotate, they cut and grind the fruits in the cup.
Note, the motor must not be allowed to run for a long time because it may get too hot, and the coils may be burnt.

b. CASSAVA GRINDER
The cassava grinder has similar parts and also operates in the same way as the fruit grinder.
The motor rotates when the current flows through it. The rotating motor turns the blades which are connected to it through the pulley. The rotating blades grind the cassava in the cup. The cassava grinder is shown below:

EVALUATION
1) Name three parts of a fruit grinder
2) Describe how the electric fan works
SUB-TOPIC 2: Working principles of generators, bicycles, dynamos
THE GENERATOR:
A Generator is an electrical machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The parts of a generator are:
i. The frame (housing)
ii. The armature or rotor
iii. The pole and its windings
iv. The shaft
v. The commutator or slip ring.
vi. The Carbon brush.
The frame is where the poles and their windings are mounted. The poles are made of magnetic material which produces a magnetic field. The shaft suspends the armature in the magnetic field of the generator. The frame, with the poles and their windings make up what is known as the field. The armature is made up of coils wound on it; it is the rotating part of the generator. The armature is rotated in the magnetic field (between two powerful magnets) by mechanical energy. Current is induced in the coil (whose ends are connected to the slip ring mounted on the coil spindle) because the coils cut across the magnet lines of force. The electrical energy that is induced in the windings (conductors) when the armature rotates in the magnetic field is led out of the generator via carbon brushes which are made to press lightly against the commutator (for DC machine) or the slip ring (for AC machine).
NOTE, DC means Direct Current and AC means Alternating Current. The generator which produces direct current is called D.C. generator while the generator which produces alternating current is called A.C generator.

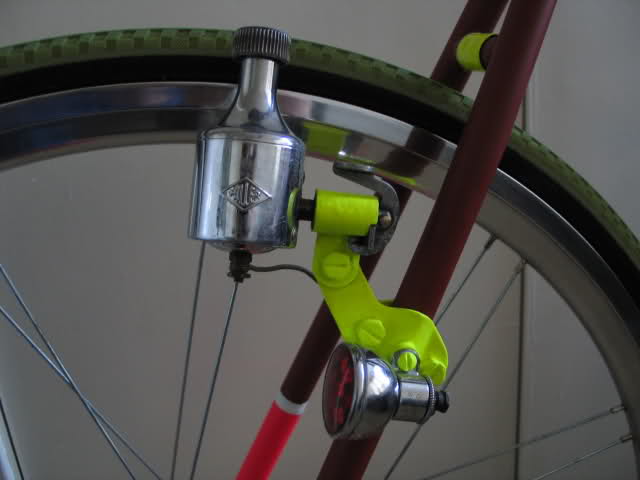
BICYCLES DYNAMO
The dynamo is the earliest invented kind of generator. It is used to produce direct current; a dynamo is a device which makes electricity to flow through wire. An electric dynamo produces electricity that is much economical than the batteries. It does not create electrical energy but it converts mechanical energy of a turbine of a manually operated bicycle to electrical energy. The dynamo consists of case, a serrated wheel soft iron core and a U-shaped soft iron, and coil of wire.
The mode of operation: the coil or wire loops make the armature. Some current collecting device called a commulator is connected to it and then the wire brushes lead off the resulting current to produce electric current.

EVALUATION
1. What is the function of the bicycle dynamo?
2. Explain the working principle of the generator
ASSIGNMENT
Identify and explain the principles of appliances based on conversion of (i) electrical energy to heat energy. (ii) Mechanical energy to heat.
READING ASSIGNMENT
NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 2, UBE EDITION, Chapter 10 Pages 111 – 120
CONTENTS
1. Principles of operation of electric fan, grinder
2. Working principles of generators, bicycles dynamos
Sub-Topic 1: Principles of operation of electric fan, grinder
ELECTRIC FAN
The electric fan converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
The parts of an electric fan are the:
a. Motor which rotates, and carries the blade
b. Blades which circulate the air
c. Guard which prevents contact with the blade (present in table and standing fans)
d. Power plug for supplying electricity to the motor of the fan
e. Switch selector which regulates the speed of rotation of the fan blade.
The electric fan rotates by connecting the fan to the source of electrical energy, when connected, the motor which carries the blades rotates, therefore making the blades. The switch selector helps to increase or lower the speed of rotation of the blades.
The fans should be properly taken care of by regular dusting and greasing, to keep them functioning well.

GRINDER
a. FRUIT GRINDER (BLENDER); The parts of the fruit grinder are as follows:
The housing which contains the motor
The motor
The cup which contains the blades, and houses the fruits to be grinded.
The blades which grinds the fruits
The pulley
The switch
The power plug.
The motor which carries the grinder
The motor which carries the cup rotates the blades as soon as the grinder is connected to a source of electricity and switched on. As the blades rotate, they cut and grind the fruits in the cup.
Note, the motor must not be allowed to run for a long time because it may get too hot, and the coils may be burnt.

b. CASSAVA GRINDER
The cassava grinder has similar parts and also operates in the same way as the fruit grinder.
The motor rotates when the current flows through it. The rotating motor turns the blades which are connected to it through the pulley. The rotating blades grind the cassava in the cup. The cassava grinder is shown below:

EVALUATION
1) Name three parts of a fruit grinder
2) Describe how the electric fan works
SUB-TOPIC 2: Working principles of generators, bicycles, dynamos
THE GENERATOR:
A Generator is an electrical machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The parts of a generator are:
i. The frame (housing)
ii. The armature or rotor
iii. The pole and its windings
iv. The shaft
v. The commutator or slip ring.
vi. The Carbon brush.
The frame is where the poles and their windings are mounted. The poles are made of magnetic material which produces a magnetic field. The shaft suspends the armature in the magnetic field of the generator. The frame, with the poles and their windings make up what is known as the field. The armature is made up of coils wound on it; it is the rotating part of the generator. The armature is rotated in the magnetic field (between two powerful magnets) by mechanical energy. Current is induced in the coil (whose ends are connected to the slip ring mounted on the coil spindle) because the coils cut across the magnet lines of force. The electrical energy that is induced in the windings (conductors) when the armature rotates in the magnetic field is led out of the generator via carbon brushes which are made to press lightly against the commutator (for DC machine) or the slip ring (for AC machine).
NOTE, DC means Direct Current and AC means Alternating Current. The generator which produces direct current is called D.C. generator while the generator which produces alternating current is called A.C generator.

BICYCLES DYNAMO
The dynamo is the earliest invented kind of generator. It is used to produce direct current; a dynamo is a device which makes electricity to flow through wire. An electric dynamo produces electricity that is much economical than the batteries. It does not create electrical energy but it converts mechanical energy of a turbine of a manually operated bicycle to electrical energy. The dynamo consists of case, a serrated wheel soft iron core and a U-shaped soft iron, and coil of wire.
The mode of operation: the coil or wire loops make the armature. Some current collecting device called a commulator is connected to it and then the wire brushes lead off the resulting current to produce electric current.

EVALUATION
1. What is the function of the bicycle dynamo?
2. Explain the working principle of the generator
ASSIGNMENT
Identify and explain the principles of appliances based on conversion of (i) electrical energy to heat energy. (ii) Mechanical energy to heat.
READING ASSIGNMENT
NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 2, UBE EDITION, Chapter 10 Pages 111 – 120
WEEK 4
MAIN TOPIC : Electric motor
SPECIFIC TOPIC : A.C motor
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define electric motor
(2) mention all the component of electric motor
CONTENT
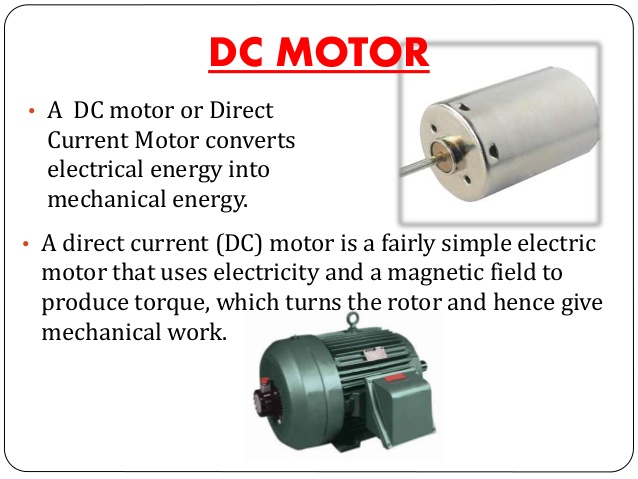
MOTOR
A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. A generator, on the other hand is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into energy. Both motors and generators are energy based technology appliances. There are two types of electric motor.
1. A.C motor which uses Alternate Current e.g. current from PHCN
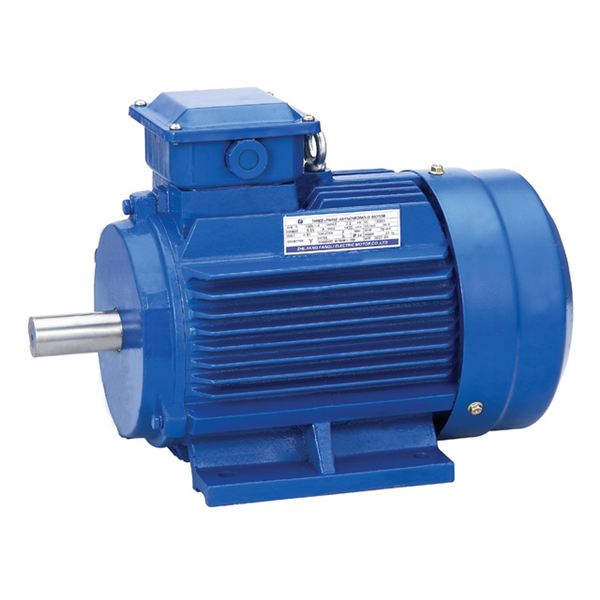

