1ST TERM
1ST TERM
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision.
2. Introduction to Business Studies
(i) Meaning and scope of business studies.
(ii) Elements of integrated business studies e.g. Accounts, Commerce, Office Practice, Shorthand, Typewriting.
3. The Office
(i) The meaning of an office
(ii) Types of office
- Small office
- Large office
(iii) Functions of an office.
4. The departments in an office/organization and heir functions
- Various departments in an organization.
- Purchasing department.
- Account department
- Sales department
- Personnel department
- Research and planning department
- Transport department.
5. Introduction to office equipment. Their functions and uses.
Types of office equipment, e.g.
- Cabinets, typewriter
- Telephone
- Stapler
- Duplicating machine
6. Clerical staff
- The definition
- Personal Qualities.
- Job Qualities.
7. Occupation
- Meaning
- Classification of occupation e.g. Extractive, Constructive and Manufacturing Industry.
8. Trade
- Meaning
- Types of trade
9. Aids to trade and their functions
- Banking
- Insurance
- Communication
- Advertising
10. Direct and indirect services
11. Revision
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Introduction to Business studies: (i) Meaning and Scope of Business Studies (ii) Elements of Integrated Business Studies e.g. Accounts, commerce. Office Practice etc (iii) importance of business studies (iv) components of business studies
2. Office practice: The office, Office staff, Office practice, commerce: book keeping, short hand, keyboarding, career opportunity.
3. Office staff clerical staff, i. meaning of clerical staff, functions ,quality and confidentiality of an office information
4. The Departments in an office/Organization and their functions
5-6. Honesty in business: meaning of truthfulness, attributes of truthfulness, steadfastness
and straight forward ,factors that causes people to lie ,consequence of not being truthful,
Meaning of fair play, attributes of fair play such as equity, openness and impartiality
7. Introduction to commerce: meaning of commerce, importance of commerce and activities
that aid commerce,
8. Division of commerce: Classification of commerce into Division, Types of trade – Home
trade: wholesale and retail sales ,Foreign trade: Import and export
9. Revision
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision.
2. Introduction to Business Studies
(i) Meaning and scope of business studies.
(ii) Elements of integrated business studies e.g. Accounts, Commerce, Office Practice, Shorthand, Typewriting.
3. The Office
(i) The meaning of an office
(ii) Types of office
- Small office
- Large office
(iii) Functions of an office.
4. The departments in an office/organization and heir functions
- Various departments in an organization.
- Purchasing department.
- Account department
- Sales department
- Personnel department
- Research and planning department
- Transport department.
5. Introduction to office equipment. Their functions and uses.
Types of office equipment, e.g.
- Cabinets, typewriter
- Telephone
- Stapler
- Duplicating machine
6. Clerical staff
- The definition
- Personal Qualities.
- Job Qualities.
7. Occupation
- Meaning
- Classification of occupation e.g. Extractive, Constructive and Manufacturing Industry.
8. Trade
- Meaning
- Types of trade
9. Aids to trade and their functions
- Banking
- Insurance
- Communication
- Advertising
10. Direct and indirect services
11. Revision
NEW
WEEK TOPIC
1. Introduction to Business studies: (i) Meaning and Scope of Business Studies (ii) Elements of Integrated Business Studies e.g. Accounts, commerce. Office Practice etc (iii) importance of business studies (iv) components of business studies
2. Office practice: The office, Office staff, Office practice, commerce: book keeping, short hand, keyboarding, career opportunity.
3. Office staff clerical staff, i. meaning of clerical staff, functions ,quality and confidentiality of an office information
4. The Departments in an office/Organization and their functions
5-6. Honesty in business: meaning of truthfulness, attributes of truthfulness, steadfastness
and straight forward ,factors that causes people to lie ,consequence of not being truthful,
Meaning of fair play, attributes of fair play such as equity, openness and impartiality
7. Introduction to commerce: meaning of commerce, importance of commerce and activities
that aid commerce,
8. Division of commerce: Classification of commerce into Division, Types of trade – Home
trade: wholesale and retail sales ,Foreign trade: Import and export
9. Revision
WEEK 1
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS STUDIES
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Revision and meaning of Business Studies
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-3
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-2
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Answer questions on topics taught in previous class correctly
explain the meaning of business studies
state the importance of business studies
CONTENTS:
Business study is a pre-vocational subject taught in junior secondary school which helps in facilitating the development of business skills.
Studying business allows people to understand strategy, marketing, finance, accounting, and managing people. By having an understanding of how these things work,people may find that they are better equipped to work in some jobs. Even if they don't end up specifically working in one of those areas, it will help them to understand what other people are working on. It also gives them credibility.
CONTENT:
(i) Meaning and Scope of Business Studies
(ii) Importance of business studies
(iii) Components of business studies: Office practice, Commerce, Financial Accounting/Book Keeping, Shorthand, Keyboarding/Typewriting
(iv) Career Opportunities
Meaning of Business Studies
Business Studies may be defined as a combination of inter-related business subjects which lead to learning of basic knowledge and skills. It is a course in education that is designed to cover the basic elementary knowledge and skills in organizing business enterprises as well as general office administration.
Importance of Business Studies
• Acquisition of basic knowledge of Business Studies.
• The development of basic skills in office practice.
• The preparation of students for further learning in Business Studies
• The provisions of orientation and skills for those who undergo further training in order to enable them start a life of work.
• The provision of basic skills for personal use in future.
• Relating the knowledge and skills to the national economy.
• Update knowledge on current information technology e.g. Internet, E-mail, fax and computer communication.
Components of Business Studies
Business Studies as a subject has an inter-related areas of study such as Office Practice, Commerce, Shorthand, Typewriting and Book-keeping which function at the same time when an enterprise is established. These inter-rated areas of study are also called the Inter-related Elements of Business Studies. There are five components of Business Studies.
(i) Office Practice: This is to acquire skills for the purpose of office occupation and administrations.
(ii) Commerce: It involves the production, exchange, distribution of goods and services in the organization.
(iii) Book-keeping: This is for keeping records of all financial transaction of the organization.
(iv) Typewriting/Keyboarding: it is for the preparation and production of office documents in the organization. Keyboarding is the technique of using the computer or typewriter keyboard to produce printed information in hard or soft copy. Hard copy refers to information on paper while soft copy refers to information on the computer storage device
(v) Shorthand: This is for speedy writing of messages in an office by the secretary using signs to represent.
Career Opportunity in Business Studies
Those who have undergone training in Business Studies can be employed as:
1. Clerks who keeps general office records
2. Typists who do copy typing in the office
3. Computer operators who use computer to produce office information
4. Bookkeepers and accounts clerks who keeps record on business transactions
5. Salesmen who sell goods in supermarkets and stores
6. Receptionists who receives visitors and make telephone calls
7. Stenographers who take dictations in shorthand in office
8. Self- employed: Those who will go to secondary level (senior), they can study the following courses in higher institution:
• Accountancy
• Business Administration
• Marketing
• Personnel Management
• Insurance
• Actuarial Science
IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS STUDIES
It helps us to acquire business skills
It enables us to be self reliant
It gives understanding of trading activities
It helps us to know more about the production of goods and services.
EVALUATION
1. What is Business Studies?
2. Mention three objectives of Business Studies
3. State five (5) components of Business Studies.
How can you define Business Studies?
4. State five Objectives of Business Studies.
5. List five career opportunity available to those who study Business Studies
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced
by Cross River State Chapter 1 Pages 1-2
ASSIGNMENT
1. Business studies is designed to cover basic elementary knowledge and skills in organizing ----------- and --------. (a) school and home (b) business enterprise and general office administration (c) farm and school
2. Business studies is divided into -------- components. (a) 10 (b) 6 (c) 5
3. All these are elements of Business Studies except (a) Fine art (b) Commerce (c Shorthand
4. The production, exchange and distribution of goods and services is ----------
(a) Book-keeping (b) Commerce (c) Typewriting
5. The use of signs to represent words can best describe (a) Business Studies (b) Agricultural Science (c) Shorthand
HOME-WORK: Mention five components of business study
further studies
http://seniorsecondary.tki.org.nz/Socia ... ss-studies
http://www.dpcdsb.org/AUGST/Learning/De ... rtance.htm
http://www.elimu.net/Secondary/Kenya/KC ... tudies.htm
LESSON 2
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS STUDIES
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Components of business studies
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-3
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-2
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the components of business studies
CONTENTS:
Business studies as a subject has many components or subjects parts. Some of
the components are account, commerce, business method, shorthand, typewriting and office practice.
EVALUATION:
Mention five components of business study.
The knowledge of Business Studies will assist students in studying the following courses in the university EXCEPT (a) Economics (b) Medicine (c) Banking and Finance (d) Accounting
HOME-WORK: Mention career opportunities in business study?
further studies
http://intranet.skhcyss.edu.hk/it-schoo ... /intro.htm
http://www.curriculumonline.ie/en/Post- ... _Syllabus/
LESSON 3
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS STUDIES
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Career opportunities in business studies
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-3
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-2
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention some career opportunities in business studies
CONTENTS:
Career means an occupation or profession that one can do to earn a living.
Some of the career opportunities opened to someone that studied business study are:
Secretary
Accountant
Banker
Transporter
Stock broker
Administrator
EVALUATION: Mention five career opportunities in business study.
HOME-WORK: What is an office?
further studies
http://gradireland.com/careers-advice/j ... ess-degree
http://www.prospects.ac.uk/options_busi ... tudies.htm
practice test
http://www.teachers-direct.co.uk/resour ... udies.aspx
http://www.tutor2u.net/business/quiz/cu ... /quiz.html
LESSON 4
MAIN TOPIC: THE RECEPTION OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Revision/ Meaning of a receptionist
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-5
WABP JSS Business Studies 2 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-8
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-10
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
describe the reception office
explain the meaning of receptionist
CONTENTS:
Many visitors call in an organization for personal or official reasons.
The first person they meet is the receptionist whose office is in the reception.
The reception office is usually located at the entrance of the building which houses the organization.

This location is necessary so as to make it easy for a visitor to the organization to receive attention as soon as he enters the premises of the organization.
A receptionist is a person who receives visitors and their messages and directs them to different offices and department of the organization.
EVALUATION:
In your own word describe a reception office in an organization
Who is a receptionist?
HOME-WORK: Mention three qualities of a receptionist.
further studies
http://www.select-answering-service.com ... uties.html
http://www.myfuture.edu.au/The%20Facts/ ... co=542111A
http://hiring.monster.com/hr/hr-best-pr ... ample.aspx
practice test
http://www.mymajors.com/skills-and-know ... ceptionist
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Revision and meaning of Business Studies
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-3
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-2
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Answer questions on topics taught in previous class correctly
explain the meaning of business studies
state the importance of business studies
CONTENTS:
Business study is a pre-vocational subject taught in junior secondary school which helps in facilitating the development of business skills.
Studying business allows people to understand strategy, marketing, finance, accounting, and managing people. By having an understanding of how these things work,people may find that they are better equipped to work in some jobs. Even if they don't end up specifically working in one of those areas, it will help them to understand what other people are working on. It also gives them credibility.
