1ST TERM
1ST TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of the work done in year one.
2. Track Events (Long distance races): 3,000m race, 5000m race, 10,000m race, Marathon race. (b) Techniques/skills: (i) starting (ii) running (iii) arm action (iv) finishing.
3. Track Events (Relay races): (a) 4x100m relay race, 4x400m relay race. *emphasis on (b) techniques/skills: take off, acceleration, smooth visual and exchange.
4. Lawn Tennis: (a) History and development of tennis. (b) Basic skills and techniques of tennis. (c) Rules of tennis. (d) Officials and functions. (e) Equipment and facilities
5. Table Tennis: (a) History and development of table tennis. (b) Basic skills and techniques of the games e.g. grip, service, drive chop, and smash. (c) Equipment. (d) Rules and regulations. (e) Officials.
6. Basketball: (a) History and development of Basketball. (b) Basic skill and techniques of the game. (c) Rules and regulations governing the game. (d) Officials of the game and their functions. (e) Equipment, facilities, dimensions and values of the basketball.
7. Handball: (a) History and development of Handball. (b) Basic skills and techniques of handball game. e.g. throwing, catching, shooting. (c) Rules and regulations governing handball. (d) Officials of the game and their duties. (e) Equipment and facilities with its dimension. (f) Values of the game.
8. Safety and Accidents: (a) Definition of safety, safety education and accidents. (b) Safety measures: (i) at home, (ii) on play ground, (iii) on the roads. (c) Classification of accidents: (i) school, (ii) home/domestic, (iii) work place, (iv) vehicle. (d) Causes of road traffic accidents. (Measures for preventing road traffic accidents.)
9. Revision.
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of the work done in year one.
2. Track Events (Long distance races): 3,000m race, 5000m race, 10,000m race, Marathon race. (b) Techniques/skills: (i) starting (ii) running (iii) arm action (iv) finishing.
3. Track Events (Relay races): (a) 4x100m relay race, 4x400m relay race. *emphasis on (b) techniques/skills: take off, acceleration, smooth visual and exchange.
4. Lawn Tennis: (a) History and development of tennis. (b) Basic skills and techniques of tennis. (c) Rules of tennis. (d) Officials and functions. (e) Equipment and facilities
5. Table Tennis: (a) History and development of table tennis. (b) Basic skills and techniques of the games e.g. grip, service, drive chop, and smash. (c) Equipment. (d) Rules and regulations. (e) Officials.
6. Basketball: (a) History and development of Basketball. (b) Basic skill and techniques of the game. (c) Rules and regulations governing the game. (d) Officials of the game and their functions. (e) Equipment, facilities, dimensions and values of the basketball.
7. Handball: (a) History and development of Handball. (b) Basic skills and techniques of handball game. e.g. throwing, catching, shooting. (c) Rules and regulations governing handball. (d) Officials of the game and their duties. (e) Equipment and facilities with its dimension. (f) Values of the game.
8. Safety and Accidents: (a) Definition of safety, safety education and accidents. (b) Safety measures: (i) at home, (ii) on play ground, (iii) on the roads. (c) Classification of accidents: (i) school, (ii) home/domestic, (iii) work place, (iv) vehicle. (d) Causes of road traffic accidents. (Measures for preventing road traffic accidents.)
9. Revision.
WEEK 1
TOPIC: TRACK EVENTS
Contents: (a) Long distance Races – 3,000 meters, 5,000 meters, 10,000metres race & Marathon race
(b) techniques/skills:
(i) Starting (ii) Running (iii)Arm Action (iv) Finishing
LONG DISTANCE RACES
These are race that are longer than middle distance races and take more time to complete.
The race is started by standing start. Examples of long distance races are:-
3,000m
5000m
10,000
Marathons

Marathon means continue running for a long time without stopping. The distance may be between 10km and 41km
Features /techniques of long distance race
- Is an open race
- Started with the standing start
- Is not run at full speed from the start
- It involves running in curves
- It is not run on specific lanes
- An athlete can only overtake on the right.
- It involves coasting/slowing down at intervals
- It is an aerobic race
- The body is in slightly erect position

Starting:-
The starting method is “standing start”
Running:-
The running can be on tracks or roads.
Overtaking is in the right
Arm action:-
The arm action is not like in spirit races since the body is in slightly erect position
Finishing
The runners must finish with speed.
The athlete need more air at the finishing coast.
Evaluation
1. What is long distance races?
2. List 3 types of long distance races.
Reading assignment
Essential of PHE for Junior Secondary School book 2. By Akinseye S.E PP 3-5
Contents: (a) Long distance Races – 3,000 meters, 5,000 meters, 10,000metres race & Marathon race
(b) techniques/skills:
(i) Starting (ii) Running (iii)Arm Action (iv) Finishing
LONG DISTANCE RACES
These are race that are longer than middle distance races and take more time to complete.
The race is started by standing start. Examples of long distance races are:-
3,000m
5000m
10,000
Marathons

Marathon means continue running for a long time without stopping. The distance may be between 10km and 41km
Features /techniques of long distance race
- Is an open race
- Started with the standing start
- Is not run at full speed from the start
- It involves running in curves
- It is not run on specific lanes
- An athlete can only overtake on the right.
- It involves coasting/slowing down at intervals
- It is an aerobic race
- The body is in slightly erect position

Starting:-
The starting method is “standing start”
Running:-
The running can be on tracks or roads.
Overtaking is in the right
Arm action:-
The arm action is not like in spirit races since the body is in slightly erect position
Finishing
The runners must finish with speed.
The athlete need more air at the finishing coast.
Evaluation
1. What is long distance races?
2. List 3 types of long distance races.
Reading assignment
Essential of PHE for Junior Secondary School book 2. By Akinseye S.E PP 3-5
WEEK 2
TOPIC: TRACK EVENTS (Relay Races)
Contents: Relay races –Types and techniques
RELAY RACES
Relay race is the only team event in athletics
It is a race in which the effort of each athlete compliments the others. It is run by 4 – runners. They are called:-
1st runners - 1st Leg
2nd runners - 2nd Leg
3 rd Runners - 3rd Leg
4th Runner - 4th Leg

Types of relay races
(a) Shuttle relay
(b) Medley relay
(c) Circular relay (e.g 4x100m, 4x 400m)
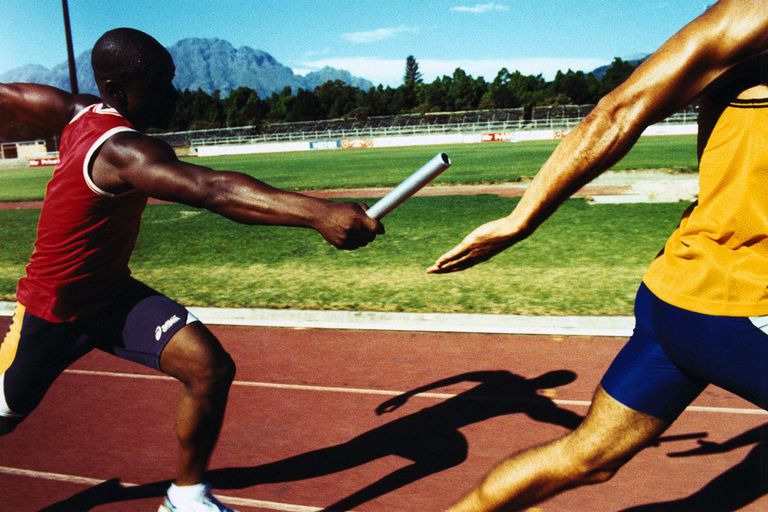
In relay races, runner covers a specified distance, the baton is passed from one runner to the other within the takeover or change over zone , race start and ends with baton in the hand of runners.
Size of baton - 30cm long, 12cm in circumstances
METHOD S OF BATON EXCHANGE
There are two methods of baton exchange
(a) The Visual method
(b) The non-visual method
(a) The visual method is the one in which the receiving runners looks back to see and collect the baton from the incoming runner. It is mostly used in middle and long distance relay races e.g 4x800m and 4x 1500m relay

(b) The non-visual method is the o e in which the receiving does not look back but extends hand behind him with the finger spread at a slightly bent position, in readiness to receive and take off.
This method has the following advantages
- It saves time
- It is quicker
- it is more interesting
- it is commonly used in 4 x 100m and 4x200m relay.

