SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1 Roles of Science and Technology in Agriculture
2 Roles of Government Agencies in Agriculture
3-6 Detailed Revision of JS 1-3 work
7 Mock Examinations
8-12 Revision and (BECE or JSC) Examinations
3RD TERM
WEEK 1
TOPIC: ROLES OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN AGRICULTURE
CONTENTS: 1. Meaning of (i) Science and (ii) Technology
2. Application of Science and Technology to Agriculture
3. Factors Affecting the Application of Science and Technology in Agriculture
Sub-Topic: MEANING OF (I) SCIENCE AND (II) TECHNOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
The urgent need of man as a result of increase in the population world over is how to improve the quantity, quality and variety of his production. Any country that desires to develop its agricultural system must apply science and technology in the production, processing, preservation and marketing of food and fibre.
MEANING OF SCIENCE:
Science can be defined as a branch of study which deals with the acquisition of knowledge through observations and testing out facts which are arranged systematically.

Meaning of Technology:
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge for the production of useful things. It is also means any innovation which will lead to improvement on the old ways of doing things.

Meaning of Science and Technology:
Science and Technology refer to the acquisition and application of knowledge for the production of useful things with increased productivity from minimum effort. Technology started with the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century, with the introduction of power-driven machinery which took over the work originally done manually. This affected agriculture because machines were introduced to carry out agricultural activities (this is called Mechanized Agriculture/Farming). Through science and technology large hectares of land can be cultivated with better methods and increased yields. The advanced countries of the world like USA, Britain, Germany, France, China etc have succeeded in using machines to improve agricultural production thus increase their efficiency from little effort.


EVALUATION
1. What do you understand by science?
2. Define Technology
3. Differentiate between science and technology.
4. Where did Industrial Revolution started and when?
Sub-Topic 2: APPLICATION OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN AGRICULTURE
Science and Technology play major roles in the development of agriculture in developed and developing countries by providing means of solving varied problems facing their farmers. The population of some countries, particularly Nigeria is growing to an alarming proportion with the result that it has become difficult to feed the people. To meet up with the food requirement of the growing population, such countries must apply science and technology. The contributions of science and technology to agricultural development are the following:
1. Farm Power and Machinery: Science and Technology have helped in inventing various machines such as tractors, tractor-coupled implements, crop protection machines, milking machines, incubators, processing machines etc to improve agric production.


2. Understanding of Climate (climatology) and weather (meteorology) conditions of different places and consequently the type of farming system suitable for such places.
3. Improved Planting Materials: seeds and seedlings through Biotechnology (modification of living things to make useful products that can be beneficial to man) like Tissue culture, Plant genetic modification, Molecular breeding, Marcotting or Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (in animals).
4. Pest and Disease Control (management): A large percentage of farm products are lost annually to diseases, pests and weeds. With the knowledge of science and technology, many chemicals such as insecticides, fungicides, nematicides, fumigants, herbicides (weedicides) etc have been developed to wage war against these enemies thereby prevent crop failure.
5. Plant and Animal Nutrition: With the knowledge gained from science, man has been able to study the mineral content of the soil and the type of soil needed for crop growth. In addition, the study of feeds and feeding has also revealed that the quantity and quality of livestock products depend on the quality and quantity of feeds given to them.
6. Harvesting, Processing and Packaging: In large farms, crops are harvested with the use of machines like combine harvester for cereal grain crops, root crop harvester for cassava, forage harvester etc. Machines like shellers, threshers are used to process crops such as cereals and legumes. Food packaging of agricultural produce helps to preserve produce from losses. Through the application of science and technology, food items can be packed in cans, plastic bags for easy storage or sale.

7. Storage of Agricultural Produce: One of the challenges facing farmers is how to store their farm produce as soon as they are harvested. Lack of good storage facilities and methods have caused serious losses of agric products via pests, diseases and even the weather. However, with the help of science and technology, many storage facilities have been invented to reduce the loss caused by the spoilage pests and micro-organisms. Storage of farm produce has been encouraged in Nigeria by the establishment of a special research institute, known as the Nigerian Stored Products Research Institute (NSPRI), with the headquarters based at Ilorin in Kwara state.
8. Transport and Communication: Transportation makes the distribution of farm produce to different markets for sale. It makes both internal and external trade easy. Different types of communication equipment have been invented such as Radio, TV, Newspaper, Journals, Magazines, Cellular telephones, The Internet (Google, Wikipedia, African Agriculture) etc for easy dissemination of important information about various modern agric practices developed in research centers for the benefit of farmers in the rural areas.
9. Plant and Animal Improvement: The science of plant and animal breeding has made it possible to cross plants or animals of different desirable qualities to produce hybrids which are high yielding and resistant to some common pests and diseases.
10. Water Supply: Agricultural production depends on natural water which may not always be sufficient. With the help of science and technology bore holes, deep wells water reservoirs, dams and irrigation systems have been constructed to supply water to the farms and villages. With this farming can be done throughout the year in many of the drier areas.

11. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for Agriculture: This involves acquiring agricultural information by using computers, fixed and mobile telephones, listening to agric programmes on radio, watching programmes on TV or videos showing the best ways of growing crops, taking care of livestock or even selling agricultural produce.
12. Agricultural Research Centres: The purpose of conducting agric research is to study and understand the major problems facing farmers and other people involved in crop farming, livestock, fisheries and forestry production in different areas and how to develop ways of reducing the problems identified. An agricultural research institute plays major roles in the application of science and technology to agriculture and is intended to develop new ways of practicing agriculture and thereby improve its production.
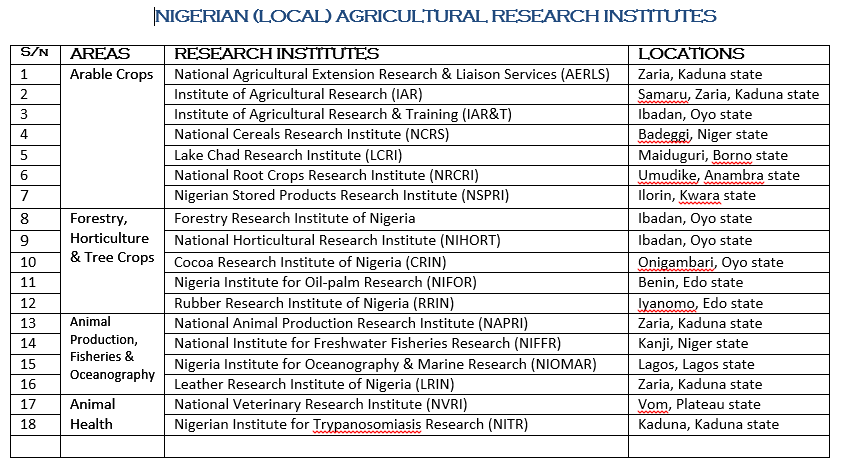
FOREIGN (INTERNATIONAL) AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH INSTITUTES IN NIGERIA
S/N RESEARCH INSTITUTES LOCATION
1 International Institute for Tropical Agriculture (IITA) Ibadan, Oyo state
2 The West-Africa Rice Development Association-Africa Rice Centre (WARDA) Ibadan, Oyo state
3 International Crop Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) Kano, Kano state
4 International Livestock Centre for Africa (ILCA)
5 International Centre for Research in Agro-Forestry
ROLES OF RESEARCH INSTITUTES IN AGRICULTURE
1. Development of improved planting materials
2. Improvement in animal production
3. Use of natural enemies and disease agents to control pests
4. Use of chemical fertilizers to improve soil fertility
5. Improved water supply through irrigation
6. Efficient use of pesticides to control pests and diseases
7. Improved harvesting, storage, processing and packaging methods
8. Better methods of marketing agricultural produce
EVALUATION
1. State seven roles of science and technology in agriculture
2. What do you understand by climatology and meteorology?
3. Mention eight powered tools that replaced crude implements
4. What do you understand by Biotechnology?
5. Mention three methods of Biotechnology.
6. Mention 10 local Research Centers and 5 foreign Research Centers.
Sub-Topic 3: FACTORS AFFECTING APPLICATION OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN AGRICULTURE:
Several factors affect the proper and successful application of science and technology in agriculture. These factors include:
Economic/Financial factors
Unavailability of farmland
Conservatism/Unwillingness to adopt scientific methods by the local farmers
Illiteracy/Ignorance of farmers
Availability of market information and facilities.
EVALUATION
State five factors that can affect application of science and technology in agriculture
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Why is it necessary to apply the knowledge gained from science and technology to food production?
2. As a student, how has science and technology been of benefit to you?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Junior Secondary Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 2 pages 209-223
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. Junior Secondary Agriculture for Nigerian Schools by Anthony et al.
2. Essential of Agricultural Science for JSS by EC Anie.
CONTENTS: 1. Meaning of (i) Science and (ii) Technology
2. Application of Science and Technology to Agriculture
3. Factors Affecting the Application of Science and Technology in Agriculture
Sub-Topic: MEANING OF (I) SCIENCE AND (II) TECHNOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
The urgent need of man as a result of increase in the population world over is how to improve the quantity, quality and variety of his production. Any country that desires to develop its agricultural system must apply science and technology in the production, processing, preservation and marketing of food and fibre.
MEANING OF SCIENCE:
Science can be defined as a branch of study which deals with the acquisition of knowledge through observations and testing out facts which are arranged systematically.