2. D.C motor which uses Direct Current e.g. current from battery
Electric motor can be found in water pumps, electric drilling machine, hair drier, vacuum cleaners, cassava grinder, fruit blenders, electric fans etc
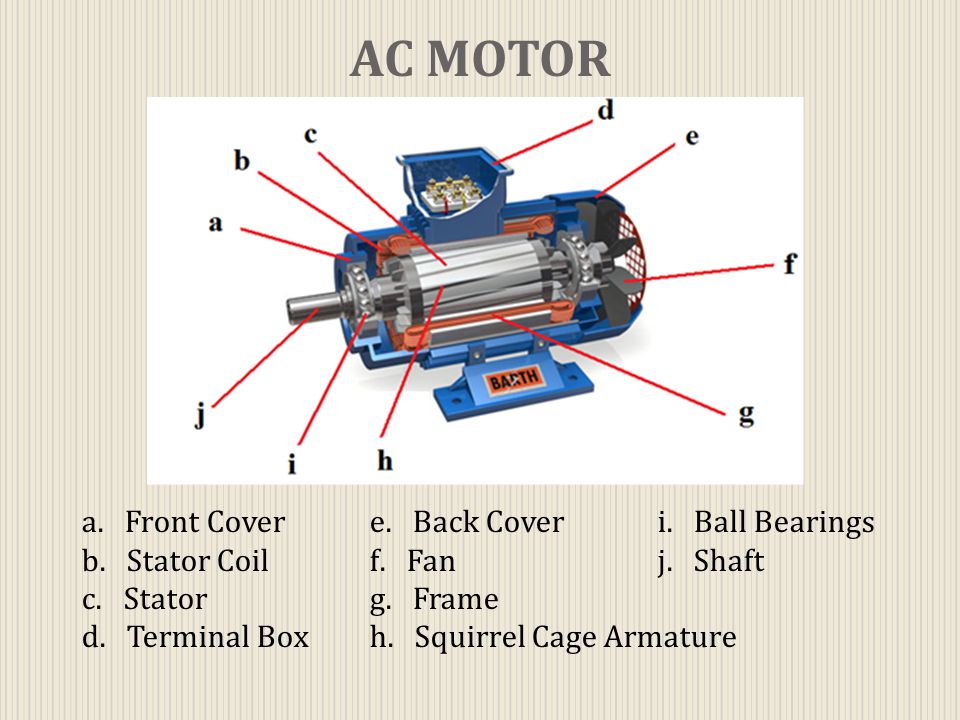
The major parts of an electric motor are :
1. The frame (housing)
2. The armature or rotor (coil)
3. The pole and its windings
4. The shaft
5. The end shield
6. The terminal box
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define electric motor
Mention all the components of an electric motor
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw an electric motor
LESSON 39
MAIN TOPIC : Electric motor
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of electric motor
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
1. Explain the operation of electric motor
2. Explain the operation of a generation
CONTENT
Principle of operation of a motor and generator
Both the motor and the generator operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction. In electromagnetic induction, if a coil is supplied with electric current, and placed in a magnetic field, that coil will rotate.
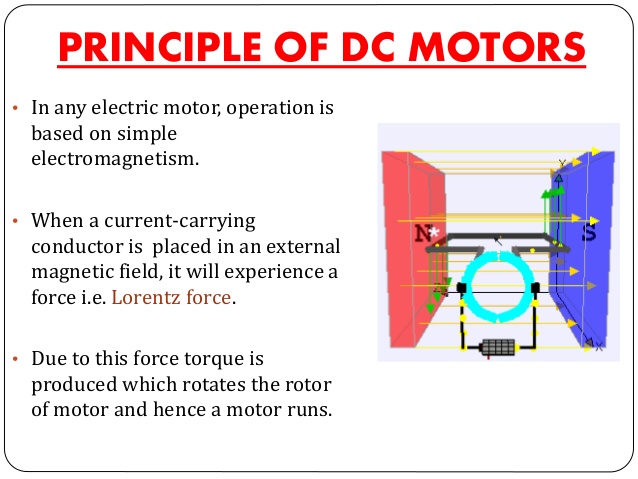
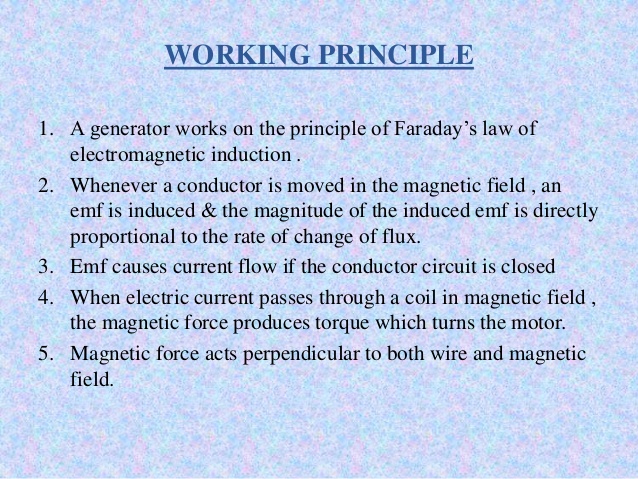
Operation of a motor and generators
A motor and a generator have magnetic poles and field windings that produce a magnetic field. They also have armatures which are made up of coils of the conductor, the shaft suspends the armature in the magnetic field of the motor. When electrical energy is passed to the armature, it will rotate if we attach any load, like the blade of a fan to the rotating armature the blade will rotate, the motor has converted the electrical energy into mechanical energy.
A generator behaves the same way. The only difference is that mechanical energy is used to rotate the amarture. The string used in pulling small domestic generators is a mechanical means for turning the armarture. A generator has a commutator for DC and Slip ring for AC. The electrical energy from a generator is obtained from a commutator or a slip ring.
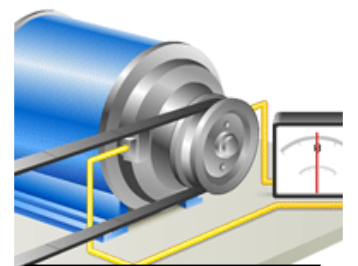
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Explains the operation of electric motor
Mention all the components of an electric motor
Explain the operation of a generator
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw a simple generator
further studies
http://www.emac-online.com/products/Com ... onents.htm
http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/View ... ID=IAU9508
http://www.howstuffworks.com/motor.htm
http://www.howstuffworks.com/motor1.htm
http://library.thinkquest.org/27948/motor.html
http://www.tutorvista.com/content/scien ... -motor.php
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hb ... motdc.html
http://neilorme.com/Electric%20Motor%20Theory.shtml
practice test
http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/el ... r-quiz.htm
http://quiz.thefullwiki.org/Motor_controller
http://www.code-electrical.com/motors-quiz/
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of Air conditioner
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. state the component of a refrigerator
II. explain the operation of a refrigerator
CONTENT
The fridge operates with gas (refrigerant) which could be Freon, ammonia or alcohol. The operation of a fridge is guided by the principle that fluid absorbs heat when changing from liquid to vapour state to a liquid state. This is called latent heat.