Notes:-
(a) The lane is 1.22m wide
(b) The baton exchange zone is 30cm divided in to 3 equal parts of 10m each
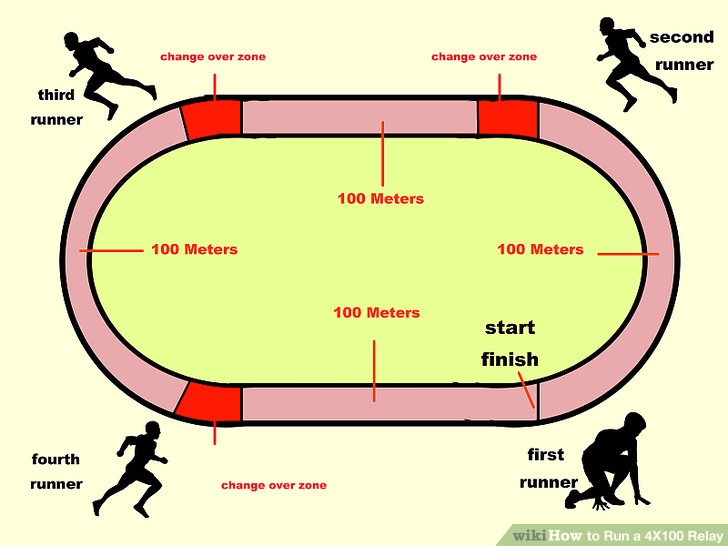
a = Accelerating zone.
b = Take over zone
c = Acceleration zone.

METHOD OF CARRYING BATON
There are two methods of carrying the baton after the handing over. They are:=
- The alternate or Zig zag method
- The non-alternate or uniform method.
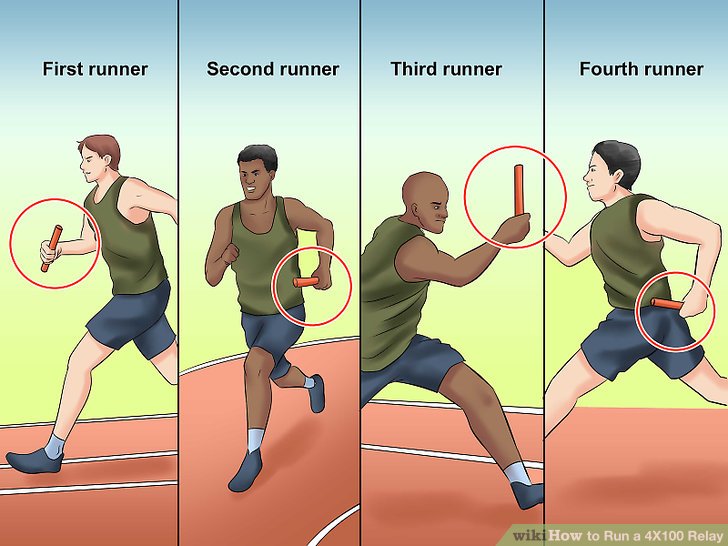
ADVANTAGES OF ALTERNATE METHOD
It prevents collision of runners
It prevents loss of speed/acceleration
It prevents loss of time i.e. saves time
It creates free/adequate space between runners
DISADVANTAGES OF ALTERNATE METHOD
Athletes are disqualified in relay race, if they commit offences of:-
- Pushing / assisting during the take over
- Throwing of baton instead of passing
- Picking of a dropped baton by another athlete
- Impeding an opposing athlete
- Crossing to the other lanes
- Passing the baton outside the take over zone
- Finishing the race without baton in hands.
Evaluation
1. Define relay race
2. How many athletes run a specified relay race
3. State the two methods of baton exchange
Reading assignment
Essentials of PHE for Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 by Akinseye S.E pp 17 – 21
Assignment
Open to the essentials of PHE for JSS Book 2 by Akinseye S.E. Page 21, Questions 1 – 10
Contents: Relay races –Types and techniques
RELAY RACES
Relay race is the only team event in athletics
It is a race in which the effort of each athlete compliments the others. It is run by 4 – runners. They are called:-
1st runners - 1st Leg
2nd runners - 2nd Leg
3 rd Runners - 3rd Leg
4th Runner - 4th Leg

Types of relay races
(a) Shuttle relay
(b) Medley relay
(c) Circular relay (e.g 4x100m, 4x 400m)
In relay races, runner covers a specified distance, the baton is passed from one runner to the other within the takeover or change over zone , race start and ends with baton in the hand of runners.
Size of baton - 30cm long, 12cm in circumstances
METHOD S OF BATON EXCHANGE
There are two methods of baton exchange
(a) The Visual method
(b) The non-visual method
(a) The visual method is the one in which the receiving runners looks back to see and collect the baton from the incoming runner. It is mostly used in middle and long distance relay races e.g 4x800m and 4x 1500m relay

(b) The non-visual method is the o e in which the receiving does not look back but extends hand behind him with the finger spread at a slightly bent position, in readiness to receive and take off.
This method has the following advantages
- It saves time
- It is quicker
- it is more interesting
- it is commonly used in 4 x 100m and 4x200m relay.

Notes:-
(a) The lane is 1.22m wide
(b) The baton exchange zone is 30cm divided in to 3 equal parts of 10m each

a = Accelerating zone.
b = Take over zone
c = Acceleration zone.

METHOD OF CARRYING BATON
There are two methods of carrying the baton after the handing over. They are:=
- The alternate or Zig zag method
- The non-alternate or uniform method.

ADVANTAGES OF ALTERNATE METHOD
It prevents collision of runners
It prevents loss of speed/acceleration
It prevents loss of time i.e. saves time
It creates free/adequate space between runners
DISADVANTAGES OF ALTERNATE METHOD
Athletes are disqualified in relay race, if they commit offences of:-
- Pushing / assisting during the take over
- Throwing of baton instead of passing
- Picking of a dropped baton by another athlete
- Impeding an opposing athlete
- Crossing to the other lanes
- Passing the baton outside the take over zone
- Finishing the race without baton in hands.
Evaluation
1. Define relay race
2. How many athletes run a specified relay race
3. State the two methods of baton exchange
Reading assignment
Essentials of PHE for Junior Secondary Schools Book 2 by Akinseye S.E pp 17 – 21
Assignment
Open to the essentials of PHE for JSS Book 2 by Akinseye S.E. Page 21, Questions 1 – 10
WEEK 3
Topic: Lawn Tennis or Tennis
Contents:
(a) History and development of tennis
(b) Basic skills and techniques of Tennis
(c) Rules of Tennis
(d) Officials and functions
(e) Equipment and facilities
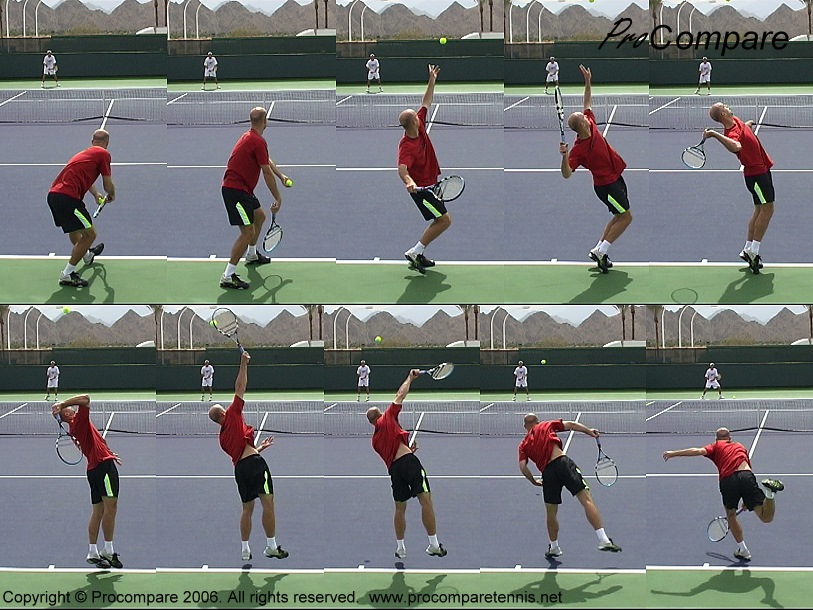
LAWN TENNIS
Tennis was originally called Lawn Tennis when the playing was done on lawns only. The name was changed to Tennis when the playing court included clay, asphalt and cement. The game was introduced to England in 1873 by Major Walter Clopton Wingfield. It was introduced to U.S in1875 by Mary Ewing Outerbridge of New York. The game is popular in most countries of the world. The game of tennis was introduced to Nigeria by the early missionaries and colonial masters. The game is played for both competitors, recreation and both sexes. Tennis is a lifetime sports and is for individual or dual game.

BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
The fundamental skills are:-
- The grip (Weston grip, eastern grip and continental)
- The serve
- The stance
- The footwork
- The strokes which includes freehand drive, backhand drive, volley, lobs, drop sheet spin, net shot, smash and half valley

RULES OF TENNIS
Scoring in a game
The score of a player who has won no points is said to stand at LOVE i.e.
No Score - LOVE
1 st Point - 15
2 nd Point - 30
3 rd Point - 40
4 th Point - Game
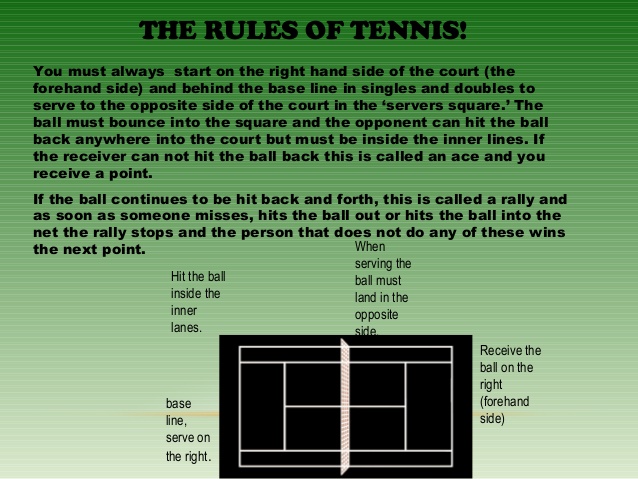
Deuce: If the players score three points each (i.e. 40 – all) the score is called deuce
Advantage In (Van-in) is the next point won by the server after a deuce.
Advantage out (Van-out) is the next point won by the receiver after a deuce
Other rules:-
1. The server should not serve until the receiver is ready.
2. The server is “left” if the served ball touches the net and fails to return the ball.
3. The receiver wins a point, if the server serves two consecutive faults.
4. A line ball is good ball
5. The service is fault if the server misses the ball in attempting to strike it.
6. A player losses a point if the ball touches him or anything he puts on (except the racket) while the ball is in play.
7. The maximum numbers of sets in a match shall be 5 for men and 3 for women.
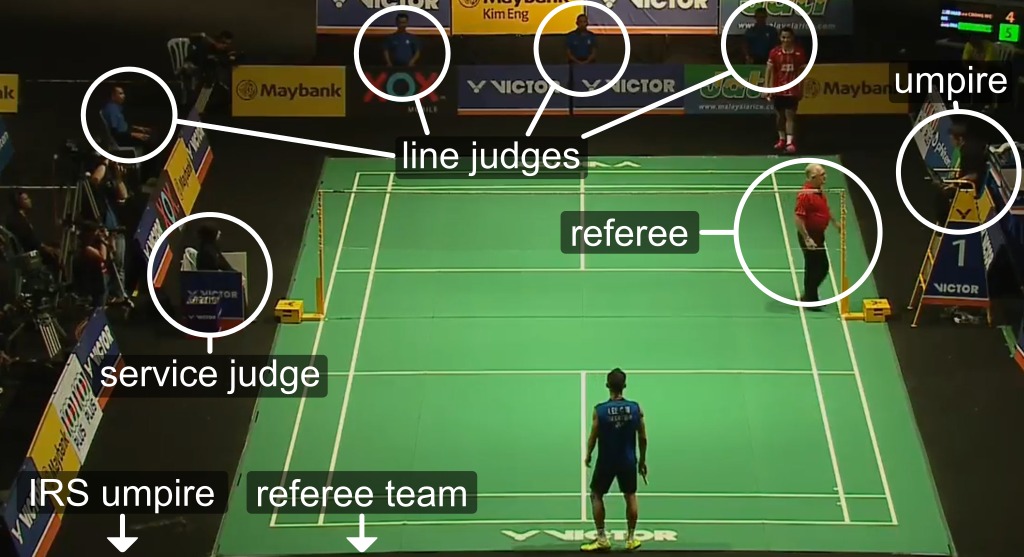
OFFICIALS AND FUNCTIONS
The officials are:-
- The referee
- The ball boys
- The umpire
- The linesmen
- The net – cord judges
EQUIPMENT AND FACILITIES
They are:-
- The playing court
- The net
- The balls
- The white “T” Shirt
- The canvass shoes
- The racket
- The towel
The racket has the following:
The butt, grip, handle, throat, face and racket edge.
The court is
Single court = 23.8m by 8.2m
Double court = 23.8m by 11m
Height of net = 0.9m
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ifI9Rib3eBU[/youtube]
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CXgfNBnetzQ[/youtube]
Evaluation:-
1. Who introduced tennis into Nigeria?
2. List 3 basic skills of tennis
3. Outline the scoring system in tennis.
ASSIGNMENT
(a) Read page 22 – 31 from essentials of PHE for JSS. Book 2. By Akinseye S.E
(b) Attempts all the questions on page 31 of the above textbook.
Contents:
(a) History and development of tennis
(b) Basic skills and techniques of Tennis
(c) Rules of Tennis
(d) Officials and functions
(e) Equipment and facilities
LAWN TENNIS
Tennis was originally called Lawn Tennis when the playing was done on lawns only. The name was changed to Tennis when the playing court included clay, asphalt and cement. The game was introduced to England in 1873 by Major Walter Clopton Wingfield. It was introduced to U.S in1875 by Mary Ewing Outerbridge of New York. The game is popular in most countries of the world. The game of tennis was introduced to Nigeria by the early missionaries and colonial masters. The game is played for both competitors, recreation and both sexes. Tennis is a lifetime sports and is for individual or dual game.

BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
The fundamental skills are:-
- The grip (Weston grip, eastern grip and continental)
- The serve
- The stance
- The footwork
- The strokes which includes freehand drive, backhand drive, volley, lobs, drop sheet spin, net shot, smash and half valley

RULES OF TENNIS
Scoring in a game
The score of a player who has won no points is said to stand at LOVE i.e.
No Score - LOVE
1 st Point - 15
2 nd Point - 30
3 rd Point - 40
4 th Point - Game

Deuce: If the players score three points each (i.e. 40 – all) the score is called deuce
Advantage In (Van-in) is the next point won by the server after a deuce.
Advantage out (Van-out) is the next point won by the receiver after a deuce
Other rules:-
1. The server should not serve until the receiver is ready.
2. The server is “left” if the served ball touches the net and fails to return the ball.
3. The receiver wins a point, if the server serves two consecutive faults.
4. A line ball is good ball
5. The service is fault if the server misses the ball in attempting to strike it.
6. A player losses a point if the ball touches him or anything he puts on (except the racket) while the ball is in play.
7. The maximum numbers of sets in a match shall be 5 for men and 3 for women.
OFFICIALS AND FUNCTIONS
The officials are:-
- The referee
- The ball boys
- The umpire
- The linesmen
- The net – cord judges

EQUIPMENT AND FACILITIES
They are:-
- The playing court
- The net
- The balls
- The white “T” Shirt
- The canvass shoes
- The racket
- The towel

The racket has the following:
The butt, grip, handle, throat, face and racket edge.
The court is
Single court = 23.8m by 8.2m
Double court = 23.8m by 11m
Height of net = 0.9m
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ifI9Rib3eBU[/youtube]
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CXgfNBnetzQ[/youtube]
Evaluation:-
1. Who introduced tennis into Nigeria?
2. List 3 basic skills of tennis
3. Outline the scoring system in tennis.
ASSIGNMENT
(a) Read page 22 – 31 from essentials of PHE for JSS. Book 2. By Akinseye S.E
(b) Attempts all the questions on page 31 of the above textbook.
WEEK 4
Topic: Table tennis
Contents:
(a) History and development of table tennis
(b) Basic skills and techniques of the game
(c) Equipment
(d) Rules and regulations of the game
(e) Officials
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF TABLE TENNIS
The origin of table tennis is not very certain but it is believed to have originated in the far East. It has been called many names such as indoor tennis, whiff-whaff, and Ping pong by the chinesse. The name table tennis was given by the Parker brothers.
The English table tennis association was formed in 1923, the international Table tennis Federation was formed in 1926 and Nigeria Table Tennis Federation was formed in 1951.


BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES OF THE GAME
The skills are:-
(a) The grip (Tennis grip, penholder grip)
(b) The serve/service (freehand, backhand, chop, side spin)
(c) The footwork/stance
(d) The stroke/drive (forehand and back hand)
(e) The drop short
(f) The smash
(g) The half volley

EQUIPMENT
1. The table 2. The net 3. The racket (bat)
4. The ball 5. The dress
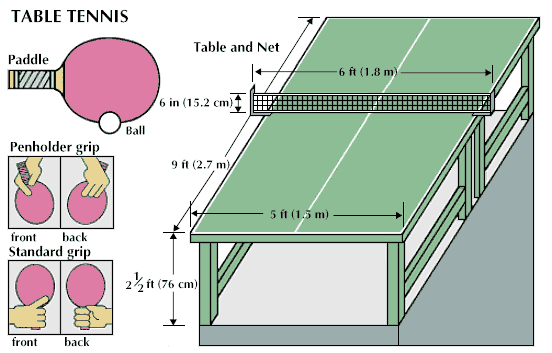
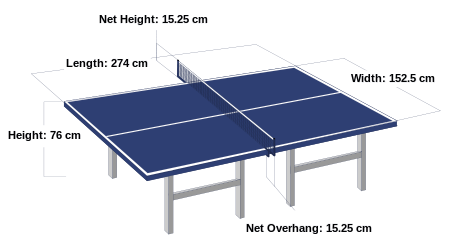
DIMENSION:-
Table = Length 2.74m
Width 1.52m
Height 0.76m
Net – 15.25cm high at the centre
Racket – may be of any size, shape or weight .
Ball – locally called “egg”, white, orange, yellow in colours and it must be celluloid.
However, table tennis can be played as singles or doubles or mixed doubles.
RULES AND REGULATIONS
1. The ball must be shown as service is deliver
2. Opponent s must be ready before service is delivered.
3. The ball must be bounce once before it is returned.
4. No part of the body is allowed to touch the table during play.
5. A served ball that touches the net before dropping on the receivers end of the table is “let” and shall be re-served. But if it bounce back to the servers side, then it is a point to the receiver.
6. A player must not distract the attention of the opponents.
7. A match consists of winning best odd numbers of games
8. The hand must not be on the table when making a return.
OFFICIALS AND FUNCTIONS
(a) Referee
(b) Umpire
(c) Table manager
(d) Recorder
(e) Scorer