Meaning of Technology:
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge for the production of useful things. It is also means any innovation which will lead to improvement on the old ways of doing things.

Meaning of Science and Technology:
Science and Technology refer to the acquisition and application of knowledge for the production of useful things with increased productivity from minimum effort. Technology started with the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century, with the introduction of power-driven machinery which took over the work originally done manually. This affected agriculture because machines were introduced to carry out agricultural activities (this is called Mechanized Agriculture/Farming). Through science and technology large hectares of land can be cultivated with better methods and increased yields. The advanced countries of the world like USA, Britain, Germany, France, China etc have succeeded in using machines to improve agricultural production thus increase their efficiency from little effort.


EVALUATION
1. What do you understand by science?
2. Define Technology
3. Differentiate between science and technology.
4. Where did Industrial Revolution started and when?
Sub-Topic 2: APPLICATION OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN AGRICULTURE
Science and Technology play major roles in the development of agriculture in developed and developing countries by providing means of solving varied problems facing their farmers. The population of some countries, particularly Nigeria is growing to an alarming proportion with the result that it has become difficult to feed the people. To meet up with the food requirement of the growing population, such countries must apply science and technology. The contributions of science and technology to agricultural development are the following:
1. Farm Power and Machinery: Science and Technology have helped in inventing various machines such as tractors, tractor-coupled implements, crop protection machines, milking machines, incubators, processing machines etc to improve agric production.


2. Understanding of Climate (climatology) and weather (meteorology) conditions of different places and consequently the type of farming system suitable for such places.
3. Improved Planting Materials: seeds and seedlings through Biotechnology (modification of living things to make useful products that can be beneficial to man) like Tissue culture, Plant genetic modification, Molecular breeding, Marcotting or Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (in animals).
4. Pest and Disease Control (management): A large percentage of farm products are lost annually to diseases, pests and weeds. With the knowledge of science and technology, many chemicals such as insecticides, fungicides, nematicides, fumigants, herbicides (weedicides) etc have been developed to wage war against these enemies thereby prevent crop failure.
5. Plant and Animal Nutrition: With the knowledge gained from science, man has been able to study the mineral content of the soil and the type of soil needed for crop growth. In addition, the study of feeds and feeding has also revealed that the quantity and quality of livestock products depend on the quality and quantity of feeds given to them.
6. Harvesting, Processing and Packaging: In large farms, crops are harvested with the use of machines like combine harvester for cereal grain crops, root crop harvester for cassava, forage harvester etc. Machines like shellers, threshers are used to process crops such as cereals and legumes. Food packaging of agricultural produce helps to preserve produce from losses. Through the application of science and technology, food items can be packed in cans, plastic bags for easy storage or sale.

7. Storage of Agricultural Produce: One of the challenges facing farmers is how to store their farm produce as soon as they are harvested. Lack of good storage facilities and methods have caused serious losses of agric products via pests, diseases and even the weather. However, with the help of science and technology, many storage facilities have been invented to reduce the loss caused by the spoilage pests and micro-organisms. Storage of farm produce has been encouraged in Nigeria by the establishment of a special research institute, known as the Nigerian Stored Products Research Institute (NSPRI), with the headquarters based at Ilorin in Kwara state.
8. Transport and Communication: Transportation makes the distribution of farm produce to different markets for sale. It makes both internal and external trade easy. Different types of communication equipment have been invented such as Radio, TV, Newspaper, Journals, Magazines, Cellular telephones, The Internet (Google, Wikipedia, African Agriculture) etc for easy dissemination of important information about various modern agric practices developed in research centers for the benefit of farmers in the rural areas.
9. Plant and Animal Improvement: The science of plant and animal breeding has made it possible to cross plants or animals of different desirable qualities to produce hybrids which are high yielding and resistant to some common pests and diseases.
10. Water Supply: Agricultural production depends on natural water which may not always be sufficient. With the help of science and technology bore holes, deep wells water reservoirs, dams and irrigation systems have been constructed to supply water to the farms and villages. With this farming can be done throughout the year in many of the drier areas.

11. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for Agriculture: This involves acquiring agricultural information by using computers, fixed and mobile telephones, listening to agric programmes on radio, watching programmes on TV or videos showing the best ways of growing crops, taking care of livestock or even selling agricultural produce.
12. Agricultural Research Centres: The purpose of conducting agric research is to study and understand the major problems facing farmers and other people involved in crop farming, livestock, fisheries and forestry production in different areas and how to develop ways of reducing the problems identified. An agricultural research institute plays major roles in the application of science and technology to agriculture and is intended to develop new ways of practicing agriculture and thereby improve its production.

FOREIGN (INTERNATIONAL) AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH INSTITUTES IN NIGERIA
S/N RESEARCH INSTITUTES LOCATION
1 International Institute for Tropical Agriculture (IITA) Ibadan, Oyo state
2 The West-Africa Rice Development Association-Africa Rice Centre (WARDA) Ibadan, Oyo state
3 International Crop Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) Kano, Kano state
4 International Livestock Centre for Africa (ILCA)
5 International Centre for Research in Agro-Forestry
ROLES OF RESEARCH INSTITUTES IN AGRICULTURE
1. Development of improved planting materials
2. Improvement in animal production
3. Use of natural enemies and disease agents to control pests
4. Use of chemical fertilizers to improve soil fertility
5. Improved water supply through irrigation
6. Efficient use of pesticides to control pests and diseases
7. Improved harvesting, storage, processing and packaging methods
8. Better methods of marketing agricultural produce
EVALUATION
1. State seven roles of science and technology in agriculture
2. What do you understand by climatology and meteorology?
3. Mention eight powered tools that replaced crude implements
4. What do you understand by Biotechnology?
5. Mention three methods of Biotechnology.
6. Mention 10 local Research Centers and 5 foreign Research Centers.
Sub-Topic 3: FACTORS AFFECTING APPLICATION OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN AGRICULTURE:
Several factors affect the proper and successful application of science and technology in agriculture. These factors include:
Economic/Financial factors
Unavailability of farmland
Conservatism/Unwillingness to adopt scientific methods by the local farmers
Illiteracy/Ignorance of farmers
Availability of market information and facilities.


EVALUATION
State five factors that can affect application of science and technology in agriculture
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Why is it necessary to apply the knowledge gained from science and technology to food production?
2. As a student, how has science and technology been of benefit to you?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Junior Secondary Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 2 pages 209-223
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. Junior Secondary Agriculture for Nigerian Schools by Anthony et al.
2. Essential of Agricultural Science for JSS by EC Anie.
WEEK 2
TOPIC: ROLES OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES IN AGRICULTURE
CONTENT: 1. Meaning and Forms of Government Agencies
2. Roles of Government Agencies in Agriculture
Sub-Topic 1: MEANING OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
Agency means an administrative division or department (within a government) providing a particular service for a state. Government Agencies are the administrative departments responsible for development of agriculture in the rural areas in order to boost food production.
FORMS OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
The government agencies in agriculture include the following:
1. Farm Settlement Scheme
2. Agricultural Development Programme/Project (ADP)
3. River Basin Development Authority and Rural Development Programmes
4. Operation Feed the Nation, Green Revolution and School-to-Land Programmes
5. Agricultural Loan Scheme and Subsidy on Agricultural inputs
6. Farm Insurance Scheme
7. National Fadama Development Project (NFDP)
8. National Agricultural Technical Support Project (NATSP)
9. National Agricultural Research Institutes
10. Agricultural Training Institutes
11. Information and Communication Support for agric growth in Nigeria (ICS-NIGERIA)
EVALUATION
1. Define government agencies
2. Mention five government agencies you know.
3. What is the full meaning of the following: NFDP, NATSP, ADP, OFN and ICS-Nigeria?
Sub-Topic 3: ROLES OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES IN AGRICULTURE
Farm Settlement Scheme: This program first started in the former Western Nigeria in 1959 with the aim of increasing agricultural production through the development of modern farming systems; discouraging young school leavers from migrating to the cities in search of office and factory jobs by providing them with necessary equipment for farming after they might have been trained in farm institutes for about two years.

AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME:
It is a set of rural based agric programmes established with emphasis on improving infra-structural facilities especially rural roads, rural electricity and rural water supply which will lead to increase in agricultural production and thereby improving the living standard of the farmers.
RIVER BASIN DEVELOPMENT AUTHORITIES AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES:
These were set up in many states of the country principally to cultivate the land and help the farmers with the production and marketing of agric produce from the farm. They also carry out rural development by providing rural farmers with infra-structural facilities.
AGRICULTURAL LOAN SCHEME AND SUBSIDY ON AGRIC INPUTS:
State and federal governments have established loan/credit schemes to farmers through commercial banks at low and considerable interest rates for agriculture. This is repayable assistance. Subsidy has been provided to farmers (in cash or kind) for the purchase of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers, fungicides, insecticides, herbicides and improved seeds at considerably reduced rates. This is non-repayable assistance.
OPERATION FEED THE NATION; GREEN REVOLUTION AND SCHOOL-TO-LAND PROGRAMMES: These three programmes were introduced by the former military presidents-Lt Gen Olusegun Obasanjo (1976); Alhaji Shehu Shagari (1980)and Gen Muhammad Buhari (1984) respectfully to encourage people to farm and return to their abandoned farms.
NATIONAL RESEARCH INSTITUTES:
Research is an advanced stage of study which deals mainly with discovering the unknown by careful and diligent search (i.e. the application of science and technology) and their discoveries are adopted by the farmers and other people involved in agriculture to improve the methods and practices they use thereby increase food production.
NATIONAL AGRICULTURAL TECHNICAL SUPPORT PROJECT (NATSP):
This is a nationally coordinated programmes designed to assist in the development and dissemination of agricultural innovations (technologies) to small scale farmers through regular field training by agricultural extension agents.
NATIONAL FADAMA DEVELOPMENT PROJECT (NFDP):
This is generally known as Fadama II and is a World Bank assisted project aim at assisting Fadama resource users to make them economically successful. It also supports production, processing and marketing of crops, livestock and fisheries in addition to development of rural infrastructures; acquisition of agro-processing equipment, tools and vehicles; settling conflict between farmers and pastoralists thus save the wanton destruction of lives and farm produce.
AGRICULTURAL TRAINING INSTITUTES:
In Nigeria, efforts have been made to establish several agricultural schools, colleges and universities to train and develop people with adequate agricultural science knowledge and skills required for agricultural development. The faculties and universities also conduct research to develop improved crop/animal varieties that are high yielding and resistant or tolerant to pests and diseases. This is to achieve food security and self sufficiency in industrial raw materials.
ICS-NIGERIA:
The Information and Communication Support for agricultural growth (ICS-Nigeria) project is involved in the dissemination of agric information to farmers through locations called ICS Resource Centres which are located in the state ADP headquarters. They support and sponsor radio programmes as well as production of materials such as extension guides, booklets, pictures, posters and other materials.
FARM INSURANCE SCHEME:
Insurance, legal contract, protects people from the financial costs that result from loss of life, loss of health, lawsuits, or property damage. Insurance provides a means for individuals and societies to cope with some of the risks faced in everyday life. People purchase contracts of insurance, called policies, from a variety of insurance organizations. Almost everyone and every organization in modern, industrialized countries buy insurance. For instance, laws in most states require people who own a car to buy insurance before driving it on public roads. Lenders require anyone who finances the purchase of a home, car or any other property with borrowed money to insure that property. Business partners take out life insurance on each other to make sure the business (agric) will succeed even if one of the partners dies
EVALUATION:
1. Mention eight government agencies you know
2. Briefly explain the following: ADP, ICS-Nigeria, NFDP, NATSP and Agric Training Institutes.
3. Mention three Universities of Agriculture established in Nigeria.
4. What is the difference between credit and subsidy?
ASSIGNMENT:
State and explain seven roles of agricultural agencies in agriculture
READING ASSIGNMENT
Students are to read JS 1 E-Note
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. Junior Secondary Agriculture for Nigerian Schools by Anthony et al.
2. Essential of Agricultural Science for JSS by EC Anie.
CONTENT: 1. Meaning and Forms of Government Agencies
2. Roles of Government Agencies in Agriculture
Sub-Topic 1: MEANING OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
Agency means an administrative division or department (within a government) providing a particular service for a state. Government Agencies are the administrative departments responsible for development of agriculture in the rural areas in order to boost food production.
FORMS OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
The government agencies in agriculture include the following:
1. Farm Settlement Scheme
2. Agricultural Development Programme/Project (ADP)
3. River Basin Development Authority and Rural Development Programmes
4. Operation Feed the Nation, Green Revolution and School-to-Land Programmes
5. Agricultural Loan Scheme and Subsidy on Agricultural inputs
6. Farm Insurance Scheme
7. National Fadama Development Project (NFDP)
8. National Agricultural Technical Support Project (NATSP)
9. National Agricultural Research Institutes
10. Agricultural Training Institutes
11. Information and Communication Support for agric growth in Nigeria (ICS-NIGERIA)
EVALUATION
1. Define government agencies
2. Mention five government agencies you know.
3. What is the full meaning of the following: NFDP, NATSP, ADP, OFN and ICS-Nigeria?
Sub-Topic 3: ROLES OF GOVERNMENT AGENCIES IN AGRICULTURE
Farm Settlement Scheme: This program first started in the former Western Nigeria in 1959 with the aim of increasing agricultural production through the development of modern farming systems; discouraging young school leavers from migrating to the cities in search of office and factory jobs by providing them with necessary equipment for farming after they might have been trained in farm institutes for about two years.

AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME:
It is a set of rural based agric programmes established with emphasis on improving infra-structural facilities especially rural roads, rural electricity and rural water supply which will lead to increase in agricultural production and thereby improving the living standard of the farmers.
RIVER BASIN DEVELOPMENT AUTHORITIES AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES:
These were set up in many states of the country principally to cultivate the land and help the farmers with the production and marketing of agric produce from the farm. They also carry out rural development by providing rural farmers with infra-structural facilities.
AGRICULTURAL LOAN SCHEME AND SUBSIDY ON AGRIC INPUTS:
State and federal governments have established loan/credit schemes to farmers through commercial banks at low and considerable interest rates for agriculture. This is repayable assistance. Subsidy has been provided to farmers (in cash or kind) for the purchase of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers, fungicides, insecticides, herbicides and improved seeds at considerably reduced rates. This is non-repayable assistance.
OPERATION FEED THE NATION; GREEN REVOLUTION AND SCHOOL-TO-LAND PROGRAMMES: These three programmes were introduced by the former military presidents-Lt Gen Olusegun Obasanjo (1976); Alhaji Shehu Shagari (1980)and Gen Muhammad Buhari (1984) respectfully to encourage people to farm and return to their abandoned farms.
NATIONAL RESEARCH INSTITUTES:
Research is an advanced stage of study which deals mainly with discovering the unknown by careful and diligent search (i.e. the application of science and technology) and their discoveries are adopted by the farmers and other people involved in agriculture to improve the methods and practices they use thereby increase food production.
NATIONAL AGRICULTURAL TECHNICAL SUPPORT PROJECT (NATSP):
This is a nationally coordinated programmes designed to assist in the development and dissemination of agricultural innovations (technologies) to small scale farmers through regular field training by agricultural extension agents.
NATIONAL FADAMA DEVELOPMENT PROJECT (NFDP):
This is generally known as Fadama II and is a World Bank assisted project aim at assisting Fadama resource users to make them economically successful. It also supports production, processing and marketing of crops, livestock and fisheries in addition to development of rural infrastructures; acquisition of agro-processing equipment, tools and vehicles; settling conflict between farmers and pastoralists thus save the wanton destruction of lives and farm produce.
AGRICULTURAL TRAINING INSTITUTES:
In Nigeria, efforts have been made to establish several agricultural schools, colleges and universities to train and develop people with adequate agricultural science knowledge and skills required for agricultural development. The faculties and universities also conduct research to develop improved crop/animal varieties that are high yielding and resistant or tolerant to pests and diseases. This is to achieve food security and self sufficiency in industrial raw materials.
ICS-NIGERIA:
The Information and Communication Support for agricultural growth (ICS-Nigeria) project is involved in the dissemination of agric information to farmers through locations called ICS Resource Centres which are located in the state ADP headquarters. They support and sponsor radio programmes as well as production of materials such as extension guides, booklets, pictures, posters and other materials.
FARM INSURANCE SCHEME:
Insurance, legal contract, protects people from the financial costs that result from loss of life, loss of health, lawsuits, or property damage. Insurance provides a means for individuals and societies to cope with some of the risks faced in everyday life. People purchase contracts of insurance, called policies, from a variety of insurance organizations. Almost everyone and every organization in modern, industrialized countries buy insurance. For instance, laws in most states require people who own a car to buy insurance before driving it on public roads. Lenders require anyone who finances the purchase of a home, car or any other property with borrowed money to insure that property. Business partners take out life insurance on each other to make sure the business (agric) will succeed even if one of the partners dies
EVALUATION:
1. Mention eight government agencies you know
2. Briefly explain the following: ADP, ICS-Nigeria, NFDP, NATSP and Agric Training Institutes.
3. Mention three Universities of Agriculture established in Nigeria.
4. What is the difference between credit and subsidy?
ASSIGNMENT:
State and explain seven roles of agricultural agencies in agriculture
READING ASSIGNMENT
Students are to read JS 1 E-Note
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. Junior Secondary Agriculture for Nigerian Schools by Anthony et al.
2. Essential of Agricultural Science for JSS by EC Anie.
REVISION QUESTIONS
REVISION QUESTIONS
1. The correct name given to a place where only fruit trees are grown is known as…. A. plantation B. orchard C. orphanage D. forestry
2. The act of giving birth to young ones in pig is called…. A. kindling B. foaling C. farrowing D. kidding
3. The food required by a germinating seed is stored in the…… A. plumule B. radicle C. cotyledon D. embryo
4. The primary source of power for green plants to manufacture their food is …. A. water B. sunlight C. wind D. electricity
5. The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles by physical, chemical and biological action is known as …. A. mineralization B. stratification C. weathering D. rock breakage
6. The removal of extra seedlings per stand of crops is ….. A. pruning B. thinning C. supplying D. seed rate
7. Farm machine used in lifting, pulling and pushing other machines is called ….. A. bulldozer B. caterpillar C. rotator D. tractor
8. The rock formed as a result of the cooling down of the molten magma is known as ……. rock A. igneous B. sedimentary C. metamorphic D. stratified
9. Germinated young growing plant is known as …….. A. seed B. seedling C. germinated plant D. adult plant
10. The addition of lime material to the soil is a measure to correct soil ……. A. neutrality B. acidity C. alkalinity D. basicity
11. Mature female cattle yet to produce or give birth to young ones is called …… A. heifer B. gilt C. foal D. hog
12. The practice of removing unhealthy or low producing animals from the farmhouse is ……. A. canning B. calling C. candling D. culling
13. The downward movement of nutrients into the soil profile beyond the reach of plant roots is …….A. percolation B. leaching C. run-off D. drainage
14. Shallow rooted crops should not follow one another. This is one of the principles of …… cropping A. mixed B. rotation C. pastoral D. mono
15. A record of a list of things owned by the farmer such as land, building, equipment, feed and other supplies is known as ….. record A. inventory B. diary C. input D. production
16. An instrument used for supplying heat or warmth to fertilized eggs for it to develop into chicks is …….. A. candler B. rotator C. cultivator D. incubator
17. The movement of seedlings from the nursery to the permanent field of growth is called …….. A. transportation B. transfiguration C. transplanting D. transpiration
18. Another name for asexual propagation is ……. Propagation A. natural B. seed C. vegetative D. transplanting
19. The structure where rabbits are kept is called …….. A. sty B. barn C. cage D. hutch
20. The cultivation of crops to provide food for the farmers and their families only is called ……. Farming A. peasant B. subsistence C. commercial D. taungya
21. Deworming drugs are useful in controlling …… A. endo-parasites B. ecto-parasites C. ticks D. liver fluke
22. Which of the following birds are commonly reared in battery cages? A. layers B. breeders C. capon D. None of the above
23. The modern farming system in which crops are grown on a piece of land year after year in a sequential order is ……. A. continuous cropping B. mixed cropping C. crop rotation D. mixed farming
24. Clay soil easily becomes water logged during raining season because …….. A. it has large particles B. it has fine pore spaces C. it has rough structure D. it has large pore spaces
25. Farm special shelter constructed for slaughtering farm animals for sales is known as …… A. shearing floor B. abattoir C. stable D. whelping pen
26. The removal of testicles of animals is called …… A. incubation B. ovulation C. inoculation D. castration
27. One of the following industries in Nigeria does not use agricultural raw materials for its production A. canning industries B. textile industries C. sap industries D. soap industries
28. The formation of soil is influenced by the following factors except ……. A. topography B. time C. climate D. soil
29. Organism that depends on another organism for essential part of its living without giving any benefit to its host is called ……. A. pathogen B. parasite C. pest D. vector
30. The type of ration fed to animals just to enable them carry out normal body activities without gaining or losing weight is …….. ration A. balanced B. maintenance C. production D. weaner
31. The form of soil water available for plant use is known as …… A. capillary B. percolated C. hygroscopic D. infiltrated
32. Soil nutrient could be conserved through one of the following A. bush burning B. mulching C. leaching D. plant uptake
33. The following are methods or processes of fish preservation except A. smoking B. soaking C. canning D. salting
34. The illegal hunting of wild animals in the forest is known as …… A. pushing B. poaching C. boaching D. game hunting
35. Bacterial diseases of farm animals are as follows except ……. A. foot and mouth B. mastitis C. brucellosis D. tuberculosis
36. The collective programmes put in place by a country to help organizations sell their produce abroad are known as …… promotion A. business B. export C. cooperative D. finance
37. The market where stocks, shares and other securities are bought and sold is referred to as ……… market A. local B. industrial C. stock exchange D. city
38. The form of agriculture that deals with rearing of bees is known as …… A. apiculture B. aquaculture C. silviculture D. horticulture
39. The activities carried out after sowing of crops include the following except A. thinning B. supplying C. storage D. plotting
40. The group of people involved in the stock exchange markets is as follows except A. jobbers B. speculators C. workers D. investors
41. Those who sell shares because they expect the price to fall are called …… A. buyers B. bear C. bulls D. brokers
42. The branch of agriculture that deals with the dissemination of information to farmers is known as agricultural ……. A. economics B. education C. engineering D. extension
43. Swollen shoot disease of cocoa is transmitted by …….. A. aphid B. mealy bug C. eelworm D. termite
44. A mature male cattle is known as bull while mature female pig is called …… A. boar B. sow C. ewe D. cow
45. The percentage volume of water in the soil is …… A. 25% B. 45% C. 35% D. 20%
46. The young shoot of banana used for propagation is known as …… A. bulbs B. crowns C. suckers D. corms
47. Colostrum is usually given to young animals at …… A. birth B. weaning C. maturity D. dehorning period
48. The main products and by-products of poultry include all the following except A. chicken B guano C. feathers D. crayfish
49. Cotton stainer is classified as ……. Insect A. biting and chewing B. piercing and chewing C. piercing and boring D. piercing and sucking
50. The system of planting a second crop and harvesting it before harvesting the first crop is known as ……. A. mixed farming B. inter planting C. inter cropping D. mono cropping
51. The machine used to separate seeds from maize cobs is called …… A. baler B. sheller C. mower D. thresher
52. In selecting a farmland site, the following factors are put into consideration except ……. A. accessibility B. land availability C. demonstration D. fertility of the soil
53. Herbicides are mainly applied using an equipment/tool called …….. A. rotator B. sprayer C. cultivator D. harrow
54. A non-settled form of farming system in which the farmer keeps grazing animals only is known as ……… A. animal farming B .pastoral farming C. ranching farming D. nomadic farming
55. Crops grown to protect the soil from erosion are called ……. A. catch crops B. fibre crops C. cover crops D. cash crops
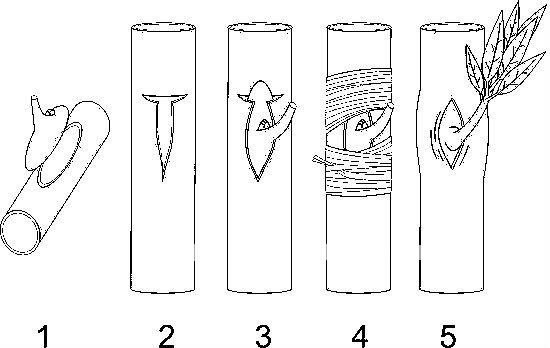
56. The method of propagation illustrated above is called …….. A. budding B. grafting C. layering D. marcotting
57. The binding together of stock and scion of two related plants to form one plant is called A. cutting B. layering C. budding D. grafting
58. When farmers propagate new plants by allowing the plant to develop roots while still attached to the parent plant, the farmer is carrying out ……. A. mar-cotting B. layering C. grafting D. budding
59. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of sexual propagation? Seeds….. A. germinate and start bearing fruits early B. are cheap to obtain C. remain viable for one season D. are small and convenient to handle
60. When ungerminated seeds are replaced with new ones, the farm operation carried out is referred to as ….. A. mulching B. planting C. thinning D. supplying
61. The date of planting crops depends on the following environmental factors except ……. A. pest incident B. soil type C. sunshine D. water
62. Agricultural school leavers in Nigeria are employed in the following establishments except ….. A. banks B. military C. industry D. University
63. A commercial method of preserving grains produced for a long time is by A. drying B. frying C. irradiation D. pasteurization
64. Which of the following is best preserved by salting? A. cheese B. meat C. fish D. oil
65. Which of the following activities is not involved in agricultural marketing of cocoa pod in Western Nigeria? A. distribution B.production C. packaging D. processing
66. Agricultural cooperative society that supplies technical services to her members is called ….. Cooperative A. consumers’ B. multi-purpose C. producers’ D. credit and thrift
67. The following are challenges in agricultural marketing of orange fruits except A. bulkiness of farm produce B. inadequate storage facility C. poor consumer credit facilities D. perishability of farm produce
Use the table below to answer questions 68-69
YEAR PLOT 1 PLOT 2 PLOT 3 PLOT 4
1 Yam Soybean Cassava Maize
2 Soybean Cassava Maize Yam
3 Cassava Maize Yam Soybean
4 Maize Yam Soybean Cassava
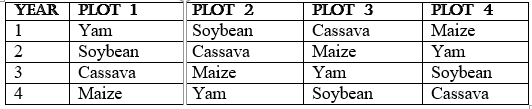
68. The system of agriculture illustrated above is called ….. A. commercial farming B. continuous cropping C. mixed cropping D .crop rotation
69. The system aims at achieving the following except A. increase risk of crop failure B. maintain the soil fertility C. solving the problem of inadequate land D. producing high yield of a crop
70. Which of the following is a benefit of forest on the environment? A. provision of foreign exchange B. purification of air C. provision of medicine D. source of employment
71. Feathery and powdery seeds are characteristic features of weeds dispersed by A. animals B explosive mechanism C. wind D. water
72. The following are mechanical methods of weed control except A crop rotation B. hoeing C. slashing D. rotary cultivation
73. Which of the following is not an effect of weeds on crops? A. harbor crop diseases B. act as cover crops C. reduce palatability of crops D. compete with crops for nutrients
74. Diseases of crops are caused by the following except A. bacterium B. fungus C. protozoan D. virus
75. .The covering of soil surface with dry grasses is known as ….. A. manuring B. tillage C. mulching D. threshing
76. Which of the following is a method of soil conservation? A. bush burning B. clean clearing C. crop rotation D. over grazing
77. Which of the following crops is used for soil conservation? A. legumes B. cereals C. fibres D. vegetables
78. Water in the soil is lost through the following except A. surface run-off B. irrigation C. transpiration D. evaporation
79. Which of the following is capable of increasing the amount of plant nutrients in the soil? A. harvesting B leaching C. manuring D. burning
80. The following are cultural methods of controlling diseases except A. regular weeding B. use of insecticides C. rotational cropping D. use of resistant varieties
81. Which of the following is not a factor affecting storage of farm produce? A. average temperature B. moisture content C. relative humidity D. quantity of produce
82. Black pod disease of cocoa is caused by a ……. A. bacterium B. fungus C. nematodes D. virus
83. Cribs are used in storing ….. A. maize cobs B. cashew fruits C. maize grains D. yam tubers
84. Which of the following symptoms may not indicate a condition of ill-health in farm animals? A. increased water intake B. increased breathing rate C. loss of appetite D. weight loss
85. Which of the following livestock diseases is not related to poultry? A. fowl typhoid B. coccidiosis C. foot and mouth disease D. Newcastle
86. The following are management systems of preventing diseases in a farm animal except…… A. vaccination B. castration C. quarantine D. sanitation
87. The following are methods of controlling endoparasites except ……. A. dipping B. deworming C. medication D. rotational grazing
88. The control of pests using their natural enemies is referred to as ……..control A. chemical B. biological C. cultural D. mechanical
89. Panicum maximum is the scientific name of …… A. gamba grass B. guinea grass C. elephant grass D. goose grass
90. Which of these crops is a dicotyledon? A. guinea corn B. cowpea C. sorghum D. wheat
91. Goat weeds are dispersed by A. animals B. water C. wind D. explosive mechanism
Use the diagram below to answer questions 92-95
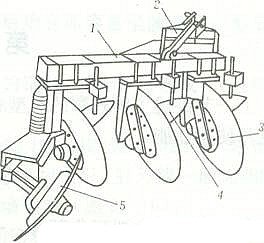
92. The implement above represents A. disc harrow B. disc plough C. seed planter D. disc ridger
93. The part labeled ‘C’ is used for A. cutting grasses B. tilling the soil C. harrowing the soil D. preparing seed bed
94. The part labeled ‘B’ is called A. beam B. furrow wheel C. share D. beam cap
95. The part labeled ‘A’ is called A. beam cap B. furrow wheel C. point of attachment D. mould board
96. The rate of erosion depends on the following except A. topography B. amount of sunshine C. vegetative cover D. force of wind