CONTENT:
(i) Meaning and Scope of Business Studies
(ii) Importance of business studies
(iii) Components of business studies: Office practice, Commerce, Financial Accounting/Book Keeping, Shorthand, Keyboarding/Typewriting
(iv) Career Opportunities
Meaning of Business Studies
Business Studies may be defined as a combination of inter-related business subjects which lead to learning of basic knowledge and skills. It is a course in education that is designed to cover the basic elementary knowledge and skills in organizing business enterprises as well as general office administration.
Importance of Business Studies
• Acquisition of basic knowledge of Business Studies.
• The development of basic skills in office practice.
• The preparation of students for further learning in Business Studies
• The provisions of orientation and skills for those who undergo further training in order to enable them start a life of work.
• The provision of basic skills for personal use in future.
• Relating the knowledge and skills to the national economy.
• Update knowledge on current information technology e.g. Internet, E-mail, fax and computer communication.
Components of Business Studies
Business Studies as a subject has an inter-related areas of study such as Office Practice, Commerce, Shorthand, Typewriting and Book-keeping which function at the same time when an enterprise is established. These inter-rated areas of study are also called the Inter-related Elements of Business Studies. There are five components of Business Studies.
(i) Office Practice: This is to acquire skills for the purpose of office occupation and administrations.
(ii) Commerce: It involves the production, exchange, distribution of goods and services in the organization.
(iii) Book-keeping: This is for keeping records of all financial transaction of the organization.
(iv) Typewriting/Keyboarding: it is for the preparation and production of office documents in the organization. Keyboarding is the technique of using the computer or typewriter keyboard to produce printed information in hard or soft copy. Hard copy refers to information on paper while soft copy refers to information on the computer storage device
(v) Shorthand: This is for speedy writing of messages in an office by the secretary using signs to represent.
Career Opportunity in Business Studies
Those who have undergone training in Business Studies can be employed as:
1. Clerks who keeps general office records
2. Typists who do copy typing in the office
3. Computer operators who use computer to produce office information
4. Bookkeepers and accounts clerks who keeps record on business transactions
5. Salesmen who sell goods in supermarkets and stores
6. Receptionists who receives visitors and make telephone calls
7. Stenographers who take dictations in shorthand in office
8. Self- employed: Those who will go to secondary level (senior), they can study the following courses in higher institution:
• Accountancy
• Business Administration
• Marketing
• Personnel Management
• Insurance
• Actuarial Science
IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS STUDIES
It helps us to acquire business skills
It enables us to be self reliant
It gives understanding of trading activities
It helps us to know more about the production of goods and services.
EVALUATION
1. What is Business Studies?
2. Mention three objectives of Business Studies
3. State five (5) components of Business Studies.
How can you define Business Studies?
4. State five Objectives of Business Studies.
5. List five career opportunity available to those who study Business Studies
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced
by Cross River State Chapter 1 Pages 1-2
ASSIGNMENT
1. Business studies is designed to cover basic elementary knowledge and skills in organizing ----------- and --------. (a) school and home (b) business enterprise and general office administration (c) farm and school
2. Business studies is divided into -------- components. (a) 10 (b) 6 (c) 5
3. All these are elements of Business Studies except (a) Fine art (b) Commerce (c Shorthand
4. The production, exchange and distribution of goods and services is ----------
(a) Book-keeping (b) Commerce (c) Typewriting
5. The use of signs to represent words can best describe (a) Business Studies (b) Agricultural Science (c) Shorthand
HOME-WORK: Mention five components of business study
further studies
http://seniorsecondary.tki.org.nz/Socia ... ss-studies
http://www.dpcdsb.org/AUGST/Learning/De ... rtance.htm
http://www.elimu.net/Secondary/Kenya/KC ... tudies.htm
LESSON 2
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS STUDIES
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Components of business studies
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-3
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-2
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the components of business studies
CONTENTS:
Business studies as a subject has many components or subjects parts. Some of
the components are account, commerce, business method, shorthand, typewriting and office practice.
EVALUATION:
Mention five components of business study.
The knowledge of Business Studies will assist students in studying the following courses in the university EXCEPT (a) Economics (b) Medicine (c) Banking and Finance (d) Accounting
HOME-WORK: Mention career opportunities in business study?
further studies
http://intranet.skhcyss.edu.hk/it-schoo ... /intro.htm
http://www.curriculumonline.ie/en/Post- ... _Syllabus/
LESSON 3
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS STUDIES
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Career opportunities in business studies
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-3
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-2
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention some career opportunities in business studies
CONTENTS:
Career means an occupation or profession that one can do to earn a living.
Some of the career opportunities opened to someone that studied business study are:
Secretary
Accountant
Banker
Transporter
Stock broker
Administrator
EVALUATION: Mention five career opportunities in business study.
HOME-WORK: What is an office?
further studies
http://gradireland.com/careers-advice/j ... ess-degree
http://www.prospects.ac.uk/options_busi ... tudies.htm
practice test
http://www.teachers-direct.co.uk/resour ... udies.aspx
http://www.tutor2u.net/business/quiz/cu ... /quiz.html
LESSON 4
MAIN TOPIC: THE RECEPTION OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Revision/ Meaning of a receptionist
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 1-5
WABP JSS Business Studies 2 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 1-8
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-10
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
describe the reception office
explain the meaning of receptionist
CONTENTS:
Many visitors call in an organization for personal or official reasons.
The first person they meet is the receptionist whose office is in the reception.
The reception office is usually located at the entrance of the building which houses the organization.
This location is necessary so as to make it easy for a visitor to the organization to receive attention as soon as he enters the premises of the organization.
A receptionist is a person who receives visitors and their messages and directs them to different offices and department of the organization.
EVALUATION:
In your own word describe a reception office in an organization
Who is a receptionist?
HOME-WORK: Mention three qualities of a receptionist.
further studies
http://www.select-answering-service.com ... uties.html
http://www.myfuture.edu.au/The%20Facts/ ... co=542111A
http://hiring.monster.com/hr/hr-best-pr ... ample.aspx
practice test
http://www.mymajors.com/skills-and-know ... ceptionist
WEEK 2
THE OFFICE
CONTENT:
- The Meaning and Types of Office
- Functions of an office
- The Different Office Departments in an Organization
Meaning of Offices
An office is defined as a room set aside in an organization for all clerical activities. An office can also be defined as a place where the planning and organization in connection with the production and distribution of goods and services are done. The example of an office is the principal’s office, Banks, Restaurant, Shops etc. In the Principal’s office, records of both students and staff are kept.
Types of Office
There are two types of office namely- a small office and a large office.
A SMALL OFFICE
A small office is usually found in a small organization because the volume of clerical activities is small. A small office usually has one to ten clerical workers. Example of small office are a trader’s shop, the Principal office Patent Medicine shop etc.
ADVANTAGES OF A SMALL OFFICE
1 The workers perform a wide variety of duties thereby reducing monotony of work and idle time.
2. It assists workers to learn more of office skills.
3. Workers are able to learn more about the activities within the whole business.
4. The workers enjoy a close relationship with their employers, customers and suppliers.
DISADVANTAGES OF A SMALL OFFICE
1. There is absence of division of labour and specialization.
2. There is little or no staff welfare.
3. Enough office aids such as photocopier, telex etc are not usually provided.
4. There may be no opportunity for the employee to further his career.
A LARGE OFFICE
A Large Office is usually found in big organizations with many clerical staff. Examples of large offices are Banks, Airports, Hospitals, Railway station etc. It has more than ten people working in it. In a large office, work is divided among many clerical staff.
ADVANTAGES OF LARGE OFFICE
1. The high degree of specialization enables workers to be efficient in their work.
2. There is provision of a variety of office aids depending on the needs of the various departments.
3. Workers enjoy attractive social and welfare facilities
4. There will be higher Salaries for the employees.
5. There are usually chances for career advancements, depending on the ability of each employee.
DISADVANTAGES OF A LARGE OFFICE
1. There is no privacy.
2. The relationship between the employer and employees is impersonal.
3 There is the problem of communal noise which results in distraction.
EVALUATION
1. What is an office?
2. Name the two types of office with two examples each.
SUBTOPIC: FUNCTIONS OF AN OFFICE
CONTENT
Whether the office is small or large, it performs six basic functions. These are:
(a) Giving Information
(b) Receiving Information
(c) Recording Information
(d) Arranging Information
(e) Processing Information
(f) Storing Information
Let’s explain each of them in detail.
a. Giving Information: In an organization, the office gives out information to people. For example, If the Principal wants to call a Parents-Teacher’s Meeting, he can do this by :
(i) sending a letter to each parent
(ii) putting notice of such meeting on notice board.
(iii) advertising such information in the newspaper.
b. Receiving Information: The office receives information in many ways such as through letters, telephone calls, fax messages, internet, newspaper etc.
c. Recording Information: The information given or received in the office is very necessary to the operation of the organization. Therefore, the office performs this important function of recording such information. This is necessary, in order to have an accurate record of information whether given out or received. The office can make reference to this information from time to time.
d. Arranging Information: The office arranges information by putting related matters together. All the information concerning JS one students can be arranged in one place, so that when needed it can be made easily available.
e. Processing Information: The office sorts out the information it receives and sends it to various sections of the organization to act. For example, letters concerning fees or accounting are sent to the bursar’s office.
f. Storing Information: storing of information involves the safe-keeping of records which are important to organization’s existence. Such information is stored in cabinet or computers. For example, every student/staff has a file opened on him/her. In this way, information about the student or staff can easily be recovered when needed from the file cabinet or the computer
MAIN TOPIC: THE OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and functions of an office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 4-9
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 4-7
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define an office
mention the functions of an office
CONTENTS:
An office may be defined as a place set aside for performing clerical or administrative duties of an organization.
It is also defined as a place where written work is done in connection with a business.

FUNCTIONS OF AN OFFICE
Receiving information
Recording and keeping of information
Processing information
Communication of information
Security of information and assets
EVALUATION:
define an office
mention five functions of an office
HOME-WORK: Mention two types of office
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2012022 ... ffice.html
http://notes.tyrocity.com/functions-of-an-office/
LESSON 6
MAIN TOPIC: THE OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Types of office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 4-9
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 4-7
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the two types of office
differentiate between the two types of offices
CONTENTS:
TYPES OF OFFICE
Basically there are two types of office, they are:
Small office
Large office
SMALL OFFICE
In a small office, a person can perform many duties; there is no division of labour.
Working in a small office gives one the opportunity of knowing how to do many things.
A small business usually has a small office with limited number of staff.
LARGE OFFICE
This is usually associated with big organisations such as the ministries, UNILEVER, CADBURY etc.
A large office may be divided into units called departments.
There is specialization in large office.