REFEREE
- It takes final decision in disputed matters
- He supervises other officials
UMPIRE
• He tosses for choice of ends and service
• He announces points made by players
• De declares the winner or looser at the end of the game
• He awards penalties to erring players
TABLE MANAGER
He ensures that the table is ready for the game.
RECORDER
He records scores of players or side in a score sheet after each game or set.
SCORER
He records scores of players and on the scoreboard.
Note:- The game of table tennis consist of 11 points. At 10 – 10 (deuce) a player must lead with 2 points in other to win a game. Matches are played to the best of 3 or 5 games
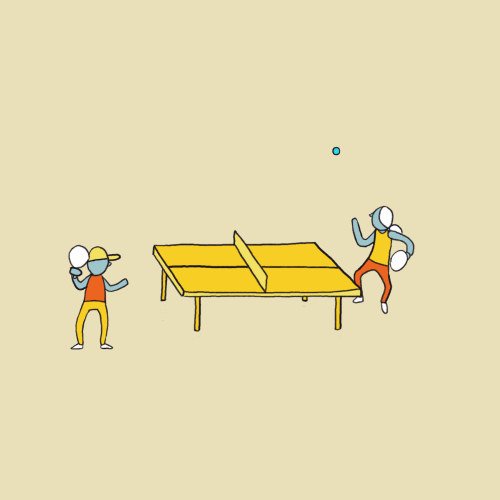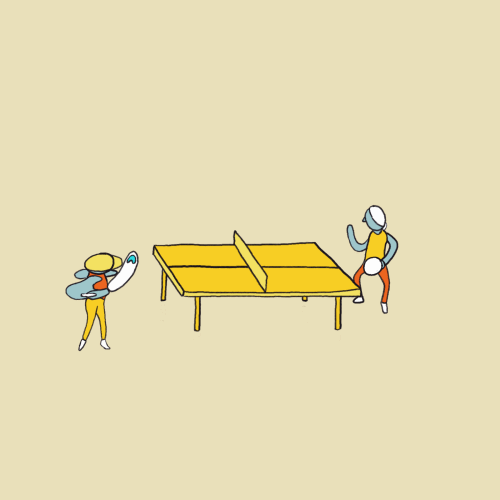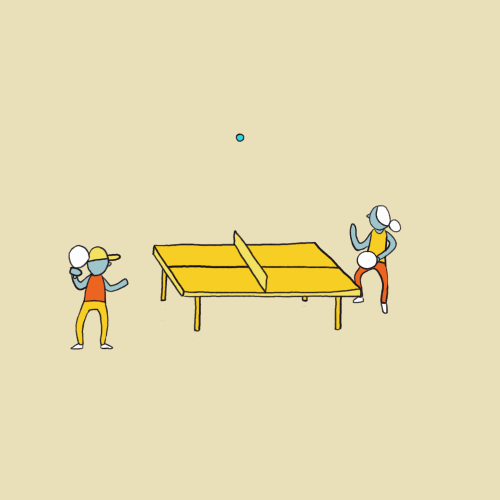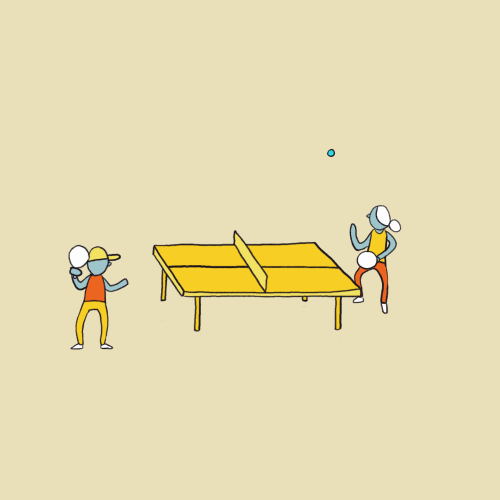
EVALUATION:
1. Mention another name for Table Tennis.
2. Describe movement of the ball from the server to the receiver.
3. State the officials in table tennis.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Essentials of PHE for Junior Secondary Schools book 2. By Akinseye S.E PP 32 – 38
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=24HKRrWRUMg[/youtube]
ASSIGNMENT
Page 38 of the above named text book by Akinseye S.E (Nos 1 – 4)
Contents:
(a) History and development of table tennis
(b) Basic skills and techniques of the game
(c) Equipment
(d) Rules and regulations of the game
(e) Officials
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF TABLE TENNIS
The origin of table tennis is not very certain but it is believed to have originated in the far East. It has been called many names such as indoor tennis, whiff-whaff, and Ping pong by the chinesse. The name table tennis was given by the Parker brothers.
The English table tennis association was formed in 1923, the international Table tennis Federation was formed in 1926 and Nigeria Table Tennis Federation was formed in 1951.


BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES OF THE GAME
The skills are:-
(a) The grip (Tennis grip, penholder grip)
(b) The serve/service (freehand, backhand, chop, side spin)
(c) The footwork/stance
(d) The stroke/drive (forehand and back hand)
(e) The drop short
(f) The smash
(g) The half volley

EQUIPMENT
1. The table 2. The net 3. The racket (bat)
4. The ball 5. The dress

DIMENSION:-
Table = Length 2.74m
Width 1.52m
Height 0.76m
Net – 15.25cm high at the centre
Racket – may be of any size, shape or weight .
Ball – locally called “egg”, white, orange, yellow in colours and it must be celluloid.
However, table tennis can be played as singles or doubles or mixed doubles.

RULES AND REGULATIONS
1. The ball must be shown as service is deliver
2. Opponent s must be ready before service is delivered.
3. The ball must be bounce once before it is returned.
4. No part of the body is allowed to touch the table during play.
5. A served ball that touches the net before dropping on the receivers end of the table is “let” and shall be re-served. But if it bounce back to the servers side, then it is a point to the receiver.
6. A player must not distract the attention of the opponents.
7. A match consists of winning best odd numbers of games
8. The hand must not be on the table when making a return.
OFFICIALS AND FUNCTIONS
(a) Referee
(b) Umpire
(c) Table manager
(d) Recorder
(e) Scorer

REFEREE
- It takes final decision in disputed matters
- He supervises other officials
UMPIRE
• He tosses for choice of ends and service
• He announces points made by players
• De declares the winner or looser at the end of the game
• He awards penalties to erring players
TABLE MANAGER
He ensures that the table is ready for the game.
RECORDER
He records scores of players or side in a score sheet after each game or set.
SCORER
He records scores of players and on the scoreboard.
Note:- The game of table tennis consist of 11 points. At 10 – 10 (deuce) a player must lead with 2 points in other to win a game. Matches are played to the best of 3 or 5 games

EVALUATION:
1. Mention another name for Table Tennis.
2. Describe movement of the ball from the server to the receiver.
3. State the officials in table tennis.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Essentials of PHE for Junior Secondary Schools book 2. By Akinseye S.E PP 32 – 38
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=24HKRrWRUMg[/youtube]
ASSIGNMENT
Page 38 of the above named text book by Akinseye S.E (Nos 1 – 4)
WEEK 5
Topic: Basket Ball
Contents
(a ) History and Development
(b) Basic skills and techniques of the game
(c) Rules and regulation governing the game
(d) Officials of the game and their functions
(e) Equipment, facilities and dimensions
(f) Values of basketball.
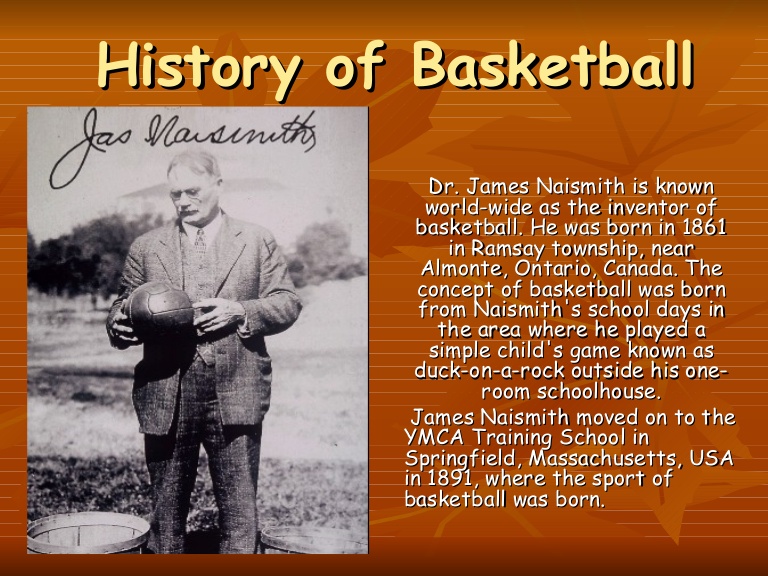
History And Development
Basketball is an Americans game invented by AR. Naismith in 1891. Naismith was a physical education instructor at the Intonuture Young Men’s Christian Association training school in Spring Field, U.S.A. the game is played by two teams of five players each side. The game is started by centre jump ball. It was first played during the Berlin Olympic in 1936.
Today, rules of basketball are being set out by the international Amateur Basket ball Federation (F.I.B.A). it was founded in 1932. It has its headquarters in Egypt. The Nigeria Amateur Basketball Federation was formed in 1965.
BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
1. Passing and catching - types of pass includes
- Chest pass , - under arm pass
- Bounce pass – javelin pass
- Two hand over head pass
2. Shooting:- Types are
- Lay up shot – free throw shot
- Hook shot -dunk shot
- Jump shot one hand set shot
3. Dribbling(High and low dribbling)
4. Footwork
5. The individual offence
6. The individual defense (Zone, man to man)