The essential components of a refrigerator
I. Refrigerant
II. Evaporator
III. Condenser
IV. Thermostat
Refrigerant operates between the liquid and gaseous states. The refrigerant is a fluid which in liquid state, gain heat and changes very easily to vapour, and at vapour state loses heat and changes back to liquid state. The refrigerant moves through the in closed piping it enters the space to be refrigerated as a low temperature liquid. It then takes heat from the space containing food items, drinks etc. Which is at a higher temperature, the items in the refrigerator becomes cooler and on the other hand the refrigerant is gaining heat and changes from liquid state to vapour inside a coil called Evaporator.
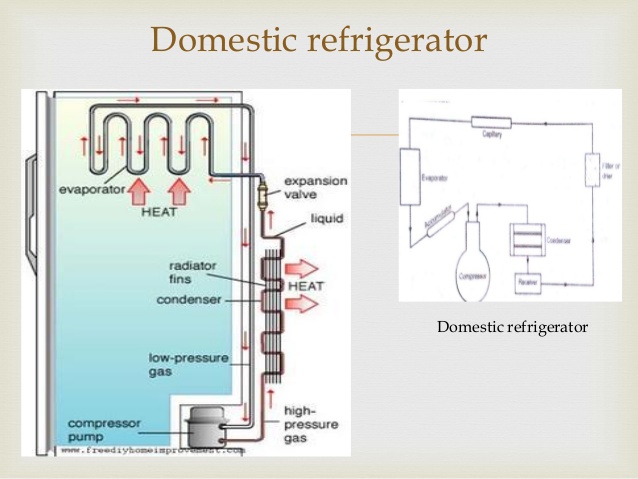
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the major components of a refrigerator
Explain the principle of operation of a refrigerator
further studies
http://www.achrnews.com/articles/the-ba ... tion-cycle
http://home.howstuffworks.com/refrigerator2.htm
practice test
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... s-quiz.htm
http://www.calculatoredge.com/quiz/mechq1.htm
LESSON 41
MAIN TOPIC : Technology of appliances
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Working Principle of a loudspeaker
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. state the uses of a loudspeaker
II. demonstrate the construction of a loudspeaker
CONTENT
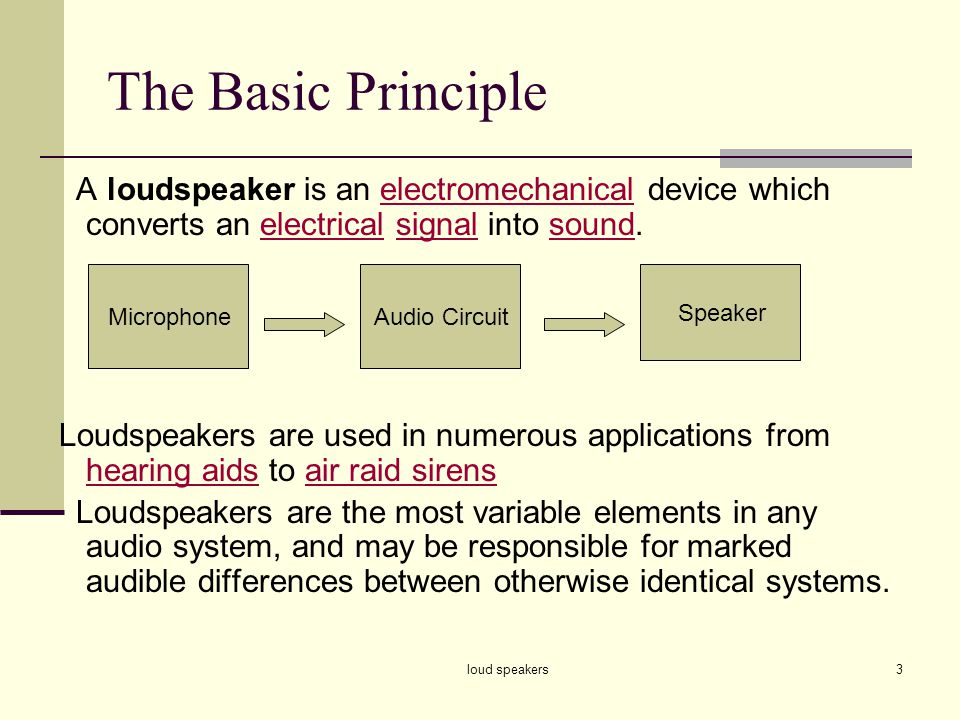
The loudspeaker is used to convert electrical energy into sound energy. It is based on the fact that a force acts on a current-carrying conductor in the presence of a magnetic field. When the coil is connected to a voltage source like a power amplifier, current flows in the coil and a force act on it because of the presence of the magnet. The force cause the coil to move, compressing and rectifying the air. This produces sound.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the major components of a loudspeaker
Explain the principle of operation of a loudspeaker
further studies
http://www.engineersgarage.com/insight/ ... aker-works
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hb ... o/spk.html
http://lenardaudio.com/education/05_speakers.html
http://www.ustudy.in/node/976
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AP2Nu4MZJRs
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.britannica.com/quiz/115/soun ... -fiction/7
SPECIFIC TOPIC : A.C motor
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define electric motor
(2) mention all the component of electric motor
CONTENT
MOTOR
A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. A generator, on the other hand is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into energy. Both motors and generators are energy based technology appliances. There are two types of electric motor.
1. A.C motor which uses Alternate Current e.g. current from PHCN

2. D.C motor which uses Direct Current e.g. current from battery

Electric motor can be found in water pumps, electric drilling machine, hair drier, vacuum cleaners, cassava grinder, fruit blenders, electric fans etc

The major parts of an electric motor are :
1. The frame (housing)
2. The armature or rotor (coil)
3. The pole and its windings
4. The shaft
5. The end shield
6. The terminal box

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Define electric motor
Mention all the components of an electric motor
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw an electric motor
LESSON 39
MAIN TOPIC : Electric motor
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of electric motor
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
1. Explain the operation of electric motor
2. Explain the operation of a generation
CONTENT
Principle of operation of a motor and generator
Both the motor and the generator operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction. In electromagnetic induction, if a coil is supplied with electric current, and placed in a magnetic field, that coil will rotate.


Operation of a motor and generators
A motor and a generator have magnetic poles and field windings that produce a magnetic field. They also have armatures which are made up of coils of the conductor, the shaft suspends the armature in the magnetic field of the motor. When electrical energy is passed to the armature, it will rotate if we attach any load, like the blade of a fan to the rotating armature the blade will rotate, the motor has converted the electrical energy into mechanical energy.
A generator behaves the same way. The only difference is that mechanical energy is used to rotate the amarture. The string used in pulling small domestic generators is a mechanical means for turning the armarture. A generator has a commutator for DC and Slip ring for AC. The electrical energy from a generator is obtained from a commutator or a slip ring.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Explains the operation of electric motor
Mention all the components of an electric motor
Explain the operation of a generator
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw a simple generator
further studies
http://www.emac-online.com/products/Com ... onents.htm
http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/View ... ID=IAU9508
http://www.howstuffworks.com/motor.htm
http://www.howstuffworks.com/motor1.htm
http://library.thinkquest.org/27948/motor.html
http://www.tutorvista.com/content/scien ... -motor.php
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hb ... motdc.html
http://neilorme.com/Electric%20Motor%20Theory.shtml
practice test
http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/el ... r-quiz.htm
http://quiz.thefullwiki.org/Motor_controller
http://www.code-electrical.com/motors-quiz/
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of Air conditioner
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. state the component of a refrigerator
II. explain the operation of a refrigerator
CONTENT
The fridge operates with gas (refrigerant) which could be Freon, ammonia or alcohol. The operation of a fridge is guided by the principle that fluid absorbs heat when changing from liquid to vapour state to a liquid state. This is called latent heat.

The essential components of a refrigerator
I. Refrigerant
II. Evaporator
III. Condenser
IV. Thermostat
Refrigerant operates between the liquid and gaseous states. The refrigerant is a fluid which in liquid state, gain heat and changes very easily to vapour, and at vapour state loses heat and changes back to liquid state. The refrigerant moves through the in closed piping it enters the space to be refrigerated as a low temperature liquid. It then takes heat from the space containing food items, drinks etc. Which is at a higher temperature, the items in the refrigerator becomes cooler and on the other hand the refrigerant is gaining heat and changes from liquid state to vapour inside a coil called Evaporator.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the major components of a refrigerator
Explain the principle of operation of a refrigerator
further studies
http://www.achrnews.com/articles/the-ba ... tion-cycle
http://home.howstuffworks.com/refrigerator2.htm
practice test
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... s-quiz.htm
http://www.calculatoredge.com/quiz/mechq1.htm
LESSON 41
MAIN TOPIC : Technology of appliances
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Working Principle of a loudspeaker
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. state the uses of a loudspeaker
II. demonstrate the construction of a loudspeaker
CONTENT