97. The diagram above illustrates A. army worm B. cotton stainer C. grasshopper D. termite
98. Which of the following is not a method of fertilizer application? A. row placement B. top dressing C. broadcasting D. branding
99. The following are macro-nutrients except A. Zinc B. Magnesium C. Nitrogen D. Potassium
100. The meat of goat is known as ……. A. mutton B. chevon C. pork D. chicken
1. The correct name given to a place where only fruit trees are grown is known as…. A. plantation B. orchard C. orphanage D. forestry
2. The act of giving birth to young ones in pig is called…. A. kindling B. foaling C. farrowing D. kidding
3. The food required by a germinating seed is stored in the…… A. plumule B. radicle C. cotyledon D. embryo
4. The primary source of power for green plants to manufacture their food is …. A. water B. sunlight C. wind D. electricity
5. The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles by physical, chemical and biological action is known as …. A. mineralization B. stratification C. weathering D. rock breakage
6. The removal of extra seedlings per stand of crops is ….. A. pruning B. thinning C. supplying D. seed rate
7. Farm machine used in lifting, pulling and pushing other machines is called ….. A. bulldozer B. caterpillar C. rotator D. tractor
8. The rock formed as a result of the cooling down of the molten magma is known as ……. rock A. igneous B. sedimentary C. metamorphic D. stratified
9. Germinated young growing plant is known as …….. A. seed B. seedling C. germinated plant D. adult plant
10. The addition of lime material to the soil is a measure to correct soil ……. A. neutrality B. acidity C. alkalinity D. basicity
11. Mature female cattle yet to produce or give birth to young ones is called …… A. heifer B. gilt C. foal D. hog
12. The practice of removing unhealthy or low producing animals from the farmhouse is ……. A. canning B. calling C. candling D. culling
13. The downward movement of nutrients into the soil profile beyond the reach of plant roots is …….A. percolation B. leaching C. run-off D. drainage
14. Shallow rooted crops should not follow one another. This is one of the principles of …… cropping A. mixed B. rotation C. pastoral D. mono
15. A record of a list of things owned by the farmer such as land, building, equipment, feed and other supplies is known as ….. record A. inventory B. diary C. input D. production
16. An instrument used for supplying heat or warmth to fertilized eggs for it to develop into chicks is …….. A. candler B. rotator C. cultivator D. incubator
17. The movement of seedlings from the nursery to the permanent field of growth is called …….. A. transportation B. transfiguration C. transplanting D. transpiration
18. Another name for asexual propagation is ……. Propagation A. natural B. seed C. vegetative D. transplanting
19. The structure where rabbits are kept is called …….. A. sty B. barn C. cage D. hutch
20. The cultivation of crops to provide food for the farmers and their families only is called ……. Farming A. peasant B. subsistence C. commercial D. taungya
21. Deworming drugs are useful in controlling …… A. endo-parasites B. ecto-parasites C. ticks D. liver fluke
22. Which of the following birds are commonly reared in battery cages? A. layers B. breeders C. capon D. None of the above
23. The modern farming system in which crops are grown on a piece of land year after year in a sequential order is ……. A. continuous cropping B. mixed cropping C. crop rotation D. mixed farming
24. Clay soil easily becomes water logged during raining season because …….. A. it has large particles B. it has fine pore spaces C. it has rough structure D. it has large pore spaces
25. Farm special shelter constructed for slaughtering farm animals for sales is known as …… A. shearing floor B. abattoir C. stable D. whelping pen
26. The removal of testicles of animals is called …… A. incubation B. ovulation C. inoculation D. castration
27. One of the following industries in Nigeria does not use agricultural raw materials for its production A. canning industries B. textile industries C. sap industries D. soap industries
28. The formation of soil is influenced by the following factors except ……. A. topography B. time C. climate D. soil
29. Organism that depends on another organism for essential part of its living without giving any benefit to its host is called ……. A. pathogen B. parasite C. pest D. vector
30. The type of ration fed to animals just to enable them carry out normal body activities without gaining or losing weight is …….. ration A. balanced B. maintenance C. production D. weaner
31. The form of soil water available for plant use is known as …… A. capillary B. percolated C. hygroscopic D. infiltrated
32. Soil nutrient could be conserved through one of the following A. bush burning B. mulching C. leaching D. plant uptake
33. The following are methods or processes of fish preservation except A. smoking B. soaking C. canning D. salting
34. The illegal hunting of wild animals in the forest is known as …… A. pushing B. poaching C. boaching D. game hunting
35. Bacterial diseases of farm animals are as follows except ……. A. foot and mouth B. mastitis C. brucellosis D. tuberculosis
36. The collective programmes put in place by a country to help organizations sell their produce abroad are known as …… promotion A. business B. export C. cooperative D. finance
37. The market where stocks, shares and other securities are bought and sold is referred to as ……… market A. local B. industrial C. stock exchange D. city
38. The form of agriculture that deals with rearing of bees is known as …… A. apiculture B. aquaculture C. silviculture D. horticulture
39. The activities carried out after sowing of crops include the following except A. thinning B. supplying C. storage D. plotting
40. The group of people involved in the stock exchange markets is as follows except A. jobbers B. speculators C. workers D. investors
41. Those who sell shares because they expect the price to fall are called …… A. buyers B. bear C. bulls D. brokers
42. The branch of agriculture that deals with the dissemination of information to farmers is known as agricultural ……. A. economics B. education C. engineering D. extension
43. Swollen shoot disease of cocoa is transmitted by …….. A. aphid B. mealy bug C. eelworm D. termite
44. A mature male cattle is known as bull while mature female pig is called …… A. boar B. sow C. ewe D. cow
45. The percentage volume of water in the soil is …… A. 25% B. 45% C. 35% D. 20%
46. The young shoot of banana used for propagation is known as …… A. bulbs B. crowns C. suckers D. corms
47. Colostrum is usually given to young animals at …… A. birth B. weaning C. maturity D. dehorning period
48. The main products and by-products of poultry include all the following except A. chicken B guano C. feathers D. crayfish
49. Cotton stainer is classified as ……. Insect A. biting and chewing B. piercing and chewing C. piercing and boring D. piercing and sucking
50. The system of planting a second crop and harvesting it before harvesting the first crop is known as ……. A. mixed farming B. inter planting C. inter cropping D. mono cropping
51. The machine used to separate seeds from maize cobs is called …… A. baler B. sheller C. mower D. thresher
52. In selecting a farmland site, the following factors are put into consideration except ……. A. accessibility B. land availability C. demonstration D. fertility of the soil
53. Herbicides are mainly applied using an equipment/tool called …….. A. rotator B. sprayer C. cultivator D. harrow
54. A non-settled form of farming system in which the farmer keeps grazing animals only is known as ……… A. animal farming B .pastoral farming C. ranching farming D. nomadic farming
55. Crops grown to protect the soil from erosion are called ……. A. catch crops B. fibre crops C. cover crops D. cash crops