RULES AND REGULATIONS GOVERNING THE GAME
Some rules of Basketball are:-
a. A goal is nude when a ball enters the basket from above
b. A player is not allowed to hit the ball with his feet.
c. A player should not kick the ball.
d. A player should not carry the ball more than one pace.
e. A player must not double dribble.
f. He must not remain in the restricted areas for more than 3 seconds.
g. A player should not push, hold, or drip opponents.
h. A game is decided by scoring of greater number of points in the playing time.
i. A team can only be in the possession or control of the ball for 24 seconds
j. A score outside the three point arc is 3 points
k. The playing time is of four sections.

EVALUATION:
1. Who introduced the game of basketball and in what year?
2. List 5 types of posses.
SUB TOPIC: Basketball (Contd)
Contents:
(a) officials and their functions
(b) Equipment, facilities and dimensions
(c) Values of basketball
OFFICIAL AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
1. Referee 2. Umpires 3. Scorer
3. Time Keeper 5. Match Commissioner
A game is specified by a referee and an umpire who are known as officials and are assisted by a time keeper and a scorer.
However, the referee and umpire are responsible for:-
- Putting the ball into play
- Deciding when the ball becomes “dead”
- Stopping play when the ball is “dead”
- Ordering or allowing time-out.
- Beckoning substitutes on the court.
- Passing the ball to a player for a specific throw
- Counting of seconds when a player must play the ball or shoot within a time limit.
- Pushing un-sport-manlike conduct.

The controlling body are:-
1. F.I.B.A – International federation of Amateur Basketball
2. N.B.B.F- Nigeria Basketball Federation
SCORER
- Records the names and number of all players.
- Records the number of points scored by each player and team.
- Records all fouls, personal and technical and tell an official immediately when a player has committed a total of 5 fouls
- Records the time-out
TIME KEEPER
- Inform the referee when it is 3 minutes before each half is started.
- Records both the playing time and the time of stoppages.
- Indicates the end of playing time in each half or extra period with a pistol or bell.

EQUIPMENT, FACILITIES AND DIMENSIONS
1. The playing court
2. The backboard and rings
3. The basketball shoes
4. The scoreboard
5. The baskets
6. The bell
7. The whistles and stop watches
8. The vest

PLAYING COURT SPECIFICATIONS
- Shape -rectangular
- Length -28meters
Width 15metres
- All lines -5cm wide preferably white
- Centre circle –diameter of 3.60m
- Free throw line – should be drawn parallel to the end line and it must be 5.80m from the end line.
There are 3 restraining circles and each has a radius of 1.80m. the circles are areas where the game is started or restarted.
There are 2 restricted areas. They are bowled by the free throw line and the restraining circles.
The backboards – 1.20m into the court
The rings – diameter of 45cm and raised 3.05m above the floor.
The Nets – should be with white cord and attached to the under edge of the ring by 12 loops
The ball circumference is between 74.9cm and 76.2cm. The weight is between 567gm and 624gm.
The dress – the players are recommended to wear shorts and vests special basketball boots and two pairs of socks for comforts
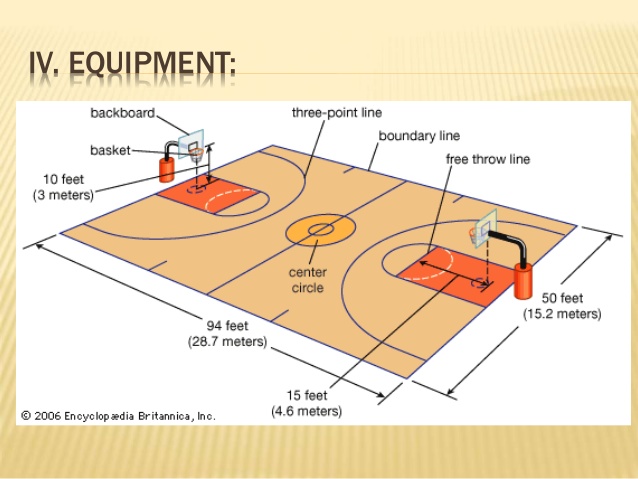
SCORING SYSTEM IN BASKETBALL GAME
1. A goal can be scored from any part of the court; score is by system of points.
2. 2 points are awarded for a field goal.
3. 1 points is awarded for a basket made from free throw.
4. 3 points are awarded for a field goal scored outside the three- point circle

Values of Basket ball
The values of basketball include
_ development of safety skill and habits
_ physical fitness and strength development
_ For income and competitions
_ Mental Accuracy and coordination

Evaluation
1. Give the dimension of a basketball court.
2. List 5 facilities and equipment of basketball.
Reading Assignment
Essential of PHE for Junior Secondary School, book 2 by Akiseye S.E pp. 39-53.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Cjxfu1AcQA[/youtube]
Assignment
1.The length of a basketball court is (a) 20 (b) 28 metres (c) 14 metres
2. Basketball was invented by (a) Nainsmith (b) W. Morgan (c) Adedeji
3. The Nigerian Amateur Basketball Federation was formed in (a) 1935 (b) 1945 (c) 1965
4. One of these is not a type of shot in the game of basketball (a) sail shot (b) Jump shop (c) dunk shot
5. The game of basketball is supervised by (a) Referee and Time keeper (b) Referee and scorer (c) Referee and umpire
Theory:
1. Mention 5 types of posses in basketball.
2. What is the point s given to a goal made outside the 3- points arc/circle?
3. The game of basketball is started at the centre circle with________
Contents
(a ) History and Development
(b) Basic skills and techniques of the game
(c) Rules and regulation governing the game
(d) Officials of the game and their functions
(e) Equipment, facilities and dimensions
(f) Values of basketball.
History And Development
Basketball is an Americans game invented by AR. Naismith in 1891. Naismith was a physical education instructor at the Intonuture Young Men’s Christian Association training school in Spring Field, U.S.A. the game is played by two teams of five players each side. The game is started by centre jump ball. It was first played during the Berlin Olympic in 1936.
Today, rules of basketball are being set out by the international Amateur Basket ball Federation (F.I.B.A). it was founded in 1932. It has its headquarters in Egypt. The Nigeria Amateur Basketball Federation was formed in 1965.

BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
1. Passing and catching - types of pass includes
- Chest pass , - under arm pass
- Bounce pass – javelin pass
- Two hand over head pass
2. Shooting:- Types are
- Lay up shot – free throw shot
- Hook shot -dunk shot
- Jump shot one hand set shot
3. Dribbling(High and low dribbling)
4. Footwork
5. The individual offence
6. The individual defense (Zone, man to man)

RULES AND REGULATIONS GOVERNING THE GAME
Some rules of Basketball are:-
a. A goal is nude when a ball enters the basket from above
b. A player is not allowed to hit the ball with his feet.
c. A player should not kick the ball.
d. A player should not carry the ball more than one pace.
e. A player must not double dribble.
f. He must not remain in the restricted areas for more than 3 seconds.
g. A player should not push, hold, or drip opponents.
h. A game is decided by scoring of greater number of points in the playing time.
i. A team can only be in the possession or control of the ball for 24 seconds
j. A score outside the three point arc is 3 points
k. The playing time is of four sections.

EVALUATION:
1. Who introduced the game of basketball and in what year?
2. List 5 types of posses.
SUB TOPIC: Basketball (Contd)
Contents:
(a) officials and their functions
(b) Equipment, facilities and dimensions
(c) Values of basketball
OFFICIAL AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
1. Referee 2. Umpires 3. Scorer
3. Time Keeper 5. Match Commissioner
A game is specified by a referee and an umpire who are known as officials and are assisted by a time keeper and a scorer.
However, the referee and umpire are responsible for:-
- Putting the ball into play
- Deciding when the ball becomes “dead”
- Stopping play when the ball is “dead”
- Ordering or allowing time-out.
- Beckoning substitutes on the court.
- Passing the ball to a player for a specific throw
- Counting of seconds when a player must play the ball or shoot within a time limit.
- Pushing un-sport-manlike conduct.