The loudspeaker is used to convert electrical energy into sound energy. It is based on the fact that a force acts on a current-carrying conductor in the presence of a magnetic field. When the coil is connected to a voltage source like a power amplifier, current flows in the coil and a force act on it because of the presence of the magnet. The force cause the coil to move, compressing and rectifying the air. This produces sound.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the major components of a loudspeaker
Explain the principle of operation of a loudspeaker
further studies
http://www.engineersgarage.com/insight/ ... aker-works
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hb ... o/spk.html
http://lenardaudio.com/education/05_speakers.html
http://www.ustudy.in/node/976
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AP2Nu4MZJRs
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.britannica.com/quiz/115/soun ... -fiction/7
WEEK 5
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Operation of a generator
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Define a generator
ii. Explain the working principle of a generator
CONTENT
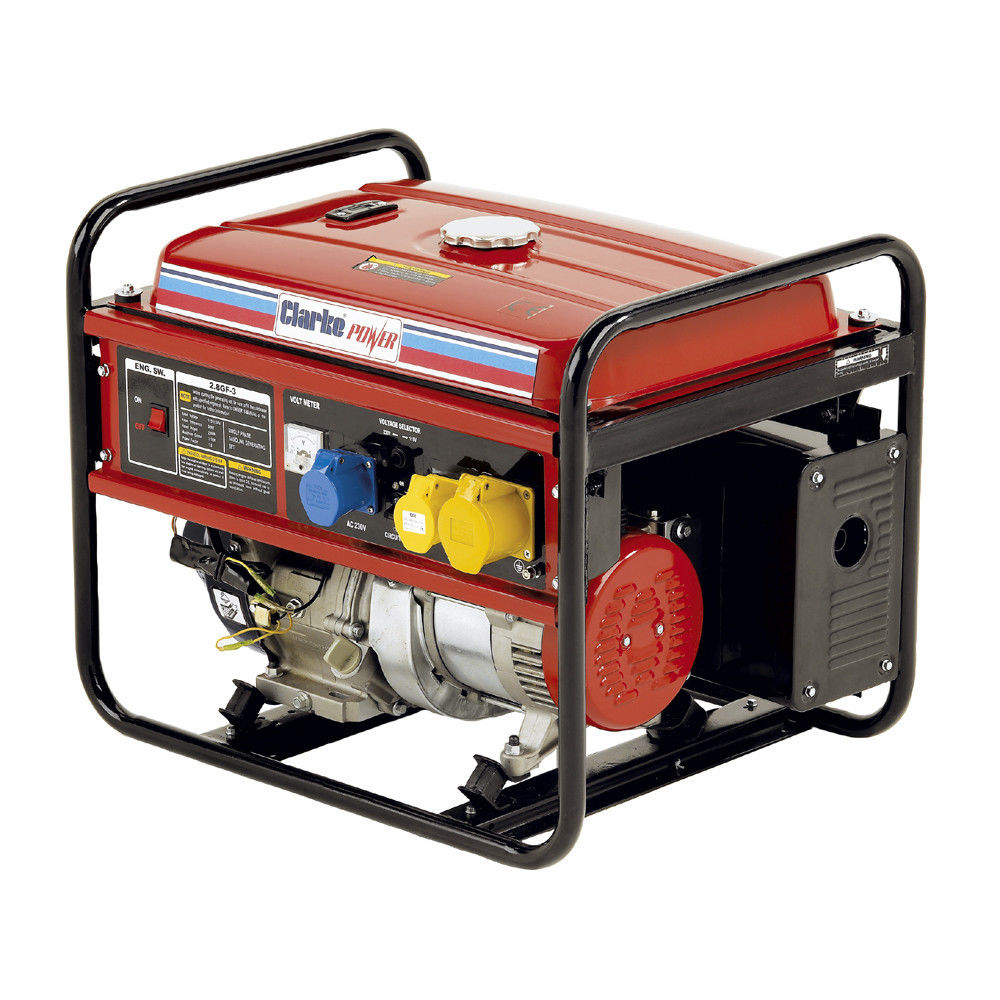
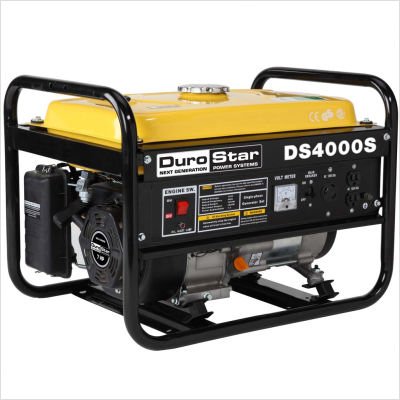
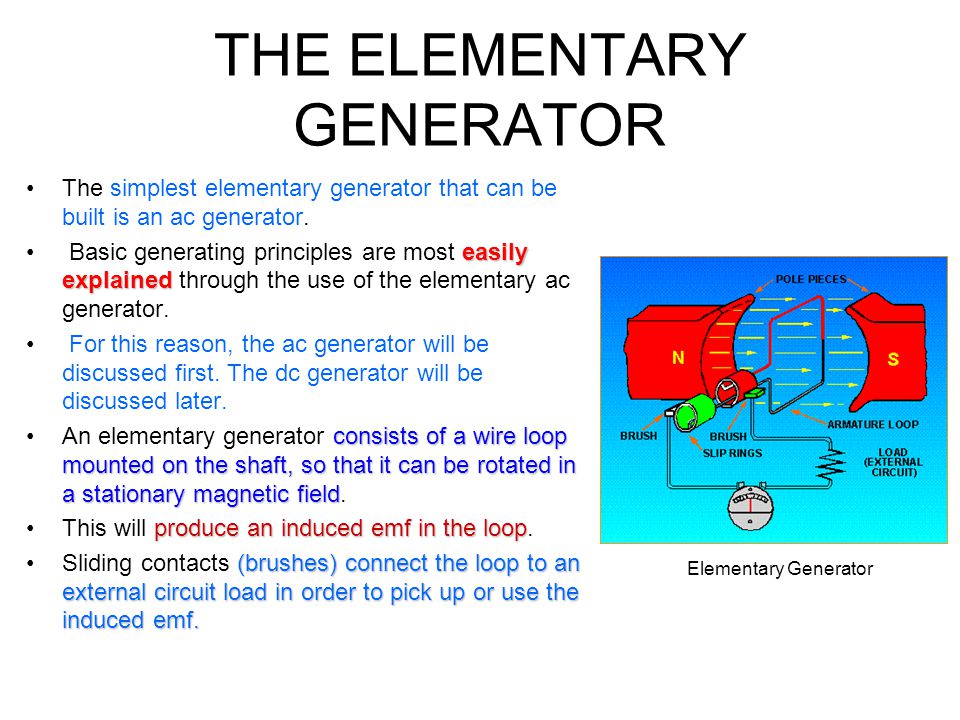
GENERATOR
A generator is a device for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. It comprises of armature, field coil and other parts which, when rotated, generate electricity. It is usually driven by a belt from the engine.

Principles of Operation
The generator operation on the principle that any conductor connected to a complete circuit will have a flow of current induced in it when it moves through a magnetic field. Basically the electric generator consists of a two-part field coil which supplies the magnetic field and the armature winding which rotates in the magnetic field produced by the field coils.
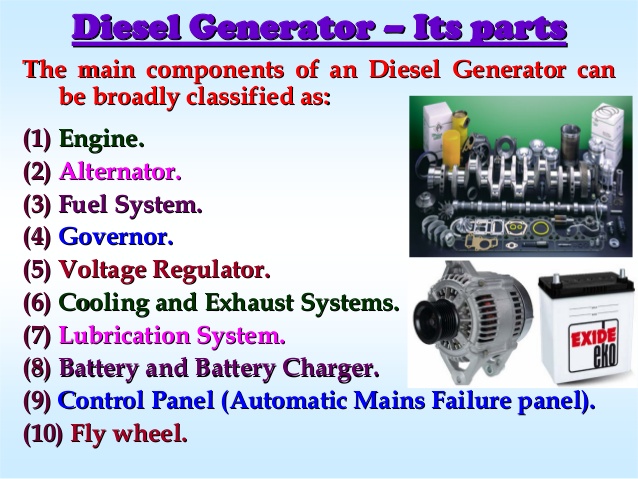
Generator are available in both diesel and petrol engine.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
to mention types of generator they use at home
explain the operation of a generator
further studies
http://www.jobsite-generators.com/generator_theory.html
http://www.slideshare.net/guest2749c1f/ ... -operation
http://www.dieselserviceandsupply.com/H ... _Work.aspx
http://www.generatorjoe.net/html/stepxs ... rator.html
http://www.ncert.nic.in/html/learning_b ... erator.htm
http://www.ustudy.in/node/3944
practice test
http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/View ... D=IAU10608
http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/View ... D=IAU14008
LESSON 44
MAIN TOPIC : Transmission of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : meaning of transmission of electricity
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define transmission of electricity
II. State the components of transmission of electricity
CONTENT
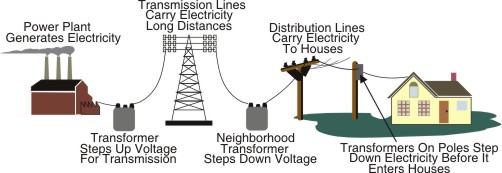
Transmission of electricity means the conveying of electricity from the point of generation to the point of consumption through the transmission lines. Transmission of electricity can be through overhead lines or underground cable. The transmission of electricity starts from the generating stations which may be far from where the electricity may be consumed.
Examples of generating station in Nigeria are
Afam power station in River state---------------------Gas fired

Kainji dam power station in kwara state -----------Hydropowered

Egbin thermal station in Lagos state --------------------gas fired

Orji river station--------------------------------------------Coal fired

The major components are:
1. Control panel
2. Transmission lines
3. Insulators
4. Circuit breaker
5. Bus bars
6. Transformers
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
mention the uses of electricity
mentions all the components of transmission of electricity
further studies
http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/story/chapter07.html
http://physicsservello.com.au/Transmiss ... icity.html
http://solareis.anl.gov/guide/transmission/
practice test
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... q85760214/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... q37657054/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... q64524902/
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Define a generator
ii. Explain the working principle of a generator
CONTENT
GENERATOR
A generator is a device for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. It comprises of armature, field coil and other parts which, when rotated, generate electricity. It is usually driven by a belt from the engine.

Principles of Operation
The generator operation on the principle that any conductor connected to a complete circuit will have a flow of current induced in it when it moves through a magnetic field. Basically the electric generator consists of a two-part field coil which supplies the magnetic field and the armature winding which rotates in the magnetic field produced by the field coils.