56. The method of propagation illustrated above is called …….. A. budding B. grafting C. layering D. marcotting
57. The binding together of stock and scion of two related plants to form one plant is called A. cutting B. layering C. budding D. grafting
58. When farmers propagate new plants by allowing the plant to develop roots while still attached to the parent plant, the farmer is carrying out ……. A. mar-cotting B. layering C. grafting D. budding
59. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of sexual propagation? Seeds….. A. germinate and start bearing fruits early B. are cheap to obtain C. remain viable for one season D. are small and convenient to handle
60. When ungerminated seeds are replaced with new ones, the farm operation carried out is referred to as ….. A. mulching B. planting C. thinning D. supplying
61. The date of planting crops depends on the following environmental factors except ……. A. pest incident B. soil type C. sunshine D. water
62. Agricultural school leavers in Nigeria are employed in the following establishments except ….. A. banks B. military C. industry D. University
63. A commercial method of preserving grains produced for a long time is by A. drying B. frying C. irradiation D. pasteurization
64. Which of the following is best preserved by salting? A. cheese B. meat C. fish D. oil
65. Which of the following activities is not involved in agricultural marketing of cocoa pod in Western Nigeria? A. distribution B.production C. packaging D. processing
66. Agricultural cooperative society that supplies technical services to her members is called ….. Cooperative A. consumers’ B. multi-purpose C. producers’ D. credit and thrift
67. The following are challenges in agricultural marketing of orange fruits except A. bulkiness of farm produce B. inadequate storage facility C. poor consumer credit facilities D. perishability of farm produce
Use the table below to answer questions 68-69
YEAR PLOT 1 PLOT 2 PLOT 3 PLOT 4
1 Yam Soybean Cassava Maize
2 Soybean Cassava Maize Yam
3 Cassava Maize Yam Soybean
4 Maize Yam Soybean Cassava

68. The system of agriculture illustrated above is called ….. A. commercial farming B. continuous cropping C. mixed cropping D .crop rotation
69. The system aims at achieving the following except A. increase risk of crop failure B. maintain the soil fertility C. solving the problem of inadequate land D. producing high yield of a crop
70. Which of the following is a benefit of forest on the environment? A. provision of foreign exchange B. purification of air C. provision of medicine D. source of employment
71. Feathery and powdery seeds are characteristic features of weeds dispersed by A. animals B explosive mechanism C. wind D. water
72. The following are mechanical methods of weed control except A crop rotation B. hoeing C. slashing D. rotary cultivation
73. Which of the following is not an effect of weeds on crops? A. harbor crop diseases B. act as cover crops C. reduce palatability of crops D. compete with crops for nutrients
74. Diseases of crops are caused by the following except A. bacterium B. fungus C. protozoan D. virus
75. .The covering of soil surface with dry grasses is known as ….. A. manuring B. tillage C. mulching D. threshing
76. Which of the following is a method of soil conservation? A. bush burning B. clean clearing C. crop rotation D. over grazing
77. Which of the following crops is used for soil conservation? A. legumes B. cereals C. fibres D. vegetables
78. Water in the soil is lost through the following except A. surface run-off B. irrigation C. transpiration D. evaporation
79. Which of the following is capable of increasing the amount of plant nutrients in the soil? A. harvesting B leaching C. manuring D. burning
80. The following are cultural methods of controlling diseases except A. regular weeding B. use of insecticides C. rotational cropping D. use of resistant varieties
81. Which of the following is not a factor affecting storage of farm produce? A. average temperature B. moisture content C. relative humidity D. quantity of produce
82. Black pod disease of cocoa is caused by a ……. A. bacterium B. fungus C. nematodes D. virus
83. Cribs are used in storing ….. A. maize cobs B. cashew fruits C. maize grains D. yam tubers
84. Which of the following symptoms may not indicate a condition of ill-health in farm animals? A. increased water intake B. increased breathing rate C. loss of appetite D. weight loss
85. Which of the following livestock diseases is not related to poultry? A. fowl typhoid B. coccidiosis C. foot and mouth disease D. Newcastle
86. The following are management systems of preventing diseases in a farm animal except…… A. vaccination B. castration C. quarantine D. sanitation
87. The following are methods of controlling endoparasites except ……. A. dipping B. deworming C. medication D. rotational grazing
88. The control of pests using their natural enemies is referred to as ……..control A. chemical B. biological C. cultural D. mechanical
89. Panicum maximum is the scientific name of …… A. gamba grass B. guinea grass C. elephant grass D. goose grass
90. Which of these crops is a dicotyledon? A. guinea corn B. cowpea C. sorghum D. wheat
91. Goat weeds are dispersed by A. animals B. water C. wind D. explosive mechanism
Use the diagram below to answer questions 92-95

92. The implement above represents A. disc harrow B. disc plough C. seed planter D. disc ridger
93. The part labeled ‘C’ is used for A. cutting grasses B. tilling the soil C. harrowing the soil D. preparing seed bed
94. The part labeled ‘B’ is called A. beam B. furrow wheel C. share D. beam cap
95. The part labeled ‘A’ is called A. beam cap B. furrow wheel C. point of attachment D. mould board
96. The rate of erosion depends on the following except A. topography B. amount of sunshine C. vegetative cover D. force of wind