EVALUATION:
Mention the two types of office
Explain the two types of offices mentioned above
HOME-WORK: Give two advantages of small and large office.
further studies
http://smallbusiness.chron.com/organiza ... 10678.html
LESSON 7
MAIN TOPIC: THE OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Types of office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 4-9
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 4-7
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention advantages and disadvantages of small office
Mention advantages and disadvantages of large office
CONTENTS:
ADVANTAGES OF SMALL OFFICE
The workers enjoy doing a wide variety of jobs.
The owner of the business is able to keep in constant touch with the day - to-day running of the business.
Workers learn more about the business and are able to use the knowledge gained to establish their own business in future.
DISADVANTAGES OF SMALL OFFICE
A small office can only take few office equipment
Employers pay wages based on what he can afford.
ADVANTAGES OF LARGE OFFICE
Employees enjoy team work and specialization
A large office can take different office equipment
Salaries of employees will depend on both the salary scale used and profit which the business organisation makes.
DISADVANTAGES OF LARGE OFFICE
Workers have limited experience of other jobs other than the ones they regularly perform
There is no close relationship between employers and employees.
EVALUATION:
Mention two advantages of small office.
Mention two disadvantages of large office.
HOME-WORK: Explain open plan office
further studies
http://blogs.abc.net.au/abc_tv/2012/09/ ... types.html
http://www.city-office.lv/en/zinasanas/ ... uli_zonas/
practice test
http://www.quizrocket.com/office-character-quiz
http://wps.prenhall.com/chet_quible_adm ... .utf8.html
CONTENT:
- The Meaning and Types of Office
- Functions of an office
- The Different Office Departments in an Organization
Meaning of Offices
An office is defined as a room set aside in an organization for all clerical activities. An office can also be defined as a place where the planning and organization in connection with the production and distribution of goods and services are done. The example of an office is the principal’s office, Banks, Restaurant, Shops etc. In the Principal’s office, records of both students and staff are kept.
Types of Office
There are two types of office namely- a small office and a large office.
A SMALL OFFICE
A small office is usually found in a small organization because the volume of clerical activities is small. A small office usually has one to ten clerical workers. Example of small office are a trader’s shop, the Principal office Patent Medicine shop etc.
ADVANTAGES OF A SMALL OFFICE
1 The workers perform a wide variety of duties thereby reducing monotony of work and idle time.
2. It assists workers to learn more of office skills.
3. Workers are able to learn more about the activities within the whole business.
4. The workers enjoy a close relationship with their employers, customers and suppliers.
DISADVANTAGES OF A SMALL OFFICE
1. There is absence of division of labour and specialization.
2. There is little or no staff welfare.
3. Enough office aids such as photocopier, telex etc are not usually provided.
4. There may be no opportunity for the employee to further his career.
A LARGE OFFICE
A Large Office is usually found in big organizations with many clerical staff. Examples of large offices are Banks, Airports, Hospitals, Railway station etc. It has more than ten people working in it. In a large office, work is divided among many clerical staff.
ADVANTAGES OF LARGE OFFICE
1. The high degree of specialization enables workers to be efficient in their work.
2. There is provision of a variety of office aids depending on the needs of the various departments.
3. Workers enjoy attractive social and welfare facilities
4. There will be higher Salaries for the employees.
5. There are usually chances for career advancements, depending on the ability of each employee.
DISADVANTAGES OF A LARGE OFFICE
1. There is no privacy.
2. The relationship between the employer and employees is impersonal.
3 There is the problem of communal noise which results in distraction.
EVALUATION
1. What is an office?
2. Name the two types of office with two examples each.
SUBTOPIC: FUNCTIONS OF AN OFFICE
CONTENT
Whether the office is small or large, it performs six basic functions. These are:
(a) Giving Information
(b) Receiving Information
(c) Recording Information
(d) Arranging Information
(e) Processing Information
(f) Storing Information
Let’s explain each of them in detail.
a. Giving Information: In an organization, the office gives out information to people. For example, If the Principal wants to call a Parents-Teacher’s Meeting, he can do this by :
(i) sending a letter to each parent
(ii) putting notice of such meeting on notice board.
(iii) advertising such information in the newspaper.
b. Receiving Information: The office receives information in many ways such as through letters, telephone calls, fax messages, internet, newspaper etc.
c. Recording Information: The information given or received in the office is very necessary to the operation of the organization. Therefore, the office performs this important function of recording such information. This is necessary, in order to have an accurate record of information whether given out or received. The office can make reference to this information from time to time.
d. Arranging Information: The office arranges information by putting related matters together. All the information concerning JS one students can be arranged in one place, so that when needed it can be made easily available.
e. Processing Information: The office sorts out the information it receives and sends it to various sections of the organization to act. For example, letters concerning fees or accounting are sent to the bursar’s office.
f. Storing Information: storing of information involves the safe-keeping of records which are important to organization’s existence. Such information is stored in cabinet or computers. For example, every student/staff has a file opened on him/her. In this way, information about the student or staff can easily be recovered when needed from the file cabinet or the computer
MAIN TOPIC: THE OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and functions of an office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 4-9
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 4-7
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define an office
mention the functions of an office
CONTENTS:
An office may be defined as a place set aside for performing clerical or administrative duties of an organization.
It is also defined as a place where written work is done in connection with a business.
FUNCTIONS OF AN OFFICE
Receiving information
Recording and keeping of information
Processing information
Communication of information
Security of information and assets
EVALUATION:
define an office
mention five functions of an office
HOME-WORK: Mention two types of office
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2012022 ... ffice.html
http://notes.tyrocity.com/functions-of-an-office/
LESSON 6
MAIN TOPIC: THE OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Types of office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 4-9
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 4-7
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the two types of office
differentiate between the two types of offices
CONTENTS:
TYPES OF OFFICE
Basically there are two types of office, they are:
Small office
Large office
SMALL OFFICE
In a small office, a person can perform many duties; there is no division of labour.
Working in a small office gives one the opportunity of knowing how to do many things.
A small business usually has a small office with limited number of staff.
LARGE OFFICE
This is usually associated with big organisations such as the ministries, UNILEVER, CADBURY etc.
A large office may be divided into units called departments.
There is specialization in large office.
EVALUATION:
Mention the two types of office
Explain the two types of offices mentioned above
HOME-WORK: Give two advantages of small and large office.
further studies
http://smallbusiness.chron.com/organiza ... 10678.html
LESSON 7
MAIN TOPIC: THE OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Types of office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 4-9
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 4-7
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 3-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention advantages and disadvantages of small office
Mention advantages and disadvantages of large office
CONTENTS:
ADVANTAGES OF SMALL OFFICE
The workers enjoy doing a wide variety of jobs.
The owner of the business is able to keep in constant touch with the day - to-day running of the business.
Workers learn more about the business and are able to use the knowledge gained to establish their own business in future.
DISADVANTAGES OF SMALL OFFICE
A small office can only take few office equipment
Employers pay wages based on what he can afford.
ADVANTAGES OF LARGE OFFICE
Employees enjoy team work and specialization
A large office can take different office equipment
Salaries of employees will depend on both the salary scale used and profit which the business organisation makes.
DISADVANTAGES OF LARGE OFFICE
Workers have limited experience of other jobs other than the ones they regularly perform
There is no close relationship between employers and employees.
EVALUATION:
Mention two advantages of small office.
Mention two disadvantages of large office.
HOME-WORK: Explain open plan office
further studies
http://blogs.abc.net.au/abc_tv/2012/09/ ... types.html
http://www.city-office.lv/en/zinasanas/ ... uli_zonas/
practice test
http://www.quizrocket.com/office-character-quiz
http://wps.prenhall.com/chet_quible_adm ... .utf8.html
WEEK 3
CLERICAL STAFF
CONTENT:
- Meaning, functions and qualities
- Confidentiality of office information
MEANING OF A CLERICAL STAFF
A Clerical staff is someone who is employed either in a private business organization or government establishment to perform clerical duties with a corresponding payment of wages called salary. Examples are typists, account clerk, messengers etc.
QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
Qualities of a Clerical Staff are divided into two: Personal Qualities and Job Qualities
Personal Qualities of a Clerical Staff
1. Sound educational qualification required of his/her position in the office.
2. A good appearance which means that he/she has to be neatly dressed at all times.
3. Interest in job and ability to finish his assignments on schedule
4. He/she must be physically fit.
5. Honesty and Integrity
6. Punctuality and Integrity
7. Ability to carry out instructions.
5. He/she must work in harmony with other office workers.
6. He/she must have good communication ability. He/she should be able communicate well in the language used in the establishment
JOB QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
1. A clerical staff must always come to the office on time and stay till the close of work.
2. He/she must have self control; he should not leave the office before his boss.
3. A clerk must keep all confidential matters to himself.
4. He must be able to carry out his duties without being told.
5. He/she must keep office environment tidy and be able to take good care of all equipment and stationery under his/her care.
6. He/she must avoid letting personal or family problems to affect his or her attitude to work in the office.
EVALUATION:
1. Explain the meaning of a clerical staff.
2. State 3 personal qualities of a clerical staff.
Sub-Topic 2
DUTIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
1. A clerk may be asked to work as a messenger who handles both outgoing and incoming mails.
2. A clerk may work as a telephone operator who receives calls.
3. He/she may be asked to collate document
4. A clerk may act as a Receptionist.
5. A clerk may act as a tea server.
CONFIDENTIALITY OF OFFICE INFORMATION
The office worker has the responsibility of ensuring that office information and document are secured. Confidential record should not be kept in such a way as to allow unauthorized staff or visitors to have access to them .Confidential record should be marked “CONFIDENTIAL” to show that it is not for everyone to see .It is advisable to place all confidential information in a folder so that it is not immediately seen/visible to the onlooker. All confidential document not in used should be carefully kept in appropriate places under lock and key.
EVALUATION 1
1. State four (4) job qualities of a clerical staff
2. Mention three (3) duties of a clerical staff
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 3 pages15 - 17
ASSIGNMENT
1. One of the personal qualities of a clerical staff is (a) late coming (b) neatness (c) serving tea
2. A clerical staff must be physically fit is a -------- quality. (a) duty (b) job (c) Personal
3. Ability to come to work early and stay till close of work is a -------- quality (a) Personal (b) Job (c) duty
4. The following are job qualities except (a) Ability to work without supervision (b) Ability to keep confidential matters to himself (c) ability to work in harmony with other staff.
5. One of the duties of a clerical staff is to (a) collate document (b) work in harmony with other staff (c) personal neatness
THEORY
1. Define the term a Clerical Staff
2. State 3 duties of a clerical staff
EVALUATION 2
State the various functions of an office.
What is the main function of an office?
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 2 pages 5-8
ASSIGNMENT
1. There are ------- types of office . (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4
2. The Principal’s office is an example of -----------
(a) Large office (b) small office (c) Bank
3. Twenty or more persons can operate in a ------- office. (a) new office (b) small office (c) large office
4. The process of safe-keeping records is regarded as -------------
(a) storing information (b) receiving information (c) giving information
5. A Large office is usually found in --------- organization with many clerical staff.
(a) every (b) big (c) small
THEORY
1. Explain the term an office
2. State all the functions of an office
MAIN TOPIC: OPEN AND CLOSED OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Open office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-7
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define an open office set up
mention the advantages and disadvantages of open office set up
CONTENTS:
An open office is an office with floor space that is not partitioned into smaller rooms or offices.