Generator are available in both diesel and petrol engine.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
to mention types of generator they use at home
explain the operation of a generator
further studies
http://www.jobsite-generators.com/generator_theory.html
http://www.slideshare.net/guest2749c1f/ ... -operation
http://www.dieselserviceandsupply.com/H ... _Work.aspx
http://www.generatorjoe.net/html/stepxs ... rator.html
http://www.ncert.nic.in/html/learning_b ... erator.htm
http://www.ustudy.in/node/3944
practice test
http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/View ... D=IAU10608
http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/View ... D=IAU14008
LESSON 44
MAIN TOPIC : Transmission of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : meaning of transmission of electricity
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. Define transmission of electricity
II. State the components of transmission of electricity
CONTENT
Transmission of electricity means the conveying of electricity from the point of generation to the point of consumption through the transmission lines. Transmission of electricity can be through overhead lines or underground cable. The transmission of electricity starts from the generating stations which may be far from where the electricity may be consumed.
Examples of generating station in Nigeria are
Afam power station in River state---------------------Gas fired

Kainji dam power station in kwara state -----------Hydropowered

Egbin thermal station in Lagos state --------------------gas fired

Orji river station--------------------------------------------Coal fired

The major components are:
1. Control panel
2. Transmission lines
3. Insulators
4. Circuit breaker
5. Bus bars
6. Transformers
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
mention the uses of electricity
mentions all the components of transmission of electricity
further studies
http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/story/chapter07.html
http://physicsservello.com.au/Transmiss ... icity.html
http://solareis.anl.gov/guide/transmission/
practice test
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... q85760214/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... q37657054/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesi ... q64524902/
WEEK 6
TOPIC: TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY
CONTENTS:
1. Transmission: Low frequency, High frequency
2. Distribution
3. Utilization
4. Materials and Equipment: transformer, cables, insulators, separators, fuses, etc.
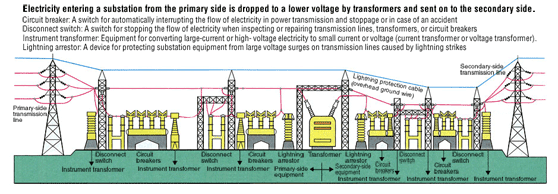
SUB-TOPIC I: TRANSMISSION: LOW FREQUENCY, HIGH FREQUENCY.
Transmission of electricity is the movement of electricity from the point of generation to the point of consumption. This is done through transmission lines called cables. The transmission lines are made of copper wire coated with lead or aluminum, and the can be single or stranded. The line can be laid overhead or underground.
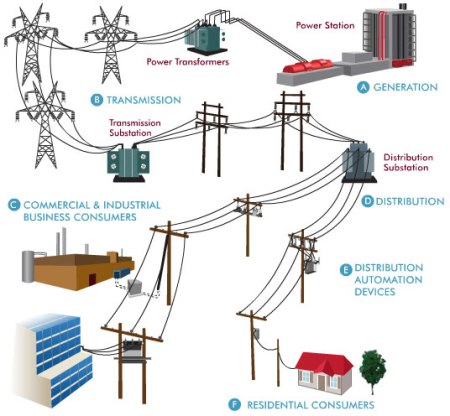
TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY AT LOW FREQUENCY
The number of cycle per second is called frequency, it unit is the Hertz. When Electricity is transmitted from the point of generation at a frequency of 50Hz (In Nigeria) or 60Hz (In America) to the final consumer, this type of transmission is said to be Low frequency transmission.
The generating station may be far from the towns or villages where the generated power is consumed.
Transmission is done at voltages much higher than those used in our home to operate electrical equipment and appliances. Transmission of electricity across towns and villages is made possible by building or stringing the 3 phases or 4-wire on concrete or wooden high tension poles planted along the high tension route. These high voltages are brought into domestic or industrial houses by the use of step-down transformers. Individuals domestic houses make use of either single-phase supply or 3-phase 4-wire gives a voltage of about 450-500 volts.
TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY AT HIGH FREQUENCY
Transmission at high frequency is done through electromagnetic waves or Radio waves. This is practically explains in the operation of a Radio communication system. The radio waves which are received in our radio and television sets are first generated and transmitted. In radio communication system, the message is given through a microphone connected to transmitter, which generate the radio wave at a high frequency. An aerial connected to the transmission line, sends out the radio wave into space. A receiver aerial connected to receiver equipment e.g. Radio, TV, or GSM set, comes across the wave radiated into the space and send them into the receiver equipment. At the receiver, the desired transmitter signal is selected, amplified and converted to the original message. Thus the information is then extracted out of the Radio waves.

SUB-TOPIC 2: DISTRIBUTION
The interconnection of the distribution lines forms the distribution system. This system operates at a much lower voltage than the transmission system; the operational voltages for distributions are normally 33KV and 11KV. These voltages are used by heavy based industries. For domestic consumers these voltages are further reduced or stepped down to 415V.The 415V lines are called the low voltage distribution lines. The lines are of 4-wire arrangement comprising three live-conductors and a neutral conductor.
The voltage across any two live conductors is 415V while the voltage across a live conductor and a neutral conductor, called the phase voltage, and is 240V.
Domestic consumers take a single-phase supply, i.e. their supply is connected between any one of the lines and the neutral conductor.
There are four available alternating current (A.C) supply system provided by PHCN PLC in Nigeria. They are: the single phase 2 wire system, the single phase 3 wire system, the three phase 3 wire system, the three phase 4 wire system. The three phase 4 wire system is the one that is mostly and widely used, because all other system could be readily obtained from it.
EVALUATION
1) Briefly describe how electricity is transmitted at:
i) High velocity
ii) Low velocity
2) Describe how electricity is distributed in Nigeria
Sub-Topic 3: Utilization of Electricity.
The electric power generated at any power station is transmitted through transmission lines and consumed in different homes and industries. Thus consumers of electricity are classified into two: domestic (the rate of electricity consumption is low) and commercial consumers (the rate of electricity consumption is very high).
Electric power is brought into the house through a meter box which monitors the amount of electrical energy consumed in a house.
The house and appliances are protected against possible fire out- break that could arise from the faulty equipment by installing Circuit breaker and fuses. The electric current is delivered to the house by using two wires conductors. Such as,
(i) The live wire (is the conductor through which the current flows in).
(ii) The Neutral wire (it is the conductor through which the current return out).
The electricity supply in a house is controlled by switch gear and fuses. The fuse box contains fuses. The function of each fuse is to prevent the overloading of the electrical cable.

SUB-TOPIC 4: MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT: TRANSFORMER, CABLES, INSULATORS, SEPARATORS, FUSES
THE TRANSFORMER: A transformer is a device used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. The transformer consist of two insulating coils; the primary coils, where the power is supplied, and the secondary coils where the power is obtained.
The transformer can be used to step-up voltage of an A.C. supply or to step-down voltage of an A.C supply.

THE INSULATOR: An insulator is a material that is resistant to the flow or passage of electric current. Therefore, insulators are used to prevent any kind of electrical shock.
Insulators are used in overhead transmission to hold the cable to the towers and poles. The common insulators are made of porcelain and glass. The three basic types of insulators are pin insulators, strain insulators and suspension insulators.

THE SEPARATOR: Our range of spacers or isolators are used for isolating the electrical power supply of electrical installations maintenance, cleaning or repair work. These protective systems are made using innovative engineering concepts that guarantees reliable performance.

THE FUSE: Fuses are metal resistors with the low resistance and low melting point. When the current is too high above the rating of the fuse, the fuse blow out and open the circuit. When the power consumed by the fuse raises the temperature of the metal too high, the metal melts and the fuse blows.
Fuses function to protect the electrical equipment from excessive current. Fuses are of different rating and types e.g. the renewable fuse, cartridge fuse, high breaking capacity fuse etc. the rating of the fuse you select should be slightly higher than the maximum current which you expect to flow in a circuit.

EVALUATION
I. Explain the function of the fuse
II. How is electricity utilized in Nigeria
ASSIGNMENT
What is a transformer and what are its functions?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Basic Technology for Junior Secondary school 2, UBE Edition, Chapter 11, pages 121 – 126 against next lesson
CONTENTS:
1. Transmission: Low frequency, High frequency
2. Distribution
3. Utilization
4. Materials and Equipment: transformer, cables, insulators, separators, fuses, etc.
SUB-TOPIC I: TRANSMISSION: LOW FREQUENCY, HIGH FREQUENCY.
Transmission of electricity is the movement of electricity from the point of generation to the point of consumption. This is done through transmission lines called cables. The transmission lines are made of copper wire coated with lead or aluminum, and the can be single or stranded. The line can be laid overhead or underground.

TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY AT LOW FREQUENCY
The number of cycle per second is called frequency, it unit is the Hertz. When Electricity is transmitted from the point of generation at a frequency of 50Hz (In Nigeria) or 60Hz (In America) to the final consumer, this type of transmission is said to be Low frequency transmission.
The generating station may be far from the towns or villages where the generated power is consumed.
Transmission is done at voltages much higher than those used in our home to operate electrical equipment and appliances. Transmission of electricity across towns and villages is made possible by building or stringing the 3 phases or 4-wire on concrete or wooden high tension poles planted along the high tension route. These high voltages are brought into domestic or industrial houses by the use of step-down transformers. Individuals domestic houses make use of either single-phase supply or 3-phase 4-wire gives a voltage of about 450-500 volts.

TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY AT HIGH FREQUENCY
Transmission at high frequency is done through electromagnetic waves or Radio waves. This is practically explains in the operation of a Radio communication system. The radio waves which are received in our radio and television sets are first generated and transmitted. In radio communication system, the message is given through a microphone connected to transmitter, which generate the radio wave at a high frequency. An aerial connected to the transmission line, sends out the radio wave into space. A receiver aerial connected to receiver equipment e.g. Radio, TV, or GSM set, comes across the wave radiated into the space and send them into the receiver equipment. At the receiver, the desired transmitter signal is selected, amplified and converted to the original message. Thus the information is then extracted out of the Radio waves.

SUB-TOPIC 2: DISTRIBUTION
The interconnection of the distribution lines forms the distribution system. This system operates at a much lower voltage than the transmission system; the operational voltages for distributions are normally 33KV and 11KV. These voltages are used by heavy based industries. For domestic consumers these voltages are further reduced or stepped down to 415V.The 415V lines are called the low voltage distribution lines. The lines are of 4-wire arrangement comprising three live-conductors and a neutral conductor.
The voltage across any two live conductors is 415V while the voltage across a live conductor and a neutral conductor, called the phase voltage, and is 240V.
Domestic consumers take a single-phase supply, i.e. their supply is connected between any one of the lines and the neutral conductor.
There are four available alternating current (A.C) supply system provided by PHCN PLC in Nigeria. They are: the single phase 2 wire system, the single phase 3 wire system, the three phase 3 wire system, the three phase 4 wire system. The three phase 4 wire system is the one that is mostly and widely used, because all other system could be readily obtained from it.