97. The diagram above illustrates A. army worm B. cotton stainer C. grasshopper D. termite
98. Which of the following is not a method of fertilizer application? A. row placement B. top dressing C. broadcasting D. branding
99. The following are macro-nutrients except A. Zinc B. Magnesium C. Nitrogen D. Potassium
100. The meat of goat is known as ……. A. mutton B. chevon C. pork D. chicken
REVISION QUESTIONS
101. Which of the following is not an animal by-production? A. beef B. fur C. bone D. horn
102. A marketing activity which involves the grouping of produce into various weight and sizes is known as …… A. advertisement B. grading C. packaging D. storage
103. Forage that is processed and preserved for future use is called …. A. fodder B. soilage C. silage D. hay
104. The soil property that can be determined by sieving is called A. colour B. pH C. structure D. texture
105. Which of the following is not an ecto-parasite? A. flea B. liver-fluke C. lice D. mite
106. Young ones of pig are called farrows while that of turkey are known as A. kittens B poults C. calves D. chicks
107. The introduction of fingerlings into the pond is called A. stocking B. fertilization C. introduction D. inoculation
108. Which of the following practices would a farmer not likely adopt in pig management? A. ear notching B. castration C. dehorning D. deworming
109. Feeds with high amount of fibre are classified as A. additives B. concentrate C. supplements D. roughages
110. A female fowl that is below one year old is called A. capon B. chick C. pullet D. cockerel
111. The primary purpose of keeping farm records is to ……. A.aid accurate budgeting B. give a history of the farm C. combat the incidence of theft in the farm D. know day-to-day activities on the farm
112. Oyster shell is an important ingredient in livestock feed component because it supplies A. carbohydrates B. proteins C. fat D. calcium
113. The following are fresh water fish except A. tilapia B. dolphin C. cat fish D. mud fish
114. In farm animal production, weaning can be described as …… A. mother and young one, winning one another B. removal of the male adult C. removal of the young ones from the mother D. removal of the hairs from farm animals.
115. The roles of government in agriculture include the following except A. credit facilities B. quarantine services C, research institutes D. disease susceptible breeds of animals
116. Seeds for planting must possess the following qualities except A. some degree of dormancy B. high percentage of viability C. must be matured and well filled D. must be clean
117. Staking of yam is done mainly to ….. A. expose the leaves to more sunlight B. give more space for breathing C. keep the vines away from soil micro-organisms D. protect the vines from rotting
118. The phrase ‘chew the cud’ is common with the following animals except A. cattle B sheep C. goat D. pig
119. Trypanosomiasis in cattle is caused by ….. A. bacteria B fungi C. protozoan D. tsetse fly
120. An example of viral disease is A. tomato root knot B. cassava mosaic C. maize rust D. damping off of tomato
121. Sandy soil can be made suitable for plant growth by …… A. adding organic matter B. planting crops early C. liming the soil D. using nitrogen fertilizer
122. Draught animals used for work on the farm must possess the following qualities except A. must not be docile B. good body size C. must be energetic D. strong hind limbs
123. Which of the following farm power is most unreliable? A. electricity B. machine C. man D. water
124. Which of the following is not a method of disseminating new ideas and techniques to farmer? A. telephone call B. television C. agricultural show D. teaching of agriculture in the classroom
125. The following are problems of mechanization in Nigeria except A. insufficient technical know-how B. land tenure system C. provision of large farm outputs D. lack of capital
126. The following are functions of plant roots except A. fruit formation B. absorption of soil nutrients C. anchorage of plants D. storage of food
127. It is necessary to transplant seedlings with the ‘ball of earth’ because it A. drains away excess water B. makes seedlings to resist pest attack C. protect the root from damage D. keeps away soil borne disease
128. Which of the following crops exhibit hypogeal germination? A. cowpea B. sorghum C. soybean D. groundnut
129. The act of mating in poultry is known as ….. A. treading B. tupping C. servicing D. ejaculating
130. The castrated male fowl is called …… A. broiler B. pullet C. capon D. barrow
131. The following are breeds of rabbits except A. Flemish giant B. Newzea land C. Duroc jersey D. Norfork
132. Which of the following farming systems has the highest risk of spreading crop diseases? A. mono cropping B. crop rotation C. mixed farming D. shifting cultivation
133. Low fibre and high energy feeds are classified as ……. A. basal feeds B. additives C. concentrates D. supplements
134. The movement of water and nutrients down the soil profile is called ……. A. erosion B. leaching C. percolation D. flooding
135. Which of the following colours will indicate that soil pH is neutral? A. green B. blue C. red D. pink
136. Which of these occurs in a crowded condition in poultry house? A. candling B. cannibalism C. debeaking D. incubation
137. The farm operation which involves the breaking and loosening up of the top soil is called …… A. ploughing B. harrowing C. ridging D. thinning
138. Which of the following statements is most true? A. ploughing and harrowing are the same B. ploughing is the first tillage operation in mechanized farming C. ploughing is the first farm operation D. you harrow before planting
139. One of the following is not a forest tree A.Gmelina B Teak C. Mansonia D. Oil palm
140. The scientific name for pig weed is ….. A. Aspilia africana B. Boerhavia diffusa C. Eleusin indica D. Cyprus rotundus
141. The common name for Axonopus compressus is …….. A. Elephant grass B. Carpet grass C. Goose grass D. Guinea grass
142. The process by which plants can be multiplied without seed is called ….. propagation A. seed B. sexual C. asexual D. embryo
143. Soil is made up of the following except A. mineral matter B. organic matter C. water D. winter
144. N P K is an example of ……. fertilizer A. complete B. single C. straight D. simple
145. When a fowl bends neck, spins round and suddenly falls down, this indicates that the bird is suffering from ……….. disease A. coccidiosis B. new castle C. fowl typhoid D. fowl cholera
146. A fertilizer that supplies only one essential nutrient to the soil is called …….. fertilizer A. farm yard B. single C. mixed D. compound
147. A trained agriculturist who carries research findings to local farmers is called ……. A. extension officer B. research officer C. farm manager D. agricultural representative
148. The danger of introducing diseases and pests with crops from other countries can be prevented by …… A. mass selections B cross breeding C. artificial insemination D. plant quarantine
149. The equatorial rainforest belt is not usually used for cattle production because of the following except …… A. low relative humidity B. dense vegetative growth C. incidence of tsetse fly D. absence of natural grassland
150. Which of the following programmes is not concerned with development of agriculture? A. River Basin Development Authority B. Operation Feed the Nation C.Expanded Programme on Immunization Programme D. Green Revolution
151. Weed seed or fruit to be dispersed by water must have ……. A. hooks B. air space C. hairs D. explosive mechanism
152. The branch of agriculture that deals with planting of fruits, vegetables and ornamental crops is called ……. A. apiculture B. horticulture C. heliculture d. silviculture
153. The upward movement of water in the soil is called ….. A. osmosis B. infilteration C. capillary D. percolation
154. A branch of agriculture that studies animal and plant diseases is known as …….. A. pathology B. horticulture C. agric biology D. diseasiology
155. The following parts of a flowering plant serve as storage as well as vegetative organs except
A. flowers B. roots C. stems D. leaves
Use the diagram below to answer questions 157 and 158