It is a large room where different department or sections of an organisation work together instead of using separate small rooms.
ADVANTAGE OF AN OPEN OFFICE
Ease of supervision
Office equipment and facilities can be jointly used e.g. telephone
Close relationship among workers
Workers can easily perform the job of other workers absent from work.
DISADVANTAGE OF AN OPEN OFFICE
Movement of visitors can distract the workers
It encourages gossiping among the workers
The spread of an infectious disease is very fast in an open office.
EVALUATION:
What is an open office
mention three advantages and two disadvantages of an open office
HOME-WORK: Write short note on a closed office
further studies
http://www.insidebusiness360.com/index. ... ice-13607/
LESSON 9
MAIN TOPIC: OPEN AND CLOSED OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Closed office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-7
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define a closed office set up
mention advantages and disadvantages of closed office set up
CONTENTS:
This is an example of a small office occupied by only one officer.
It is normally partitioned into a small room or office for a particular officer to have privacy in the performance of normal routine office duties.
ADVANTAGES
Workers have better concentration
Confidential matters are better handled in this type of office
Noise making is reduced to the barest minimum.
There is better and judicious use of office equipment.
DISADVANTAGES
It does not encourage division of labour
It does not encourage close relationship among workers
It does not give room for effective supervision.
EVALUATION:
What is a closed office?
Mention three advantages and two disadvantages of closed office
HOME-WORK: Mention five departments in an office
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2011010 ... ffice.html
http://articles.markdeo.com/2009/04/adv ... f-open.asp
http://lerablog.org/business/economy/re ... n-offices/
http://www.avanta.co.uk/news/article/pr ... fice-space
CONTENT:
- Meaning, functions and qualities
- Confidentiality of office information
MEANING OF A CLERICAL STAFF
A Clerical staff is someone who is employed either in a private business organization or government establishment to perform clerical duties with a corresponding payment of wages called salary. Examples are typists, account clerk, messengers etc.
QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
Qualities of a Clerical Staff are divided into two: Personal Qualities and Job Qualities
Personal Qualities of a Clerical Staff
1. Sound educational qualification required of his/her position in the office.
2. A good appearance which means that he/she has to be neatly dressed at all times.
3. Interest in job and ability to finish his assignments on schedule
4. He/she must be physically fit.
5. Honesty and Integrity
6. Punctuality and Integrity
7. Ability to carry out instructions.
5. He/she must work in harmony with other office workers.
6. He/she must have good communication ability. He/she should be able communicate well in the language used in the establishment
JOB QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
1. A clerical staff must always come to the office on time and stay till the close of work.
2. He/she must have self control; he should not leave the office before his boss.
3. A clerk must keep all confidential matters to himself.
4. He must be able to carry out his duties without being told.
5. He/she must keep office environment tidy and be able to take good care of all equipment and stationery under his/her care.
6. He/she must avoid letting personal or family problems to affect his or her attitude to work in the office.
EVALUATION:
1. Explain the meaning of a clerical staff.
2. State 3 personal qualities of a clerical staff.
Sub-Topic 2
DUTIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
1. A clerk may be asked to work as a messenger who handles both outgoing and incoming mails.
2. A clerk may work as a telephone operator who receives calls.
3. He/she may be asked to collate document
4. A clerk may act as a Receptionist.
5. A clerk may act as a tea server.
CONFIDENTIALITY OF OFFICE INFORMATION
The office worker has the responsibility of ensuring that office information and document are secured. Confidential record should not be kept in such a way as to allow unauthorized staff or visitors to have access to them .Confidential record should be marked “CONFIDENTIAL” to show that it is not for everyone to see .It is advisable to place all confidential information in a folder so that it is not immediately seen/visible to the onlooker. All confidential document not in used should be carefully kept in appropriate places under lock and key.
EVALUATION 1
1. State four (4) job qualities of a clerical staff
2. Mention three (3) duties of a clerical staff
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 3 pages15 - 17
ASSIGNMENT
1. One of the personal qualities of a clerical staff is (a) late coming (b) neatness (c) serving tea
2. A clerical staff must be physically fit is a -------- quality. (a) duty (b) job (c) Personal
3. Ability to come to work early and stay till close of work is a -------- quality (a) Personal (b) Job (c) duty
4. The following are job qualities except (a) Ability to work without supervision (b) Ability to keep confidential matters to himself (c) ability to work in harmony with other staff.
5. One of the duties of a clerical staff is to (a) collate document (b) work in harmony with other staff (c) personal neatness
THEORY
1. Define the term a Clerical Staff
2. State 3 duties of a clerical staff
EVALUATION 2
State the various functions of an office.
What is the main function of an office?
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 2 pages 5-8
ASSIGNMENT
1. There are ------- types of office . (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4
2. The Principal’s office is an example of -----------
(a) Large office (b) small office (c) Bank
3. Twenty or more persons can operate in a ------- office. (a) new office (b) small office (c) large office
4. The process of safe-keeping records is regarded as -------------
(a) storing information (b) receiving information (c) giving information
5. A Large office is usually found in --------- organization with many clerical staff.
(a) every (b) big (c) small
THEORY
1. Explain the term an office
2. State all the functions of an office
MAIN TOPIC: OPEN AND CLOSED OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Open office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-7
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define an open office set up
mention the advantages and disadvantages of open office set up
CONTENTS:
An open office is an office with floor space that is not partitioned into smaller rooms or offices.
It is a large room where different department or sections of an organisation work together instead of using separate small rooms.
ADVANTAGE OF AN OPEN OFFICE
Ease of supervision
Office equipment and facilities can be jointly used e.g. telephone
Close relationship among workers
Workers can easily perform the job of other workers absent from work.
DISADVANTAGE OF AN OPEN OFFICE
Movement of visitors can distract the workers
It encourages gossiping among the workers
The spread of an infectious disease is very fast in an open office.
EVALUATION:
What is an open office
mention three advantages and two disadvantages of an open office
HOME-WORK: Write short note on a closed office
further studies
http://www.insidebusiness360.com/index. ... ice-13607/
LESSON 9
MAIN TOPIC: OPEN AND CLOSED OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Closed office
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-7
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define a closed office set up
mention advantages and disadvantages of closed office set up
CONTENTS:
This is an example of a small office occupied by only one officer.
It is normally partitioned into a small room or office for a particular officer to have privacy in the performance of normal routine office duties.
ADVANTAGES
Workers have better concentration
Confidential matters are better handled in this type of office
Noise making is reduced to the barest minimum.
There is better and judicious use of office equipment.
DISADVANTAGES
It does not encourage division of labour
It does not encourage close relationship among workers
It does not give room for effective supervision.
EVALUATION:
What is a closed office?
Mention three advantages and two disadvantages of closed office
HOME-WORK: Mention five departments in an office
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2011010 ... ffice.html
http://articles.markdeo.com/2009/04/adv ... f-open.asp
http://lerablog.org/business/economy/re ... n-offices/
http://www.avanta.co.uk/news/article/pr ... fice-space
WEEK 4
TOPIC: The Departments in an Office/Organization and their functions
CONTENT:
- General office organization.
- Functions of the Departments in an organization
FULL CONTENT
There are generally two kinds of offices in an organization. These are General office and Departmental office.
1. GENERAL OFFICE: This office deals with all the activities in the day to day running of the organization. The Administrative Manager is the head of this office. His responsibility is to coordinate the various activities of other offices. He controls the office workers, employs and deploys them to the department where their services are needed.
2. DEPARTMENTAL OFFICE: Departmental offices are set up as supporting unit to assist the department in performing their day to day clerical activities. In each departmental office, there are departmental heads that controls the works of the subordinate.
EVALUATION
1. How many kinds of offices are there in an organization?
2. Explain the duties of each of these offices.
SUB-TOPIC
VARIOUS DEPARTMENTS AND THEIR DUTIES IN AN ORGANIZATION
The following are the departments and their functions:
(a) ACCOUNT DEPARTMENT: This department keeps accounting records. All monetary matters are referred to it. It prepares and pays salaries to all employees. The head of this department is called the Accounting Manager.
(b) PERSONNEL DEPARTMENT: This department is concerned with all matters about staff welfare, training, recruitment, evaluation, termination, promotion and retirement. It is usually headed by a person trained in Personnel Administration or Business Management called Personnel Manager.
(c) PURCHASING DEPARTMENT: This department is in charge of buying of all materials and equipment needed in the organization such as stationery, office furniture, equipment and all other essential goods needed for effective operation of business. The head of the purchasing department is called Purchasing Officer.
(d) SALES DEPARTMENT: This department is mainly responsible for selling the products of the organization. The head of Sales department is called the Sales Manager. This department has other sub-units or sections e.g. Advertising unit, Customer Service unit and after sales Services unit under it.
(e) Advertising Unit: This unit is responsible for all sales promotion and advertisement in both local and national news media e.g. Radio, Television, newspaper etc. The head of this department is called the Advertising Manager.
(f) Customer Service Unit: It is responsible for handling customer’s complaints concerning defective goods and merchandize. The unit brings customer closer to the organization. The head of the unit is called Customer’s Service Manager.
(g) TRANSPORT DEPARTMENT: This is a department is charge of procuring of new vehicles, disposing of the junk vehicles and maintenance of existence vehicles in the organization’s vehicles. The head of the department is called the Transport Manager.
(h) PLANNING DEPARTMENT: This department is concerned with planning the business activities of the organization. The head of the department is called Planning Manager.
EVALUATION
1. Mention four departments in the organization.
2. Who is the head of Personnel Department?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 2 pages 9 -12
ASSIGNMENT
1. The office in charge of day to day running of the organization is
(a) Personnel department (b) General Office (b) Departmental office
2. The department in charge of all monetary matters in the organization is
(a) Purchasing Department (b) Account Department (c) Transport Department
3. The head of Personnel Department is called
(a) Personnel Manager (b) Purchasing Officer (c) Chief Accountant
4. The Sales Department is divided into ---------- and ----------- units
(a) Account and personnel (b) Advertising and Customer Service (c) Purchasing and
Transport
5. The department that looks after the organization’s vehicles is (a) Transport (b) Personnel (c) Account
THEORY
1. Which of the offices is a supporting unit to the organization?
2. List five departments and their functions.
MAIN TOPIC: THE DEPARTMENTS IN AN OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Admin, Personnel and Accounts department
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 14-18
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 11-13
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 14-17
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
list different departments within an organisation
mention the functions of Admin, Personnel and Accounts departments
mention the heads of Admin, Personnel and Accounts departments
CONTENTS:
ADMINISTRATIVE DEPARTMENT
This department monitors the effective functioning of other departments.
It is responsible for the welfare and discipline of the members of staff.
They are also responsible for documenting records of in-coming and out-going mails.