The controlling body are:-
1. F.I.B.A – International federation of Amateur Basketball
2. N.B.B.F- Nigeria Basketball Federation
SCORER
- Records the names and number of all players.
- Records the number of points scored by each player and team.
- Records all fouls, personal and technical and tell an official immediately when a player has committed a total of 5 fouls
- Records the time-out
TIME KEEPER
- Inform the referee when it is 3 minutes before each half is started.
- Records both the playing time and the time of stoppages.
- Indicates the end of playing time in each half or extra period with a pistol or bell.

EQUIPMENT, FACILITIES AND DIMENSIONS
1. The playing court
2. The backboard and rings
3. The basketball shoes
4. The scoreboard
5. The baskets
6. The bell
7. The whistles and stop watches
8. The vest

PLAYING COURT SPECIFICATIONS
- Shape -rectangular
- Length -28meters
Width 15metres
- All lines -5cm wide preferably white
- Centre circle –diameter of 3.60m
- Free throw line – should be drawn parallel to the end line and it must be 5.80m from the end line.
There are 3 restraining circles and each has a radius of 1.80m. the circles are areas where the game is started or restarted.
There are 2 restricted areas. They are bowled by the free throw line and the restraining circles.
The backboards – 1.20m into the court
The rings – diameter of 45cm and raised 3.05m above the floor.
The Nets – should be with white cord and attached to the under edge of the ring by 12 loops
The ball circumference is between 74.9cm and 76.2cm. The weight is between 567gm and 624gm.
The dress – the players are recommended to wear shorts and vests special basketball boots and two pairs of socks for comforts

SCORING SYSTEM IN BASKETBALL GAME
1. A goal can be scored from any part of the court; score is by system of points.
2. 2 points are awarded for a field goal.
3. 1 points is awarded for a basket made from free throw.
4. 3 points are awarded for a field goal scored outside the three- point circle

Values of Basket ball
The values of basketball include
_ development of safety skill and habits
_ physical fitness and strength development
_ For income and competitions
_ Mental Accuracy and coordination

Evaluation
1. Give the dimension of a basketball court.
2. List 5 facilities and equipment of basketball.
Reading Assignment
Essential of PHE for Junior Secondary School, book 2 by Akiseye S.E pp. 39-53.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Cjxfu1AcQA[/youtube]
Assignment
1.The length of a basketball court is (a) 20 (b) 28 metres (c) 14 metres
2. Basketball was invented by (a) Nainsmith (b) W. Morgan (c) Adedeji
3. The Nigerian Amateur Basketball Federation was formed in (a) 1935 (b) 1945 (c) 1965
4. One of these is not a type of shot in the game of basketball (a) sail shot (b) Jump shop (c) dunk shot
5. The game of basketball is supervised by (a) Referee and Time keeper (b) Referee and scorer (c) Referee and umpire
Theory:
1. Mention 5 types of posses in basketball.
2. What is the point s given to a goal made outside the 3- points arc/circle?
3. The game of basketball is started at the centre circle with________
WEEK 6
Topic: Hand ball
Contents
(a) History and development
(b) Basic skill and techniques of Handball game
(c) Rules and regulations.
(d) Officials of the game and their duties.
(e) Equipment and facilities with its dimension.
(f) Values of handball game.
History and Development of handball
The game of handball is believed to have originated in Germany and was introduced by Konrad Koch. The first name given to the game was Rartball, later in 1230, both Greece and Rome change the name to Catch Ball in 1919 and is today known as the name Hand ball. He developed the rules and reduced the playing area to 40m by 29m. Handball, became an Olympic sport in 1972 during the Munich Olympic in Germany. It was the same year, the handball Federation of Nigeria was formed (H.F.N).
Handball game is played by two teams of 7 players a side in the field of play five substitutes are allowed for each team.



BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
The fundamental skills of handball game are:
1. Throwing and catching
2. Passing
3. Shooting
4. Dribbling
5. Pivoting
6. Faking and feinting
7. Goal keeping
8. Guarding

SHOOTING
We have:-
Jump shot, dive shot, fall shot, pivot shot and overhead shot.
PASSING
We have:
Chest pass, bounce pass, overhead pass, under arm pass, across body pass, javelin pass, back pass and roll pass.
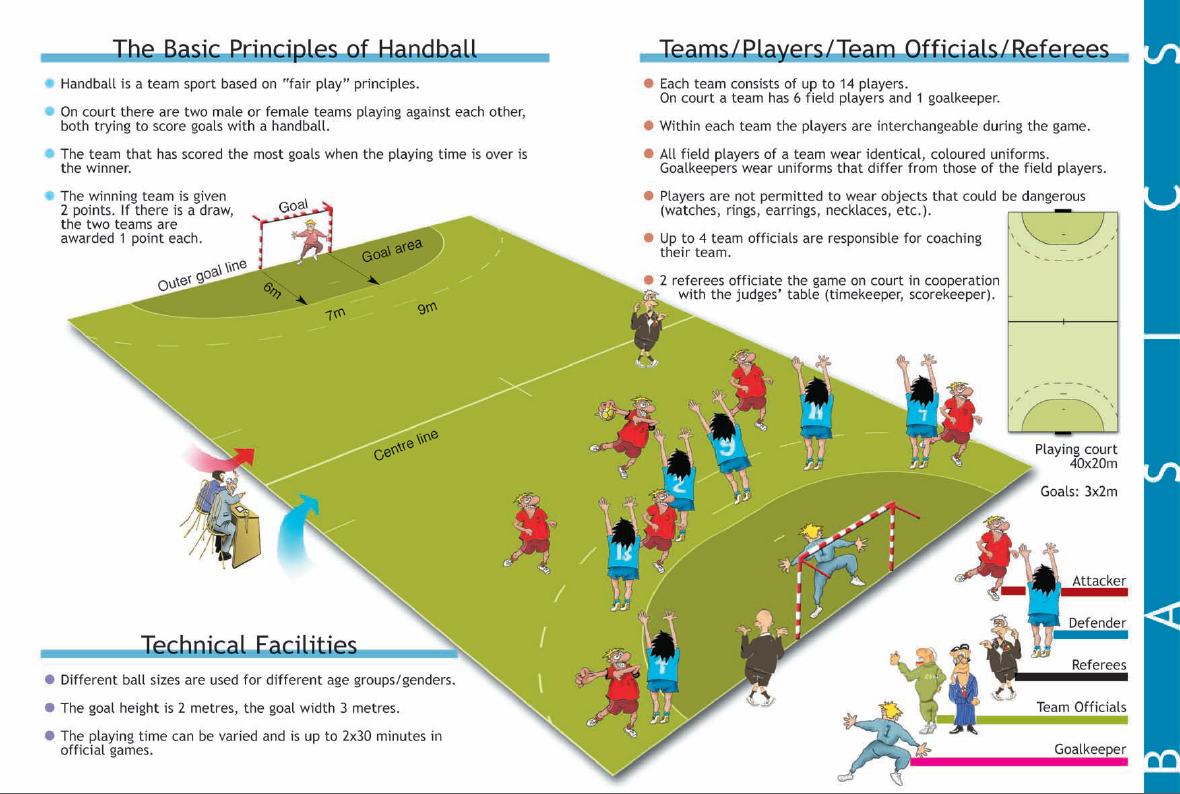
Officials and their duties.
The officials of handball game are as follows
1. Two referee
2. A score-taker
3. A time keeper.
THE REFEREE
- The two referee alternately play the role of court referee and line referee
- The court referee checks the appearance of the players, dresses and finger nails.
- Checks the ball and other equipment
- Conducts the toss for the team to choose ends.
- Controls and enforces the rules of the game.
- Cautions the players
- Penalizes any infringements
- Gives signal to the time keeper to stop or start the clock.
Score taker
He checks the team list
He is in charge of the score sheet and makes appropriate rates (goal, waving, suspension, exclusion etc).
TIME KEEPER
- He Keeps control of the playing time
- He keeps control over the number of players and officials on the substitute’s bench.
- He keep control of the suspension time of the players
- He stop the game at half time and at the end of the game with a clearly given signal.
EVALUATION
- Who is the father of handball
- How many players play the game of handball
- Mention 5 skills of handball
Contents
(a) History and development
(b) Basic skill and techniques of Handball game
(c) Rules and regulations.
(d) Officials of the game and their duties.
(e) Equipment and facilities with its dimension.
(f) Values of handball game.
History and Development of handball
The game of handball is believed to have originated in Germany and was introduced by Konrad Koch. The first name given to the game was Rartball, later in 1230, both Greece and Rome change the name to Catch Ball in 1919 and is today known as the name Hand ball. He developed the rules and reduced the playing area to 40m by 29m. Handball, became an Olympic sport in 1972 during the Munich Olympic in Germany. It was the same year, the handball Federation of Nigeria was formed (H.F.N).
Handball game is played by two teams of 7 players a side in the field of play five substitutes are allowed for each team.