EVALUATION
1) Briefly describe how electricity is transmitted at:
i) High velocity
ii) Low velocity
2) Describe how electricity is distributed in Nigeria
Sub-Topic 3: Utilization of Electricity.
The electric power generated at any power station is transmitted through transmission lines and consumed in different homes and industries. Thus consumers of electricity are classified into two: domestic (the rate of electricity consumption is low) and commercial consumers (the rate of electricity consumption is very high).
Electric power is brought into the house through a meter box which monitors the amount of electrical energy consumed in a house.
The house and appliances are protected against possible fire out- break that could arise from the faulty equipment by installing Circuit breaker and fuses. The electric current is delivered to the house by using two wires conductors. Such as,
(i) The live wire (is the conductor through which the current flows in).
(ii) The Neutral wire (it is the conductor through which the current return out).
The electricity supply in a house is controlled by switch gear and fuses. The fuse box contains fuses. The function of each fuse is to prevent the overloading of the electrical cable.

SUB-TOPIC 4: MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT: TRANSFORMER, CABLES, INSULATORS, SEPARATORS, FUSES
THE TRANSFORMER: A transformer is a device used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. The transformer consist of two insulating coils; the primary coils, where the power is supplied, and the secondary coils where the power is obtained.
The transformer can be used to step-up voltage of an A.C. supply or to step-down voltage of an A.C supply.

THE INSULATOR: An insulator is a material that is resistant to the flow or passage of electric current. Therefore, insulators are used to prevent any kind of electrical shock.
Insulators are used in overhead transmission to hold the cable to the towers and poles. The common insulators are made of porcelain and glass. The three basic types of insulators are pin insulators, strain insulators and suspension insulators.

THE SEPARATOR: Our range of spacers or isolators are used for isolating the electrical power supply of electrical installations maintenance, cleaning or repair work. These protective systems are made using innovative engineering concepts that guarantees reliable performance.

THE FUSE: Fuses are metal resistors with the low resistance and low melting point. When the current is too high above the rating of the fuse, the fuse blow out and open the circuit. When the power consumed by the fuse raises the temperature of the metal too high, the metal melts and the fuse blows.
Fuses function to protect the electrical equipment from excessive current. Fuses are of different rating and types e.g. the renewable fuse, cartridge fuse, high breaking capacity fuse etc. the rating of the fuse you select should be slightly higher than the maximum current which you expect to flow in a circuit.

EVALUATION
I. Explain the function of the fuse
II. How is electricity utilized in Nigeria
ASSIGNMENT
What is a transformer and what are its functions?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Basic Technology for Junior Secondary school 2, UBE Edition, Chapter 11, pages 121 – 126 against next lesson
WEEK 7
MAIN TOPIC : Transmission of electricity at high frequency
SPECIFIC TOPIC : meaning and components of transmission at high frequency
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Define transmission of electricity at high frequency
(2) Mention all the components of radio communication
CONTENT
TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY AT HIGH FREQUENCY
Transmission of electricity at low frequency is simply the transfer of radio signal or sound wave through the space. The production of sound waves do not involves the use of transmission lines , unlike the transmission of electricity at low frequency. Typical examples of this transmission are radio and television communication, Global system of mobile communication i.e. GSM, Intercellular.
Radio communication is one of the methods of sending messages or disseminating information through sound waves.
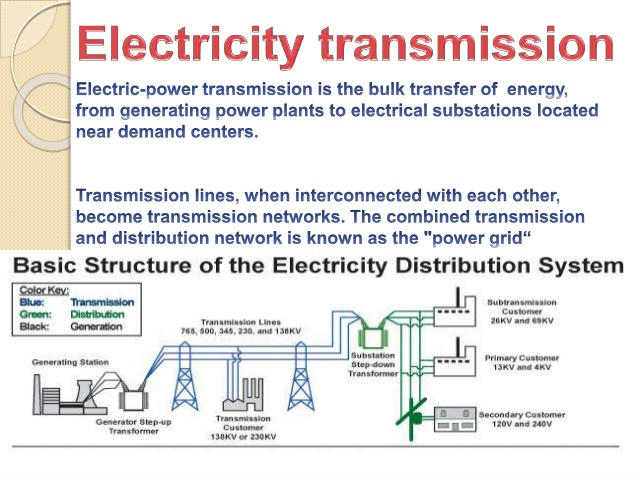
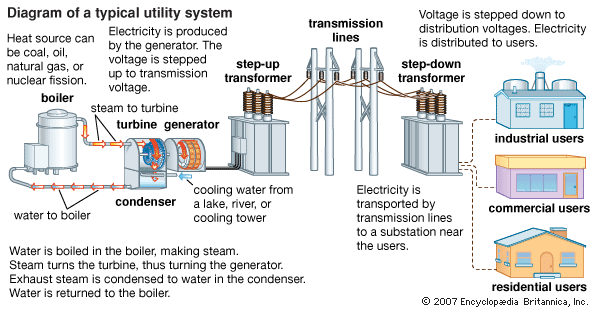
Basic Elements of Radio communication
i. Microphone
ii. Radio transmitter
iii. Transmitting aerial
iv. Receiving aerial
v. Radio receiver
vi. Loudspeaker

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Define transmission of electricity at high frequency
2. Mention all the differences between high and low frequency
3. Mention all the components of radio communication
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_p ... ansmission
http://www.bbemg.ulg.ac.be/en/general-i ... twork.html
LESSON 46
MAIN TOPIC : Transmission of electricity at high frequency
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Functions of Basic elements of radio communication
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Define transmission of electricity at high frequency
(2) Mention all the components of radio communication
CONTENT
Functions of elements of radio communication
1. Microphone
2. Radio transmitter
3. Transmitting aerial
4. Receiving aerial
5. Radio receiver
6. Loudspeaker
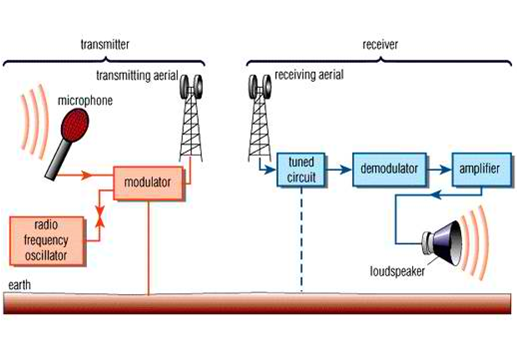
Microphone is a device that converts sound energy into electrical energy thereby controlling the radio waves based on the information to be transmitted.
Radio transmitter is equipment that generates the radio frequency waves.
Transmitting aerial - this is the device that sends and spread out radio waves into space.
Receiving aerial: This comes across and receives a portion of the radio waves that is radiated into space
Radio receiver: this will select and amplify the signal from the transmitter. Also, it will pick out the information from the radio waves.
Loudspeaker: this convert the electric energy ( i.e information signal in form of electric current) into sound energy, which is the original information given out.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Mention all the elements of radio transmission
2. Explain all the components of radio communication
further studies
https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Radio
http://physicswirelessconnection.wordpr ... on-system/
http://www.reference.com/browse/radio
practice test
http://pirate.shu.edu/~yatesdan/Tutorial.htm
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
SPECIFIC TOPIC : meaning and components of transmission at high frequency
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Define transmission of electricity at high frequency
(2) Mention all the components of radio communication
CONTENT
TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICITY AT HIGH FREQUENCY
Transmission of electricity at low frequency is simply the transfer of radio signal or sound wave through the space. The production of sound waves do not involves the use of transmission lines , unlike the transmission of electricity at low frequency. Typical examples of this transmission are radio and television communication, Global system of mobile communication i.e. GSM, Intercellular.
Radio communication is one of the methods of sending messages or disseminating information through sound waves.


Basic Elements of Radio communication
i. Microphone
ii. Radio transmitter
iii. Transmitting aerial
iv. Receiving aerial
v. Radio receiver
vi. Loudspeaker

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Define transmission of electricity at high frequency
2. Mention all the differences between high and low frequency
3. Mention all the components of radio communication
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_p ... ansmission
http://www.bbemg.ulg.ac.be/en/general-i ... twork.html
LESSON 46
MAIN TOPIC : Transmission of electricity at high frequency
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Functions of Basic elements of radio communication
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Define transmission of electricity at high frequency
(2) Mention all the components of radio communication
CONTENT
Functions of elements of radio communication
1. Microphone
2. Radio transmitter
3. Transmitting aerial
4. Receiving aerial
5. Radio receiver
6. Loudspeaker

Microphone is a device that converts sound energy into electrical energy thereby controlling the radio waves based on the information to be transmitted.
Radio transmitter is equipment that generates the radio frequency waves.
Transmitting aerial - this is the device that sends and spread out radio waves into space.
Receiving aerial: This comes across and receives a portion of the radio waves that is radiated into space
Radio receiver: this will select and amplify the signal from the transmitter. Also, it will pick out the information from the radio waves.
Loudspeaker: this convert the electric energy ( i.e information signal in form of electric current) into sound energy, which is the original information given out.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Mention all the elements of radio transmission
2. Explain all the components of radio communication
further studies
https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Radio
http://physicswirelessconnection.wordpr ... on-system/
http://www.reference.com/browse/radio
practice test
http://pirate.shu.edu/~yatesdan/Tutorial.htm
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0 ... _quiz.html
WEEK 8
MAIN TOPIC : Distribution of electricity
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Distribution of electricity
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the distribution methods in Nigeria
(2) Mention the different wiring system
CONTENT
DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRICITY IN NIGERIA
The generation and distribution of electricity in Nigeria is carried out with alternating current (ac). This is simply because it can be converted by transformer (step up and step down) into higher and lower voltages.
The major distribution systems in Nigeria for both domestic and industrial consumer are:
Single phase 2-wires
Single phase 3-wires
Three phase 3-wires
Three phase 4-wires
Three phase 4-wires is of high importance because other systems can be obtained from it.
TYPES OF WIRING SYSTEM
1. Surface wiring system