156. The diagram above is called ……… A. watering can B. boom sprayer C. knapsack sprayer D. hand trowel
157. The machine is used for ……. A. fetching water B. applying chemicals C. spraying petrol D. drinking
158. Which of the following groups is a monocotyledon? A. millet, maize, guinea-corn and cowpea B. cowpea, guinea-corn, guinea grass and millet C. maize, millet, elephant and rice D. carpet grass, millet, maize and beans
159.In planning farm, which of the following is least considered? A. kinds of crops B. species of animals C. nearness to stores D. size of the farm
160. The physical appearance of the soil depending on how individual particles are packed is called ….. A. profile B. structure C. capillary D. texture
161. The following are characteristics of commercial farm except A. high degree of specialization B. investment of large sum of money C. skilled technical and management staff D. small size of farm land
162. All the measures aimed at preventing soil erosion, sustaining soil fertility and ensuring good and productive use of soil come under soil …….. A. maintenance B. conservation C. analysis D. formation
163. The gestation period of sow is ………days A. 150 B. 124 C. 114 D. 283
164. A farm implement with a long wooden handle and four or five prongs as the metal head is called A. sickle B. garden fork C. drill D. tined
165. The record of all assets in the farm is referred to as …….. A. farm diary B. farm inventory C. input record D. production record
166. Which of the following crops is most suitable for a farmland deficient in nitrogen? A. rice B. maize C. Cowpea D. sorghum
167. One of the following crops is not a vegetable A. onion B. cowpea C. okra D. tomato
168. Under what farm operations will you classify harvesting? A. planting B. post-planting C. pre-planting D. early-planting
169. The following provide career opportunity in agriculture except A. agronomy B. soil science C. veterinary service D. aeronautics
170. Pollination of crops can described as a process of A. sexual propagation B. asexual propagation C. vegetative reproduction D. shoot development
171. The method of poultry management whereby birds are allowed to wander about to look for food without restriction is called ….. A. extensive B. intensive C. semi-intensive D. fold system
172. An animal that possesses four compartment stomach is called A. mammal B. ruminant C,.herbivore D. omnivore
173. The following are the main objectives of fencing of farm except A. preventing damage of crops B. controlling livestock breeding C. improving the management of grazing D. providing areas for recreation
174. Which of these stored produce is easily attacked by weevils? A. kola B. maize C. cocoa D. cotton
175. The farm tool used for transplanting seedlings from nursery to the field is A. hand fork B. shovel C. hand trowel D. cutlass
176. Which of the following is not a workshop operation? A. painting B. tightening of bolts and nuts C. washing of overall D. spraying
177. The degree of fineness or coarseness of soil particles is known as its …. A. composition B. profile C. texture D. structure
178. A farmer can use the following methods to control evaporation of water from the soil except A. bush fallowing B. bush burning C. cover cropping D. mulching
179. Which of the following should be best considered in selecting seeds for planting? A. method of storage B. maturity C. moisture content D. viability
180. A cattle disease that causes abortion and sterility is known as A. brucellosis B. rinder pest C. coccidiosis D. pleuropnemonia
102. A marketing activity which involves the grouping of produce into various weight and sizes is known as …… A. advertisement B. grading C. packaging D. storage
103. Forage that is processed and preserved for future use is called …. A. fodder B. soilage C. silage D. hay
104. The soil property that can be determined by sieving is called A. colour B. pH C. structure D. texture
105. Which of the following is not an ecto-parasite? A. flea B. liver-fluke C. lice D. mite
106. Young ones of pig are called farrows while that of turkey are known as A. kittens B poults C. calves D. chicks
107. The introduction of fingerlings into the pond is called A. stocking B. fertilization C. introduction D. inoculation
108. Which of the following practices would a farmer not likely adopt in pig management? A. ear notching B. castration C. dehorning D. deworming
109. Feeds with high amount of fibre are classified as A. additives B. concentrate C. supplements D. roughages
110. A female fowl that is below one year old is called A. capon B. chick C. pullet D. cockerel
111. The primary purpose of keeping farm records is to ……. A.aid accurate budgeting B. give a history of the farm C. combat the incidence of theft in the farm D. know day-to-day activities on the farm
112. Oyster shell is an important ingredient in livestock feed component because it supplies A. carbohydrates B. proteins C. fat D. calcium
113. The following are fresh water fish except A. tilapia B. dolphin C. cat fish D. mud fish
114. In farm animal production, weaning can be described as …… A. mother and young one, winning one another B. removal of the male adult C. removal of the young ones from the mother D. removal of the hairs from farm animals.
115. The roles of government in agriculture include the following except A. credit facilities B. quarantine services C, research institutes D. disease susceptible breeds of animals
116. Seeds for planting must possess the following qualities except A. some degree of dormancy B. high percentage of viability C. must be matured and well filled D. must be clean
117. Staking of yam is done mainly to ….. A. expose the leaves to more sunlight B. give more space for breathing C. keep the vines away from soil micro-organisms D. protect the vines from rotting
118. The phrase ‘chew the cud’ is common with the following animals except A. cattle B sheep C. goat D. pig
119. Trypanosomiasis in cattle is caused by ….. A. bacteria B fungi C. protozoan D. tsetse fly
120. An example of viral disease is A. tomato root knot B. cassava mosaic C. maize rust D. damping off of tomato
121. Sandy soil can be made suitable for plant growth by …… A. adding organic matter B. planting crops early C. liming the soil D. using nitrogen fertilizer
122. Draught animals used for work on the farm must possess the following qualities except A. must not be docile B. good body size C. must be energetic D. strong hind limbs
123. Which of the following farm power is most unreliable? A. electricity B. machine C. man D. water
124. Which of the following is not a method of disseminating new ideas and techniques to farmer? A. telephone call B. television C. agricultural show D. teaching of agriculture in the classroom
125. The following are problems of mechanization in Nigeria except A. insufficient technical know-how B. land tenure system C. provision of large farm outputs D. lack of capital
126. The following are functions of plant roots except A. fruit formation B. absorption of soil nutrients C. anchorage of plants D. storage of food
127. It is necessary to transplant seedlings with the ‘ball of earth’ because it A. drains away excess water B. makes seedlings to resist pest attack C. protect the root from damage D. keeps away soil borne disease
128. Which of the following crops exhibit hypogeal germination? A. cowpea B. sorghum C. soybean D. groundnut
129. The act of mating in poultry is known as ….. A. treading B. tupping C. servicing D. ejaculating
130. The castrated male fowl is called …… A. broiler B. pullet C. capon D. barrow
131. The following are breeds of rabbits except A. Flemish giant B. Newzea land C. Duroc jersey D. Norfork
132. Which of the following farming systems has the highest risk of spreading crop diseases? A. mono cropping B. crop rotation C. mixed farming D. shifting cultivation
133. Low fibre and high energy feeds are classified as ……. A. basal feeds B. additives C. concentrates D. supplements
134. The movement of water and nutrients down the soil profile is called ……. A. erosion B. leaching C. percolation D. flooding
135. Which of the following colours will indicate that soil pH is neutral? A. green B. blue C. red D. pink
136. Which of these occurs in a crowded condition in poultry house? A. candling B. cannibalism C. debeaking D. incubation
137. The farm operation which involves the breaking and loosening up of the top soil is called …… A. ploughing B. harrowing C. ridging D. thinning
138. Which of the following statements is most true? A. ploughing and harrowing are the same B. ploughing is the first tillage operation in mechanized farming C. ploughing is the first farm operation D. you harrow before planting
139. One of the following is not a forest tree A.Gmelina B Teak C. Mansonia D. Oil palm
140. The scientific name for pig weed is ….. A. Aspilia africana B. Boerhavia diffusa C. Eleusin indica D. Cyprus rotundus
141. The common name for Axonopus compressus is …….. A. Elephant grass B. Carpet grass C. Goose grass D. Guinea grass
142. The process by which plants can be multiplied without seed is called ….. propagation A. seed B. sexual C. asexual D. embryo
143. Soil is made up of the following except A. mineral matter B. organic matter C. water D. winter
144. N P K is an example of ……. fertilizer A. complete B. single C. straight D. simple
145. When a fowl bends neck, spins round and suddenly falls down, this indicates that the bird is suffering from ……….. disease A. coccidiosis B. new castle C. fowl typhoid D. fowl cholera
146. A fertilizer that supplies only one essential nutrient to the soil is called …….. fertilizer A. farm yard B. single C. mixed D. compound
147. A trained agriculturist who carries research findings to local farmers is called ……. A. extension officer B. research officer C. farm manager D. agricultural representative
148. The danger of introducing diseases and pests with crops from other countries can be prevented by …… A. mass selections B cross breeding C. artificial insemination D. plant quarantine
149. The equatorial rainforest belt is not usually used for cattle production because of the following except …… A. low relative humidity B. dense vegetative growth C. incidence of tsetse fly D. absence of natural grassland
150. Which of the following programmes is not concerned with development of agriculture? A. River Basin Development Authority B. Operation Feed the Nation C.Expanded Programme on Immunization Programme D. Green Revolution
151. Weed seed or fruit to be dispersed by water must have ……. A. hooks B. air space C. hairs D. explosive mechanism
152. The branch of agriculture that deals with planting of fruits, vegetables and ornamental crops is called ……. A. apiculture B. horticulture C. heliculture d. silviculture
153. The upward movement of water in the soil is called ….. A. osmosis B. infilteration C. capillary D. percolation
154. A branch of agriculture that studies animal and plant diseases is known as …….. A. pathology B. horticulture C. agric biology D. diseasiology
155. The following parts of a flowering plant serve as storage as well as vegetative organs except
A. flowers B. roots C. stems D. leaves
Use the diagram below to answer questions 157 and 158

156. The diagram above is called ……… A. watering can B. boom sprayer C. knapsack sprayer D. hand trowel
157. The machine is used for ……. A. fetching water B. applying chemicals C. spraying petrol D. drinking
158. Which of the following groups is a monocotyledon? A. millet, maize, guinea-corn and cowpea B. cowpea, guinea-corn, guinea grass and millet C. maize, millet, elephant and rice D. carpet grass, millet, maize and beans
159.In planning farm, which of the following is least considered? A. kinds of crops B. species of animals C. nearness to stores D. size of the farm
160. The physical appearance of the soil depending on how individual particles are packed is called ….. A. profile B. structure C. capillary D. texture
161. The following are characteristics of commercial farm except A. high degree of specialization B. investment of large sum of money C. skilled technical and management staff D. small size of farm land
162. All the measures aimed at preventing soil erosion, sustaining soil fertility and ensuring good and productive use of soil come under soil …….. A. maintenance B. conservation C. analysis D. formation
163. The gestation period of sow is ………days A. 150 B. 124 C. 114 D. 283
164. A farm implement with a long wooden handle and four or five prongs as the metal head is called A. sickle B. garden fork C. drill D. tined
165. The record of all assets in the farm is referred to as …….. A. farm diary B. farm inventory C. input record D. production record
166. Which of the following crops is most suitable for a farmland deficient in nitrogen? A. rice B. maize C. Cowpea D. sorghum
167. One of the following crops is not a vegetable A. onion B. cowpea C. okra D. tomato
168. Under what farm operations will you classify harvesting? A. planting B. post-planting C. pre-planting D. early-planting
169. The following provide career opportunity in agriculture except A. agronomy B. soil science C. veterinary service D. aeronautics
170. Pollination of crops can described as a process of A. sexual propagation B. asexual propagation C. vegetative reproduction D. shoot development
171. The method of poultry management whereby birds are allowed to wander about to look for food without restriction is called ….. A. extensive B. intensive C. semi-intensive D. fold system
172. An animal that possesses four compartment stomach is called A. mammal B. ruminant C,.herbivore D. omnivore
173. The following are the main objectives of fencing of farm except A. preventing damage of crops B. controlling livestock breeding C. improving the management of grazing D. providing areas for recreation
174. Which of these stored produce is easily attacked by weevils? A. kola B. maize C. cocoa D. cotton
175. The farm tool used for transplanting seedlings from nursery to the field is A. hand fork B. shovel C. hand trowel D. cutlass
176. Which of the following is not a workshop operation? A. painting B. tightening of bolts and nuts C. washing of overall D. spraying
177. The degree of fineness or coarseness of soil particles is known as its …. A. composition B. profile C. texture D. structure
178. A farmer can use the following methods to control evaporation of water from the soil except A. bush fallowing B. bush burning C. cover cropping D. mulching
179. Which of the following should be best considered in selecting seeds for planting? A. method of storage B. maturity C. moisture content D. viability
180. A cattle disease that causes abortion and sterility is known as A. brucellosis B. rinder pest C. coccidiosis D. pleuropnemonia