BASIC SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
The fundamental skills of handball game are:
1. Throwing and catching
2. Passing
3. Shooting
4. Dribbling
5. Pivoting
6. Faking and feinting
7. Goal keeping
8. Guarding

SHOOTING
We have:-
Jump shot, dive shot, fall shot, pivot shot and overhead shot.
PASSING
We have:
Chest pass, bounce pass, overhead pass, under arm pass, across body pass, javelin pass, back pass and roll pass.

Officials and their duties.
The officials of handball game are as follows
1. Two referee
2. A score-taker
3. A time keeper.
THE REFEREE
- The two referee alternately play the role of court referee and line referee
- The court referee checks the appearance of the players, dresses and finger nails.
- Checks the ball and other equipment
- Conducts the toss for the team to choose ends.
- Controls and enforces the rules of the game.
- Cautions the players
- Penalizes any infringements
- Gives signal to the time keeper to stop or start the clock.
Score taker
He checks the team list
He is in charge of the score sheet and makes appropriate rates (goal, waving, suspension, exclusion etc).
TIME KEEPER
- He Keeps control of the playing time
- He keeps control over the number of players and officials on the substitute’s bench.
- He keep control of the suspension time of the players
- He stop the game at half time and at the end of the game with a clearly given signal.

EVALUATION
- Who is the father of handball
- How many players play the game of handball
- Mention 5 skills of handball
WEEK 7
Sub topic: Handball (Continued)
Contents:
(a) Rules and regulations of the game.
(b) Equipment and facilities with the dimensions
(c) Values of handball game.
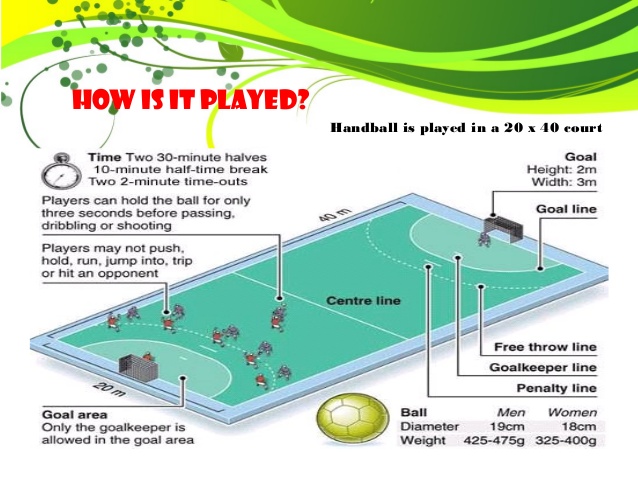
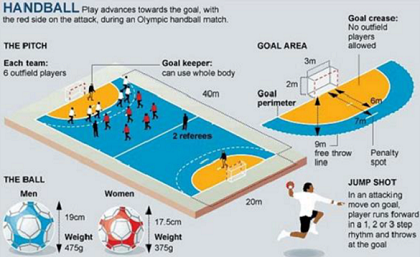
Rules and regulations of handball
1. Duration: the game is played for a total time of 60 minutes and 10 minutes rest at half time.
2. The start of the game is with “ throw-off It is also used after a goal is scored.
3. No player is allowed to take more than 3 steps before the ball is passed on.
4. No player should use his leg on the ball except the goal keeper.
5. Players must not grasp any part of the opponents body, must neither push nor harass from behind.
6. The goal keeper can catch the ball outside the goal area and throw it from the spot but he is not allowed to enter the 6m line with the bell he caught outside.
7. Fumbling is when a player tries to catch or stop the ball but fails to controls it

Equipment and facilities
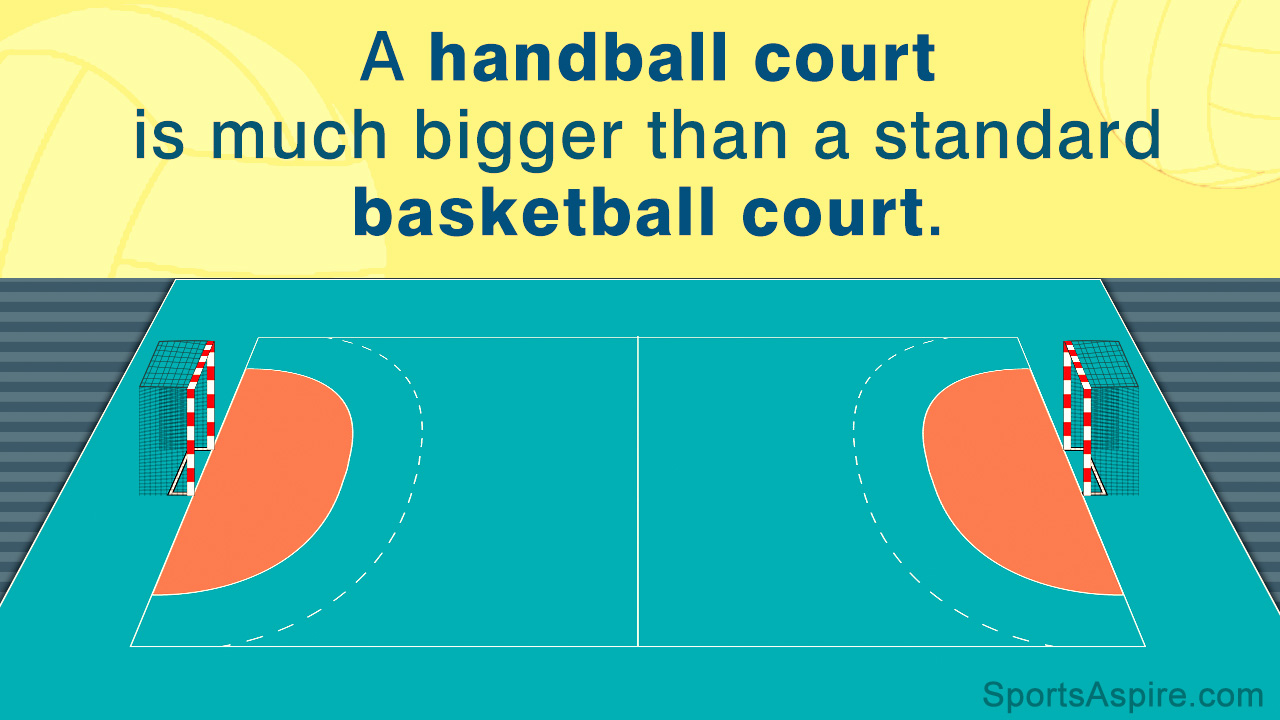
1. Court :
The playing court is 40m long and 20m wide or 44m by 22m
- The longer boundary lines = side lines
- The shorter boundary lines = goal lines
- The goal area line = 6m
- The attack line = 9m
- The Penalty mark = 7m
- The height of goal post = 2m
- The length of goal post = 3m
2. The Balls
The ball is made of leather or a synthetic material. It must be spherical .

3. The Net
A net is attached to the back of each goal post to check the ball when it is scored
4. The jerseys
5. The tennis shocks
6 The whistle and stop watches.

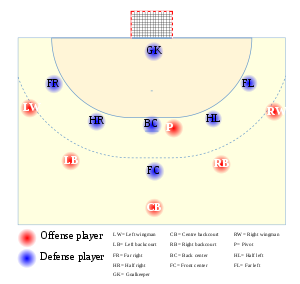
TEAM FORMATION IN HANDBALL
The game is played by two teams of 7 players each. Five substitutes or reserves are allowed. It is played by both male and female.
Defense formation in handball
- The 6 – 0 formation.
- The 5 – 1 formation
- The 4 – 2 formation
- The 3 – 3 formation
- The 3-2-2 formation
VALUES OF HANDBALL GAME
- for competition and recreation
- for physical fitness and strength development
- for speed development
- for enhancement of safety skills.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G9QJSjhOgM8[/youtube]
Evaluation
1. What is the dimension of hand bill court?
2. What is the duration of a game in hand ball?
3. List the five defensive formations.
Reading Assignment
Essential of PHE for junior secondary schools, Book 2 by Akinseye S.E. pp.54-64.
Assignment
1. One of these is the father of hand ball (a) Scelenz (b) Koch (c) Naismith.
2 .We can use leg some times in the game of hand ball. (a)yes (b) No
3. One of the following is not a skill in hand ball. (a) Passing (b) Pivoting (c ) Volleying
4. The side line of a hand ball pitch is maximum of ___________ metres (a) 44 (b) 42 (c) 40
5. Who among the following penalize any infringement? (a) Linesmen (b) umpire (c) Referee.
Theory
1. What is fumbling in a hand game?
2. List 5 passes in hand ball game.
Contents:
(a) Rules and regulations of the game.
(b) Equipment and facilities with the dimensions
(c) Values of handball game.