2. Conduit wiring system

3. Trunking wiring system
further studies
http://looksmart.hubpages.com/hub/Types ... cal-wiring
http://electrical.about.com/od/typesofe ... fwires.htm
http://www.ehow.com/how_8486646_hide-su ... iring.html
http://www.familyhandyman.com/electrica ... t/view-all
http://www.csunderlal.com/pvc_conduit_pipes.asp
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_conduit
LESSON 48
MAIN TOPIC : Building Construction
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Site preparation
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. explain site location
ii. mention the step in site preparation
CONTENT
BUILDING CONSTRUCTION
Building Construction, procedures involved in the erection of various types of structures. The major trend in present-day construction continues away from handcrafting at the building site and toward on-site assembly of ever larger, more integrated sub assemblies manufactured away from the site.

SITE LOCATION
The preparation of site work must follow the following steps before the real site work which is the clearing of the place.
1. Choice of site : the choice of site is determined by the owner i.e. the Client and not the Builder
2. Access to site : this is the studying and construction of access road to the site by the builder.
3. Temporary water and electricity provision: It becomes necessary for the contractor to have water and electricity connected to the site.
4. Shelter for workmen and materials.
SITE PREPARATION
All building sites are not the same. The way a building site is prepared for construction depends on three main factors which are:
1. location of site
2. The type of building
3. The type of site
After the location of the building the next action is to design the building drawing which is prepared by the Architect. The steps in site preparation are:
1. Movement of site preparation equipments and tools
2. Site Clearing and removal of vegetable soil, where necessary
3. Leveling of site , where necessary
4. Setting out the building line
5. Setting up of temporary
Site preparation tools and equipments
Mechanical tools and equipment for site preparation are used in big construction works. They are used to speed up heavy duty work the major mechanical plant or equipment for site preparation are :
Tractors shovel
Graders
Levelers
Bulldozers
Excavator
Power Chain Saw
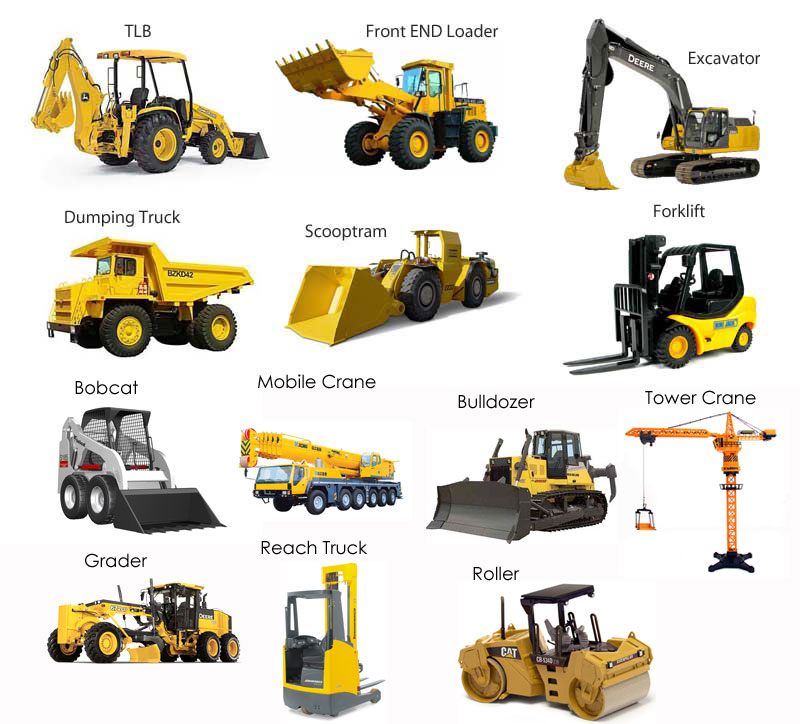

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Write all the necessary things that you will need in an area to build your house there
further studies
http://www.ncturfgrass.com/sodpage/site ... tion_steps
http://www.propertyobserver.com.au/land ... 2062755311
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... house2.htm
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... house3.htm
http://www.homedesigndirectory.com.au/c ... tion.shtml
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Distribution of electricity
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the distribution methods in Nigeria
(2) Mention the different wiring system
CONTENT
DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRICITY IN NIGERIA
The generation and distribution of electricity in Nigeria is carried out with alternating current (ac). This is simply because it can be converted by transformer (step up and step down) into higher and lower voltages.
The major distribution systems in Nigeria for both domestic and industrial consumer are:
Single phase 2-wires
Single phase 3-wires
Three phase 3-wires
Three phase 4-wires
Three phase 4-wires is of high importance because other systems can be obtained from it.
TYPES OF WIRING SYSTEM
1. Surface wiring system


2. Conduit wiring system

3. Trunking wiring system

further studies
http://looksmart.hubpages.com/hub/Types ... cal-wiring
http://electrical.about.com/od/typesofe ... fwires.htm
http://www.ehow.com/how_8486646_hide-su ... iring.html
http://www.familyhandyman.com/electrica ... t/view-all
http://www.csunderlal.com/pvc_conduit_pipes.asp
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_conduit
LESSON 48
MAIN TOPIC : Building Construction
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Site preparation
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. explain site location
ii. mention the step in site preparation
CONTENT
BUILDING CONSTRUCTION
Building Construction, procedures involved in the erection of various types of structures. The major trend in present-day construction continues away from handcrafting at the building site and toward on-site assembly of ever larger, more integrated sub assemblies manufactured away from the site.

SITE LOCATION
The preparation of site work must follow the following steps before the real site work which is the clearing of the place.
1. Choice of site : the choice of site is determined by the owner i.e. the Client and not the Builder
2. Access to site : this is the studying and construction of access road to the site by the builder.
3. Temporary water and electricity provision: It becomes necessary for the contractor to have water and electricity connected to the site.
4. Shelter for workmen and materials.
SITE PREPARATION
All building sites are not the same. The way a building site is prepared for construction depends on three main factors which are:
1. location of site
2. The type of building
3. The type of site
After the location of the building the next action is to design the building drawing which is prepared by the Architect. The steps in site preparation are:
1. Movement of site preparation equipments and tools
2. Site Clearing and removal of vegetable soil, where necessary
3. Leveling of site , where necessary
4. Setting out the building line
5. Setting up of temporary
Site preparation tools and equipments
Mechanical tools and equipment for site preparation are used in big construction works. They are used to speed up heavy duty work the major mechanical plant or equipment for site preparation are :
Tractors shovel
Graders
Levelers
Bulldozers
Excavator
Power Chain Saw

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Write all the necessary things that you will need in an area to build your house there
further studies
http://www.ncturfgrass.com/sodpage/site ... tion_steps
http://www.propertyobserver.com.au/land ... 2062755311
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... house2.htm
http://home.howstuffworks.com/home-impr ... house3.htm
http://www.homedesigndirectory.com.au/c ... tion.shtml
WEEK 9
TOPIC: SITE PREPARATION
CONTENTS
(i) Tools for site preparation
(ii) Techniques for site preparation
SUB-TOPIC 1:TOOLS FOR SITE PREPARATION.
More often than not, the site of a new building is on virgin or agricultural land. It is necessary to prepare the land for the erection of a building by clearing the site, demolishing old structure, removing the top soil and grubbing out roots.
Site preparation can be done manually and also mechanically. The following are the hand tools for site preparation:
• Cutlass: used to cut grass, clear bush, cut tree at site
• Hoe: this is used for breaking up soil and removing weeds at site.
• Axe: used for chopping wood and cutting trees.
• Digger: used to make hole in the ground, also used to demolish unwanted mass of sand or materials on the building site.
• Shovel: or packing refuse, sand into another container.
• Wheel barrow: for transporting refuse, grass, sand and other materials.