PERSONNEL DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for employing new staff, arranging staff training, looking after staff welfare, keeping staff records and executing staff dismissal
ACCOUNTS DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for keeping the records of all financial transaction in the organisation.
It ensures proper and judicious spending of money.
It prepares and pays out wages and salaries to workers and collects revenue for the organisation.
EVALUATION:
mention six departments in an organisation
who is the head of the Accounts department
mention five functions of personnel department
HOME-WORK: Mention two functions of sales department
LESSON 11
MAIN TOPIC: THE DEPARTMENTS IN AN OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Sales, Production and Purchasing department
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 14-18
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 11-13
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 14-17
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the functions of sales, production and purchasing departments
mention the heads of sales, production and purchasing departments
CONTENTS:
SALES DEPARTMENT
This department works hand in hand with the production department by changing the product of the production department into money.
They are responsible for advertising the finished products in the media.
PRODUCTION DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for using raw materials to make goods.
It has to make goods in the right quantity and quality and at minimum cost.
They work hand in hand with sales and research and development department in order to find ways of producing at minimum cost.
PURCHASING DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for buying raw materials, semi-finished goods and spare parts for the organisation and at very low cost.
EVALUATION:
Mention the functions of production department
Sales department works hand in hand with which department?
HOME-WORK: mention the function of research and development department
LESSON 12
MAIN TOPIC: THE DEPARTMENTS IN AN OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: R&D, Transport and Stores department
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 14-18
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 11-13
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 14-17
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the functions of R&D, Transport and Stores department
mention the heads of these departments
CONTENTS:
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT (R&D)
This department is concerned with the development of new products and reducing the the production costs of existing ones.
It looks for possible and new areas of investment and also for the improvement of the organizational profit.
TRANSPORT DEPARTMENT
Large organizations usually have many vehicles that are used for transporting raw materials and for delivery of finished products to customers.
STORES DEPARTMENT
They are responsible for the custody of goods manufactured or purchased by the organization before they are issued to sales or production department and other units of the organization.
EVALUATION:
Mention two advantages of small office.
Mention two disadvantages of large office.
HOME-WORK:
Who is a clerical staff? list different departments within an organization
further studies
http://www.floorit.info/index.php?optio ... Itemid=573
http://www.dineshbakshi.com/igcse-busin ... epartments
CONTENT:
- General office organization.
- Functions of the Departments in an organization
FULL CONTENT
There are generally two kinds of offices in an organization. These are General office and Departmental office.
1. GENERAL OFFICE: This office deals with all the activities in the day to day running of the organization. The Administrative Manager is the head of this office. His responsibility is to coordinate the various activities of other offices. He controls the office workers, employs and deploys them to the department where their services are needed.
2. DEPARTMENTAL OFFICE: Departmental offices are set up as supporting unit to assist the department in performing their day to day clerical activities. In each departmental office, there are departmental heads that controls the works of the subordinate.
EVALUATION
1. How many kinds of offices are there in an organization?
2. Explain the duties of each of these offices.
SUB-TOPIC
VARIOUS DEPARTMENTS AND THEIR DUTIES IN AN ORGANIZATION
The following are the departments and their functions:
(a) ACCOUNT DEPARTMENT: This department keeps accounting records. All monetary matters are referred to it. It prepares and pays salaries to all employees. The head of this department is called the Accounting Manager.
(b) PERSONNEL DEPARTMENT: This department is concerned with all matters about staff welfare, training, recruitment, evaluation, termination, promotion and retirement. It is usually headed by a person trained in Personnel Administration or Business Management called Personnel Manager.
(c) PURCHASING DEPARTMENT: This department is in charge of buying of all materials and equipment needed in the organization such as stationery, office furniture, equipment and all other essential goods needed for effective operation of business. The head of the purchasing department is called Purchasing Officer.
(d) SALES DEPARTMENT: This department is mainly responsible for selling the products of the organization. The head of Sales department is called the Sales Manager. This department has other sub-units or sections e.g. Advertising unit, Customer Service unit and after sales Services unit under it.
(e) Advertising Unit: This unit is responsible for all sales promotion and advertisement in both local and national news media e.g. Radio, Television, newspaper etc. The head of this department is called the Advertising Manager.
(f) Customer Service Unit: It is responsible for handling customer’s complaints concerning defective goods and merchandize. The unit brings customer closer to the organization. The head of the unit is called Customer’s Service Manager.
(g) TRANSPORT DEPARTMENT: This is a department is charge of procuring of new vehicles, disposing of the junk vehicles and maintenance of existence vehicles in the organization’s vehicles. The head of the department is called the Transport Manager.
(h) PLANNING DEPARTMENT: This department is concerned with planning the business activities of the organization. The head of the department is called Planning Manager.
EVALUATION
1. Mention four departments in the organization.
2. Who is the head of Personnel Department?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 2 pages 9 -12
ASSIGNMENT
1. The office in charge of day to day running of the organization is
(a) Personnel department (b) General Office (b) Departmental office
2. The department in charge of all monetary matters in the organization is
(a) Purchasing Department (b) Account Department (c) Transport Department
3. The head of Personnel Department is called
(a) Personnel Manager (b) Purchasing Officer (c) Chief Accountant
4. The Sales Department is divided into ---------- and ----------- units
(a) Account and personnel (b) Advertising and Customer Service (c) Purchasing and
Transport
5. The department that looks after the organization’s vehicles is (a) Transport (b) Personnel (c) Account
THEORY
1. Which of the offices is a supporting unit to the organization?
2. List five departments and their functions.
MAIN TOPIC: THE DEPARTMENTS IN AN OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Admin, Personnel and Accounts department
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 14-18
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 11-13
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 14-17
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
list different departments within an organisation
mention the functions of Admin, Personnel and Accounts departments
mention the heads of Admin, Personnel and Accounts departments
CONTENTS:
ADMINISTRATIVE DEPARTMENT
This department monitors the effective functioning of other departments.
It is responsible for the welfare and discipline of the members of staff.
They are also responsible for documenting records of in-coming and out-going mails.
PERSONNEL DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for employing new staff, arranging staff training, looking after staff welfare, keeping staff records and executing staff dismissal
ACCOUNTS DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for keeping the records of all financial transaction in the organisation.
It ensures proper and judicious spending of money.
It prepares and pays out wages and salaries to workers and collects revenue for the organisation.
EVALUATION:
mention six departments in an organisation
who is the head of the Accounts department
mention five functions of personnel department
HOME-WORK: Mention two functions of sales department
LESSON 11
MAIN TOPIC: THE DEPARTMENTS IN AN OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Sales, Production and Purchasing department
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 14-18
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 11-13
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 14-17
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the functions of sales, production and purchasing departments
mention the heads of sales, production and purchasing departments
CONTENTS:
SALES DEPARTMENT
This department works hand in hand with the production department by changing the product of the production department into money.
They are responsible for advertising the finished products in the media.
PRODUCTION DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for using raw materials to make goods.
It has to make goods in the right quantity and quality and at minimum cost.
They work hand in hand with sales and research and development department in order to find ways of producing at minimum cost.
PURCHASING DEPARTMENT
This department is responsible for buying raw materials, semi-finished goods and spare parts for the organisation and at very low cost.
EVALUATION:
Mention the functions of production department
Sales department works hand in hand with which department?
HOME-WORK: mention the function of research and development department
LESSON 12
MAIN TOPIC: THE DEPARTMENTS IN AN OFFICE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: R&D, Transport and Stores department
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 14-18
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 11-13
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 14-17
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the functions of R&D, Transport and Stores department
mention the heads of these departments
CONTENTS:
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT (R&D)
This department is concerned with the development of new products and reducing the the production costs of existing ones.
It looks for possible and new areas of investment and also for the improvement of the organizational profit.
TRANSPORT DEPARTMENT
Large organizations usually have many vehicles that are used for transporting raw materials and for delivery of finished products to customers.
STORES DEPARTMENT
They are responsible for the custody of goods manufactured or purchased by the organization before they are issued to sales or production department and other units of the organization.
EVALUATION:
Mention two advantages of small office.
Mention two disadvantages of large office.
HOME-WORK:
Who is a clerical staff? list different departments within an organization
further studies
http://www.floorit.info/index.php?optio ... Itemid=573
http://www.dineshbakshi.com/igcse-busin ... epartments
WEEK 5
TOPIC: HONESTY IN BUSINESS
CONTENT:
a. Meaning of truthfulness,
b. Attributes of truthfulness, steadfastness and straight forward.
c. Factors that causes people to lie
Meaning and characteristics of truthfulness.
Honesty is the quality of being truthful and trustworthy. To be honest is to tell the truth at all times even at personal risk to oneself. Whether in business or at individual level reputations are made or broken over issues of honesty or trustworthiness. Honesty is the opposite of lying. It is important to be honest trustworthy with the people. Lying, stealing and cheating are wrong. Honesty in business is the most important thing .This is also known as ethical behavior in business.
Truthfulness means: making true statement about something or somebody. It is very important for developing trust and building lasting relationships among people both in and outside of business .It helps people to objective and lead to confidence and trust between/among business associates.
ATTRIBUTES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF TRUTHFULNESS
1. Consistence behavior: it is being able to maintain a particular standard that one has been known for. It means one is reliable and can therefore be trusted in all circumstances and by everyone concerned.
2. Steadfastness: This means, the quality of being firm in one’s dealing with people. Those who are steadfast are loyal, they can be depended in all situation.
3. Straightforwardness: it is the ability to be honest and frank.
4. Integrity: is the quality of being honest and having strong moral and ethical principles.
5. Other attributes of truthfulness include responsibility, courage and accountability.
FACTORS THAT CAUSES PEOPLE TO LIE
A lie is a false statement deliberately told to be true in order to give a wrong impression about something. It is therefore an untruth or a deviation from what is real. People lie:
1. To escape punishment
2. To make gain
3. To get other people’s attention or sympathy or boost one’s ego
4. To make themselves look more interesting to others by exaggerating, bragging or boasting.
5. To cover up their past
6. To cover up lies
7. To cover up the truth
8. To avoid hurting other people’s feeling
9. Out of ignorance
10. To avoid embarrassment
11. To avoid work or taking part in an assignment
12. To keep secrets
13. To keep themselves safe
14. To keep a friend from trouble
MAIN TOPIC: THE CLERICAL STAFF
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and Functions of clerical staff
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 10-13
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 8-10
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 8-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of a clerical staff
mention the duties/functions of clerical staff
give examples of clerical staff
CONTENTS:
A clerical staff is someone who performs the functions of an office. That is, receiving and recording mails, filing, attending to visitors, collation and typing of office correspondence.
Examples of clerical staff include Receptionist, Account clerk, Secretary, Messenger e.t.c.
DUTIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
Receiving information
Recording information
Communication of information
Processing of information
Security of information and assets
EVALUATION:
who is a clerical staff
mention five duties of a clerical staff
mention three examples of a clerical staff in the school
HOME-WORK: Mention two major qualities of a clerical staff
LESSON 14
MAIN TOPIC: THE CLERICAL STAFF
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Qualities of a clerical staff
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 10-13
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 8-10
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 8-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention the two major qualities of a clerical staff
mention personal qualities of a clerical staff
CONTENTS:
QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
PERSONAL QUALITIES
Possession of sound educational background
Possession of good health
Neatness and good appearance
Politeness
Honesty
Ability to communicate
High aspiration
Dexterity
Initiative
EVALUATION:
mention the two major duties of a clerical staff
mention five personal qualities
HOME-WORK: mention five job qualities of a clerical staff
LESSON 15
MAIN TOPIC: THE CLERICAL STAFF
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Job qualities of a clerical staff
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 10-13
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 8-10
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 8-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention the job qualities of a clerical staff
CONTENTS: JOB QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
Punctuality
Loyalty
Confidentiality
Tactfulness
Self-control
Intelligence
Good handwriting
Interest in the job
Willingness to accept responsibility
Soft spoken
EVALUATION: Mention five job qualities of a clerical staff
HOME-WORK: Write short note on fair play state the meaning of a clerical staff
further studies
http://www.skooolnigeria.com/ec_office.aspx
http://job-descriptions.careerplanner.c ... eneral.cfm
http://www.co.champaign.il.us/descript/ ... LK-ASS.HTM
CONTENT:
a. Meaning of truthfulness,
b. Attributes of truthfulness, steadfastness and straight forward.
c. Factors that causes people to lie
Meaning and characteristics of truthfulness.
Honesty is the quality of being truthful and trustworthy. To be honest is to tell the truth at all times even at personal risk to oneself. Whether in business or at individual level reputations are made or broken over issues of honesty or trustworthiness. Honesty is the opposite of lying. It is important to be honest trustworthy with the people. Lying, stealing and cheating are wrong. Honesty in business is the most important thing .This is also known as ethical behavior in business.
Truthfulness means: making true statement about something or somebody. It is very important for developing trust and building lasting relationships among people both in and outside of business .It helps people to objective and lead to confidence and trust between/among business associates.
ATTRIBUTES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF TRUTHFULNESS
1. Consistence behavior: it is being able to maintain a particular standard that one has been known for. It means one is reliable and can therefore be trusted in all circumstances and by everyone concerned.
2. Steadfastness: This means, the quality of being firm in one’s dealing with people. Those who are steadfast are loyal, they can be depended in all situation.
3. Straightforwardness: it is the ability to be honest and frank.
4. Integrity: is the quality of being honest and having strong moral and ethical principles.
5. Other attributes of truthfulness include responsibility, courage and accountability.
FACTORS THAT CAUSES PEOPLE TO LIE
A lie is a false statement deliberately told to be true in order to give a wrong impression about something. It is therefore an untruth or a deviation from what is real. People lie:
1. To escape punishment
2. To make gain
3. To get other people’s attention or sympathy or boost one’s ego
4. To make themselves look more interesting to others by exaggerating, bragging or boasting.
5. To cover up their past
6. To cover up lies
7. To cover up the truth
8. To avoid hurting other people’s feeling
9. Out of ignorance
10. To avoid embarrassment
11. To avoid work or taking part in an assignment
12. To keep secrets
13. To keep themselves safe
14. To keep a friend from trouble
MAIN TOPIC: THE CLERICAL STAFF
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and Functions of clerical staff
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 10-13
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 8-10
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 8-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of a clerical staff
mention the duties/functions of clerical staff
give examples of clerical staff
CONTENTS:
A clerical staff is someone who performs the functions of an office. That is, receiving and recording mails, filing, attending to visitors, collation and typing of office correspondence.
Examples of clerical staff include Receptionist, Account clerk, Secretary, Messenger e.t.c.
DUTIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
Receiving information
Recording information
Communication of information
Processing of information
Security of information and assets
EVALUATION:
who is a clerical staff
mention five duties of a clerical staff
mention three examples of a clerical staff in the school
HOME-WORK: Mention two major qualities of a clerical staff
LESSON 14
MAIN TOPIC: THE CLERICAL STAFF
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Qualities of a clerical staff
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 10-13
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 8-10
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 8-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention the two major qualities of a clerical staff
mention personal qualities of a clerical staff
CONTENTS:
QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
PERSONAL QUALITIES
Possession of sound educational background
Possession of good health
Neatness and good appearance
Politeness
Honesty
Ability to communicate
High aspiration
Dexterity
Initiative
EVALUATION:
mention the two major duties of a clerical staff
mention five personal qualities
HOME-WORK: mention five job qualities of a clerical staff
LESSON 15
MAIN TOPIC: THE CLERICAL STAFF
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Job qualities of a clerical staff
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 10-13
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 8-10
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 8-9
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention the job qualities of a clerical staff
CONTENTS: JOB QUALITIES OF A CLERICAL STAFF
Punctuality
Loyalty
Confidentiality
Tactfulness
Self-control
Intelligence
Good handwriting
Interest in the job
Willingness to accept responsibility
Soft spoken
EVALUATION: Mention five job qualities of a clerical staff
HOME-WORK: Write short note on fair play state the meaning of a clerical staff
further studies
http://www.skooolnigeria.com/ec_office.aspx
http://job-descriptions.careerplanner.c ... eneral.cfm
http://www.co.champaign.il.us/descript/ ... LK-ASS.HTM
WEEK 6
TOPIC: HONESTY IN BUSINESS (Contd.)
REWARD OF BEING TRUTHFUL
1. Widespread respect from people
2. A feeing of liberation and self – worth
3. Peace of mind
4. Additional responsibility
5. Happiness
CONSEQUENCES OF NOT BEING TRUTHFUL
1. Misery: A life of lie lead to misery. It leads to discomfort guilt and worthiness in the mind of the person.
2. Damage reputation: People become unkind to you even when you tell the truth, they find it difficult to believe you.
3. Loss of respect: Nobody respect a liar no matter your position in the society
4. Loss of peace
5. Withdrawal of responsibility
MEANING OF FAIR PLAY
Fair play in business means fair treatment of people without cheating them or being dishonest to them. It also means respect for other people’s right and view.
QUALITIES OF FAIR PLAY
1. Equity: this is the ability to be fair to all, that is, equal treatment of everyone at all times.
2. Openness: being straightforward and truthful, so that people will easily understand what you do or say.
3. Responsibility: ability to carry out the job given to you properly and not passing it to other when they have theirs to do.
4. Play by the rules: always keep to the rules and regulation of the organization.
5. Admitting when you are wrong: it is always good to admit when you are wrong and apologize. Do not claim to be right when you know that you are wrong.
SIX PILLARS OF CHARACTER
1. Trustworthiness
2. Respect
3. Responsibility
4. Fairness
5. Caring
6. Citizenship
ASSIGNMENT
1. Explain the meaning of honesty in business
2. List five attributes of truthfulness
3. State four reasons why people lie
4. Identify four rewards for truthfulness
5. Explain five consequence of untruthfulness
6. What is fair play?
MAIN TOPIC: HONESTY IN BUSINESS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and attributes of a truthful person
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 19-20
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 14-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of truthfulness
mention attributes of truthful person
CONTENTS:
Truthfulness is a quality that is exhibited by a person who tells the truth all the time even if it puts him/her in trouble.
A truthful person is an honest person. He/she does not lie, cheat or steal.
ATTRIBUTES OF A TRUTHFUL PERSON
Consistent behavior
Steadfastness
Straight forwardness
Avoiding lies
Standing by the truth always even if it hurts
Reliability
EVALUATION:
What is truthfulness
mention five attributes of a truthful person
HOME-WORK: Mention two factors that make people to tell lies
LESSON 17
MAIN TOPIC: HONESTY IN BUSINESS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Fair play
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 19-20
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 14-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention factors that make people to tell lies
define fair play
mention attributes of fair play
CONTENTS:
FACTORS THAT MAKE PEOPLE TO TELL LIES
Laziness
Fear
Friendship
Habit
Greed
To save face for promise not kept
FAIRPLAY
This simply means acting, playing honestly, fairly and according to the rule without cheating.
ATTRIBUTES OF FAIR PLAY
Equity
Openness
Impartiality
EVALUATION:
mention the factors that make people to lie
What is fair play?
mention two attributes of fair play
HOME-WORK: what is commerce?
further studies
http://www.k12.hi.us/~mkunimit/honesty.htm
http://www.52virtues.com/virtues/the-52 ... hp#honesty
http://www.lifestyle-homeschool.com/Cha ... lness.html
REWARD OF BEING TRUTHFUL
1. Widespread respect from people
2. A feeing of liberation and self – worth
3. Peace of mind
4. Additional responsibility
5. Happiness
CONSEQUENCES OF NOT BEING TRUTHFUL
1. Misery: A life of lie lead to misery. It leads to discomfort guilt and worthiness in the mind of the person.
2. Damage reputation: People become unkind to you even when you tell the truth, they find it difficult to believe you.
3. Loss of respect: Nobody respect a liar no matter your position in the society
4. Loss of peace
5. Withdrawal of responsibility
MEANING OF FAIR PLAY
Fair play in business means fair treatment of people without cheating them or being dishonest to them. It also means respect for other people’s right and view.
QUALITIES OF FAIR PLAY
1. Equity: this is the ability to be fair to all, that is, equal treatment of everyone at all times.
2. Openness: being straightforward and truthful, so that people will easily understand what you do or say.
3. Responsibility: ability to carry out the job given to you properly and not passing it to other when they have theirs to do.
4. Play by the rules: always keep to the rules and regulation of the organization.
5. Admitting when you are wrong: it is always good to admit when you are wrong and apologize. Do not claim to be right when you know that you are wrong.
SIX PILLARS OF CHARACTER
1. Trustworthiness
2. Respect
3. Responsibility
4. Fairness
5. Caring
6. Citizenship
ASSIGNMENT
1. Explain the meaning of honesty in business
2. List five attributes of truthfulness
3. State four reasons why people lie
4. Identify four rewards for truthfulness
5. Explain five consequence of untruthfulness
6. What is fair play?
MAIN TOPIC: HONESTY IN BUSINESS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and attributes of a truthful person
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 19-20
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 14-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of truthfulness
mention attributes of truthful person
CONTENTS:
Truthfulness is a quality that is exhibited by a person who tells the truth all the time even if it puts him/her in trouble.
A truthful person is an honest person. He/she does not lie, cheat or steal.
ATTRIBUTES OF A TRUTHFUL PERSON
Consistent behavior
Steadfastness
Straight forwardness
Avoiding lies
Standing by the truth always even if it hurts
Reliability
EVALUATION:
What is truthfulness
mention five attributes of a truthful person
HOME-WORK: Mention two factors that make people to tell lies
LESSON 17
MAIN TOPIC: HONESTY IN BUSINESS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Fair play
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 19-20
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 14-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention factors that make people to tell lies
define fair play
mention attributes of fair play
CONTENTS:
FACTORS THAT MAKE PEOPLE TO TELL LIES
Laziness
Fear
Friendship
Habit
Greed
To save face for promise not kept
FAIRPLAY
This simply means acting, playing honestly, fairly and according to the rule without cheating.