Rules and regulations of handball
1. Duration: the game is played for a total time of 60 minutes and 10 minutes rest at half time.
2. The start of the game is with “ throw-off It is also used after a goal is scored.
3. No player is allowed to take more than 3 steps before the ball is passed on.
4. No player should use his leg on the ball except the goal keeper.
5. Players must not grasp any part of the opponents body, must neither push nor harass from behind.
6. The goal keeper can catch the ball outside the goal area and throw it from the spot but he is not allowed to enter the 6m line with the bell he caught outside.
7. Fumbling is when a player tries to catch or stop the ball but fails to controls it

Equipment and facilities
1. Court :
The playing court is 40m long and 20m wide or 44m by 22m
- The longer boundary lines = side lines
- The shorter boundary lines = goal lines
- The goal area line = 6m
- The attack line = 9m
- The Penalty mark = 7m
- The height of goal post = 2m
- The length of goal post = 3m

2. The Balls
The ball is made of leather or a synthetic material. It must be spherical .

3. The Net
A net is attached to the back of each goal post to check the ball when it is scored
4. The jerseys
5. The tennis shocks
6 The whistle and stop watches.

TEAM FORMATION IN HANDBALL
The game is played by two teams of 7 players each. Five substitutes or reserves are allowed. It is played by both male and female.
Defense formation in handball
- The 6 – 0 formation.
- The 5 – 1 formation
- The 4 – 2 formation
- The 3 – 3 formation
- The 3-2-2 formation

VALUES OF HANDBALL GAME
- for competition and recreation
- for physical fitness and strength development
- for speed development
- for enhancement of safety skills.
[youtube]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G9QJSjhOgM8[/youtube]
Evaluation
1. What is the dimension of hand bill court?
2. What is the duration of a game in hand ball?
3. List the five defensive formations.
Reading Assignment
Essential of PHE for junior secondary schools, Book 2 by Akinseye S.E. pp.54-64.
Assignment
1. One of these is the father of hand ball (a) Scelenz (b) Koch (c) Naismith.
2 .We can use leg some times in the game of hand ball. (a)yes (b) No
3. One of the following is not a skill in hand ball. (a) Passing (b) Pivoting (c ) Volleying
4. The side line of a hand ball pitch is maximum of ___________ metres (a) 44 (b) 42 (c) 40
5. Who among the following penalize any infringement? (a) Linesmen (b) umpire (c) Referee.
Theory
1. What is fumbling in a hand game?
2. List 5 passes in hand ball game.
WEEK 8
Topic:- Safety and Accidents.
Contents:-
a. Definition of safety, Safety education and accidents.
b. Safety measures
. At home
. On play ground
. On the road
c. Classifications of accidents
School accidents
Home /domestic accidents
Work place
Vehicle
d. Causes of Road traffic accidents
e. Measures for preventing road traffic accidents
SAFETY
Safety means “Freedom from Hazards”.
Freedom from hazards can only be achieved if these hazards are identified and removed
SAFETY EDUCATION
Safety education is the acquisition of knowledge and skills for dealing with emergencies
Resulting from accidents, and also preventing accidents; through early removal of hazards
Accidents
Accident is an unintended and unforeseen event usually resulting in injuries or property damaged.
Safety Measures
At Home:-
Safety living is an important aspect of living comfortably at home . Therefore the following measures should be taken at home:-
Discord defective house hold utensils
Good structural design
Clean environment
Take adequate rest when necessary
Avoid being in haste
Always maintain proper arrangement at home
Always keep drugs and dangerous material out of reach of the children.
Avoid slippery floor.

On play ground
Check for broken sticks, bottles and stones
Ensure a swampy free play ground
If a play ground is with grass, it should be well trimmed,
Do not play with defective materials, equipments/facilities.
Be conscious of safely rules and avoid rough play.

On the road
High way should be made wider.
Public awareness about drivers education.
Existence of federal road safely corps.
Driving test for the issuance of drivers license made more vigorously
Enforcement of traffic rules and regulations by the road safety corps.
More road signs that are clearly and boldly written should be installed in strategic places.

CLASSIFICATION OF ACCIDENTS
Accidents are classified into the following areas;-
1. Home/domestics accidents
2. School accidents
3. Transportation accidents
4. Work place accidents.

CAUSES OF ACCIDENTS:
1. Home/Domestic Accidents
Poor environment
Haste (Hurrying)
Tiredness
Slippery floor
Defective house hold utensils
Poor home design
Congestion/poor property arrangements
Poor lightening

2. School Accidents
Lack of skills
Ignorance
Poor ventilation
Improper use of equipments and machines
Faulty equipment and machines
Dilapidated building/ damaged facilities
Slippery play ground
3. Transportation Accidents
Poor conditions of engine
Over speeding
Lack of concentration
Sudden loss of contact
Poor weather condition
Carelessness
Lack of road/route signs
Sudden mechanical break down
Dangerous overtaking

4. Work Place (Industrial) Accidents
Improper handling of objects
Carelessness
Fatigue
Disobedience of safety rules
Emotional upset
Faulty machine or gadget
Unsafe environments

Evaluation
1. Define (i) safety (ii) Safety education
2. List 3 classes of accidents
Reading Assignment
Essential of PHE for junior secondary schools book 2 by Akinseye S.E pp 65-68.
Contents:-
a. Definition of safety, Safety education and accidents.
b. Safety measures
. At home
. On play ground
. On the road
c. Classifications of accidents
School accidents
Home /domestic accidents
Work place
Vehicle
d. Causes of Road traffic accidents
e. Measures for preventing road traffic accidents
SAFETY
Safety means “Freedom from Hazards”.
Freedom from hazards can only be achieved if these hazards are identified and removed
SAFETY EDUCATION
Safety education is the acquisition of knowledge and skills for dealing with emergencies
Resulting from accidents, and also preventing accidents; through early removal of hazards
Accidents
Accident is an unintended and unforeseen event usually resulting in injuries or property damaged.
Safety Measures
At Home:-
Safety living is an important aspect of living comfortably at home . Therefore the following measures should be taken at home:-
Discord defective house hold utensils
Good structural design
Clean environment
Take adequate rest when necessary
Avoid being in haste
Always maintain proper arrangement at home
Always keep drugs and dangerous material out of reach of the children.
Avoid slippery floor.

On play ground
Check for broken sticks, bottles and stones
Ensure a swampy free play ground
If a play ground is with grass, it should be well trimmed,
Do not play with defective materials, equipments/facilities.
Be conscious of safely rules and avoid rough play.

On the road
High way should be made wider.
Public awareness about drivers education.
Existence of federal road safely corps.
Driving test for the issuance of drivers license made more vigorously
Enforcement of traffic rules and regulations by the road safety corps.
More road signs that are clearly and boldly written should be installed in strategic places.

CLASSIFICATION OF ACCIDENTS
Accidents are classified into the following areas;-
1. Home/domestics accidents
2. School accidents
3. Transportation accidents
4. Work place accidents.

CAUSES OF ACCIDENTS:
1. Home/Domestic Accidents
Poor environment
Haste (Hurrying)
Tiredness
Slippery floor
Defective house hold utensils
Poor home design
Congestion/poor property arrangements
Poor lightening

2. School Accidents
Lack of skills
Ignorance
Poor ventilation
Improper use of equipments and machines
Faulty equipment and machines
Dilapidated building/ damaged facilities
Slippery play ground
3. Transportation Accidents
Poor conditions of engine
Over speeding
Lack of concentration
Sudden loss of contact
Poor weather condition
Carelessness
Lack of road/route signs
Sudden mechanical break down
Dangerous overtaking

4. Work Place (Industrial) Accidents
Improper handling of objects
Carelessness
Fatigue
Disobedience of safety rules
Emotional upset
Faulty machine or gadget
Unsafe environments

Evaluation
1. Define (i) safety (ii) Safety education
2. List 3 classes of accidents
Reading Assignment
Essential of PHE for junior secondary schools book 2 by Akinseye S.E pp 65-68.
WEEK 9
Sub- topic:- Accident And Safety Education
Contents:-(a) Causes of road traffic accidents
(b) Measures of preventing road traffic accidents
Road Traffic Accidents
Causes:- As in the causes of transportation accidents written above.
Prevention of road accidents
EVALUATION
Mention 5 causes of raod accident
State 3 ways of preventing road accident
READING ASSIGNMENT
ESSENTIAL OF PHE FOR JUNIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL BOOK 2 BY AKINSEYE S.E pp 65 – 68
ASSIGNMENT
Go to page 68 of essential of PHE for Junior Secondary School Book 2. by Akinseye S.E and answer the question from nos 1 – 5.
Contents:-(a) Causes of road traffic accidents
(b) Measures of preventing road traffic accidents
Road Traffic Accidents
Causes:- As in the causes of transportation accidents written above.
Prevention of road accidents
- Avoid over confidence
- Take adequate rest when necessary
- Adequate enlighten for drivers
- Avoid being in an hurray or over speeding
- Use of safety devices should always be encouraged
- Compliance with traffic rules and regulation
- Avoid driving/ piloting under the influence of drug/ alcohol.
- Avoid unnecessary distraction.
- Ensure efficient communication system.

EVALUATION
Mention 5 causes of raod accident
State 3 ways of preventing road accident
READING ASSIGNMENT
ESSENTIAL OF PHE FOR JUNIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL BOOK 2 BY AKINSEYE S.E pp 65 – 68
ASSIGNMENT
Go to page 68 of essential of PHE for Junior Secondary School Book 2. by Akinseye S.E and answer the question from nos 1 – 5.