Mechanical plants for site preparation include:
- Bull dozer: used to push down unwanted structures for excavating the soil.
- Tractor shovel (pay loader): for lifting large quantity of loose materials at a time and loading the same into truck or lorry tipper.
- Grader: used for leveling the site, cutting and filling all holes and gullies, for final leveling of the excavated areas.
EVALUATION
List 5 preparation tools and state their functions
SUB-TOPIC 2: TECHNIQUES FOR SITE PREPARATION
• Grubbing out roots and leveling the soil: grubbing out of roots can be done manually with diggers, cutlasses and shovels.. if the stump is big, the removal is best done by the use of mechanical plants e.g bull dozer. The leveling is done after the removal of all stumps either manually or mechanically using scrapers or graders. Valleys are filled and hills are lowered.
• Exterminating insects and fungi: the presence of insects and fungi in buildings causes decay because these insects and fungi feed on timber. Where the presence of these insects is discovered on a building site, preservatives should be applied.
• Removal of the top soil. The top soils are removed to a depth of about 150mm and herbicides are applied to prevent weeds growing on the site.
• Soil investigation: this is carried out in order to determine the bearing capacity of the soil.
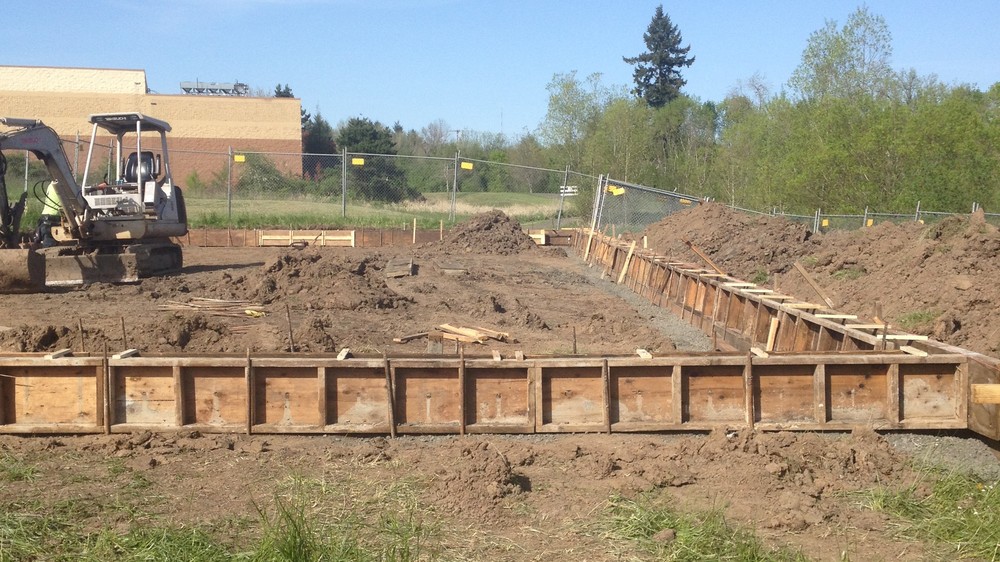

EVALUATION
1. Name the stages involved in the preparation of a site for a building.
2. Explain the meaning of site preparation.
3. Name the various means of removing vegetation on a building site.
READING ASSIGNMENT
read about setting out of a building.
TEXT : NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 Chapter 11 pgs 123-126 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT
Study the questions on page 126 of your text book and answer all .
TOPIC: SETTING OUT AND MATERIALS
CONTENTS:
i) Setting out materials.
(ii) Setting out techniques.
SUB TOPICS 1: SETTING OUT MATERIALS.
Setting out of a building is the process of transferring or establishing the foundation plan of any building structure in full to the ground with high degree of accuracy using surveying techniques and instruments. To set out a building on a site requires the knowledge of building drawing, and the ability to read drawings accurately as any mistake made at this point may be costly to correct at a later stage; and it could spoil the building project.

Settings out materials include:
• Pegs: these are wooden pieces hammered into the ground to mark points which are read from the building plan.
• Lines: ropes are tied to the pegs to represent lines which demarcate the excavation pits needed for the placement of the foundation of the building or structure.
• Tapes: these are used for measuring.
• Builders’ square: it is a tool used to mark out angles on site.
• Building plans: are the approved drawings or blue prints for the project which is been undertaken.
• Plumb: this is a tool used to establish properly aligned vertical on the building site. It is also used to align walls, columns, beams and other building parts to desirable angles.
• Hammer: a hammer is used to drive pegs into the ground.
• Profile board: these are used to mark the outer limits of the areas of the foundation.
• Theodolite: this is also used for setting out building
• Sliding Bevel:
• Compasses
EVALUATION
1. what is setting out?
2. Name any 5 materials used for setting out and state what each is used for.
SUB-TOPIC 2: SETTING OUT TECHNIQUES
Techniques of setting out a building include:
• 3-4-5 method
• Builders square method
EVALUATION
1. List the setting out techniques that you know.
2. Outlines the steps involved in any one setting out technique mentioned in (1) above.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Students should read about simple maintenance of common goods against the next lesson.
TEXT: NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 Chapter 12 pgs 127-141 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw all the setting out materials that you know
Topic: Site Preparation.
- Classification of tools/plants used for site preparation.
http://www.ehow.com/list_7650037_tools- ... ation.html
http://reveg-catalog.tamu.edu/07-Site%20Preparation.htm

[youtube]https://youtu.be/2nk_GVQSfBE[/youtube]
Topic: Setting out:
- Definition, tools used during setting out,

http://autonopedia.org/buildings-and-sh ... tting-out/
http://www.gmsurveys.co.uk/setting_out
- Excavation/timbering


http://www.civilmania.com/forum/topic/1 ... timbering/
http://www.anthonyoconnor.co.uk/?gclid= ... tAodHnoA6g
CONTENTS
(i) Tools for site preparation
(ii) Techniques for site preparation
SUB-TOPIC 1:TOOLS FOR SITE PREPARATION.
More often than not, the site of a new building is on virgin or agricultural land. It is necessary to prepare the land for the erection of a building by clearing the site, demolishing old structure, removing the top soil and grubbing out roots.
Site preparation can be done manually and also mechanically. The following are the hand tools for site preparation:
• Cutlass: used to cut grass, clear bush, cut tree at site
• Hoe: this is used for breaking up soil and removing weeds at site.
• Axe: used for chopping wood and cutting trees.
• Digger: used to make hole in the ground, also used to demolish unwanted mass of sand or materials on the building site.
• Shovel: or packing refuse, sand into another container.
• Wheel barrow: for transporting refuse, grass, sand and other materials.

Mechanical plants for site preparation include:
- Bull dozer: used to push down unwanted structures for excavating the soil.
- Tractor shovel (pay loader): for lifting large quantity of loose materials at a time and loading the same into truck or lorry tipper.
- Grader: used for leveling the site, cutting and filling all holes and gullies, for final leveling of the excavated areas.
EVALUATION
List 5 preparation tools and state their functions
SUB-TOPIC 2: TECHNIQUES FOR SITE PREPARATION
• Grubbing out roots and leveling the soil: grubbing out of roots can be done manually with diggers, cutlasses and shovels.. if the stump is big, the removal is best done by the use of mechanical plants e.g bull dozer. The leveling is done after the removal of all stumps either manually or mechanically using scrapers or graders. Valleys are filled and hills are lowered.
• Exterminating insects and fungi: the presence of insects and fungi in buildings causes decay because these insects and fungi feed on timber. Where the presence of these insects is discovered on a building site, preservatives should be applied.
• Removal of the top soil. The top soils are removed to a depth of about 150mm and herbicides are applied to prevent weeds growing on the site.
• Soil investigation: this is carried out in order to determine the bearing capacity of the soil.

EVALUATION
1. Name the stages involved in the preparation of a site for a building.
2. Explain the meaning of site preparation.
3. Name the various means of removing vegetation on a building site.
READING ASSIGNMENT
read about setting out of a building.
TEXT : NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 Chapter 11 pgs 123-126 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT
Study the questions on page 126 of your text book and answer all .
TOPIC: SETTING OUT AND MATERIALS
CONTENTS:
i) Setting out materials.
(ii) Setting out techniques.
SUB TOPICS 1: SETTING OUT MATERIALS.
Setting out of a building is the process of transferring or establishing the foundation plan of any building structure in full to the ground with high degree of accuracy using surveying techniques and instruments. To set out a building on a site requires the knowledge of building drawing, and the ability to read drawings accurately as any mistake made at this point may be costly to correct at a later stage; and it could spoil the building project.

Settings out materials include:
• Pegs: these are wooden pieces hammered into the ground to mark points which are read from the building plan.
• Lines: ropes are tied to the pegs to represent lines which demarcate the excavation pits needed for the placement of the foundation of the building or structure.
• Tapes: these are used for measuring.
• Builders’ square: it is a tool used to mark out angles on site.

• Building plans: are the approved drawings or blue prints for the project which is been undertaken.
• Plumb: this is a tool used to establish properly aligned vertical on the building site. It is also used to align walls, columns, beams and other building parts to desirable angles.
• Hammer: a hammer is used to drive pegs into the ground.
• Profile board: these are used to mark the outer limits of the areas of the foundation.
• Theodolite: this is also used for setting out building
• Sliding Bevel:
• Compasses
EVALUATION
1. what is setting out?
2. Name any 5 materials used for setting out and state what each is used for.
SUB-TOPIC 2: SETTING OUT TECHNIQUES
Techniques of setting out a building include:
• 3-4-5 method


• Builders square method

EVALUATION
1. List the setting out techniques that you know.
2. Outlines the steps involved in any one setting out technique mentioned in (1) above.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Students should read about simple maintenance of common goods against the next lesson.
TEXT: NERDC BASIC TECHNOLOGY For Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 Chapter 12 pgs 127-141 BY G.NNneji et al.
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw all the setting out materials that you know
Topic: Site Preparation.
- Classification of tools/plants used for site preparation.
http://www.ehow.com/list_7650037_tools- ... ation.html
http://reveg-catalog.tamu.edu/07-Site%20Preparation.htm

[youtube]https://youtu.be/2nk_GVQSfBE[/youtube]
Topic: Setting out:
- Definition, tools used during setting out,

http://autonopedia.org/buildings-and-sh ... tting-out/
http://www.gmsurveys.co.uk/setting_out
- Excavation/timbering


http://www.civilmania.com/forum/topic/1 ... timbering/
http://www.anthonyoconnor.co.uk/?gclid= ... tAodHnoA6g