ATTRIBUTES OF FAIR PLAY
Equity
Openness
Impartiality
EVALUATION:
mention the factors that make people to lie
What is fair play?
mention two attributes of fair play
HOME-WORK: what is commerce?
further studies
http://www.k12.hi.us/~mkunimit/honesty.htm
http://www.52virtues.com/virtues/the-52 ... hp#honesty
http://www.lifestyle-homeschool.com/Cha ... lness.html
WEEK 7
TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO COMMERCE
CONTENT:
1. Meaning and importance of commerce
2. Activities which aids commerce.
Commerce is the study of trade and aids to trade. It is concerned with the exchange of goods and services and the agencies that facilitate the exchanges. Branches of Commerce
These are the two areas of commerce: Trade and Aids to Trade. Trade refers to the act of buying and selling of goods and services. Aids to trade refer to that other activities that help facilitate trade.
IMPORTANCE OF COMMERCE
1. Commerce serves as a link between manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers
2. Provides employment
3. Creates awareness of goods and services through advertising
4. Enhances a good banking system
5. Revenue for the government
6. Creates the need for road improvement and infrastructure which lead to development of economy
7. Minimizes risk in business through agencies of insurance
8. Encouraged friendship and international cooperation between nation
ACTIVITIES THAT AID TRADE/AIDS TO TRADE There are various services which facilitate trade. These services are known as Aids to trade. These are:
(i) Banking:
Banking Services are provided by an institution set-up to help business transactions. Such banking services are:
(a) Providing business with capital: Capital is the money a businessman needs to enable
him carry on his business.
(b) Accepting money as deposits: Bank accepts to keep money made out of business safely until it is needed for business transaction.
(c) Helping business to transfer money: Banks help business to transfer money from one place to another.
(ii) Insurance: This is a measure taken to safeguard against risk of life or property. The insurance company is called the insurer while the person taking out the policy is called the insured. There are insurance coverage for fire hazards, theft of goods, goods under shipment and goods in the warehouse. In the event of any risk the insured will be indemnified (i.e. compensated the insured for the loss).
(iii) Communication: This is the passing of information from one person to another. Buying and selling of goods requires communication between two or more persons. To facilitate communication between the sellers and the buyers, there are organizations which provide aid to both parties. The Nigerian postal services (NIPOST) and the Nigerian Telecommunication Limited (NITEL) and Courier Organizations such as United Parcel Services (UPS) provide communication services to business.
iv). Advertising: This is the creating of awareness of the existence of new and old goods. This is done through the following means of advertising: Newspaper, magazines, radio, television, bill boards etc.
(v) Warehousing: This is the act of storing goods in a warehouse until they are needed. Goods are sometimes stored for future use. This storage function is performed by the warehouse.
(vi) Transportation: This is carrying of goods and persons from one place to another by land, air and sea. Transport helps persons and goods to reach where they are needed
EVALUATION
1. State three services provided by bank in order to facilitate trade.
2. How does businesses safeguard against unforeseen events?
3. Explain transportation as an aid to trade.
4. Explain advertising as an aid to trade.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 4 pages 23-24
ASSIGNMENT
1. The passing of information from one person to another is known as -----
(a) banking (b) communication (c) transportation
2. The creating of awareness of the existence of old and new goods to the public is called –------ (a) advertising (b) insurance (c) transportation
3. Where raw materials and finished goods are kept is known as --------
(a) warehouse (b) banking (c) communication
4. The person that takes insurance policy is called ---
(a) insured (b) insurer (c) insurance
5. The three methods of transportation are (a) road, bus and car (b) land, air and water (c) land , water and road
THEORY
1. What do you understand by the term Aids to trade?
2. State the aids to trade.
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO COMMERCE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and importance of commerce
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 21-23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 17-18
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define commerce
list the importance of commerce
mention the division of commerce
list the activities which aid commerce
CONTENTS:
Commerce is any activity which involves the distribution of goods from manufacturers to the consumers, and includes all who aid or facilitate this distribution.
DIVISION OF COMMERCE IMPORTANCE OF COMMERCE
Commerce creates a link between the producers, the sellers and the buyers.
Commerce provides a strong link between countries
It enhances the development of a good banking system
Commerce enhances the development of any nation.
EVALUATION:
What is commerce
mention five importance of commerce
mention the activities which aid trade
discuss the division of commerce
HOME-WORK: What are aids to trade?
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commerce
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/03 ... tance.html
CONTENT:
1. Meaning and importance of commerce
2. Activities which aids commerce.
Commerce is the study of trade and aids to trade. It is concerned with the exchange of goods and services and the agencies that facilitate the exchanges. Branches of Commerce
These are the two areas of commerce: Trade and Aids to Trade. Trade refers to the act of buying and selling of goods and services. Aids to trade refer to that other activities that help facilitate trade.
IMPORTANCE OF COMMERCE
1. Commerce serves as a link between manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers
2. Provides employment
3. Creates awareness of goods and services through advertising
4. Enhances a good banking system
5. Revenue for the government
6. Creates the need for road improvement and infrastructure which lead to development of economy
7. Minimizes risk in business through agencies of insurance
8. Encouraged friendship and international cooperation between nation
ACTIVITIES THAT AID TRADE/AIDS TO TRADE There are various services which facilitate trade. These services are known as Aids to trade. These are:
(i) Banking:
Banking Services are provided by an institution set-up to help business transactions. Such banking services are:
(a) Providing business with capital: Capital is the money a businessman needs to enable
him carry on his business.
(b) Accepting money as deposits: Bank accepts to keep money made out of business safely until it is needed for business transaction.
(c) Helping business to transfer money: Banks help business to transfer money from one place to another.
(ii) Insurance: This is a measure taken to safeguard against risk of life or property. The insurance company is called the insurer while the person taking out the policy is called the insured. There are insurance coverage for fire hazards, theft of goods, goods under shipment and goods in the warehouse. In the event of any risk the insured will be indemnified (i.e. compensated the insured for the loss).
(iii) Communication: This is the passing of information from one person to another. Buying and selling of goods requires communication between two or more persons. To facilitate communication between the sellers and the buyers, there are organizations which provide aid to both parties. The Nigerian postal services (NIPOST) and the Nigerian Telecommunication Limited (NITEL) and Courier Organizations such as United Parcel Services (UPS) provide communication services to business.
iv). Advertising: This is the creating of awareness of the existence of new and old goods. This is done through the following means of advertising: Newspaper, magazines, radio, television, bill boards etc.
(v) Warehousing: This is the act of storing goods in a warehouse until they are needed. Goods are sometimes stored for future use. This storage function is performed by the warehouse.
(vi) Transportation: This is carrying of goods and persons from one place to another by land, air and sea. Transport helps persons and goods to reach where they are needed
EVALUATION
1. State three services provided by bank in order to facilitate trade.
2. How does businesses safeguard against unforeseen events?
3. Explain transportation as an aid to trade.
4. Explain advertising as an aid to trade.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 4 pages 23-24
ASSIGNMENT
1. The passing of information from one person to another is known as -----
(a) banking (b) communication (c) transportation
2. The creating of awareness of the existence of old and new goods to the public is called –------ (a) advertising (b) insurance (c) transportation
3. Where raw materials and finished goods are kept is known as --------
(a) warehouse (b) banking (c) communication
4. The person that takes insurance policy is called ---
(a) insured (b) insurer (c) insurance
5. The three methods of transportation are (a) road, bus and car (b) land, air and water (c) land , water and road
THEORY
1. What do you understand by the term Aids to trade?
2. State the aids to trade.
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO COMMERCE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and importance of commerce
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 21-23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 17-18
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define commerce
list the importance of commerce
mention the division of commerce
list the activities which aid commerce
CONTENTS:
Commerce is any activity which involves the distribution of goods from manufacturers to the consumers, and includes all who aid or facilitate this distribution.
DIVISION OF COMMERCE IMPORTANCE OF COMMERCE
Commerce creates a link between the producers, the sellers and the buyers.
Commerce provides a strong link between countries
It enhances the development of a good banking system
Commerce enhances the development of any nation.
EVALUATION:
What is commerce
mention five importance of commerce
mention the activities which aid trade
discuss the division of commerce
HOME-WORK: What are aids to trade?
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commerce
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/03 ... tance.html
WEEK 8
TOPIC: DIVISION OF COMMERCE
CONTENT:
i. Classification of commerce into Division,
ii. Types of trade –
a. Home trade :wholesale and retail sales
b. Foreign trade: Import and export
CLASSIFICATION OF COMMERCE/DIVISION OF COMMERCE TRADE
MEANING OF TRADE: Trade could be defined as the exchange or buying and selling of goods and services.
Division of Trade: Trade is basically divided into two namely – Home Trade and Foreign Trade.
HOME TRADE: This is the buying and selling of goods and services within the country. Examples are trade between Calabar and Uyo, Lagos and Enugu. One of the features of Home trade is that a common unit of money (naira) is accepted as a means of payment for the trade. Home trade is further divided into Wholesale and Retail trade.
a. Wholesale Trade: This involves buying goods in large quantity from the manufacturer or producer and selling in small quantity to the retailer.
b. Retail Trade: This involves buying goods in small quantity from the wholesalers and selling in bits or units to the final consumers.
There are two types of retail traders in Nigeria namely large scale retailers and small scale retailers. Large scale retailers are Department stores, supermarkets, mail order firm etc. Small scale retailers are market stall owner, kiosk, hawkers etc.
SUB TOPIC: FOREIGN TRADE
CONTENT
Foreign Trade: This is the buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries. It is divided into Imports and Exports trade.
Import Trade: This is the buying of goods and services from other countries into our country. For example, trade between Abuja and Accra; Lagos and USA etc. Nigeria imports goods like automobile parts, electronics etc. It is further divided into visible and invisible import.
Export Trade: is the selling of goods and services produced in Nigeria to other countries that need them to satisfy the needs of their citizen. Nigeria exports goods like groundnuts, palm produce, rubber and cocoa, crude oil etc. This is also divided into visible and invisible export.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 4 pages 23-24
ASSIGNMENT
1. Trade is basically divided into -------- (a) Home trade and Commerce (b) Home trade and Foreign trade (c) Import trade and Export trade
2. The buying and selling of goods and services within a country is (a) Foreign trade (b) Home trade (c) Export trade
3. The buying of goods in large quantity from producer and selling in small quantity to the retailer is known as (a) Wholesale trade (b) Import trade (c) Foreign trade
4. Foreign is divided into ------- and ------- trade. (a) Home and Foreign trade (b) Wholesale and retail trade (c) Import and Export trade
5. Supermarkets are examples of -------. (a) Retail trade (b) Foreign trade (c) import trade
THEORY
1. Define trade
2. State the divisions of trade2. State the two divisions of trade.
MAIN TOPIC: TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 24-27
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 19-23
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 31-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define trade
mention forms of trade
draw a diagram showing types of trade
CONTENTS:
Trade can be defined as an act of buying and selling of goods and services.

FORMS OF TRADE
Trade is divided into two.
Home trade
Foreign trade
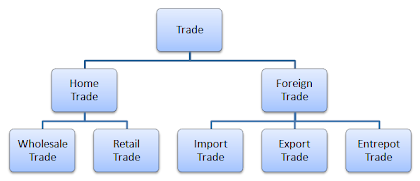
EVALUATION:
what is trade
mention two forms of trade
with the aid of a diagram explain types of trade
HOME-WORK: who is a wholesaler?
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC: TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Home trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 24-27
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 19-23
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 31-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define home trade
mention product of home trade
mention the duties of the middlemen
CONTENTS:
HOME TRADE
This is the buying and selling of goods and services within the country.
The same currency is involved, no custom duty is paid.
Home trade can further be divided into wholesale and retail
Wholesaler is someone who buys goods in large quantities from the producer and sell in small quantities to the retailer.
A retailer is someone who buys goods from the wholesalers and sells them to the final consumer.
Some of the products of home trade include: Anambra people bring palm oil, brooms, yam to the west to sell.
EVALUATION:
what is home trade
mention five products traded in home trade
write short note on the meaning and duties of the middlemen
HOME-WORK: what is foreign trade?
LESSON 21
MAIN TOPIC: TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Foreign trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 24-27
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 19-23
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 31-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define foreign trade
mention division of foreign trade
mention products traded in foreign trade
differentiate between foreign and home trade
CONTENTS:
FOREIGN TRADE
This is a trade between two or more countries.
It involves the use of two or more currencies; it may also require the use of two official languages.
Foreign trade is divided into three. They are:
Import
Export
Entrepot
IMPORT: This involves the bringing in of goods made in one country into another country. E.g. Nigeria buys cars from Japan into the country.
EXPORT: This is concerned with selling to other countries raw materials or finished goods made in one country. E.g. Nigeria sells crude oil to United Kingdom.
ENTREPOT: This is the re-exporting of goods bought into Nigeria from another country as import.
EVALUATION:
What is foreign trade
Mention three divisions of foreign trade
Mention four differences between home and foreign trade.
HOME-WORK: What are aids to trade?
further studies
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/03 ... ature.html
http://www.xtremepapers.com/revision/gc ... _trade.php
CONTENT:
i. Classification of commerce into Division,
ii. Types of trade –
a. Home trade :wholesale and retail sales
b. Foreign trade: Import and export
CLASSIFICATION OF COMMERCE/DIVISION OF COMMERCE TRADE
MEANING OF TRADE: Trade could be defined as the exchange or buying and selling of goods and services.
Division of Trade: Trade is basically divided into two namely – Home Trade and Foreign Trade.
HOME TRADE: This is the buying and selling of goods and services within the country. Examples are trade between Calabar and Uyo, Lagos and Enugu. One of the features of Home trade is that a common unit of money (naira) is accepted as a means of payment for the trade. Home trade is further divided into Wholesale and Retail trade.
a. Wholesale Trade: This involves buying goods in large quantity from the manufacturer or producer and selling in small quantity to the retailer.
b. Retail Trade: This involves buying goods in small quantity from the wholesalers and selling in bits or units to the final consumers.
There are two types of retail traders in Nigeria namely large scale retailers and small scale retailers. Large scale retailers are Department stores, supermarkets, mail order firm etc. Small scale retailers are market stall owner, kiosk, hawkers etc.
SUB TOPIC: FOREIGN TRADE
CONTENT
Foreign Trade: This is the buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries. It is divided into Imports and Exports trade.
Import Trade: This is the buying of goods and services from other countries into our country. For example, trade between Abuja and Accra; Lagos and USA etc. Nigeria imports goods like automobile parts, electronics etc. It is further divided into visible and invisible import.
Export Trade: is the selling of goods and services produced in Nigeria to other countries that need them to satisfy the needs of their citizen. Nigeria exports goods like groundnuts, palm produce, rubber and cocoa, crude oil etc. This is also divided into visible and invisible export.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 4 pages 23-24
ASSIGNMENT
1. Trade is basically divided into -------- (a) Home trade and Commerce (b) Home trade and Foreign trade (c) Import trade and Export trade
2. The buying and selling of goods and services within a country is (a) Foreign trade (b) Home trade (c) Export trade
3. The buying of goods in large quantity from producer and selling in small quantity to the retailer is known as (a) Wholesale trade (b) Import trade (c) Foreign trade
4. Foreign is divided into ------- and ------- trade. (a) Home and Foreign trade (b) Wholesale and retail trade (c) Import and Export trade
5. Supermarkets are examples of -------. (a) Retail trade (b) Foreign trade (c) import trade
THEORY
1. Define trade
2. State the divisions of trade2. State the two divisions of trade.
MAIN TOPIC: TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 24-27
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 19-23
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 31-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define trade
mention forms of trade
draw a diagram showing types of trade
CONTENTS:
Trade can be defined as an act of buying and selling of goods and services.

FORMS OF TRADE
Trade is divided into two.
Home trade
Foreign trade

EVALUATION:
what is trade
mention two forms of trade
with the aid of a diagram explain types of trade
HOME-WORK: who is a wholesaler?
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC: TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Home trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 24-27
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 19-23
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 31-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define home trade
mention product of home trade
mention the duties of the middlemen
CONTENTS:
HOME TRADE
This is the buying and selling of goods and services within the country.
The same currency is involved, no custom duty is paid.
Home trade can further be divided into wholesale and retail
Wholesaler is someone who buys goods in large quantities from the producer and sell in small quantities to the retailer.
A retailer is someone who buys goods from the wholesalers and sells them to the final consumer.
Some of the products of home trade include: Anambra people bring palm oil, brooms, yam to the west to sell.
EVALUATION:
what is home trade
mention five products traded in home trade
write short note on the meaning and duties of the middlemen
HOME-WORK: what is foreign trade?
LESSON 21
MAIN TOPIC: TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Foreign trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 24-27
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 19-23
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 31-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define foreign trade
mention division of foreign trade
mention products traded in foreign trade
differentiate between foreign and home trade
CONTENTS:
FOREIGN TRADE
This is a trade between two or more countries.
It involves the use of two or more currencies; it may also require the use of two official languages.
Foreign trade is divided into three. They are:
Import
Export
Entrepot
IMPORT: This involves the bringing in of goods made in one country into another country. E.g. Nigeria buys cars from Japan into the country.
EXPORT: This is concerned with selling to other countries raw materials or finished goods made in one country. E.g. Nigeria sells crude oil to United Kingdom.
ENTREPOT: This is the re-exporting of goods bought into Nigeria from another country as import.
EVALUATION:
What is foreign trade
Mention three divisions of foreign trade
Mention four differences between home and foreign trade.
HOME-WORK: What are aids to trade?
further studies
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/03 ... ature.html
http://www.xtremepapers.com/revision/gc ... _trade.php
WEEK 9
MAIN TOPIC: AIDS TO TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of aids to trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 18
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 33-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of aids to trade
mention the activities which aid trade
CONTENTS:
Aids to trade are those things that facilitates {i.e helps} buying and selling of goods and services.
They are:
Transport
Warehousing
Banking and Finance
Insurance
Advertising
Tourism

EVALUATION:
what are aids to trade
mention six aids to trade
HOME-WORK: Write short note on communication
LESSON 23
MAIN TOPIC: AIDS TO TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of aids to trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 18
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 33-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to explain the following:
Advertising
Communication
Transportation
CONTENTS:
TRANSPORT: It involves the transfer of goods from one place to another. It involves the transfer of raw materials; semi finished goods and finished goods from the manufacturers to the final consumers.
COMMUNICATION: This deals with the passage of information from one person to another, or from one organization to another organization.
ADVERTISING: This helps business to expand and develop by spreading information about goods and services to a large number of consumers. Goods and services are advertised on radio, television and in newspaper.
EVALUATION: Write short note on the following:
Communication
Transport
Advertising
HOME-WORK: what is warehousing?
LESSON 24
MAIN TOPIC: AIDS TO TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of aids to trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 18
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 33-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to explain the following:
Warehousing
Banking and finance
Insurance
CONTENTS:
WAREHOUSING: This is the commercial function of storage. It allows goods to be made available when and where they are wanted. A wholesaler performs more of this function.
BANKING AND FINANCE: This helps to provide money and credit facilities. It provides convenient means of payment. Commercial banks lend money to people and also receive money from people for safekeeping.
INSURANCE: This involves transfer of risks. These are risks of fire, accident, burglary, theft etc.
Businessmen usually insure against these risks. If a factory is burnt down, the insurance company will compensate the factory owner in order to enable him rebuild the factory.
EVALUATION: Write short note on the following:
Warehousing
Banking and finance
Insurance
HOME-WORK: What is tourism?
further studies
http://www.xtremepapers.com/revision/gc ... _trade.php
http://olevelonline.blogspot.com/2011/1 ... trade.html
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/03 ... merce.html
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of aids to trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 18
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 33-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of aids to trade
mention the activities which aid trade
CONTENTS:
Aids to trade are those things that facilitates {i.e helps} buying and selling of goods and services.
They are:
Transport
Warehousing
Banking and Finance
Insurance
Advertising
Tourism

EVALUATION:
what are aids to trade
mention six aids to trade
HOME-WORK: Write short note on communication
LESSON 23
MAIN TOPIC: AIDS TO TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of aids to trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 18
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 33-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to explain the following:
Advertising
Communication
Transportation
CONTENTS:
TRANSPORT: It involves the transfer of goods from one place to another. It involves the transfer of raw materials; semi finished goods and finished goods from the manufacturers to the final consumers.
COMMUNICATION: This deals with the passage of information from one person to another, or from one organization to another organization.
ADVERTISING: This helps business to expand and develop by spreading information about goods and services to a large number of consumers. Goods and services are advertised on radio, television and in newspaper.
EVALUATION: Write short note on the following:
Communication
Transport
Advertising
HOME-WORK: what is warehousing?
LESSON 24
MAIN TOPIC: AIDS TO TRADE
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types of aids to trade
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 23
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 18
Spectrum Business Study for JSS2 by Eno L. Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo. Pages 33-35
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to explain the following:
Warehousing
Banking and finance
Insurance
CONTENTS:
WAREHOUSING: This is the commercial function of storage. It allows goods to be made available when and where they are wanted. A wholesaler performs more of this function.
BANKING AND FINANCE: This helps to provide money and credit facilities. It provides convenient means of payment. Commercial banks lend money to people and also receive money from people for safekeeping.
INSURANCE: This involves transfer of risks. These are risks of fire, accident, burglary, theft etc.
Businessmen usually insure against these risks. If a factory is burnt down, the insurance company will compensate the factory owner in order to enable him rebuild the factory.
EVALUATION: Write short note on the following:
Warehousing
Banking and finance
Insurance
HOME-WORK: What is tourism?
further studies
http://www.xtremepapers.com/revision/gc ... _trade.php
http://olevelonline.blogspot.com/2011/1 ... trade.html
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/03 ... merce.html
